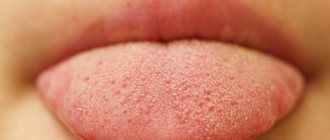
Often, after a night's sleep, a gray coating forms on the tongue of adults. This phenomenon causes a lot of trouble, because in most cases it is accompanied by bad breath. But with the constant formation of a dense film, it is worth listening to the work of your body. After all, plaque formation is often a symptom of a disease of the internal organs.
Common causes of plaque
The causes of gray plaque on the tongue in adults are varied, and it all depends on its characteristics:
- in what part of the organ are deposits concentrated: at the tip, along the edges, at the root, throughout the tongue;
- density and thickness of formations;
- time of appearance (in the morning, constantly, after a heavy lunch or dinner); accompanying symptoms.
The most dangerous is plaque, which causes bad breath, cracks and sores on the surface. Possible reasons for organ taxation include:
- Antibacterial therapy
. When taking antibiotics, the surface of the tongue often becomes covered with plaque, which can be easily removed with a toothbrush. The symptom disappears after completing the treatment course. - Sore throat
. The disease is characterized by the appearance of white purulent rashes on the throat. And since it is infectious, bacteria multiply at high speed in the oral cavity. They lead to the accumulation of plaque on the tongue. - HIV
. Gray deposits on the tongue are one of the first signs of HIV infection, which first affects the digestive system. - Poor nutrition and gastrointestinal diseases caused by it
. In diseases of any organs of the gastrointestinal tract, the tongue becomes coated. A more accurate diagnosis can be made after examination by a gastroenterologist. - Dehydration
. In this case, the deposits will be persistent and dry. - Slagging of the body
. The accumulation of waste and toxins appears in the form of a thick, wet coating on the surface, reminiscent of mucus.
If plaque appears in the morning and is easily removed after brushing your teeth, the cause may be normal physiological processes. There is no cause for concern if such formations do not return after 3-4 hours. Deposits that have formed once after a feast with an abundance of salty, fried and spicy foods and alcoholic beverages do not require medical intervention.
How to remove plaque from the tongue: techniques and treatments
Plaque cleaning is carried out in the classic hygienic way. The process can use the reverse (rough) side of a toothbrush or a special dental scraper.
The cleaning procedure is carried out in several stages:
- Place the toothbrush with the rough side facing your tongue;
- Apply toothpaste to the surface of the brush;
- Place the brush on the root of the tongue and clean off deposits with smooth movements;
- Rinse your mouth with running water.
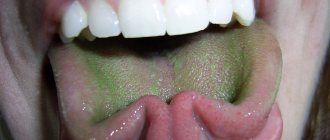
This procedure is very effective for eliminating the natural whitish bacterial plaque that appears in most healthy people during sleep or during the working day, but to eliminate a specific “colored” plaque, you need to use special products: Miramistin (an antimicrobial/antiviral agent for green plaque ), peach oil (for yellow plaque), chlorophyllipt (for brown plaque), resorcinol 5% (for black plaque), hexetidine (for gray plaque).
It is worth understanding that the problem of “colored” plaque can be completely eliminated only after the underlying disease has been completely cured.
How to deal with an infection
If there is a source of chronic infection in the oral cavity, brushing your teeth alone will not be enough to solve the problem. To destroy pathogenic bacteria, you can use medications in the form of ointments, gels, pastes and solutions.
- "Rotokan"
. A herbal solution for mouth rinsing with a distinct herbal odor. It contains three medicinal plants: chamomile, yarrow and calendula. The drug is effective for stomatitis, periodontitis, gingivitis, and bad breath. You need to rinse your mouth with the solution 2-3 times a day for 10 days. Before use, the product must be diluted in water (1-3 spoons per glass of water). - "Holisal"
. This is a combined anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial gel with a pronounced analgesic effect. It must be rubbed into the gums 2-3 times a day after meals and before bed. - "Kamistad"
. The drug contains chamomile, which disinfects the oral cavity and soothes inflamed mucous membranes. In case of pain, for example, when a coating on the tongue is combined with small ulcers and blisters, Kamistad helps to quickly improve the patient’s condition due to the lidocaine included in the composition.
