Implants used to restore lost teeth appeared several decades ago. And work on their improvement continues to this day. Experts are interested in both increasing reliability and durability, as well as high-quality integration with living tissues.
It is equally important to get an excellent cosmetic effect after installing even the most budget-friendly artificial roots. The result of the work of analysts and dental practitioners has been the emergence of a wide range of implants used to restore the aesthetic and chewing functions of the maxillofacial apparatus.
History of the first patient
The first attempts to replace lost teeth with artificial ones were made by people in antiquity and even earlier. In the form in which we know dental implants now, they appeared in the second half of the 20th century. The first successful implantation was performed in 1965 on an ordinary carpenter, Gust Larsson, who lost all his lower teeth at the age of 34, had a cleft palate, a deformed upper jaw and chin, and experienced constant pain and significant difficulty eating and speaking. Larsson volunteered for a new study led by Professor Ingvar Brånemark at the University of Gothenburg, which Güsta had heard about by chance from his dentist. After the treatment, he was able to chew, eat and speak normally. The installed implants served Gust Larsson all his life. The experience of this brave man proved that installing dental implants is the most effective way to restore lost teeth.
Options for the number of lost teeth
The method of restoration is determined depending on the number and location of lost teeth. Only the attending physician will answer the question of what to choose. The table shows general indications:
| Pathology | Implants | Removable dentures | Dental bridges |
| 1 tooth missing | Yes | yes, if the patient does not want to grind healthy crowns | Yes |
| Several teeth missing in a row | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Scattered defects | Yes | depends on the length and location of defects | Yes |
| End defect | Yes | No | No |
| Completely edentulous | Yes | Yes | No |
Dental implants – what are they?
Dental implants, implants, implants are all artificial structures that replace missing teeth. They are firmly fixed in the bone tissue of the jaw and serve as a reliable support for fixed or removable dentures in the form of single crowns and bridges of varying lengths (you can see what dental implants look like in the photo above). There are several types of dental implants, but the most popular today are root-shaped dental implants, which have earned favorable reviews from both patients and leading implantologists around the world. Prices for dental implants depend on their quality, features of the installation system, the presence of special coating and other factors. Which implants are better is a topic for a separate article.
Preparatory stage
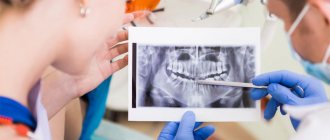
If there are no contraindications to surgery, preparation of the oral cavity for implant installation begins. The dentist identifies areas affected by caries and carries out sanitation, removing objects that are subject to prosthetics. At this time, the doctor performs a computed tomography scan or orthopantomogram to examine in detail the condition of the gums and jaw bones.
Surgical stage
During the surgical stage, the implant is directly installed. With the one-step technique, the structure is installed immediately after tooth extraction.
If during the preparatory stage areas of bone tissue deficiency were identified, a sinus lift procedure is performed. The technique involves increasing the volume and height of bone tissue, compacting it so that it is possible to further secure the pins. The procedure is performed under anesthesia and takes from 60 to 90 minutes.
Sinus lift is indicated in the following cases:
- With atrophy of bone tissue due to prolonged absence of a tooth.
- If bone tissue is lost due to traumatic removal.
- With individual structural features, when the maxillary sinus is large.
After sinus lifting, you will need to wait 3-4 months; only after the material has been fixed can you begin to fix the implant.
If there is enough bone tissue, an operation to insert an implant is performed. The doctor cuts or punctures the gum, makes indentations in the bone, installs a pin or plate, and sutures the gum. You should wait for complete osseointegration before proceeding to the next stage.
Abutment installation
An abutment is an implant element that is placed above the bone to secure a crown or bridge. It is recommended to fix the abutment after the gums have healed and the implant has been implanted.
To install the abutment, the doctor opens the gum, removes the plug from the pin, and then screws in the product. The holes for the abutment screw are closed with a temporary filling.
The product is made from various materials - plastic, ceramics, metal and their combinations. According to their purpose, abutments are divided into:
- Gum former. A temporary abutment that prepares the gums for the installation of a permanent product and crown.
- Standard. Sold ready-made, not adjusted to the anatomical characteristics of the patient. Such products are produced in different sizes and are inexpensive.
