A wisdom tooth is the third molar, which appears later than the others, and sometimes does not erupt at all. A person cannot have more than 4 wisdom teeth. The approximate time when teething begins is 18 - 27 years.
Modern experts classify wisdom teeth as rudiments - elements that, in the course of evolution, have lost their role for humans. The specific location of third molars causes a number of difficulties in terms of caring for them.
“Eights” are not loaded like other teeth. In addition, they almost always tend to erupt painfully. It is not surprising that they are called the most problematic, and most dentists recommend removing wisdom teeth at the first opportunity.
Why does wisdom tooth hurt?
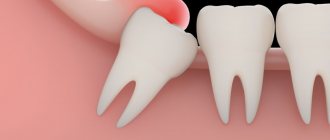
Wisdom teeth almost always grow crooked. Problems with teething are dictated by the following anatomical features:
- “Eights” appear later than all other teeth. As a rule, the jaw bones are fully formed, the dentition is stable, and the “newbie” simply does not have enough space;
- The third molars do not have milk “predecessors”, and the rudiments of wisdom teeth developed for too long and not in very favorable conditions. Because of this, they erupt chaotically, damaging the adjacent tooth or causing inflammation of the gums.
When talking about the causes of pain associated with one or more molars, it is worth distinguishing between some concepts. Toothache can occur against the background of abnormal eruption, due to deformations of soft tissues of neighboring teeth. This clinical picture is typical only for “eights”; other teeth are cut much more smoothly.
Causes
However, the cause of toothache may also lie in fairly classic causes associated with common dental pathologies: caries, periodontal disease or periodontitis. If you systematize all the reasons that cause tooth pain, you will get the following list:
- The wisdom tooth rests too much on the tissues of the oral cavity, squeezing and injuring them;
- The tooth is rotated around its axis. The greater the angle of rotation, the more tense the dental nerve is, which provokes pain;
- Carious cavities have formed on the surface of the wisdom teeth; if they reach the dental tissues, the pain will intensify;
- Tartar deposits have formed, which rub the gums and cause inflammation;
- Due to the fact that the rapid growth of the “eight” and crooked eruption damaged the root system of the neighboring molar, it is this neighboring tooth that hurts;
- If the wisdom tooth, due to its incorrect position, begins to pinch the jaw nerve, pain occurs in the lower jaw. In this case, neuritis manifests itself in this way;
- A follicular cyst has formed at the neck of the tooth. It often occurs against the background of permanent damage to the gum tissue and the tooth itself.
It is worth noting the fact that a follicular cyst near wisdom teeth is often accompanied by all sorts of complications. For example, an abscess may occur that can even deform the jaw in a neglected state. The periodontal tissues may also become inflamed and pericoronitis may develop.
Inflammatory processes of the tissue covering the wisdom tooth
Inflammation of the hood is a common phenomenon. If a wisdom tooth erupts through several crown cusps at once, phenomena may occur when the chewing surface of the crown is partially covered by tissue. The part of the gum and mucous membrane that overhangs the molar and is called the hood. He is constantly susceptible to injury and prone to inflammation.
Under the surface of the hood, particularly favorable conditions arise for the accumulation of various biological “garbage” and the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Often even the slightest damage causes irritation. The gums around the “eight” may not hurt much, so they don’t always turn to people with such a problem.
However, if the inflammatory process is severe, the tissues not only swell, but are also irritated. The patient complains of painful swallowing, sometimes it is difficult even to simply open his mouth. There may be pus and severe hyperemia on the gum near the wisdom tooth. Only a doctor can save you from such an obsessive and severe dental inflammation by excision of the hood.
Lack of space during teething
If there is not enough space for the wisdom tooth in the dentition, neighboring tissues are injured during eruption. The pain is total. It hurts not only the place where the molar erupts, but also the neighboring teeth. Swelling, hyperemia, and severe pain that are permanent may also be observed. It is difficult for the patient to open his mouth, especially if the “eights” grow in the direction opposite to the jaw. Such teeth must be removed. This is due to the fact that a crooked tooth can damage the entire dentition, up to its noticeable curvature.
Caries
If a wisdom tooth is affected by caries, the first symptom indicating the disease will be pathological increased sensitivity of the teeth. They will react painfully to any irritants - sour, spicy, salty foods, sweets, cold irritants.
