From this article you will learn:
- how many baby teeth does a person have,
- How are temporary teeth different from permanent teeth?
- Scheme of loss of baby teeth in children.
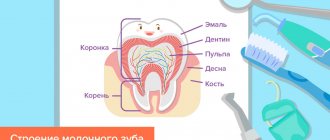
Milk teeth are a set of twenty temporary teeth that begin to erupt in a child, usually at the age of 5-6 months (the central incisors of the lower jaw erupt first). The need for temporary teeth is evolutionarily determined by the small size of the jaws of newborns. Permanent teeth are much larger than milk teeth, and their number is 1.5 times greater, and therefore, if children immediately had permanent teeth, they simply would not be able to fit into small jaws.
Because of this, in small jaws, smaller temporary teeth (in a reduced number) erupt first, and only when the jaws reach the desired size does the child replace milk teeth with permanent ones. Therefore, the time when baby teeth fall out in children is integrally connected with the growth of the jaw bones and the development of the rudiments of permanent teeth. Typically, the loss of primary teeth begins in children at the age of 6 years, and in girls this process begins earlier and proceeds faster.
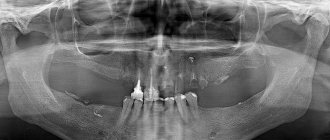
In Fig. 2 you can see how the change of baby teeth to permanent ones in children looks like on an x-ray. In this case, we see that the child has already erupted permanent central and lateral incisors, as well as the first permanent molars. But in the lateral sections of the jaws we also see still preserved milk teeth, between the roots of which the rudiments of permanent teeth are located.
What are baby teeth?
A child may believe that baby teeth are needed only so that the Tooth Fairy has something to build her snow-white castle from. But adults should know the truth. When a child is still very small, his head, and therefore his jaw, are small. If the baby, instead of milk teeth, began to cut molars immediately, they would not fit into the mouth either in size or in number. Therefore, nature gave us a temporary solution for the first ten years.
There are 20 primary teeth in total (10 each on the upper and lower jaws). These are incisors - central and lateral, canines, and molars. Usually, a child already has all of them at the age of 3-3.5 years.
Milk teeth differ from primary teeth not only in size, but also in structure. The enamel of primary teeth is approximately 2 times thinner and not as rich in minerals. Therefore, the child needs to carefully monitor oral hygiene - caries on baby teeth develops very quickly. Milk teeth have thin not only enamel, but also the layer underneath it - dentin - so caries quickly develops into pulpitis. Baby teeth have both nerves and roots, but they are shorter than molars. The latter gradually “dissolve” during the period of change of bite. This is why the teeth begin to loosen.
If baby teeth are not taken care of and treated, the child’s gums may become inflamed, and the embryos of the molars may suffer or die. Don't leave caries unattended!
Bookmarking teeth
The formation of baby teeth occurs at approximately 4-6 weeks of fetal development. At the same time, the formation of the fundamental elements occurs much later - during the first months of the child’s life. For this reason, new mothers who are bottle-feeding are strongly recommended to supplement their baby’s diet with calcium. This substance promotes the proper formation of tooth enamel.
At an early age, unprotected baby teeth are extremely susceptible to carious lesions. Parents should monitor this closely, as infection can subsequently cause destruction of permanent teeth. The fact is that the rudiments of permanent teeth are in close proximity to the roots of milk teeth, so as soon as you discover dark spots on your child’s enamel, immediately go to pediatric dentistry.
How and when do teeth change?
Loss of primary teeth begins at approximately 6-7 years of age and usually lasts until 10-12 years of age. Note that girls say goodbye to temporary teeth earlier than boys and the replacement process itself is more dynamic for them.
Parents will be able to guess that their child’s baby teeth are about to change due to a number of factors: due to jaw growth, the distance between the incisors will increase, the rudiments of molars become visible under the baby teeth, and the primary teeth become loose.
On average, the age at which a child changes teeth corresponds to the years given in the tables below:
Order of loss of baby teeth
| Age | What teeth fall out |
| 6-7 years | Central incisors fall out |
| 7-8 years | Lateral incisors fall out |
| 9-11 years | The child loses his first molars |
| 10-12 | Canines and second molars fall out |
⠀
Please note that the new tooth may not be in a hurry to take the place of the fallen one. If a couple of weeks or even more than a month have passed and there is still no molar, this is not a reason to panic. Also keep in mind that there are more molars, so some take their place without changing their predecessors. For example, molars or (the first permanent molars), erupt from scratch at the age of 5-7 years - they should not be confused with milk teeth.
