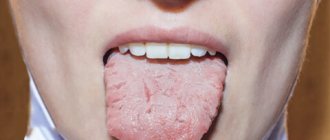
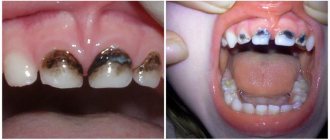
ICD - deposits (growths) on teeth:
- K03.6 - deposits (growths) on teeth
- K03.60 - pigmented coating (black, green, orange)
- K03.61 - due to the habit of using tobacco
- K03.62 - due to the habit of chewing betel nut
- K03.63 - other extensive soft deposits (white deposits)
- K03.64 - supragingival calculus
- K03.65 - subgingival calculus
- K03.66 - dental plaque
- K03.68 - other specified deposits on teeth
- K03.69 - deposits on teeth, unspecified
Mechanism of plaque formation
Plaque formation on teeth begins 2 hours after brushing.
Dental plaque has the following formation mechanisms:7
1.
The surface of the tooth is coated with saliva; it contains proteins to which microorganisms attach more easily.
2. The number of microorganisms gradually increases, they produce acids and polysaccharides - high molecular weight carbohydrates that serve as food for acid-producing bacteria.
3. Subsequently, the number of bacteria increases, and the plaque structure becomes stronger. And acids destroy tooth and gum tissue.
Local immunity
Local immunity provides local protection of the body from the penetration of foreign agents. Barrier functions are provided by the skin and mucous membranes. Any microtrauma to the skin and damage to the mucous membranes contribute to the unhindered penetration of harmful viruses and bacteria, which leads to the development of diseases.
Local mucosal immunity
provided by epithelial cells and the lymphoid apparatus of subepithelial spaces. Lymphoid cells secrete secretory immunoglobulins types A, G and M.
Local immunity of the oral cavity
Every day it resists the attack of pathogenic microorganisms that penetrate the oral cavity, therefore it is the most vulnerable place that should be given special attention.
How does local immunity differ from general immunity?
General immunity is the entire human immune system, which protects the body from foreign agents. It includes internal protective mechanisms: immune cells of various organs, lymph nodes, cerebrospinal fluid barrier, etc.
Local immunity is the first barrier of the body's immune defense, preventing further penetration of microorganisms, ensuring their death or cessation of vital activity. This is the main function of local immunity and its distinctive feature.
Methods for detecting plaque
To determine the quality of home hygiene, you can use solutions of dyes: erythrosine, basic fuchsin, bismarck brown fluorescent sodium. These dyes do not have a pathological effect on the enamel or the oral mucosa. Special tablets are widely used.6
Directions for use: Chew 1 tablet thoroughly and then rinse your mouth with water. What is colored is plaque on the teeth.
It is recommended to use the tablets for children over 6 years of age.5
Contraindication for use is individual intolerance to the constituent components of tablets or solutions.
Normal appearance, structure and functions of the palate
The palate is the top of the oral cavity in the form of a dome or vault, separating it from the nasal passages. The sky is divided into two parts:
- hard - at the base there is a bone plate covered with a mucous membrane;
- soft - these are muscles covered with a mucous membrane that raise the palatine during swallowing and lower during breathing.
Sky functions:
- respiratory protection;
- participation in the chewing process;
- assistance in the formation of speech sounds.
Normally, both parts of the palate are a soft pink hue. In diseases of the nasopharynx, redness of the mucous membrane occurs. A purple or bluish tint may appear. The acquisition of a yellow color by the palate in a child or adult indicates the presence of pathology.
The influence of dental plaque on the development of periodontal diseases
Periodontal tissue is the tissue that holds the tooth in the jaw. If you remove at least one of them, the mobility of the tooth increases, which ultimately leads to its loss.
In 80% of cases, the leading role in the occurrence of periodontal pathology belongs to dental plaque. Of course, there are a number of factors (iatrogenic effects on the periodontium, for example, braces; occlusal trauma, malocclusion; malnutrition; stress; chronic diseases of organs and systems) that contribute to the occurrence of periodontal diseases.2
Plaque microorganisms and their toxins damage the epithelium and cause irritation, which leads to connective epithelial damage and inflammation.
Endotoxins (waste products of gram-negative bacteria) are aggressive; they increase capillary permeability, disrupt cell metabolism, which leads to necrosis. In response to this, the body produces many antibodies (proteins to destroy dangerous cells and viruses) and enzymes that destroy periodontal tissue. And due to the high amount of antibodies, periodontal tissue weakens its protective functions, which allows bacteria to easily destroy them.
The most common microorganisms found in dental plaque are Actinomyces, Actinobacillus, Bacteroides, Eikinella corrodens, Fusobacterium, Vielonella recta, Treponema denticola, Capnocytophaga.8
Reasons for color change
A yellow tint may appear due to smoking. Tar and tobacco smoke stain the mucous membrane, settling on the surface. A yellow coating appears. Due to vascular contraction and changes in blood composition, blood supply is disrupted. With a lack of oxygen, the mucous membrane turns pale and yellow.