Situations often occur when the curvature of a wisdom tooth injures the neighboring tooth, which causes caries in it. The most dangerous situation is when the “eight” damages the root of the neighboring “seven”. Caries develops just below the gum, and the doctor is not always able to visually identify the carious lesion. At the same time, a severely advanced form of “root” caries is difficult to treat and the tooth can almost never be saved.
Pulpitis
In acute pulpitis that affects the wisdom tooth, patients complain of acute pain that occurs in attacks. The disease and its main manifestations are characterized by a spontaneous nature. Unpleasant sensations can occur spontaneously and last up to 15 - 30 minutes. At night the pain intensifies.
In the chronic form of wisdom tooth pulpitis, the pain is not so pronounced. Unpleasant, aching sensations occur against the background of exposure to cold or heat. If the irritant is removed, the pain continues for some time.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is characterized by aching pain that constantly worries the patient. At the same time, the diseased tooth will react to any irritant with acute pulsating, shooting pain. Slight mobility of the affected tooth is also noted, and swelling and soreness of the gums are often observed.
It is interesting that with chronic periodontitis the pain is almost not disturbing. Very minor unpleasant sensations can only appear when the “figure eight” is tapped on the patient’s tissues.
Caries and other diseases
With caries, especially advanced ones, cariogenic microbes actively multiply in the oral cavity. There are several types of them, many of them are dangerous not only because they cause the development of caries. These bacteria can end up on the tonsils, get into the lymph nodes, soft tissues, pulp, etc. Caries can be complicated by pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, meningitis and chronic tonsillitis.
Such a combination of circumstances is facilitated by factors such as weak immunity and high susceptibility to certain pathologies. For example, people with chronic tonsillitis who do not treat caries are more likely to suffer from tonsillitis. There are other patterns that are determined by the interconnectedness of all processes occurring in the body.
In some cases, for example, with diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and problems with the digestive system, treating caries alone is not enough. Carious lesions and other oral diseases will constantly recur. For this reason, an integrated approach to treatment is required. Of course, caries rarely causes complications, but it is better to reduce the likelihood of their occurrence as much as possible than to then deal with the treatment of several pathologies.
Let's move on to the next question and find out why inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs, what role dental diseases, including caries, play in this.
Diagnostics
Any pathology associated with the problematic eruption of one or more wisdom teeth should always be investigated through x-ray diagnostics. To determine the position of the tooth in the jaw (inclination, shape, configuration, structure, how it grows), an orthopantomogram is used.
OPTG is a high-quality panoramic image of all teeth on both jaws. Another diagnostic method that will help you understand why your wisdom tooth hurts is visiography.
What are the symptoms of inflammation of the lymph nodes?
The submandibular lymph nodes become inflamed against the background of other pathologies, each of which has its own specific symptoms. We list the most common signs of lymphadenitis:
- sudden enlargement of the lymph nodes under the lower jaw, their pain when pressed and hardening;
- first slight and then severe redness of the inflamed areas, they become burgundy and sometimes bluish;
- swelling at the site of inflammation on one or both sides, depending on the etiology of lymphadenitis;
- sharp and short-term attacks of pain that radiate to the ear, temple or eyebrow;
- discomfort when chewing food, increased pain during swallowing;
- inflammation of the oral mucosa, which is accompanied by redness and increased sensitivity;
- increased body temperature, general weakness, sleep disturbance, fatigue.
To make a diagnosis, it is important to determine not only the cause, but also the type of lymphadenitis, since the clinical picture of each of them may be different.
Treatment methods
Experts practice removal of wisdom teeth in case of carious lesions or in cases where extremely problematic eruption is observed for people of any age. Pain and inflammation indicate a serious problem. If it is not resolved in a timely manner, complications cannot be avoided.
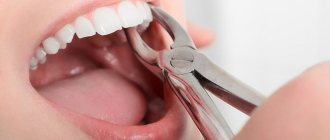
Easy removal
The doctor decides what to do in each specific situation based on the research results obtained. This can be either a simple removal or a rather complex multi-stage operation.
Before the procedure, the specialist must make sure that the patient is not allergic to the medications that will be used during the procedures. First, the soft tissue around the tooth and the nerves are numbed. After the anesthesia has taken effect, the tooth is removed using forceps. The duration of the entire procedure does not exceed 10 minutes.