Growth of molars
Image source
Molars are called a little differently than baby teeth. Try not to get confused:
| Molar | Age of appearance | Which milk tooth replaces |
| Central incisors | 6-8 years | Central incisors |
| Lateral incisors | 7-9 years | Lateral incisors |
| Fangs | 10-13 years | Fangs |
| First premolars | 9-12 years | First molar |
| Second premolars | 10-13 years | Second molar |
| First molars | 5-7 years | Do not replace baby teeth |
| Second molars | 11-14 years old | Do not replace baby teeth |
| Third molars | 17-25 years old | Do not replace baby teeth |
⠀
If you do not take into account the third molars (which are also called wisdom teeth), girls receive a fully formed jaw by 11-13 years, and boys by 13-14 years.
It is important to understand that the baby tooth may not be replaced. For example, if the germ of a molar tooth has died, then nothing pushes the temporary tooth to leave the mouth. People live with partial milk teeth even into their 30s. Therefore, if a baby tooth does not fall out, you should not try to loosen it or try to pull it out at home. Below we will look at other problems when changing teeth.
How it all happens
First of all, a little anatomy. Baby teeth are formed in the prenatal period, but the formation of permanent teeth begins after the baby is born. Thus, when you rejoice at the first tooth that has erupted, its replacement is already waiting in the wings. The time and order of eruption of permanent teeth, as well as milk teeth, is individual for each child. But temporary teeth fall out in approximately the same order as they appeared. The permanent first molars appear first. There is no milk analogue for these teeth, because in a small child’s jaw there was simply not enough space for them. The baby grows, the gaps in the dentition increase and the first adult teeth appear in the mouth - the so-called “sixes”. After the molars have erupted, it is time to replace the baby teeth with permanent ones. Loss occurs, as a rule, in the same order as appearance.
Deviations in timing and problems when changing teeth
One or another problem with the loss of baby teeth and the germination of molars occurs in at least every tenth child. Fortunately, dentists are ready to correct the bite during the growth stage, remove extra teeth, and even insert an implant if there is no point in waiting for a root one.
Let's look at the main deviations that may cause concern:
"Shark's Mouth"
Sometimes baby teeth do not have time to fall out, but the molars have already grown “second row”. The “shark’s mouth” is not worth admiring. You need to go to the dentist as soon as possible and remove unnecessary temporary teeth, otherwise your bite may be significantly damaged.
Untimely change of teeth
If the first baby teeth begin to leave the baby’s mouth before 5 years of age or after 8 years of age, then this is a deviation from the norm, which means you need to understand the reason. Trauma, caries, ecology, nutrition, congenital problems with bite or other heredity, various infectious diseases, hormonal problems (for example, thyroid disease), as well as diseases due to which the child is at risk for underdevelopment and delay may be to blame. formation of permanent dentition (diabetes, leukemia, immunodeficiency and others).
The molar does not grow in place of the lost milk tooth
There is no need to panic, but it is worth consulting with a specialist. For example, if a molar tooth does not erupt, although the baby tooth has fallen out a long time ago, the reason cannot be determined with ordinary eyes, but an x-ray will help. If there is no tooth germ in the picture, this is called adentia. This problem is extremely rare - the tooth simply has nothing to grow from. The decision will require the help of a prosthetist.
With retention, the germ of a new tooth is present, but it is directed incorrectly or is deep in the gum. All that remains is to wait for the tooth to grow. This problem occurs more often in the lower third molars, as well as in the upper incisors and canines.
With impaction, the tooth cannot come out due to the close fit of neighboring teeth. Here, too, you cannot do without the help of professionals.
We also advise you to consult a doctor if:
- molars appear darkened or grow crooked;
- the order of tooth loss and growth differs significantly from the above graphs;
- the child’s gums hurt and his cheek is swollen;
- baby tooth is corroded by caries;
- a tooth fell out, but blood from the socket does not stop oozing for more than an hour (not to be confused with ichor).
How to determine that a child will soon have molars?
An increase in jaw size is the main sign of a future change of teeth. Visually this may not be noticeable. But the appearance of three and diastema (gaps) between the baby teeth indicates that the child’s jaw is growing and preparing for the formation of a permanent bite.