- Angular. A type of standard abutment, which is made at an angle.
- Individual. It is made for the patient, taking into account anatomical features.
- Ball. It is made in the form of a rod with a ball at the end. Difficult to produce and expensive, but it holds the crown more securely.
After installing the abutment, you will have to wait 7 to 14 days for the gums to heal completely. The first two days after the operation you can clean the oral cavity; on the 2-3rd day you are allowed to carefully clean the area where the abutment is installed with a soft brush. Plaque should not be allowed to accumulate in this area.
Orthopedic stage
The last stage is the manufacture of the prosthesis and its installation. First, the implantologist makes impressions of the jaws, and a crown or bridge is made from the impressions. When producing crowns, the shade is selected so that the dentition looks realistic.
Fastening is carried out in the following ways:
- crowns and bridges - on the abutment, using cement or screw fastening;
- the removable one is fixed using a screw fastening, on a beam or using a push-button fixation method.
Once the permanent crowns are installed, the procedure is completed.
Structure of a dental implant
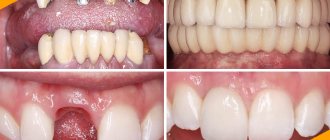
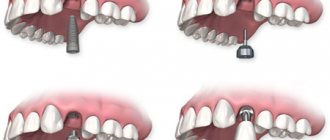
A root-shaped implant, as mentioned above, is the most common and sought-after type of dental implant. What does a dental implant consist of? Root-shaped structures have three parts: root, abutment and crown. A titanium rod replaces the root of a lost tooth. The abutment externally is an artificial tooth ground for a crown. It serves as a link between the components of the implant - the rod and the prosthesis, and is also the basis for the latter. Root-like artificial roots are divided into cylindrical and helical. The latter are more in demand in implantology, as they have a thread applied to their surface, which contributes to a more durable fusion of the titanium rod with the jaw bone. Dental implants come in different sizes – they can be short or long, thick or thin. See the photo below for what a dental implant looks like.
Photo of a dental implant
Possibilities of a conditionally removable denture supported by natural teeth
A fixed bridge supported by your own teeth will help replace 1 to 4 missing teeth in a row. The undoubted advantage of such dentures is a better restoration of chewing function compared to removable dentures, the absence of discomfort and good aesthetic characteristics. Bridges do not need to be maintained or adjusted: up to a certain point, the patient may not notice them at all. Of course, this design will also cost significantly less than an implant-supported prosthesis. But there are some nuances here too.
✔
With a classic bridge, only a few teeth can be restored, because the supporting teeth also need to be taken into account. For example, to replace 1 tooth, the patient is given a prosthesis on 2 supporting teeth.
✔
Abutment teeth (even completely healthy ones) must be ground down for crowns.
✔
In this case, the tissues surrounding the tooth, the so-called periodontium, have an increased chewing function, taking on the load of the missing tooth. Over a long period of operation, the reserve forces of the periodontium of the supporting teeth will weaken, which, as a consequence, sooner or later will lead to their loss. That is why the service life of bridges, as a rule, does not exceed 7-10 years.
How do dental implants take root?
What material are dental implants made of? The answer to this question will help us understand why they take root well. Almost all of the newest dental implants are made from titanium. This unique material is ideal for the manufacture of artificial tooth roots, since it is not perceived by the human body as something foreign and is not itself subject to the destructive effects of the surrounding biological environment. But the most important thing is that it can reliably fuse with the jawbone. These unique properties of titanium solved the problem of rejection and made implantation a reliable and durable technique. However, in very rare cases when a patient is allergic to titanium dental implants, zirconium dioxide is used as a base to make the prosthesis.
How long does it take for a dental implant to take root? Experts believe that the survival of dental implants is an individual process. The timing of osseointegration depends on the area of the dentition in which the implantation was performed, as well as on the quality of the bone tissue. In general, the healing of dental implants lasts from three months on the lower jaw and up to six months on the upper jaw. If the implantation is successful, then removal of the prosthesis becomes almost impossible, which proves the reliability of the structure. What is the survival rate of dental implants that worries many patients? It varies among different manufacturers, but in general it does not exceed 5%. In addition, the success of the operation is also influenced by the skill of the implant surgeon, so the choice of dentistry should be approached with special care.
