The most common form of jaw injury is a bruise. No one is immune from this. For example, with a strong blow to the jaw, soft tissues, blood vessels, and capillaries are affected, resulting in the formation of hematomas and swelling. This is accompanied by severe pain and discomfort.
To avoid complications, it is recommended to consult a doctor immediately after injury. The fact is that impaired jaw function entails a chain of negative consequences: difficulties while eating, deterioration in the quality of spoken speech, etc.
What causes bruises?
Jaw injury may result from:
- falls;
- blow;
- fights;
- children's games;
- accidents, etc.
The severity of the injury is determined taking into account the following factors:
- features of the surface or object that caused the injury;
- impact intensity;
- affected area of the face;
- condition of bone tissue before the incident.
The strength of the bruise and possible complications depend on the listed indicators. Regardless of the severity, it is important to see a doctor to evaluate the condition and prescribe appropriate treatment. This will avoid unforeseen consequences and quickly restore the damaged area.
First aid
Immediately after the impact, carefully place the child on the bed and carefully examine his head. At the same time, there is no need to rush and fuss so that the baby does not become even more frightened. After all, hysteria can increase intracranial pressure or increase bleeding from a wound.
When a lump forms, apply ice wrapped in a piece of cloth to it. A cold water bottle or a bag of frozen food wrapped in a towel will do. A cooling compress will help relieve swelling and prevent the development of a hematoma. But you need to hold it for no more than five minutes.
If you find a wound, treat its edges with hydrogen peroxide and apply a gauze or cloth swab to absorb the blood. If bleeding does not stop within 10 minutes, call a doctor.
If there is no damage at the site of impact, the child's condition should be closely monitored for at least a week. Moreover, in the first few hours it is better not to put the baby to bed, since the main symptoms of a concussion appear precisely at this time.
Children of the first year of life cannot talk about their health. Consult a doctor if you notice prolonged crying, refusal to eat, restless sleep, or vomiting.
An older child needs to be asked in detail how he fell and where the pain is felt. If the impact is muffled by the carpet, and the fall itself was not dangerous, medical attention is not required. But it doesn’t hurt to watch the baby for a few days to make sure there are no dangerous consequences.
Clinical picture
First of all, the doctor conducts a visual examination of the bruised area to identify hidden injuries that cannot be identified by a person without medical education. For example, symptoms of dislocations or fractures may not appear immediately. Professional consultation allows you to begin timely treatment, if required.
To recognize a jaw bruise, it is important to pay attention to the following symptoms:
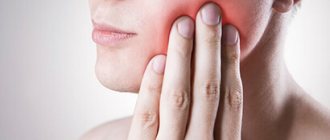
- severe pain in the place where the blow fell, intensifying when pressed;
- visual signs (eg, swelling, redness, abrasions, bruises);
- limitation of jaw mobility when yawning, talking, chewing;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- general weakness.
Jaw bruises are less dangerous than more severe injuries, so recovery is usually quick.
The doctor may order an x-ray or computed tomography to establish an accurate diagnosis. These studies will assess the condition of the internal tissues of the affected area.
Injury
5350 12 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Bruise: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Bruise is a closed mechanical damage to internal tissues or organs without significant disruption of their structure. Bruises are characterized by suddenness, speed and short duration of action of the traumatic factor. Bruises are mostly local in nature. The most vulnerable are the dermis and the vessels located under it, which leads to the formation of hematomas and edema. As a result of a severe bruise, internal organs may be injured. The severity of the process is determined by the type of damaged tissue or organ that is affected by the traumatic agent (skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles, parenchymal or hollow organs, brain or spinal cord, etc.).
In cases where the damage is severe, multiple ruptures of small vessels occur, followed by hemorrhage and dysfunction of the organ.
Causes of bruises
A bruise is considered the most common type of household injury and usually occurs when falling or hitting hard objects. In children of the first years of life, household and play injuries, bruises of the soft tissues of the face and neck predominate. At older ages, the main ones are considered to be transport, sports and street injuries.
Lung contusion and/or heart contusion as a result of mechanical impact on the chest is a potentially dangerous injury - the vast majority of victims are drivers who hit their chest against the steering column of a car.
Contusion of superficial soft tissues is always accompanied by swelling of the injury site as a result of soaking of the skin with lymph, blood and local aseptic inflammation. The severity of edema depends on the area of damage to the subcutaneous tissue at the site of the injury. For example, in the area of the cranial vault, due to the thin layer of subcutaneous fatty tissue, the swelling is insignificant, while even mild bruises of the face are accompanied by severe swelling.
A concussion can develop as a result of a head injury.
Severe deep bleeding often leads to additional injury to adjacent tissues as a result of their compression, which is accompanied by a gradual increase in pain and dysfunction of the injured organ.
Often, abrasions and shallow wounds are observed at the site of injury, which serve as entry points for infectious agents.
