Changing children's baby teeth to permanent ones is always an exciting time for parents. This process is quite lengthy and often painful for the child, because it can be accompanied by various inflammations and discomfort. To help parents, for a better understanding of the physiological processes associated with the formation of teeth, dentists offer to look at the pattern of loss of baby teeth in children.
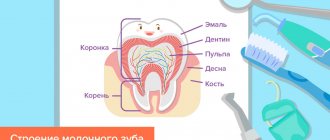
Bookmarking teeth
The formation of baby teeth occurs at approximately 4-6 weeks of fetal development. At the same time, the formation of the fundamental elements occurs much later - during the first months of the child’s life. For this reason, new mothers who are bottle-feeding are strongly recommended to supplement their baby’s diet with calcium. This substance promotes the proper formation of tooth enamel.
At an early age, unprotected baby teeth are extremely susceptible to carious lesions. Parents should monitor this closely, as infection can subsequently cause destruction of permanent teeth. The fact is that the rudiments of permanent teeth are in close proximity to the roots of milk teeth, so as soon as you discover dark spots on your child’s enamel, immediately go to pediatric dentistry.
Children's dentition and everything about it
All parents carefully search for information about the correct number of teeth in the baby’s mouth in relation to his age. They are often interested in shape and size. It is worth remembering that the information received should not exempt the child from visiting the dentist for preventive purposes. Sometimes there may be congenital manifestations of anomalies in the oral cavity. We are talking about defects in the growth of teeth, as well as their incomplete composition in the upper or lower jaw.
Directly, baby teeth do not remain in the oral cavity throughout life, but only for a limited time, after which they fall out. After them, permanent ones grow up, which stay with the person for life, provided they are treated with care. Primary and permanent teeth have a number of differences, namely:
- The incisors of baby teeth have a more convex shape.
- Permanent teeth have a more developed root system than baby teeth, which fall out without causing discomfort.
- The enamel of primary teeth is thinner, but their pulp capsule is more pronounced. Baby teeth are more susceptible to caries.
The first teeth begin to appear at 4-5 months, but a delay of six months is not a violation. There is a certain sequence in which a baby’s first teeth appear:
- Incisors: central ones appear from 4 to 9 months, and lateral ones are expected from 8 months to 12 months.
- The first molars appear after the child is one year old.
- Clicks are expected from 1 to 2 years.
- By the age of 3, the second molars begin to emerge.
It is worth noting that at the age of three, a baby already has about 20 teeth in his mouth. Then, in their further growth, a pause is expected until the child reaches 5 or 6 years of age.
Baby teeth in children: loss pattern
Many mothers are concerned about the question of when their children’s baby teeth begin to fall out. As a rule, this process starts immediately before primary school, that is, at the age of 6-7 years. In this case, the pattern of loss of baby teeth in children is similar to the sequence of their eruption. Only the fangs differ, which are replaced later, by the age of 13.
The order in which baby teeth fall out is the same for almost all children. First, molars grow - molars, which were absent in the “milk” set. As soon as there is enough space in the child’s jaw, “sixes” begin to appear. Only after this comes the time to change temporary teeth.
First, the lower incisors fall out, and then the upper ones. After this, the premolars appear at about 9-11 years of age. The last in line are the fangs, which usually fall out by the age of 10-12 years. At the same time, there should already be molars in the child’s mouth. After 18 years, third molars or, as we used to call them, wisdom teeth begin to emerge. However, they do not appear in everyone, which, by the way, does not indicate the presence of any pathologies.
Features of the period.
During this period, the formation and further development of the roots of baby teeth occurs: they are strengthened in the bone tissue of the jaws. The processes of root formation smoothly flow into the processes of their resorption and replacement with permanent teeth, the rudiments of which are located under the milk teeth.
The presence of interdental spaces between the incisors and canines of the upper and lower jaws is a sign of a “normal” correctly developing occlusion of primary teeth. The absence of interdental spaces in the primary dentition indirectly indicates a lack of space for the eruption of permanent incisors and canines, the crowns of which are significantly wider.
PHOTO: Teeth of a 3-year-old child. By the age of 3, a child already has a full set of teeth in his mouth. There should be spaces between baby teeth.
Starting from 5-6 years of age, the bite of temporary (baby) teeth is replaced with permanent ones. This is preceded by the growth of the rudiments of permanent teeth and the physiological resorption of the roots of milk teeth. As the roots of baby teeth are reabsorbed, mobility of these teeth appears. At this age, parents often note mobility of the lower and upper front teeth (deciduous incisors). When the root is completely absorbed, the tooth may fall out on its own: sometimes children “help” the tooth fall out with their tongue, constantly rocking it. Sometimes the “loss” of a resorbed tooth occurs while eating or playing.
Closer to 6 years, the first permanent chewing tooth (first molar) erupts behind the last milk tooth. The eruption of the first permanent molar is not accompanied by the loss of any tooth and does not cause any discomfort to the child, so it often goes unnoticed.
Parents often take the first permanent chewing tooth for additional milk, as it bursts behind all the milk teeth and this does not precede the loss of the milk tooth: it seems that the child has 24 malate tooth.
PHOTO: Milk teeth in children aged 6 years. The lower lateral incisors fell out. Soon permanent lateral incisors will appear in their place.
What should parents do?
