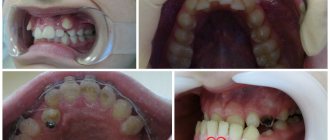
Each tooth in a row has its own unique shape; it is standard for every person. Of course, this does not mean that all people on the planet have the same teeth. On the contrary, dental impressions, like fingerprints, are unique in their anatomical features.
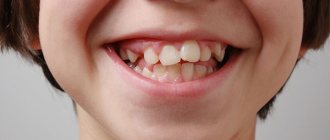
The presence of deviations in the formation of dental crowns from the standard, physiological form is called an anomaly in the development of tooth shape. As a rule, abnormal tooth shapes are combined with changes in the size of the dental units.
Reasons contributing to the development of abnormal tooth shapes
Based on numerous studies, scientists have come to the conclusion that the formation of dental anomalies occurs during pregnancy.
There are two main reasons that contribute to the abnormal development of tooth shape:
- Endogenous (independent of external factors, inherent within the body) - Down syndrome, Shershevsky-Turner syndrome, Waardenburg syndrome, Seckel syndrome, Lobstein-Vrolik disease (osteogenesis imperfecta), endocrine disorders.
- Exogenous (the result of external influences) - fetal hypoxia, deep toxicosis, infectious diseases of the mother, use of drugs, alcohol, narcotics during pregnancy, complicated childbirth.
Due to the above reasons, hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of tooth enamel may develop, which also leads to deformation of dental units.
Causes
Small jaw. First of all, bad childhood habits and developmental features affect them: infantile type of swallowing, mouth breathing, prolonged sucking of a pacifier or bottle, poor nutrition, predominance of soft foods, lack of chewing load. Also, underdevelopment of the jaw bone can be caused by the early loss of baby teeth and the long absence of permanent teeth in their place, heredity, and intrauterine disorders.
Narrowing of the dental arches. It occurs due to soft tissue dysfunction, which, in turn, can be caused by hormonal disorders, injuries, metabolic disorders, heredity, or malocclusion.
Too rapid change of teeth (up to 6-7 years). The jaw bones cannot keep up with the growth of permanent teeth, so they do not have enough space. It is not known for certain why in some children the replacement of baby teeth with molars occurs earlier than expected. This feature is due to individual anomalies in the formation and eruption of teeth.
Pathological growth of teeth. “Eights”, or third molars, erupt quite late, at 16-27 years old, and they often no longer have enough space. As they grow, they move adjacent molars and push the entire row, which can cause crowding of teeth. Other provoking factors are hyperdentia, or supernumerary, extra teeth, and macrodentia - an increase in the size of one or more teeth.
Types of tooth shape anomalies
The abnormal shape of the dental crown is mainly distinguished by the front, lateral incisors, both upper and lower, supernumerary teeth, and less commonly, molars.
Depending on the appearance of the manifestation of the pathology, anomalies in the shape of the teeth have the following varieties:
- Giant teeth - an increase in the central incisors by one and a half times. The result is a violation of physiological occlusion.
- Spike-shaped teeth - the central and lateral incisors of the upper jaw and the lateral incisors of the lower jaw acquire this shape.
- Ugly teeth - come in many forms; the crowns of the anterior teeth are affected.
- Fournier's teeth - the incisors of the central part of the upper jaw have a barrel-shaped, screwdriver-shaped appearance. The cutting edge of the dental crown is smaller than its neck.
- Hutchinson's teeth differ from Fournier's teeth by the presence of a semicircular hole on the cutting surface of the tooth. The enamel in this place is thinned, or even completely absent.
- Pflueger's teeth - the first molars are modified. They differ in the smaller size of the chewing surface from their coronal part.
Consequences
The incorrect size of even single specimens can lead to deformation of the entire row of teeth, which in turn provokes the development of possible consequences.
Most often, pathologists note the following consequences :
- displacement of the anterior incisors in the distal direction. This result can only be observed if the lateral incisors are also small in size;
- violation of stability .
The small dimensions mean that there is no full contact between the side surfaces, which provided additional stability. Without constant support, the ligaments in the dental bed are stretched, causing the tooth to become mobile; - violation of speech functionality . With microdentia, a change in diction is often observed, whistling and hissing sounds are most pronounced;
- improper functioning of the temporomandibular joint . It is observed in a generalized form of the disease, due to improper distribution of the load during chewing and increased muscle tone in a separate area of the jaw;
- psychological discomfort , which is provoked by the presence of trema and diastemas;
- inflammation of periodontal tissue caused by bacteria accumulating in wide spaces between teeth and enlarging gum pockets when loosened.
What is such an anomaly in the number of teeth as hyperdontia, we will tell in a new review.
In the next article we will talk about cases in which macrodentia in a child is considered a deviation.
At this address https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/zubov/polozheniya/krivyie.html you will find photos and recommendations on how to prevent the appearance of crooked teeth in children.
How modern methods are used for dental restoration in case of dimensional pathologies, watch the video:
Diagnosis of tooth shape abnormalities
Consultation with an endocrinologist and geneticist will help determine the cause of this pathology. Choosing the right method for eliminating pathology is the job of a dentist, orthodontist, or surgeon.
For diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a series of studies, which include:
- careful collection of anamnesis;
- studying diagnostic casts of the patient’s dentition;
- cone tomography;
- various types of radiographic examinations;
- electromyography (study of the functionality of facial muscles).