Alternatives to Dental Implants
Currently, there are 2 types of prosthetics, in addition to implantation:
- installing a crown if the tooth root is alive;
- removable dentures.
If for some reason surgical intervention is not possible, patients are recommended to have removable dentures. They will help restore chewing function and aesthetic appearance. But the technique has its drawbacks. The removable structure can fall out, they often break and the patient does not always get used to them quickly. The product can press and rub for a long time.
Lifespan of dental implants
Although implantation is significantly more expensive than traditional prosthetics, with a long-term calculation the costs are equalized. This is due to the fact that traditional bridges, crowns, clasp or nylon dentures need to be replaced on average every 5 to 7 years, and the supporting teeth will have to be ground down again each time. How long does a dental implant last? The minimum service life of a dental implant is about 30 years, and if all the doctor’s instructions are followed, the implant will last you a lifetime. Most manufacturing companies, including world industry leaders, who invest considerable funds in the latest developments, provide a multi-year or even lifetime warranty on their products. This applies to the part of the structure that is located inside - that is, the root (base plate, etc.) and the abutment. A crown installed on an abutment has a more limited service life, but it is also significantly longer than that of a traditional prosthesis installed on ground natural teeth. This is on average 10 – 15, sometimes 20 years. If we are talking about implantation for a young person, then, of course, he will be interested in what happens to implants in old age. With proper care and preventive examinations, nothing should happen to the artificial root.
Types of dental implantation
All clinical cases encountered by dentists are individual. Especially when it comes to dental prosthetics. The implantation method is recommended to the patient after examination and assessment of the condition of the jaw bones and surrounding tissues. Currently, the following methods exist:
- classic two-stage with delayed loading;
- basal one-stage with immediate load;
- immediate or express implantation immediately after removal;
- mini-implantation, using small pins;
- combined.
Mini-implantation is used for additional fixation of a removable denture. Combined is used to treat several teeth in a short period of time. In this case, the restoration of the anterior incisors is carried out using a one-step technology, and large molars using the classical technology. Let's look at the other methods in more detail.
Classical
The classical technique can be called universal, since it is carried out for any medical indication. This method is effective when it is not possible to immediately achieve stability of the implant or bone grafting is required. If you put stress on a tooth prematurely, there is a high risk of rejection.
The classical method is carried out in 2 stages:
- Implantation. An operation is performed, a pin is secured with a plug, and the gum is sutured.
- Prosthetics. After 4-6 months, when the implant has taken root, an operation is performed to open it, and a gum former is installed. When the wound heals, an abutment and a plastic crown are installed. After 3 months, the crown is replaced with a permanent one.
Classical technology is famous for its good implant survival rate. In addition, the doctor has the opportunity to shape the gums beautifully and achieve a beautiful result. The disadvantage of the technique is long-term treatment, from 4 to 8 months and repeated surgery.
One-step
The one-stage technique involves installing an implant immediately after tooth extraction. This technology is often used for the restoration of anterior incisors, since not all patients are ready to live for months with a large gap in the smile area.
Simultaneous implantation is carried out in two ways:
- with immediate prosthetics;
- with delayed prosthetics.
With immediate prosthetics, immediately after tooth extraction, an implant with a gum former is inserted and sutures are applied. After the wound has healed, the former is removed and the abutment and crown are installed.
With delayed prosthetics, the abutment and crown are installed after 3-6 months, when osseointegration is complete. When restoring chewing teeth, it is recommended to choose a delayed technique, since the chewing load can lead to rejection of the pin.
Simultaneous implantation is not possible if the bone density is insufficient.
Basal
Basal technology with immediate load involves the introduction of a structure into the deep layers of the jaw, in particular, into the basal layer, which is characterized by increased density.
The procedure is called one-stage, since the implantation of pins and prosthetics occurs with an interval of 3-5 days. Due to the deep placement of the implant, there is no need to wait for complete osseointegration. The load during chewing is evenly distributed to the jaw bones.
General and specific contraindications
Who is contraindicated for dental implants? Implantation is a surgical operation and, like any other operation, it has contraindications. They are divided into two types: general for any type of implantation and specific dental ones.