The following signs are purely individual - they may or may not be present in the child.
- Increased salivation.
- Redness, swelling of the gums and oral mucosa.
- Sore gums.
- Unpleasant itching of the gums.
- Increased body temperature.
- Unreasonable cough, runny nose.
- Stool disorder.
- General malaise, lethargy.
- Loss of appetite.
- Sleep disturbance or, on the contrary, drowsiness.
- Anxiety, irritation, whims.
Important! During the period of permanent teeth erupting, parents should monitor the condition of the child, the oral cavity and gums. If symptoms that cause concern appear, you should immediately consult a doctor - a pediatrician or pediatric dentist.
Is it possible to pull out a baby tooth yourself?
At home, you can remove a baby tooth only if it is well loosened and you can walk freely in the socket.
It is important that the child does not have a cold: coughing, sneezing, runny nose - these are stop signals for home removal of a baby tooth. Examine the child’s mouth - if there is swelling or bleeding of the gums, your manipulations may lead to infection in the socket. It's better to see a dentist.
If you still decide to pull out a baby tooth, it is better not to experiment with tying the object to be removed to the door handle.
The best way is this: wrap the tooth with gauze soaked in alcohol and pull it out of the hole until it comes out. The tooth can also be wrapped with sterile thread and pulled strictly perpendicular to the jaw.
After the manipulations are successful, the child needs to rinse his mouth, the parent needs to see if there are any parts of the tooth left in the socket (if the tooth is broken and something remains, you need to go to the doctor). Sterile cotton wool is placed in the hole for 20 minutes: the child must press it with his teeth to stop the bleeding. Make sure your child does not drink or eat for a couple of hours after tooth extraction.
If the tooth falls out on its own, also put cotton wool in the hole and do not let the baby drink or eat for a while.
Why do empty spaces remain unoccupied for a long time?
It often happens that a child walks around with a toothless smile for a long time, but the situation still does not change. When examining his oral cavity, the parents do not see even a hint of an imminent full bite. This happens when:
- Retentions. Dental pathology in which a segment of gum tissue is shown very little or not at all. The violation may be complete or partial. In any case, if it occurs, you should consult your dentist. Sometimes the situation can only be corrected through surgery.
- Edentia. The banal absence of a permanent germ. So, for example, a temporary fang falls out, and there is nothing to replace it with. The anomaly can be confirmed using x-ray diagnostics - the images show that the rudiment is missing. Fortunately, congenital adentia is rarely diagnosed in young patients. If it is, only prosthetics will save you.
- Impacts. Difficulties with eruption with this diagnosis are explained by the fact that the crowns of the “neighbors” are too close to each other and do not leave room for the crown, which should be between them. Deviations can also be detected using x-rays.
If there are any problems with the bite, parents should show the baby to the doctor. Moreover, children should have annual checkups at the dentist's office. This simple measure serves as an excellent prevention of serious complications and reduces the likelihood of an unattractive smile in adulthood.
What not to do?
The following rules will help you avoid bite problems and the appearance of various defects:
- do not allow your child to loosen his teeth if they are not yet going to fall out and are firmly in place;
- teach your child not to touch a loose tooth with dirty hands (and, of course, he should not pick the hole when the tooth has just fallen out);
- Do not give your child a lot of solid foods during the period of bite changes. This way he can break a baby tooth;
- do not fill the hole after tooth loss with alcohol;
- You shouldn’t make fun of your child’s temporary toothlessness.
At what age do radical units appear?
We can talk about adult occlusion only a few years after the start of the change in time units. Typically, a stronger replacement will erupt several weeks or months (or, if pulled out prematurely, years) after the baby teeth fall out.
Central incisors grow from 6 to 8 years of age, lateral incisors from 7 to 9, premolars and canines from 9 to 12. Molars begin to grow at approximately six years of age. They immediately grow permanently, replacing the empty space.
Where to put baby teeth after they fall out?
The first tooth can be kept as a souvenir or given to the child to put in a box with children's valuables. If sentimentality is not accepted in your family, then the tooth can be thrown out.
In many families, the tooth is placed under the pillow to be taken away in exchange for a coin or small treat by the Tooth Fairy. This character came to us from the West. The fairy builds a castle from children's teeth in which good dreams are born.
