It is better to carry out all dental procedures at the stage of preparation for pregnancy, when there are no hormonal surges in the body and comprehensive treatment of the oral cavity can be carried out without fear. However, it happens that caries appears during pregnancy.
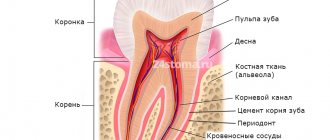
Pregnancy is a difficult period for a woman, since the nascent body needs a lot of nutrients for normal development: calcium and other minerals, vitamins. The fetus actively takes these substances from the mother. And therefore, if before pregnancy the teeth were in order, then during the period of bearing the baby the teeth may begin to deteriorate: the enamel weakens, caries appears, which destroys the incisors outside and inside, reaching the nerve endings, and later to the jaw bone.
It happens that it is almost impossible to cope with toothache, active caries and crumbling incisors before giving birth. A woman can lose a tooth without promptly visiting a dentist.
From the article you will learn:
- Is it possible to treat teeth during pregnancy?
- Differences in dental treatment in early and late pregnancy.
- Safe anesthesia for pregnant women.
- Is it possible to have teeth removed during pregnancy?
- What to do if a tooth hurts during pregnancy.
Is it possible to treat teeth during pregnancy?
Should teeth be treated during pregnancy? During the period of gestation, the female body experiences serious changes in hormonal levels, consumes more vitamins, minerals, fats and acids so that the fetus can fully develop and grow. Even with a balanced diet and vitamin intake, a pregnant woman may periodically experience a deficiency of iron, calcium and other beneficial substances.
The deficiency affects the condition of the teeth: the enamel deteriorates, the teeth become vulnerable to mechanical damage and caries, a feeling of pain appears, and chronic oral diseases worsen. Toothache and discomfort while eating are stressful for a woman and baby. And chronic diseases can lead to infection of the fetus, which has a detrimental effect on its development. Therefore, dental treatment during pregnancy is not only possible, but necessary.
During pregnancy you can treat:
- Inflammation of the gums (stomatitis, periodontitis, gingivitis) is a common occurrence in pregnant women. It is aggravated by the presence of dental plaque and dental plaques, due to the content of estrogens and progesterone (female sex hormones that affect the menstrual cycle, pregnancy and embryonic development) in saliva.
- Dental hypersensitivity is also a common phenomenon in pregnant women, when a woman experiences severe discomfort from eating sour, sweet, spicy, hard, hot and cold foods and drinks.
- Caries. An exacerbation of the development of caries during pregnancy occurs due to changes in hormonal levels, increased acidity in saliva and consumption of large amounts of carbohydrates.
- Pulpitis is a direct consequence of advanced caries development, leading to inflammation of the nerves and severe toothache. It is treated using x-rays and anesthesia.
- Periodontitis is a consequence of caries and inflammation around the root tissues. It is also treated using x-rays and anesthesia.
Symptoms
The inflammatory process develops quickly, leading to a rapid deterioration in well-being. Its pronounced manifestations are:
- severe pain, most often manifested at night;
- high tooth sensitivity when eating cold or hot food;
- increased body temperature, which in some cases can reach 38°C.
Experiencing unremitting pain, the expectant mother is in a constant state of stress. At the same time, the body releases hormonal substances, which is very unsafe for the baby in the womb.
Differences in dental treatment during early and late pregnancy
During this difficult and, at the same time, wonderful period for a woman, dental treatment for the above diseases in the early and late stages of pregnancy differs significantly.
First trimester
Dental treatment during pregnancy up to 13 weeks is carried out only in case of emergency indications: active or advanced caries, acute toothache. This is explained by the fact that in the first trimester the active formation of the baby’s vital organs takes place.
Until the 16th week, the fetus is most vulnerable. Natural selection is inherent in our body, which begins to work from the first days of pregnancy. The body aims to reject a weak fetus and bear a more viable one, which will withstand any external influences and will develop normally. During this period, any changes in the mother’s body can affect the baby.