Difficult removal
If the crown of a tooth is destroyed, it has large branched roots, and also if the “eight” has not erupted at all, and the entire jaw is involved in the inflammatory process, complex removal is practiced. During the intervention, the dental surgeon makes one or more incisions, removes the tooth, washes the wound surface, and then applies sutures.
It is also worth mentioning the procedure for excision of the hood. If it is the wisdom tooth that hurts at the time of eruption due to inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane, the doctor removes fragments of “excess” tissue. There may be situations when the wisdom tooth is not removed, but only soft tissue correction is performed. This is true if the tooth itself does not hurt and is located correctly in the socket.
Pulpitis and inflammation of the lymph nodes
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the pulp - the nerve tissue inside the tooth. It often occurs in people with advanced caries at a deep stage. The following symptoms are characteristic of pulpitis:
- Acute pain that occurs both at rest and when the tooth is exposed to various irritants: food, brushes, water, etc. After eliminating the factor that provoked the pain, the symptom persists for some time, but gradually subsides. The pain is usually sharp and intense; it cannot be eliminated with analgesics.
- Headaches, pain in the ear area from the affected tooth, general malaise and increased fatigue. The pain may radiate to the temple and eyebrow.
- Increase in local and general temperature. In adults it can rise to 38°C, and in children even higher.
- Swelling of the submandibular lymph nodes, pain when swallowing and chewing food.
With pulpitis, as a rule, it is necessary to remove the diseased nerve, after which the tooth becomes dead and noticeably darkens.
What not to do if you have swollen lymph nodes
On the one hand, lymph nodes become inflamed quite often, and often the inflammation goes away on its own without any treatment, so many people do not take this problem seriously. In most cases, it really does not cause any consequences.
On the other hand, submandibular lymph nodes can make themselves felt in severe pathologies that cannot be left without treatment. Doctors recommend not delaying a visit to the hospital if inflammation and pain do not go away within 2 days or occur systematically. Experts also advise:
- Do not try to cure inflammation on your own. It is not possible to find out what caused it at home. In some cases, this cannot always be done quickly and in a medical institution, as a result of which the patient undergoes many examinations. Attempts to cure inflammation with folk remedies can lead to the development of complications.
- Do not heat inflamed lymph nodes. They cannot be heated even in the absence of elevated temperature. Warming up can increase swelling and pain. With the bacterial nature of lymphadenitis, heat stimulates the proliferation of bacteria and causes the infection to spread through the lymphatic system.
- Do not apply ice to the sore area. Cold is contraindicated in inflammatory and infectious processes, since hypothermia can greatly aggravate the situation and lead to even more severe inflammation.
However, a person can take certain measures on his own. You need to switch to proper nutrition, quit smoking and alcohol and make an appointment with a doctor. To reduce the risk of developing inflammation of the lymph nodes, treat all diseases in a timely manner, visit the dentist every six months, exercise and carefully observe hygiene rules.
Types and forms of submandibular lymphadenitis
Inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs in acute or chronic form. The first is characterized by high intensity of symptoms, the disease develops quickly, and it is almost impossible to ignore it. The patient suffers from pain, fever and other symptoms. Immediate medical intervention is required, especially if the pain increases and cannot be relieved with painkillers.
Chronic submandibular lymphadenitis is characterized by a long incubation period, during which a person may not be bothered by any symptoms. In such cases, he usually does not see a doctor, which allows the pathology to progress. An exacerbation may occur at any time, which will require urgent diagnosis and treatment.
Depending on the nature of the contents of the lymph nodes, inflammation can be purulent or non-purulent. The first occurs with great complications and is accompanied by an increase in temperature, the second - in a milder form. Based on the causes of inflammation, it is divided into simple, hyperplastic and destructive. Downtime is accompanied by classic symptoms and tends to become chronic.
Hyperplastic submandibular lymphadenitis is a more complex type of inflammatory process, which is accompanied by redness of the skin and significant enlargement of the lymph nodes. Pathology covers not only the node, but also the tissues surrounding it.
Destructive lymphadenitis is characterized by the destruction of lymph nodes, as well as adjacent tissues, which occurs against the background of a purulent process. This is the most dangerous type of disease that requires urgent treatment.
In most cases, the type and form of inflammation of the lymph nodes is determined by etiological factors and the patient’s state of health, his immunity. Let's consider how it is possible to identify the cause of the inflammatory process in the lymph nodes.