To remove plaque from the tongue caused by pathogenic microorganisms, you can also rinse your mouth with a decoction of linden, oak bark, St. John's wort, and calendula.
Plaque for bronchitis and pneumonia
The area of the tongue immediately following its tip is an indicator of the health or disease of the respiratory system (bronchi and lungs). Based on the condition of this area, one can judge the presence of bronchitis or pneumonia:
- Red spots indicate that pneumonia or bronchial asthma is possible.
- A light film on the front of the tongue indicates the presence of a respiratory allergy or congestion in the lungs.
Plaque on the tongue caused by inflammatory processes of the upper and lower respiratory tract is not decisive in the diagnosis of these diseases.
Liver diseases
The liver is the most important organ of the human body, related in its structure and functions to the endocrine glands. The liver performs a huge number of vital functions, the main one of which is cleansing the blood of toxic, poisonous substances and allergens, as well as removing from the body excess amounts of hormones and compounds hazardous to health: ammonia, ethanol, ketones and their acids, etc.
With any liver disease, a person develops a gray coating on the tongue, which may be accompanied by a change in the color of the skin, mucous membranes, deterioration in general well-being, and pain in the right hypochondrium. The danger of many diseases of the hepatobiliary system lies in their practically asymptomatic course in the early stages, so it is important to know the signs and symptoms of these pathologies and be able to identify them before irreversible changes in the functioning of the liver begin.
Liver cirrhosis disease
Liver cirrhosis is a chronic disease accompanied by structural changes in the liver with the formation of scar tissue, shrinkage of the organ and a decrease in its functionality. Early symptoms indicating cirrhosis include the following:
- A feeling of bitterness and dryness appears in the mouth, especially often in the morning;
- The patient loses some weight, becomes irritable, and gets tired faster;
- A person may be bothered by periodic stool disorders, increased flatulence;
- Periodically occurring pain localized in the right hypochondrium. They tend to increase after intense physical activity or after taking fatty and fried foods, alcoholic beverages;
- Some forms of the disease, for example, postnecrotic cirrhosis, manifest themselves in the form of jaundice already in the early stages of development.
- In some cases, the disease manifests itself acutely and there are no early signs.
General advice for patients with liver cirrhosis:
- Rest as soon as you feel tired.
- To improve digestion, patients are prescribed multienzyme drugs.
- Avoid heavy lifting (this may cause gastrointestinal bleeding)
- Measure your body weight and abdominal volume at the navel level daily (an increase in abdominal volume and body weight indicates fluid retention);
- If there is fluid retention in the body (edema, ascites), it is necessary to limit the intake of table salt to 0.5 g per day, liquid intake to 1000-1500 ml per day.
Following a diet for liver cirrhosis involves, first of all, avoiding foods that have a high protein content. After all, in patients with liver cirrhosis, the digestion of protein foods is disrupted, and as a result, the intensity of putrefaction processes in the intestines increases. The diet for liver cirrhosis involves periodic fasting days, during which the patient does not eat food containing protein at all.
Anatomical structure of the tongue
The structure of human language corresponds to its multifunctionality, which lies in the fact that it participates in the processes:
- chewing;
- salivation;
- taste perception;
- speech.
The body of the tongue consists of striated muscle tissue, which is covered by a membrane of mucous tissue. Its surface, called the back, is conventionally divided into three parts:
- the last third, located near the pharynx, is called the root;
- the first two thirds are the body of the tongue.
A longitudinal groove runs in the middle, which is an external manifestation of the internal septum; it is, in fact, a reduced thyroglossal duct.
The mucous membrane, tightly adjacent to the muscle tissue, is covered on the outside with stratified squamous epithelium. It contains:
- salivary glands;
- taste buds;
- lymphatic ducts.