In early pregnancy, dental treatment using anesthesia is especially dangerous for the baby. Anesthesia has an additional negative effect on the baby through the mother's body. It affects the formation of the fetus and its organs, and can lead to the development of various diseases and pathologies. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to carry out treatment procedures only in case of emergency indications.
Second trimester
From 14 to 25 weeks of pregnancy is the safest period for dental treatment for both mother and child. The placenta and baby's organs have already formed. During this period, treatment is carried out only on the recommendation of the attending physician.
When visiting a dentist, you need to inform him about your stage of pregnancy so that the doctor can correctly assess the need for treatment and select procedures. Sometimes your doctor may advise you to wait until delivery.
If necessary, carry out:
- professional oral hygiene;
- comprehensive treatment of gums and teeth;
- tooth extraction under local anesthesia;
- canal filling, pulp removal and filling installation.
It is important to understand that treatment should only be carried out if absolutely necessary. Every unnecessary change in your body affects your baby.
It is strongly not recommended to remove tartar, wisdom teeth, install braces or other complex dental procedures during pregnancy. In any case, before dental treatment during pregnancy, you should consult with your supervising doctor and treating dentist.
Third trimester
Dental treatment cannot be carried out between 26 and 42 weeks. Late pregnancy is an equally difficult period for a woman. The expectant mother is worried, experiencing discomfort and severe stress. The fetus is already large, which makes it difficult for the patient to fit in the dental chair: she has to sit on her side or lie down, while the fetus puts pressure on the vena cava and aorta. The placenta becomes thinner and is not able to fully protect the baby from toxins and bacteria. There is a possible risk of premature birth.
Before removing or treating teeth during pregnancy, you should consult your attending physician or get a free consultation at a dental clinic. It is important to immediately notify the doctor about your situation and indicate the exact stage of pregnancy so that the dentist can choose the right treatment for you.
Safe anesthesia for pregnant women
Dental treatment during pregnancy is carried out under local anesthesia. Painkillers that have a low impact on blood vessels are selected. However, any anesthesia that enters the mother’s blood is transmitted to the fetus, since during pregnancy they have a single circulatory system. The baby has its own circulatory system from the moment the umbilical cord is cut, until this moment it depends on the mother’s body. When anesthesia is administered, the fetus becomes lethargic and sleepy, which affects its development.
The decision on the use of anesthesia, as well as the choice of the drug itself, is made only by the doctor based on the individual characteristics of the woman’s body and the duration of her pregnancy. The doctor will definitely ask a number of questions: about the presence of past and chronic diseases, about operations performed, allergies, etc. Based on the answers received, the doctor will make recommendations for treatment.
Is it possible to have teeth removed during pregnancy?
Tooth extraction is a surgical operation that carries a psycho-emotional burden for any patient. And for pregnant women, such an operation should not be performed unless there is an urgent need.
During pregnancy, a tooth can be removed if:
- Deep caries, causing inflammation, pus and fever;
- The presence of a cyst with a diameter greater than 1 cm;
- Fracture of the crown or root of a tooth;
- Acute toothache, when conservative treatment does not bring results.
Please note that wisdom teeth cannot be removed during pregnancy. The consequence of the operation may be inflammation of the tooth socket, which can only be treated with antibiotics.
The danger of toothache during pregnancy
The appearance of any painful sensations or general malaise in the body is fraught with the development of a number of complications, because pain is the body’s reaction, signaling the brain about the presence of problems. If a woman “without position” can take medications to relieve or eliminate pain, then during pregnancy there are many restrictions that do not allow the use of a standard set of drugs.
Toothache can be dangerous:
- The formation and development of an inflammatory process with a source of infection. Such lesions are especially dangerous when toothache occurs in the 1st trimester of pregnancy;
- Intense release of adrenaline during attacks of pain, which are accompanied by vasoconstriction and a parallel decrease in the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the embryo;
- The progress of the underlying disease and the formation of complications, up to the need to remove the causative tooth or perform surgery in the affected area.