The following concomitant diseases are common to all types of implantation (and to surgical interventions in general):
- violation of coagulation (blood clotting), diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, chronic rheumatism - these diseases complicate wound healing and implant placement;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- childhood and adolescence – children and adolescents continue to grow, and this is fraught with displacement of implants or their rejection, or slowdown in the growth of individual organs as a result of the installation of dental implants in them;
- diseases of bone tissue that reduce its regenerative abilities;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- cancer during exacerbation, HIV and AIDS, specific diseases of the immune system that weaken the body as a whole and do not allow it to recover after operations.
The following can be considered specific contraindications to dental implantation:
- when installing implants in the upper jaw, it is necessary to take into account such factors as the proximity of the sinuses (aka the maxillary sinuses), as well as the width and density of the bone at the point of contact of the jaw with the sinuses; in some cases, the implantation procedure may be preceded by a sinus lift;
- chronic, including inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa;
- patient's failure to comply with oral hygiene;
- insufficient height and density of bone tissue at the site of proposed implantation (this applies to both the upper and lower jaws) - in such a case, bone grafting can correct the situation.
It is worth noting that diabetes and advanced age are not currently included in the list of contraindications for dental implantation.
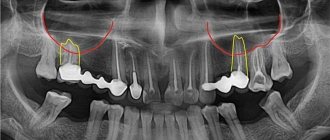
Dental implants in the upper jaw
Dental implant technologies
Modern dentistry is constantly evolving; every year patients are offered new technologies for treatment, extraction and prosthetics. When choosing a technique, you should pay attention to such factors as the condition of the jaws, the patient’s desire to wait a long time, and the amount of money that the patient is willing to spend on restoration.
Implantation technologies are distinguished by the method of fastening the structure:
- root-shaped.
- under the mucous membrane of the oral cavity;
- through the jaw bones;
- between bone and periosteum;
The best option for replacing one or more teeth is a root-shaped product, which is a threaded pin that imitates a root. The pin is screwed into the bone tissue, and the crown is fixed on top. This technology allows you to get a beautiful smile for many years and prevent bone and mucous atrophy. The disadvantage of this method is that it cannot be used if the bone tissue has already atrophied and cannot be restored.
Technologies are also distinguished by the method of operation. To install the structure, an incision is made in the gums, which can be done either classically - using a scalpel, or minimally invasive - using a laser.
Intramucosal
Intramucosal technology involves fixing the structure under the soft tissue of the gums. The technique is used to stabilize a removable denture; it is not suitable for installing crowns.
Such products are elastic plates and buttons that are placed in soft tissues. A part remains above the gum that connects to the removable denture, similar to a snap fastener on clothing. Thanks to the product, wearing a removable denture becomes much more pleasant, as it is securely fixed.
The indication for the use of the technique is the patient wearing removable dentures, as well as the impossibility of using other implantation techniques due to bone tissue atrophy. The only requirement for installing an intramucosal implant is sufficient gum thickness.
Transosseous
Transosseous implantation involves installing an implant in the form of a bracket on which pins are attached. This type of brace is attached to the chin and mouth. To carry out the procedure, you need to make an incision in the jaw from the outside and insert a staple. The pins protruding from the mouth will be used to install the denture.
This technique is considered outdated and is used in rare cases, with bone tissue atrophy. It entails a painful recovery period, and visible scars may remain on the face. Often the transosseous technique ends in complications and rejection of the structure due to the inflammatory process.
Modern prosthetic methods make it possible to install an implant without cutting the soft tissue of the jaw and without a difficult rehabilitation period. Thanks to the sinus lift technique, it became possible to restore bone tissue and perform surgery using the classical technique.
Subperiosteal
The subperiosteal technique involves fixing the structure under the periosteum without penetrating into the bone tissue. In this case, the implant has the form of a saddle-shaped frame onto which the dentition is attached.
The technology is indicated in cases where it is not possible to install a pin:
- with bone tissue atrophy;
- with insufficient size of the alveolar zone;
- if it is not possible to perform a sinus lift procedure.
The product is made individually for each patient using impressions. First, the doctor cuts the gum, places the structure under the periosteum without damaging it, then the wound is sutured. After the structure has healed, a bridge is placed.