The mucous membrane of the posterior part forms three supraglottic folds, with the help of which the tongue is attached to the larynx:
- median;
- two lateral.
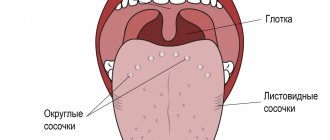
The tongue is abundantly covered with papillae, including:
- filamentous - act as organs of touch and, thanks to the rough surface, hold food on the tongue;
- cone-shaped – responsible for sensitivity to temperature and pain;
- mushroom-shaped - equipped with taste buds, thanks to them we distinguish many taste sensations;
- groove-shaped - located near the root, have serous glands and are also responsible for the sense of taste;
- leaf-shaped - equipped with lingual glands that secrete a mucous secretion.
The tongue is attached to the oral cavity by a fold of mucous membrane called the frenulum.
Liver cysts
Cysts are sac-like cavity protrusions, filled inside with inflammatory fluid (exudate) or pus. Cysts in the liver can appear for various reasons, but hepatologists consider the main one to be infection by various parasites.
In the early stages, while the cyst is small, the patient does not feel any symptoms, but as the formation grows, the patient develops typical symptoms, for example:
- dull or aching pain under the right rib;
- roughness of the tongue, the formation of a dirty gray coating on its surface;
- bad breath;
- increased sweating;
- dyspnea;
- increased heart rate;
- functional diarrhea;
- lack of appetite (possible weight loss);
- asthenia (chronic fatigue).
In most cases, surgical methods using laparoscopy are used to treat cysts.
Hepatitis
A very dangerous liver disease, the mortality rate from which is comparable to the mortality rate from AIDS, HIV infection and other diseases with severe impairment of the functioning of the immune system.
A gray coating on the tongue may be one of the first signs of pathology, but as it progresses, the patient develops more pronounced and specific symptoms. This may be intolerance to fried and fatty foods (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, feeling of fullness after eating high-fat foods), dull pain under the right rib, yellowing of the skin. The majority of patients (more than 50%) experience instability of body temperature. Blood tests may show elevated levels of liver enzymes (transaminases) and bilirubin.
Treatment of hepatitis in almost all cases is conservative. Therapy may include indolylacetic acid derivatives (Indomethacin), NSAIDs (Ibuprofen), drugs for correcting blood pressure (Methyldopa, Dopegit, Nifedipine). The main drug group also includes isonicotinic acid hydrazides (“Isoniazid”) and anti-tuberculosis antibiotics (“Rifampicin”).
Black coating on the tongue
Black plaque looks especially scary; it can occur with long-term use of antibiotics and a number of other medications, and can also indicate a number of diseases:
- infectious disease, in particular cholera;
- Crohn's disease;
- acidosis – PH disturbance;
- viral sore throat.
A dark tongue may have a purple tint, which indicates blood diseases, including anemia. A plaque with a blue tint is one of the symptoms of dangerous diseases such as dysentery and typhoid.
Diseases of the stomach and intestines
These organs are directly involved in the digestive processes, so any disturbances in their functioning can lead to the appearance of bad breath, changes in taste perception and the formation of a grayish coating on the surface of the tongue. The oral cavity and pharynx are the initial sections of the digestive tract, and their condition is closely related to the functioning of the stomach and intestines. Listed below are the main pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract that can cause such symptoms, as well as traditional treatment regimens for these diseases.
Gastritis
Gastritis – millions of people suffer from this disease in various forms. In fact, the term “Gastritis” includes many diseases leading to inflammation of the stomach. In any case, if pain appears in the upper left region of the abdomen, then everyone categorically diagnoses themselves and their friends as gastritis. In this article we will try to help you understand the causes of gastritis, their symptoms and methods of effective treatment.
In the clinical diagnosis of acute gastritis, everything is obvious:
- Soreness in the left hypochondrium has the character of aching pain, sometimes with periods of cramping exacerbations in the form of cutting attacks.