Elimination of toothache should be carried out only after consultation with a specialized specialist. Self-administration of medications can lead to complications or pose a danger to the unborn child.
What to do if a tooth hurts during pregnancy
It is unacceptable to endure acute toothache during pregnancy, and also to try to cope with it using folk methods and the advice of others. Each pregnant patient has her own indications for certain treatment methods.
Refusal of professional dental care can lead to irritation of the nervous system and an unstable psycho-emotional state. And this, in combination with the use of folk remedies, can have a bad effect on the natural development of the fetus. If a tooth hurts during pregnancy, it is better to go to a dental clinic than to expose your baby to such a risk.
Where to treat teeth during pregnancy
During pregnancy, you should definitely see a dentist. This will help avoid problems with tooth decay and prevent the moment when urgent treatment with anesthesia is necessary.
Don't be afraid to treat your teeth during pregnancy, especially if recommended by your doctor. Properly selected treatment does not harm the baby in any way, but, on the contrary, supports the normal development of the fetus and the health of the mother.
Prevention and emergency dental treatment during pregnancy is carried out at the EliteDental M dental clinic. Goal: to identify and eliminate diseases of the oral cavity in order to reduce the risk of possible complications during pregnancy.
Come for a free consultation at the EliteDental M clinic, undergo an examination and receive free treatment under the compulsory medical insurance system or for a small amount compared to other private dental clinics.
You can make an appointment with our dentists by leaving a request by email or by calling +7 (988) 544-63-54 (3 Zhdanova St.) and (6 Mironova St.). Or sign up online by submitting an application using the form below.
How to relieve toothache in pregnant women
If a toothache occurs, a pregnant woman should immediately contact her dentist to find out the causes and take timely treatment measures. But it happens that pain appears at night, during a trip, or under other circumstances when it is not possible to visit a doctor. In this case, the woman should call her dentist, make an appointment and explain her condition. Your doctor will recommend what you can do to relieve your pain before visiting the clinic.
To relieve toothache, a pregnant woman can do the following:
- Rinse your mouth with warm water to remove any remaining food. You need to brush your teeth using a toothbrush and floss (dental floss). If the pain is caused by food getting into the cavity, this may be enough to provide relief.
- Periodically rinse your mouth with warm infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants: calendula, sage, chamomile, eucalyptus. You can also use a saline solution for this purpose (a teaspoon of table salt is dissolved in a glass of warm boiled water). Rinsing does not anesthetize, but has an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect, which may reduce pain.
- Take a paracetamol tablet. Panadol, Efferalgan, Paralen, Rapidol are the trade names of paracetamol. It is approved for use at any stage of pregnancy, but the dosage specified in the instructions must not be exceeded. Paracetamol is effective for headaches, moderate dental and joint pain; in acute conditions, it will only reduce the severity of pain.
- Take an ibuprofen tablet (trade names: Nurofen, Ibuprom, MIG 400, Ivalgin Rapid, Imet). The use of the drug is permitted in the 1st and 2nd trimesters of pregnancy, that is, until the 26th week, and is prohibited in the 3rd trimester. Ibuprofen should be taken with caution and only in critical situations, strictly following the dosage regimen.
- Apply Dentol 10% gel to the gums and into the cavity of the diseased tooth. The drug contains the anesthetic benzocaine, its effect after application to the diseased tooth begins within a minute. Dentol can be applied up to 4 times a day.
- During sleep or rest, take a “reclining” position so that the head is elevated: the pain is slightly reduced, as the blood flow to the periodontal tissues decreases.
Prohibited:
- Take combination medications containing ibuprofen or paracetamol. In addition to these substances, combination medications may contain components that are dangerous to the fetus.
- Warm the diseased tooth, as this threatens the spread of purulent inflammation (if any) to the tissues adjacent to the tooth.
- Take any other medications without permission from your dentist or obstetrician-gynecologist. Many drugs have a teratogenic effect - the ability to disrupt the embryonic development of a child.