Painful sensations after treatment of pulpitis may be normal or a consequence of complications. In order to differentiate these conditions and determine whether it is worth seeing a doctor immediately, it is important to assess the nature of the pain, the time during which it persists, and general well-being.
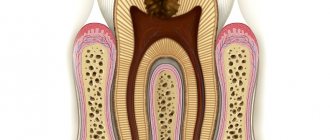
It is worth noting that in most cases, one of the most important stages in the treatment of pulpitis is the removal of the pulp or neurovascular bundle of the tooth. Many patients wonder: can a tooth hurt after treating pulpitis with this method? Despite the absence of a “nerve”, pain may be observed, this is a natural reaction to the intervention - removal of the pulp, treatment and filling of the root canals. It is important to know when it is normal and when pain is caused by a complication.
Natural pain after pulpitis treatment
Why does a tooth hurt after pulpitis treatment if there are no complications?
After the anesthesia wears off, pain may appear in the area of the causative tooth, and normally this condition is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the pain gradually subsides - an unpleasant sensation of a certain degree of severity may persist for some time, but it does not intensify;
- already 1–3 days after the procedure, the pain noticeably subsides;
- there are no other symptoms - bleeding, severe swelling and redness of the gums, increased body temperature, general weakness.
It is difficult to predict how much a tooth hurts after treatment for pulpitis; it depends on the individual characteristics, the specific tooth and the complexity of the root system, the presence or absence of concomitant diseases. The norm is that moderate pain persists for up to 7 days. Important: the intensity of pain becomes less over time.
It is difficult to talk about the norm if there are such “indicators” of complications as fever, swelling, too much pain, including increasing pain. There are several possible complications of endodontic treatment of pulpitis.
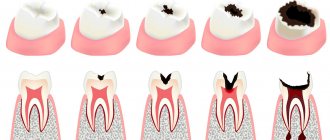
Symptoms of acute pulpitis
As the disease develops, aching pain in the tooth first appears, which has an increasing character. The pain syndrome is constant or intermittent, significantly intensifies at night and with temperature influences. A diseased tooth reacts most strongly to cold. If you knock on the surface, the patient does not have any unpleasant sensations or they are insignificant.
The manifestations of symptoms of acute pulpitis depend on its form.
Hyperemia
It develops as a result of the activity of pathogenic bacteria that enter the dental tissue during untreated caries. It can occur during tooth preparation or after it has been treated with chemicals.
With hyperemia, the patient is concerned about the following symptoms:
- It's a dull pain. Occurs as a reaction to stimuli. Mostly, the painful attack does not last long, about 2 – 3 minutes, and at night lingering pain develops. In the case of an advanced form, the pain is felt as sharp and strong lumbago.
- Severe pain reaction when enamel is exposed to cold.
Acute focal
Signs that indicate the development of this form of pulpitis:
- Painful attacks occur spontaneously.
- They last for at least 30 minutes; in advanced stages they can last up to two hours.
- A carious cavity is revealed, which is painful during examination.
In acute focal pulpitis, the pain does not radiate to adjacent teeth.
Acute diffuse
It develops as a consequence of an advanced focal form and the lack of timely treatment.
Characterized by the following symptoms:
- The pain syndrome occurs spontaneously and suddenly, without exposure to any irritants. The pain is prolonged, does not go away for many hours, and radiates to nearby teeth.
- The presence of a carious cavity, when examined, a sharp painful reaction occurs. Remnants of filling material may remain.
Acute purulent
If the acute diffuse form is not treated, it gradually turns into a purulent form. Characteristic symptoms:
- The pain attack is cutting, acute in nature. The pain is constant and may periodically weaken or intensify.
- The pain radiates to neighboring teeth, as well as along the branches of the trigeminal nerve.
- When exposed to heat, the pain becomes stronger; when applying a cold compress, it subsides a little.
- Pus accumulates in the tooth cavity and can be detected by microscopic examination.
- The soft tissues melt and abscesses with pus form in them.
- The blood vessels are dilated and have many microdamages.
Traumatic acute
Develops as a result of tooth injury due to improper preparation of a carious cavity, chipping of a dental crown or fracture.
This form of pulpitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The pulp horn bleeds, which is noticeable during a dental examination.
- The dental cavity communicates pointwise with the carious cavity.
- In the pulp tissues, a bundle of vessels and nerves is exposed.
If there are signs indicating acute pulpitis of the tooth, treatment should not be delayed. A timely visit to the clinic will help save the tooth.