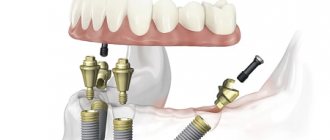
"All on four"
All-on-4 or All-on-4 technology is used to replace all teeth. The technique consists of fixing 4 structures on each jaw, onto which dentures will subsequently be attached. The technology is indicated in the following cases:
- if a large number of teeth or an entire row are missing;
- with bone tissue atrophy and the impossibility of sinus lift;
- hypermobility of teeth;
- no desire to wear removable dentures.
Prosthetics takes place in 2 stages. First, the remaining teeth are removed and titanium posts are installed. Then the doctor makes impressions of the jaws, from which one-piece dentures will be made. After 3-6 months, when osseointegration is complete, a permanent prosthesis is installed.
Laser implantation
Laser implantation differs from other technologies in the method of surgical intervention. In this case, the gum incision is made using a laser, which has its advantages:
- high accuracy of impact;
- immediate cauterization of tissue, which eliminates further infection;
- there is no bleeding, hematomas or swelling;
- the procedure proceeds faster;
- laser surgery is less painful than classical surgery.
After a conventional operation using a scalpel, inflammatory processes occur more often, and the wound healing process takes longer. The only drawback of laser technology is the increased cost of the service.
Caring for Dental Implants
Many patients who have had artificial teeth installed are concerned about the question: how to care for dental implants? In fact, caring for artificial teeth is practically no different from regular oral hygiene. The same few basic rules apply here: regularity, thoroughness, correctness. That is, you need to brush your teeth at least twice a day - in the morning and before bed, and preferably after every meal, especially after eating carbohydrates; this must be done for at least three minutes, and also use additional hygiene products: dental floss, irrigator, etc.; You need to brush your teeth correctly - with sweeping movements away from the gums. The same brushes that are used for cleaning natural teeth are suitable for cleaning dental implants, but you can purchase a special toothbrush for implants.
Doctor's advice - removable structures cannot compare in quality with an implant.
If you decide whether a removable denture or an implant is better, the choice is obvious. Removable structures cannot compare in quality to an implant. They need to be serviced every year, while an implant will last ten years without updating. Not all removable models are securely attached. In terms of comfort, removable structures are also inferior to implants. The latter do not bring discomfort to the patient, do not rub the gums and feel like natural teeth after just a couple of days.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Chief physician, Ph.D.
Prices for dental implants in Moscow
As with any other area of dentistry, the cost of dental implants varies widely. On average, the price for installing one dental implant in Moscow ranges from 15,000 in economy class dentistry to 80,000 rubles in a VIP clinic. Moreover, the budget required for the implantation procedure as a whole largely depends on the cost of the implant. In order to understand how much a dental implant costs and which price is acceptable, which is unreasonably high, and which is suspiciously low, it is necessary, first of all, to understand what it consists of.
Contraindications for implantation
Before performing an implantation procedure, the dentist must check the patient for possible contraindications. They are divided into several varieties.
Absolutes include the following:
- blood diseases;
- if there are malignant tumors;
- with immune pathology;
- if there are diseases of the central nervous system;
- if bisphosphonates are taken orally;
- in the presence of lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism, scleroderma;
- if you have tuberculosis;
- if there is recurrent stomatitis or pemphigus;
- if the function of the masticatory muscles is impaired;
- diabetics.
Relative contraindications include the following:
- Lack of oral sanitation.
- Poor oral hygiene (this is a good reason to prescribe removable dentures).
- For gingivitis.
- If there is marginal periodontitis.
- For pathological bites.
- For diseases of the temporomandibular joint.
- If there is severe atrophy or damage to bone tissue.
- If the patient smokes, drinks alcohol and drugs.
- When pregnant.
General contraindications consist of the following:
- Surgical reasons for refraining from any intervention.
- Contraindications to pain medications (negative tolerance to anesthesia).
- Certain somatic diseases that may be affected by the procedure (these include endocarditis and other heart diseases, rheumatism, etc.).
- Certain treatment methods can have an impact on the regeneration and preservation of the dental element after installation, on the tissue surrounding the dental element (if various types of depressants, anticoagulants, cytostatics and other agents are used).
- Diseases of the central nervous system.
- Distress syndrome (severe and prolonged stress, which is caused by all sorts of reasons).
- If there is exhaustion of the body.
- Poor oral hygiene (this is a good reason to prescribe removable dentures).