But there is also a domestic tradition - to give a lost tooth to a mouse, which can also thank you with a gift. Previously, the tooth was thrown underground or hidden behind the stove with the words “Here, mouse, a bast tooth! Give me a bone one, mouse!” Now this story is more suitable for residents of private houses. It's up to you to decide whether it's worth chasing a mouse into an apartment on the 20th floor, even if it's a fabulous one. But you can take absolutely any magical character that your child likes and come up with a story about where and why the baby’s tooth will end up.
Interesting fact: baby teeth contain both stem and progenitor cells. Scientists believe that in the future, with the development of science and technology, baby teeth can be used for the benefit of their owners, for example, to treat serious diseases. But in order to preserve the cells in the tooth, special storage conditions are required, which, unfortunately, cannot be created at home.
Doctors are our pride
We did the research and found out why they trust us. In reviews
On our website, parents note the highly qualified doctors who have knowledge of several related areas and have extensive experience
working with children
. This allows you to see the clinical picture as a whole and plan treatment correctly.
In 2022, family dentistry "DOMOSTOM" in Domodedovo entered the TOP 100 private children's dental clinics in Russia according to the rating of the expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile with the support of Kommersant Publishing House.
Our clinic’s team of professionals knows how to help your child. Sign up for a consultation with us. Attentive doctors will tell you in detail about the condition of the baby’s oral cavity and answer all questions.
Complications during teething
- Delay in the appearance of permanent teeth.
This may be due to genetic characteristics, immune system problems and a number of other diseases. - Uneven teeth and other malocclusions.
- Hyperdentia.
The child’s molar tooth (or teeth) grows in the second row. Hyperdentia, or supernumerary of teeth, is a fairly rare phenomenon, but requires the intervention of a dentist to eliminate the risk of malocclusion in a child.
Why do temporary teeth fall out?
The process of changing elements of the dentition does not happen just like that. The appearance of the first teeth occurs between the ages of 6 and 9 months, when children begin to eat not only mother's milk, but also denser foods. At the same time, the dimensions of the maxillofacial apparatus are small, and therefore the dimensions of the first teeth are quite compact. Over the years, primary teeth are no longer able to perform chewing functions properly, and the jaw enlarges. As a result, it is able to accommodate all molars.
Growth of milk units
How to find out that your baby is getting his first teeth:
Viburkol for teething
- the gums become red, swell, a white ball can be visually identified, from which the milk unit will later “be born”;
- the child’s cheeks are burning;
- the baby becomes capricious, whiny, refuses to eat and sleeps poorly, and the body temperature may “jump” slightly.
Increased excitability is another “identifying sign” of the onset of teething. The child begins to put foreign objects into his mouth - chewing minimizes discomfort on the oral mucosa. A typical symptom is increased salivation - when the secretion gets on the skin of the face (in the cheeks, chin), it causes the appearance of foci of irritation (rash). Many parents notice limited hyperemic areas on the child’s neck (on the side where the tooth is cut).
Teething is a difficult period for a child’s body; against the background of restructuring and weakened immunity, children can be “attacked” by ARVI. So, if a child has attacks of nausea and vomiting, cough, abdominal pain, runny nose, appetite has disappeared or the body temperature has risen, it is recommended to immediately show him to a pediatrician.
After the appearance of the first milk units, young parents should take care of proper hygienic care for them
Important: you should not additionally stimulate (try to speed up) the process of eruption of baby teeth. Some parents scratch their gums with bread crust, a piece of sugar, and other irritants. Such measures will not have any effect on the “birth” of milk units, but they can provoke injuries to the oral mucosa or “contribute” to the development of a local inflammatory process.
No ads 3
Care instructions
Since the enamel is not yet fully formed during the eruption of molars, great attention should be paid to proper oral hygiene and preventive measures to prevent the development of caries.
- In the morning and evening, teeth should be brushed using a soft brush that does not damage the gums. Children are recommended to use special toothpastes with a high content of calcium and fluoride. It is better to brush your teeth under adult supervision, as children often do it too quickly and not thoroughly enough.
- All children should visit the dentist twice a year for an examination, professional cleaning, and timely detection and treatment of tooth decay.
- After any meal, children should rinse their mouths with plain water, a special baby mouthwash, or chamomile infusion. Thanks to this, plaque will not accumulate on the teeth and the likelihood of developing an inflammatory process in the eruption zone of the molar will decrease.