Peculiarities
Dental crowding is a pathology characterized by:
- incorrect angle of rotation of some teeth relative to the rest (tortoanomaly),
- vestibular (outward) or palatal (inward) inclination of the teeth,
- “pile up” of teeth, their position is too close,
- eruption of teeth outside the dental arch due to lack of space in the dentition.
Depending on the severity, crowding of teeth can be:
- mild - crowding on one jaw is about 2-3 mm, no more than 2-3 teeth are crooked;
- medium - the displacement reaches 4-65mm;
- severe - more than 6 mm, many teeth are displaced, which is clearly visible to others;
- very severe - the lack of space in the dental arch reaches 7-8 mm, the position of all or almost all teeth is disturbed.
Methods for treating abnormal tooth shapes
It is important to remember that treatment of any pathology associated with correcting the shape of dental crowns begins after the formation of a permanent bite. Anomalies in the shape of teeth are primarily a big aesthetic problem.
Methods of modern prosthetics make it possible to correct almost the most complex cases of dental anomalies:
- Restoration using ceramic veneers - such microprosthetics are performed by attaching a thin ceramic plate to the previously prepared front surface of the tooth. This procedure allows you to cope with the rather complex task of smile aesthetics in a short period of time.
- Prosthetics with crowns is considered appropriate when additional strengthening of the tooth is required. The material for making crowns can be different: a metal alloy of medical or noble metals, metal-ceramics, metal-plastic, ceramics. The choice depends on the aesthetic preferences and financial capabilities of the patient.
- Restoration with composite materials is possible for minor dental anomalies. It is one of the most affordable and fastest methods of dental crown reconstruction.
- Tooth resection - supernumerary and giant dental units are removed. This is followed by bridge prosthetics or installation of dental implants.
Treatment
Treatment of abnormalities in the position, size and shape of teeth is carried out mainly surgically. When reducing the size of a tooth, prosthetics, implantation or restoration are used.
You can change the shape of a tooth using veneers and laminates made from composite filling materials or ceramics. If the teeth are in an abnormal position, they are moved or removed and then replaced with a prosthesis. The first is implemented using special devices or plates that cause compression of the teeth and their displacement. For this purpose, removable and non-removable orthodontic devices, braces, and a face bow are used.
Complex dental anomalies require an integrated approach to treatment, which will correct the bite and completely eliminate the defect. During a consultation at the Mositalmed clinic network, the dentist will select the necessary treatment regimen, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the clinical picture. The production of implants in our clinic is carried out using reliable technology and high-strength materials.
Prevention of dental abnormalities
The only method of preventing this disease is to provide the expectant mother with appropriate conditions:
- nutritious, varied nutrition;
- regular, high-quality medical care;
- protection from stressful situations.
It is necessary to forget about existing bad habits during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Particular attention should be paid to the development of the child in the first year of life. Natural feeding and prevention of rickets are a solid foundation for the excellent health of the baby.
Clinic doctors
Macrodentia of teeth is an increase in their size compared to normal. Such an anomaly can be observed in one, several or all teeth at once, which affects not only aesthetics, but also the bite. Since large teeth take up a lot of space in a row, their neighbors are forced to change their position - shift towards the cheeks or palate, or turn along their axis. Often, an already formed tooth simply cannot erupt - this phenomenon is called retention.
Why does macrodentia occur?
This phenomenon may have different reasons: macrodentia develops due to metabolic disorders in the fetus in the womb, genetic predisposition, or the presence of endocrine diseases in a person that cause improper growth of teeth. Excessively large teeth are the result of:
- fusion of the root parts of two adjacent teeth during the period of active growth;
- connection of two tooth primordia during their formation;
- fusion of the follicles of the supernumerary and normal teeth.
Types of macrodentia of teeth
The classification of macrodentia includes several types of pathology:
- Localized. The process involves single teeth or a small group. Their deviation in size is clearly visible against the background of the general series.
- Generalized. Each tooth on the jaw is enlarged by 1-2 mm.
- Isolated. With this type of macrodentia, only one incisor exceeds the norm (up to 5-6 mm).
- Absolute. The sum of the width of the upper incisors is 35 mm or more, the lower ones – from 27 mm.
- Relative (individual). The total width of the incisors on the upper jaw is 33-34 mm, and on the lower jaw it is 26-27 mm.
Diagnosis of macrodentia is carried out by visual examination or measurement of teeth.
How is macrodentia treated?
The treatment tactics for macrodentia depend on the severity of the disorder and the characteristics of the bite. There are several ways to solve this problem in dentistry:
- Separation. The tooth is reduced by grinding off part of the enamel, which is quite thick. In this way, up to 6 mm of volume can be removed. After grinding down the hard tissues, a fluoride preparation is applied to the treated surfaces to reduce tooth sensitivity.
- Removal of a tooth. If macrodentia in children and adults is the cause of severe crowding or the deviation from the norm is too pronounced, this method is used. The next stage of treatment is prosthetics.
- Composite restoration. Part of the tooth is ground down, then the correct anatomical shape is reproduced using filling material.
- Vining. Anomalies in the size of teeth can also be corrected with ceramic veneering. This is a very expensive, but much more reliable analogue of a composite.
- Orthodontic treatment. Indicated for curvature of teeth or changes in their position in a row. In case of primary or early mixed dentition, trainers and plates are used, and braces are placed on permanent teeth.
But most often, regardless of the cause of macrodentia, complex therapy is practiced in dentistry, combining several methods at once.