Local contraindications consist of the following:
- unsatisfactory tendency to oral hygiene;
- insufficient presence of bone tissue or its inappropriate structure;
- unsatisfactory distance to the maxillary and nasal sinuses.
Temporary contraindications include the following:
- acute diseases;
- rehabilitation and health stages;
- pregnant condition;
- addiction;
- condition after irradiation (the implantation procedure can be done after a year).
Reasons for the high cost of dental implants
Material and price of dental implants
The main material for manufacturing dental implants is titanium alloy. Titanium is bioinert, that is, it is not perceived by the human body as a foreign element and is not influenced by the surrounding biological environment. Thanks to its unique qualities, dental implantation has become a reality of modern dentistry. But this is not the only material from which implants are made. In special cases, zirconium oxide can be used as a base; this occurs when the patient is allergic to titanium. With regard to the material of manufacture, prices for dental implants depend on the purity of the alloy and the presence of a special coating that helps make the healing process faster and more reliable. It is worth noting that the above-mentioned zirconium oxide is a more expensive material than a medical titanium alloy.
Manufacturability determines how much a dental implant costs
The type of implants that have a root-like shape have long been recognized as the most reliable and physiological. Many of them have special grooves on the surface. But some systems have additional technological advantages and a more advanced form, which speeds up healing, expands the possibilities of implantation and subsequent prosthetics on implants, and also prevents bone resorption and provides better support for the soft tissue of the gums around the implant. Thanks to this, an artificial tooth serves a person throughout his life and looks as natural as possible. It is not difficult to guess that the more technologically advanced the implant, the more expensive its cost.
Overpayment for the brand or adequate price of dental implants
Undoubtedly, the brand of certain implants affects their cost. However, you should not think that in the case of an implantation system from well-known manufacturing companies you are overpaying for the brand. As a rule, world industry leaders provide a multi-year, and in some cases, a lifetime warranty on their products. Also, large manufacturing companies invest considerable funds in the latest research and development, which allows them to perfect the quality of implants, as well as develop the most effective solutions to problems arising in modern implantology.
About implant brands and price differences
The most expensive implants are those made in Europe and the USA, but this does not mean that they have no alternative. We recommend paying attention to South Korean implants. Many are quite skeptical about products from Asia, but the medical industry of South Korea is not inferior to leading Western countries in terms of technological solutions. One of the best South Korean implant systems is Osstem. The company offers a wide range of implants and abutments that can solve the problem of partial and complete tooth loss in patients of various age and social groups. The possibility of 3D planning and the availability of special sets of tools for installing Osstem implants in conditions of bone deficiency makes it universal.
It is very important that the selected company producing implants has a distributor in your city who would not only sell this system, but also conduct courses, seminars, master classes and provide all the necessary technical support to doctors and patients. There is no need to save on your health by trusting systems that have not received a license and do not have official representation in Russia.
Dental implants – pros and cons
As for expert opinions, the majority of specialists are inclined to argue for dental implants, and those who are usually against are either very elderly doctors or dentists who do not have sufficient qualifications to carry out such procedures. If we consider the pros and cons of dental implants, then among the undeniable advantages we can note durability, the absence of the need to grind adjacent teeth, in contrast to the installation of bridges, as well as the preservation of all the functions of a natural tooth, such as: full participation in chewing and speech, prevention of tooth loss bone tissue and changes in facial features. As for the disadvantages, the price becomes a significant difficulty for most patients, however, as mentioned above, this is an adequate cost of solving the problem once for a lifetime. As for an alternative to dental implants, it does not exist as such, since traditional prosthetics is inferior to it in all respects.
Dental implants make it possible to improve the quality of life, restore the full functionality of the dentition, restore the attractiveness of the smile, and also protect yourself from the loss of bone tissue in the place of the missing tooth, and therefore from the possibility of losing neighboring teeth. But, in any case, only an implantologist can confirm the need for this operation; he will also help you draw up a treatment plan and choose designs that suit you personally.
Indications
Indications for dental implantation:
- complete absence of dentition;
- missing one or more teeth;
- patient's reluctance or inability to use removable dentures;
- increased wearability of enamel;
- lack of closure of teeth.
The decision on the need to install pins is made by the dentist based on the results of a comprehensive examination.