The causes of yellowing of the palate are diseases of the oral cavity and body. This is also caused by age-related changes due to metabolic disorders and blood microcirculation.
Tartar
Tartar is mineralized plaque on teeth.
More often it is located on the crown of the tooth, i.e. above the gum. But if the periodontal tissue is destroyed and the gum moves away from the tooth, the root is exposed and the tartar is already below the gum.
It is assumed that subgingival calculus is formed from components of blood serum, since it does not have contact with saliva.2
The different topography of these types of tartar suggests a different mechanism for their removal.
- Supragingival calculus is removed using hand instruments and scalers
- Subgingival calculus is often removed surgically to allow better visualization of the approach.
Oral Care Tips
We have collected the top 5 tips from dentists that must be followed to keep your teeth beautiful and healthy.
- Don't go to bed with unclean teeth. Otherwise, the microbes will secrete lactic acid, which causes caries.
- Learn proper teeth brushing techniques. For example, clean them with smooth circular movements without strong pressure, hold the brush at an angle of 45 degrees, treat not only the outer, but also the inner and chewing surfaces of the teeth.
- Clean your tongue at the end of each brushing of your teeth, as plaque, consisting of dead mucous cells, food particles and microorganisms, is regularly deposited on it.
- Eat more fruits and vegetables. Plant foods contain dietary fiber that helps remove plaque from your teeth and tongue. In addition, fruits are excellent sources of vitamins to maintain oral health.
- Limit your consumption of starchy and sweet foods. The fast carbohydrates they contain stimulate the growth of cariogenic bacteria.
Individual oral hygiene
Individual oral hygiene is the removal of plaque by the patient himself at home using various hygiene products; in other words, it is home brushing of teeth. Home hygiene does not always remove all dental deposits, but proper hygiene will reduce the amount of plaque and bacteria.
Toothbrush
The toothbrush should be soft.
For many, this is surprising, because most are accustomed to using a brush of high and medium hardness - but this is wrong. Using a soft brush will initially seem like poor hygiene, but there are benefits to it as more time will be spent brushing and hygiene will be done properly.
Thanks to a soft toothbrush, the risk of injury to enamel and gums is reduced. The toothbrush should have smooth, thick bristles.3,13
Mono-tuft toothbrush
Allows you to thoroughly clean the gingival sulcus area.
The mono-beam cleans areas that are inaccessible to a regular brush. A mono-beam brush is convenient to use when the gag reflex is pronounced. This brush is a must-have hygiene product; you can use it to clean your teeth without using toothpaste.3,14
Rules for using a mono-beam brush:
- Hold the monotuft brush vertically
- Place the brush so that the bristles are around the gum line
- We move the beam from one tooth to another along the gum line with soft stroking movements.
- We don't put pressure
- We repeat the same steps on the inner surface of the teeth.
Dental floss
Dental floss should be safe and not injure the gums when used correctly.
Dental floss can be classified by color, thickness and fiber structure. Classification of dental floss:
| CLASSIFICATION | A COMMENT | ||
| classification: | Shape:3 | a comment: |
Superfloss - threads with different thicknesses (used in children with braces, and in adults with implants). |
| classification: | By processing: | a comment: |
|
| classification: | According to the presence of impregnations: | a comment: |
|
| classification: | Based on holder availability: | a comment: | Flosssticks are dental floss with holders. Disadvantages of floss sticks:
Dental floss should be used after every meal to prevent food from getting stuck in the teeth.10 |
Rules for using dental floss:
1. It is necessary to unwind about 40 cm of thread from the roll and cut it using the built-in cutter.
2. The ends of the thread are wound around the middle fingers.
3. The middle part of the thread is clamped with the index finger and thumb so that 5 cm remains
4. The thread is threaded between the teeth and moved with sawing movements without strong pressure.
5. The tooth is grasped from all sides and gently brushed from top to bottom.
6. The used piece of thread is wound around the middle finger (can be washed with water), the next gap is cleaned with a clean piece
7. The floss is threaded through the same gap to clean the adjacent tooth.
When should you start flossing?
- Up to 2 years of age, floss is not used - until baby teeth completely erupt. The exception is when the child has tight contacts between the front incisors.
- 2.5-6 years – the period of “contact caries”. Its occurrence is associated with densification of the dentition. A toothbrush cannot fully clean the interdental spaces. It is necessary to use dental floss. Closer to 6 years, you can use a ribbon thread or an irrigator.
- From the age of 6 – brushing teeth with floss becomes an obligatory ritual; the child can be taught to practice independent hygiene
Dental brushes
It is advisable to use a brush every time after eating.