- Heartburn is usually characteristic of gastritis caused by reflux or increased stomach acidity.
- Nausea and vomiting - sometimes this is the only possible way to reduce excess stomach acidity. However, vomiting is not as common with gastritis as the first two symptoms.
- Bloating. For the digestive system, which operates on the principle of a disassembly conveyor, it is important that all necessary enzymatic and chemical influences are carried out at all stages of digestion.
- Increased appetite is due to the fact that after eating, the acidity of the stomach temporarily decreases. However, in the case of severe damage to the stomach, eating can only increase pain, which leads to a reflex loss of appetite.
Treatment of gastritis should be preceded by a full examination to identify the causes of stomach inflammation. Only by finding out the cause of the pathology will it be possible to adequately treat it. However, in the acute period, symptomatic treatment is prescribed. This is done in order to reduce stomach pain and stop or reduce the body's inflammatory response. To do this, first of all, it is necessary to reduce the aggressiveness of gastric juice. And this can be achieved by following a diet and using drugs that reduce the production of hydrochloric acid or neutralize acidity in the lumen of the stomach.
The traditional treatment regimen for gastritis is shown in the table below.
Table. Drugs for the treatment of inflammation in the stomach
| Pharmacological group | Drugs |
| Antibiotics | "Clarithromycin", "Amoxicillin", "Tetracycline". |
| Antimicrobials | "Metronidazole". |
| Bismuth preparations | “Ventrisol”, “Tribimol”, “Vicalin”, “De-Nol”. |
| PPIs (proton pump inhibitors) | "Omeprazole", "Orthanol", "Omitox", "Rabeprazole". |
| Antacids | "Gaviscon", "Gastal", "Rennie", "Maalox". |
| Vitamins | vitamin P, vitamin U. |
Gastritis is a serious precancerous disease, so you should not try to diagnose yourself and treat the pathology at home. In the absence of adequate therapy, the risk of developing gastrinoma (a malignant tumor that produces gastrin) increases 4 times.
Gastroduodenitis
Gastroduodenitis is the most common complication of gastritis, when descending infection occurs and the duodenum is involved in the inflammatory process. In total, there are three forms of gastroduodenitis:
- superficial (the mucous membrane turns red and swells);
- hypertrophic (epithelial membranes thicken, multiple pinpoint hemorrhages appear on their surface);
- erosive (mucous membranes become ulcerated and covered with erosions).
Erosive gastroduodenitis is considered the most dangerous form of the disease, in which the risk of ulcerative damage to the gastrointestinal tract is more than 30%. The symptoms of the pathology are similar to those of gastritis, the only difference is the localization of the pain syndrome: with gastroduodenitis, it can shift from the epigastric region to the abdominal space. Also typical are changes in stool, which can manifest as sudden diarrhea (including profuse diarrhea) or prolonged retention of bowel movements.
The treatment regimen for gastroduodenitis includes drugs used to treat inflammatory processes in the stomach, but when selecting medications, etiological factors must be taken into account. If the cause of the disease is stress, the patient is prescribed sedatives and sedatives. With reduced secretion of hydrochloric acid, replacement therapy with digestive enzymes is indicated.
If the pathology has become chronic, auxiliary treatment is necessary, which is carried out outside of exacerbation attacks. It may include treatment with mud and mineral waters (sanatorium-resort treatment), physiotherapeutic methods, exercise therapy, massage and herbal medicine.
Colitis
Intestinal colitis (inflammation of the large intestine) is another disease in which a gray or off-white thin coating may form on the surface of the tongue. If the pathology occurs over a long period of time, the patient may not have any pronounced symptoms, so it is necessary to pay attention to atypical signs. These may be symptoms associated with a lack of vitamins and minerals due to impaired absorption in the colon: weight loss, dry skin and lips, hair loss, mood instability, loss of energy, anemia.
Almost always, simultaneously with the appearance of an unpleasant odor and changes in the appearance of the tongue, defecation disorders occur in the form of constipation or diarrhea. The smell of feces is fetid (less often sour).