The process of changing teeth in children worries parents, but this is quite natural, and most children do not experience significant pain. However, this does not relieve parents of the need to constantly monitor the condition of their child’s oral cavity. There is no need to remove baby teeth yourself. When the time comes to say goodbye to a tooth, a certain mechanism is activated in the child’s body that dissolves the milk tooth roots. You should seek help from a specialist only if the baby tooth does not want to fall out, but the permanent one is already beginning to appear.
After a tooth falls out, you may experience some bleeding. If desired, have your child rinse his mouth with a solution of soda with a drop of iodine as a preventative measure.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Impaired eruption of permanent teeth
Parents should start to worry if there are no signs of eruption of a permanent tooth after the loss of a primary tooth for 5 or more weeks. There are several reasons why permanent teeth are “late” to appear:
- Adverse effects on the fetus and newborn baby. What matters are the damaging factors that affected the developing organism during pregnancy and in the first year of life. Illnesses of the mother and child, past infections, taking certain medications, and the consequences of birth trauma can prolong the eruption of permanent teeth.
- Absence or damage of a permanent tooth germ. The formation of teeth occurs in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. As a rule, under the influence of unfavorable factors, the formation of an entire group or groups of teeth is disrupted. In this case, after the baby teeth fall out, there is no need to wait for permanent teeth to appear. Damage to the tooth germ is in most cases the result of careless dental treatment.
- Incorrect position of the tooth germ in the jaw bone. If the rudiment is located too deep in the tissues, oriented horizontally and not vertically, then tooth eruption will be difficult, if not impossible.
There are no external symptoms by which one could judge the cause of the disorder. You can only conduct an examination, based on the data of which a treatment plan is drawn up. For this, the child must be shown to the dentist. Perhaps, already at this stage, he will offer a consultation with a pediatric orthodontist, who, in turn, will prescribe treatment - orthodontic plates or a more modern and convenient method - aligners.
How many baby teeth do children lose?
The very first teeth appear between the ages of six months and one year. First, the incisors appear, located below and in the center, then the upper ones, and only then the lower lateral and upper lateral ones. This is followed by the first molars, canines and second molars. In pediatric practice, such a concept as a dental formula is used, that is, a standard dental set for children: 2 incisors, 2 molars and a canine. Multiplying the data obtained by four, we get 20 – the number of baby teeth is normal. Accordingly, the same number of baby teeth fall out.
Dental clinic "32 Dent" offers a full range of services in the field of pediatric dentistry. To receive complete and detailed answers to all your questions, call the numbers listed on the website.
How many teeth should a child have at 3 years old?
All twenty baby teeth appear by about 2-2.5 years. It includes eight incisors and molars, as well as four canines. By this time, they are erupting, including in the wrong direction, but by the age of three, in most cases they occupy a normal position, since the child is actively chewing food.
If by the age of three a boy or girl does not have a full set, do not panic. This may be an individual characteristic of the child. To be sure, it is advisable to consult a pediatrician and dentist to clarify the cause of the delay and rule out rickets, metabolic disorders or endocrine diseases.
What are baby teeth?
A child may believe that baby teeth are needed only so that the Tooth Fairy has something to build her snow-white castle from. But adults should know the truth. When a child is still very small, his head, and therefore his jaw, are small. If the baby, instead of milk teeth, began to cut molars immediately, they would not fit into the mouth either in size or in number. Therefore, nature gave us a temporary solution for the first ten years.
There are 20 primary teeth in total (10 each on the upper and lower jaws). These are incisors - central and lateral, canines, and molars. Usually, a child already has all of them at the age of 3-3.5 years.
Milk teeth differ from primary teeth not only in size, but also in structure. The enamel of primary teeth is approximately 2 times thinner and not as rich in minerals. Therefore, the child needs to carefully monitor oral hygiene - caries on baby teeth develops very quickly. Milk teeth have thin not only enamel, but also the layer underneath it - dentin - so caries quickly develops into pulpitis. Baby teeth have both nerves and roots, but they are shorter than molars. The latter gradually “dissolve” during the period of change of bite. This is why the teeth begin to loosen.
If baby teeth are not taken care of and treated, the child’s gums may become inflamed, and the embryos of the molars may suffer or die. Don't leave caries unattended!
Is it possible to pull out a baby tooth yourself?
At home, you can remove a baby tooth only if it is well loosened and you can walk freely in the socket.
It is important that the child does not have a cold: coughing, sneezing, runny nose - these are stop signals for home removal of a baby tooth. Examine the child’s mouth - if there is swelling or bleeding of the gums, your manipulations may lead to infection in the socket. It's better to see a dentist.
If you still decide to pull out a baby tooth, it is better not to experiment with tying the object to be removed to the door handle.
The best way is this: wrap the tooth with gauze soaked in alcohol and pull it out of the hole until it comes out. The tooth can also be wrapped with sterile thread and pulled strictly perpendicular to the jaw.
After the manipulations are successful, the child needs to rinse his mouth, the parent needs to see if there are any parts of the tooth left in the socket (if the tooth is broken and something remains, you need to go to the doctor). Sterile cotton wool is placed in the hole for 20 minutes: the child must press it with his teeth to stop the bleeding. Make sure your child does not drink or eat for a couple of hours after tooth extraction.
If the tooth falls out on its own, also put cotton wool in the hole and do not let the baby drink or eat for a while.