Removing the filling material beyond the root apex
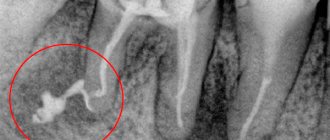
If, after treatment of pulpitis, the tooth hurts when pressed, perhaps we are talking about the removal of the filling material beyond the root of the tooth, into the adjacent tissues. The intensity of the sensation depends on how much material has gone beyond the apex of the root. Despite the fact that today a doctor has ample opportunities to control the accuracy of canal filling, as well as the use of high-quality materials, this can happen. It is worth noting that X-ray monitoring of treatment is intended to prevent the development of such a consequence - after the filling is completed, an image should be taken in which, in the event of a re-filling, the doctor will be able to notice excess material and choose the tactics for further action. Re-filling or removal of filling material beyond the root apex in itself does not pose a particular threat.
The exit of the filling material beyond the root apex can cause long-term pain immediately after the anesthetic wears off and persists for a long time - up to several months. This is a natural reaction of tissues to foreign material. Removal of material may be due to the following reasons:
- difficulties in determining the length of channels;
- incorrect selection of a pin from materials for the canal;
- lack of apical stop, etc.
However, this is not the only possible treatment difficulty that provokes pain.
What should you do if your tooth hurts when you press it?
Pain almost always accompanies the rehabilitation period after dental surgery. If the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, the discomfort disappears on its own after 2-4 days, however, in some cases, pain can signal complications. The patient should return for a follow-up appointment if:
- immediately after the anesthesia wears off, severe and sharp pain appears;
- More than a week has passed after treatment, but the toothache does not go away;
- The rehabilitation period went well, but after 1-3 months pain appeared again.
The most important thing is not to endure, but to figure out where the pain comes from.
Insufficient canal filling
The opposite situation, in which a tooth may hurt after treatment of pulpitis, is insufficient filling of the root canals, the formation of voids at the apex of the root. In this case, often unpleasant sensations do not occur immediately, but as the inflammatory process develops - this can happen either after 1-2 weeks or after a longer period of time.
Here, painful sensations are associated with the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms in the voids. This process leads to one of the diseases:
- periodontitis - inflammation of the peri-root tissues;
- tooth root apex cyst;
- granuloma.
Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, pain may appear immediately or make itself felt when the cyst or granuloma has reached an impressive size. Its intensity is often low, minor pain is more often observed when biting after treatment of pulpitis, and in the absence of mechanical impact on the tooth there is no discomfort at all.
One of the root canals was not processed
This is one of the rarest complications, since before starting endodontic treatment the doctor will definitely prescribe an x-ray diagnosis. It allows you to reliably determine the number of channels and evaluate their structure. But there are cases of abnormal location of root canals or their extremely small sizes, which makes them unnoticed in the image.
This leads to the following situation: the doctor removes the pulp in each canal, but one remains unattended - the inflamed pulp continues to hurt, and pathogenic bacteria continue to multiply. Such pain is difficult to confuse with other complications - the patient simply does not receive relief after treatment, and the pain characteristic of pulpitis itself remains. The sensations are pulsating in nature, the pain intensifies when eating, exposure to temperature on the tooth, and becomes unbearable at night.
The same symptoms can be observed with incomplete removal of the pulp in the diagnosed canal. In both cases, other symptoms may be observed:
- headache, sensations “radiate” to the ear, temple - depending on the specific tooth;
- increased body temperature;
- symptoms of general malaise.
Most complications are related to the complexity of the canal structure, and the following is no exception.
Instrument breakage in the root canal
After treatment of pulpitis, the tooth may also hurt due to a broken instrument. Part of it remains in the root canal, and unpleasant sensations occur immediately or a few days after the visit to the dental office.
The nature of the pain may vary depending on the size of the fragment and other conditions.
It is worth noting that this complication is quite rare. This is explained by the fact that a good dental clinic uses modern, high-quality instruments from reliable manufacturers that are sufficiently durable. In addition, the rules for their use must be strictly observed, including multiplicity, force during exposure, etc. And finally, the doctor will notice the presence of a foreign body in the tooth on a control image, which he will prescribe after treatment.
Root perforation
Perforation is the creation of an artificial root hole. As a rule, in this case, the pain is sharp, unbearable and makes itself felt immediately after the anesthetic stops working. This can happen during instrumental processing of canals - preparing them for filling.
As in most other cases, the structure of the root system plays an important role here. Narrow, curved canals are a common cause of perforation. In this case, the tool does not move along the canal, but into the root wall.
If a tooth hurts for this reason after treatment of pulpitis, the symptom may be accompanied by bleeding. In addition, some patients report pain even with current anesthesia - subjectively it is perceived as the feeling of an injection into the gums. If the tooth was filled after perforation, the filling material may leak beyond the root. Severe pain persists for up to 3 weeks, and the main complication of this phenomenon is the inflammatory process.