Treatment of colitis in adults depends on the symptoms present and the results of the diagnosis. Drugs for treating uncomplicated colitis are listed in the table below.
Treatment of inflammation in the large intestine
| Pharmacological group | Drugs |
| Antimicrobials | "Nifuroxazide", "Enterofuril". |
| Intestinal sorbents | "Polifepan", "Enterosgel", "Neosmectin". |
| Laxatives | "Bisacodyl", "Magnesium sulfate", "Portalac". |
| Antidiarrheal drugs | "Imodium", "Loperamide". |
| Probiotics | “Normobakt”, “Bion-3”, “Yogulakt”, “Bifiform”. |
| Antibiotics | "Amoxicillin", "Azithromycin", "Tetracycline". |
| Antiparasitic agents | "Vermox", "Pyrantel". |
| Stimulators of regeneration and repair | "Methyluracil". |
| Antispasmodics | “Spazmol”, “Spazmalgon”, “No-shpa”. |
When diagnosed with ischemic intestinal colitis, patients are also prescribed drugs that prevent platelet aggregation and blood clot formation, for example, Pentoxifylline. To identify vascular ischemia of the colon, a coagulogram, intravenous angiography and blood tests are indicated.
Infectious diseases
There are a number of infectious diseases that can cause plaque to form on the tongue. Their diagnosis can be difficult due to the lack of specific and pronounced signs, therefore, to identify such pathologies, an extensive examination is indicated, including a blood test for parasites.
Parasitic liver infections
Infection of the liver with helminths if left untreated for a long time can lead to very serious consequences - even death - therefore, if any signs of helminth infestation appear, you should seek medical help. The table below lists the main parasitic liver infections along with their symptoms.
Invasion of the liver by helminths: types and symptoms
| Diagnostic Basics | ||||
| Pathogen | Echinococcus tapeworms. | Chinese fluke. | Liver and giant fluke. | Cat fluke. |
| Sources of infection | Raw fish, water, animal meat. | Raw or poorly processed fish (maximum risk of infection in people who regularly eat sushi and rolls). | Raw water and plants on which parasite larvae live. | Raw and lightly salted fish, dishes from poorly processed fish (mainly the Karpov family). |
| Symptoms | Heaviness and compression in the right hypochondrium and chest area, dull pain under the right rib, impaired respiratory function (shortness of breath), regular diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. | Feverish syndrome, skin rashes, pain during breathing, functional digestive disorders. | Enlarged and painful liver, fever that persists for 2-4 weeks, loss of appetite. Blood biochemistry will show changes in blood chemistry. | Allergic rashes on the face, digestive disorders, diarrhea, increased sweating, instability of body temperature, pain in the right hypochondrium, inflammation of the respiratory tract. |
A common symptom of all parasitic liver infections is a gray coating on the tongue and a strong breath odor, which may be accompanied by a metallic taste in the mouth.
Helminthiasis of the intestines
The effect of worms on the body occurs over a long period of time: from two weeks to several years. The complex of actions of parasites goes through several stages. The main symptoms of the appearance of worms in the body:
- constipation/diarrhea;
- gas formation, bloating;
- poor sleep;
- allergy.
If not treated in a timely manner, acute helminthiasis progresses to the chronic stage. In this case, the following symptoms appear: indigestion, nervous system, pain in joints and muscles, anemia. Sometimes damage to organs by parasites leads to serious consequences. If you suspect their occurrence, you should consult a doctor.
Parents who form hygienic skills from an early age, teaching them to eat washed vegetables and fruits and wash their hands, help reduce the risk of disease in children. In society, a sick child is isolated, regularly diagnosed and promptly vaccinated.
A gray coating on the tongue should alert any person, especially if it appears every day and is not removed by standard hygiene procedures. As practice shows, the problem usually lies in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and with timely treatment, dietary correction and drug treatment are sufficient. The main thing is to prevent the development of serious complications.