Classification of the disease
Bruises vary in severity:
- the first is a slight injury without violating the integrity of the skin or with minor scratches and abrasions, practically painless, self-healing over several days;
- the second is a muscle bruise, accompanied by severe pain, swelling and bruising;
- third - as a result of a bruise, ligaments and tendons can be damaged;
- fourth - bruise of internal organs with severe swelling and pain, with the possibility of disruption of the damaged organs.
Symptoms of a bruise
The main signs of a bruise are pain in the damaged area, hemorrhage due to ruptured capillaries, the formation of hematoma and edema.
Hemorrhage at the site of the bruise appears as a blue-purple spot, the color of which gradually changes to greenish and yellow. Depending on the location of the injury, bruising and swelling may appear immediately, as occurs in the case of damage to the subcutaneous tissue and upper layers of the skin. In the case of bruises of deep tissues, a hematoma forms after several hours or even days.
Soft tissue injuries are accompanied by pain of varying intensity. Thus, with bruises of large nerves and their endings, the pain is always sharp, shooting. With bruises of the torso and limbs, tense hematomas with bursting pain, sometimes with superficial numbness, can occur.
The swelling that accompanies a bruise reduces the mobility of injured tissues, creating discomfort during movement or rotation of the body (for example, when the ribs are bruised). The victim experiences the most severe pain immediately after a soft tissue injury, and after a couple of hours it subsides. When pressed, the pain increases.
When a joint is bruised several hours after the injury, its volume increases, function is impaired, and pain intensifies (especially when moving).
Severe pain occurs when the periosteum, external genitalia, or large nerve trunks are bruised.
The symptoms of a bruise and a closed fracture are very similar: severe pain, swelling, limited mobility. But if in the case of a bruise the pain subsides within 2-3 hours, then with a fracture it, on the contrary, can intensify.
The general condition of patients with limited, superficial bruises usually does not suffer. But with multiple bruises of the body, large or festering hematomas, hemarthrosis (bleeding into the joint cavity), fever with a temperature of up to 38 ° C and higher is possible, caused by the absorption of blood breakdown products.
Symptoms of a lung contusion include tenderness and pain in the chest, ribs, and in some cases, shortness of breath. Other physical signs may be observed due to concomitant injuries.
Diagnosis of bruise
Basic diagnostic methods:
- chest x-ray;
Primary treatment
A bruise can be diagnosed by external signs even before seeing a doctor. To eliminate pain and discomfort, it is recommended to perform the following measures:
- apply a tight bandage;
- Apply a cold compress to the bruised area.
For quick and painless treatment, the face must be at rest. It is better to avoid warming compresses, as they can lead to the development of inflammatory processes.
The consequences of bruises can be such conditions as fractures, fractures, dislocations of the hard tissues of the jaw and even a concussion. Treatment differs depending on each case, so you should not self-medicate. It is also worth noting that most injuries have similar symptoms, so they are easy to confuse. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis. If you cannot go to the hospital yourself, it is recommended to call emergency medical help.
Medical care for jaw injuries
There is no specific treatment plan in such cases. But there is a list of general recommendations. Visits to the doctor are usually limited to one visit to evaluate the x-ray or CT scan.
If the patient escaped with an ordinary bruise, then treatment will be carried out at home. The patient will be given a bandage to hold the bones in the correct position. As mentioned above, you need to apply cold compresses. Ice, snow, and sterile gauze moistened with cold water are suitable for these purposes. Warming the affected area is contraindicated to avoid inflammation and worsening the clinical condition.
To eliminate pain, taking analgesics is allowed. Following simple rules will allow you to quickly get rid of the consequences of a bruise and return to your normal life.
Likely consequences
Any injury with negligence and non-compliance with medical recommendations can lead to all sorts of complications. If we talk about a bruise of the jaw, then it can develop into a post-traumatic form of periostitis, myositis or deformation of bone tissue. Any complications will require lengthy and likely expensive treatment. Injury to the masticatory muscles can cause limited mobility of the lower jaw, complicate chewing and swallowing, which directly affects the state of the gastrointestinal tract and metabolic functions of the body.
Signs of serious injury
Call a doctor immediately if you notice any of these symptoms:
- loss of consciousness;
- dizziness, pallor;
- lethargy, lethargy;
- bleeding from the wound for more than 10 minutes;
- bleeding from the ears or nose;
- convulsions or sudden erratic movements;
- nausea, vomiting, and for infants - frequent regurgitation;
- blood in stool, urine, vomit;
- different pupil widths;
- hearing or vision impairment;
- restless sleep.
Before the ambulance arrives, place the baby on his side to allow vomit to escape unhindered and secure him in a safe position. Check your pulse, evenness of breathing, and pupil size. Medicines should not be given, as this may complicate the examination of the child and blur the symptoms.