Tooth hurts when pressed after filling
Slight pain after the doctor has given a filling to the patient is normal: during the sanitization of cavities affected by caries, the tissues receive microtrauma. The condition is easily treated with analgesics and goes away on its own in 2-3 days. But if a filled tooth hurts when pressed hard enough, then the problem is one of five reasons:
- high filling - the occlusion is disrupted, the tooth experiences excessive pressure and becomes painful;
- the dental pulp was burned when the filling was treated with a photopolymer lamp;
- a gap has appeared between the filling and the enamel, into which bacteria and food particles have entered, causing inflammation;
- the cavities affected by caries were not drilled out thoroughly enough, and it reappeared;
- I developed an allergy to the filling.
If the tooth under the filling hurts when pressed, this means that you need to make an appointment with the doctor again and have it filled again.
Allergy
This complication of pulpitis treatment is easier to differentiate - an allergic reaction is often accompanied by tissue swelling. If it is a consequence of material moving outside the root canal, there may be swelling of the gums around the treated tooth. In some cases, it spreads to other areas - cheek, lip, depending on the specific tooth.
When pressure is applied, the pain becomes stronger, it is difficult to relieve with painkillers, and over time it only intensifies.
What to do?
What to do if your tooth hurts after pulpitis treatment? The most important recommendation if you suspect a complication after treatment of pulpitis is a return visit to the doctor. If this is not possible, you should contact another specialist and explain the situation.
If it is not possible to visit the clinic immediately, you can use a painkiller - give preference to the one that you have already taken, to which there have been no negative reactions. However, it is better to try to consult with a specialist, if not in person, then by phone.
It is difficult to say exactly how quickly the pain will subside in each case. However, on average, after visiting the dentist, relief comes quite quickly:
- When removing the filling material beyond the root apex: a visit to the doctor will allow the specialist to remove excess material, and after 2-3 days the discomfort will subside.
- If the filling is insufficient: the doctor will choose a tactic for further treatment; it is quite possible that several visits will be needed to eliminate the inflammatory process - for larger cysts or granulomas, surgical treatment is also required. This complication requires refilling to prevent recurrent complications.
- If the pulp or part of it is intact: the doctor will remove the remaining pulp and repeat the manipulations that were required to treat pulpitis. The pain in this case goes away within a few days after all measures are completed.
- If an instrument breaks off: the doctor will perform an X-ray diagnostic and, if the presence of a broken instrument is confirmed, will remove it. In rare cases, resection of the root apex is performed.
- In case of perforation: the dentist will treat the canals without affecting the hole. Using modern osteoplastic materials, he will close it, which will save the tooth. If a purulent process occurs, several visits will be required to eliminate the inflammation.
- In case of gum injury: contacting a doctor will allow you to receive recommendations regarding antiseptic and healing agents for treatment at home. Relief occurs on average within 1–3 days.
- In case of an allergic reaction: it will be necessary to refill the root canals using other materials. The doctor will perform the necessary manipulations and also prescribe decongestants that will quickly eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Is it painful to treat pulpitis?
Treatment of pulpitis is painless, since before drilling the dentist injects the gum with an anesthetic drug. After 2-4 minutes the pain goes away, only a sensation of touch or pressure remains.
Before injecting an anesthetic, the doctor may suggest topical anesthesia, that is, lubricate the gums with a “freezing” gel so as not to feel the insertion of the needle. Another popular service that complements anesthesia is sedation. The patient inhales special sedatives, completely relaxes and even falls asleep.
For allergy sufferers, hypoallergenic drugs are chosen; in extreme cases, the dentist may suggest treatment under anesthesia. Unlike local anesthesia and sedation, anesthesia negatively affects the cardiovascular system and the entire body as a whole.
What not to do?
If, after treatment, a tooth hurts when pressed or without mechanical action, you should under no circumstances resort to folk remedies such as heating, hot compresses, heating pads - if there is an inflammatory process, this can greatly worsen the condition. In case of allergic reactions, heat will also increase swelling.
It is also not recommended to use folk remedies for rinsing, which can cause a burn to the mucous membrane - iodine, tinctures of alcohol or vodka, liquids with the juice of “scorching” plants, etc. Even if there is no gum damage, such measures can worsen the situation.
It is also not worth taking various painkillers uncontrollably - firstly, you need to see a doctor in any case, and the effect of analgesics will not allow you to fully evaluate the clinical picture. Secondly, it can be dangerous to health.
It is important to visit a doctor at the first opportunity and perform all the necessary procedures to eliminate unpleasant consequences and improve the condition.
Main reasons
Pain is a kind of “alarm” from the body, drawing attention to malfunctions in its functioning. The oral cavity is no exception: if a seemingly healthy tooth hurts when pressed, this indicates that something has happened to it. As a rule, the reason is damage to the crown, root, gums, or the presence of an inflammatory process. But provoking factors can be very diverse: injuries, infections, insufficient hygiene and even medical errors. Let's look at each case in more detail.