One procedure is enough; too sudden and repeated movements can injure the gums. Terms of use:
1. It is necessary to insert a brush between the teeth closer to the gum
2. The brush should lie at a slight angle relative to the gum
3. It is necessary to carefully move the brush so that it goes right through between the teeth.
4. Strong pressure and pressure should be avoided, the brush should pass easily
5. At the end, you can carefully remove the brush and repeat the procedure with all teeth
Dental floss removes food debris between the teeth, and dental brushes clean them of plaque. At first, it will be difficult to use dental brushes, so it is recommended to start with the smallest sizes and gradually increase them. When you first start using brushes, your gums may bleed.4
Tongue scraper
Plaque on the tongue may indicate the accumulation of pathogenic bacteria that are located in the papillae of the tongue.
These bacteria, in turn, can:
- migrate to teeth and cause caries
- cause bad breath
- accumulate on the gums, causing inflammation
- negatively affect overall oral health
- yellow coating on the tongue does not look aesthetically pleasing
We must not forget about tongue hygiene, since pathogenic microorganisms can get on the teeth and nullify the effect of brushing.
It is not recommended to brush your tongue with a toothbrush or the back of it. The best cleansing effect can be achieved using a tongue scraper. Scrapers come in metal and plastic. It is recommended to use plastic ones, as they do not injure the tongue.3
Irrigator
A device for cleaning plaque and food particles between teeth. Hygiene is carried out under the pressure of a water jet. An irrigator cannot replace dental floss. Thanks to the irrigator, hydromassage of the gums occurs and blood circulation improves.
Oral mucosa: what to pay attention to
Regular dental examinations are an important part of the prevention of not only dental and periodontal diseases, but also pathologies of the oral mucosa. They make it possible to detect cancer, leukoplakia, stomatitis and other dangerous diseases in the early stages.
Inspection algorithm
The American Dental Association recommends that your oral examination include the following steps:
- a thorough visual examination of the lips, buccal mucosa, gums, anterior part of the tongue, floor of the mouth and palate;
- examination of the throat (pharynx), including tonsils, root of the tongue;
- palpation of the jaw and neck to detect nodes, tumors, any abnormalities or abnormalities.
This procedure allows you to timely identify foci of pathological processes in the oral mucosa (OM), including erosion, ulcers, compactions, and also assess the condition of the lymph nodes.
Russian specialists adhere to a similar inspection algorithm. He suggests that the dentist should pay attention to any visible abnormalities in the structure of the face, nose, cheeks or chin. Pathological changes, taking into account their localization, are recorded using special codes. Thus, ulcerations of the mucous membranes, wounds, tissue erosions, cracks, enlarged lymph nodes and any other lesions are necessarily noted.
Oral diseases
The most common symptoms of stomatitis encountered in dental practice. Acute herpetic stomatitis accounts for 85% of all diseases of the oral mucosa; chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis is also common [1].
Aphthous stomatitis is considered a diagnostic feature of aphthous stomatitis - oval ulcerations on the oral mucosa with clear edges, with a diameter of 3-12 mm or more, surrounded by a halo of hyperemia. Herpetic stomatitis is characterized by blistering rashes not only on the surface of the mucous membrane, but also on the lips and skin around the mouth.
Data from multicenter studies in different countries of the world also indicate a high level of prevalence of other oral diseases: leukoplakia, candidiasis, lichen planus.
Leukoplakia is characterized by the presence of foci of keratosis in the form of whitish thickenings on the oral mucosa and the red border of the lips. With candidiasis, spots of white plaque with a cheesy consistency form on the mucous membrane, which are easily scraped off with a spatula. With secondary bacterial infection and erosion, the plaque may acquire a brownish tint.
The most common sign of oral lichen planus is also gray-white spots. They appear on the inner surfaces of the cheeks, tongue and gums. Due to the similarity of these manifestations with the symptoms of other diseases, in particular leukoplakia, visual diagnosis can be difficult.
Unfortunately, in recent years the number of cases of oral cancer has been increasing. The World Dental Federation attributes this to widespread smoking and alcohol consumption. Therefore, early diagnosis of cancer of the oral mucosa is becoming increasingly important. It is precisely this that makes it possible to identify precancerous and cancerous states of cells at stages when treatment can be anatomically gentle.
Experts advise paying attention to the following signs, which may be symptoms of oral cancer:
- long-term non-healing wound or irritation;
- red or white spots;
- sensation of pain, numbness, sensitive areas in the mouth or on the surface of the lips;
- tumors, thickening, roughness, erosion and other changes;
- difficulty chewing, swallowing, speaking, or moving the tongue or jaw.
The number of visits to dentists by Russians is approximately 15 million per year [2]. This figure is higher than any other medical specialty. Therefore, the doctor’s compliance with the external examination algorithm, thoroughness and accuracy during its implementation are the key to the success of early detection of many dangerous diseases of the oral cavity.
List of sources
[1] Zarkumova A.E. Structure of morbidity of the oral mucosa // Bulletin of KazNMU. 2022. No. 3. URL: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/struktura-zabolevaemosti-slizistoy-obolochki-polosti-rta (date of access: 05/22/2020).
[2] Astakhov P. Chief dentist of the Ministry of Health: mortality in the dentist’s chair is below 0.001% // RT, June 7, 2022. URL: https://russian.rt.com/russia/news/397438-glavnyi-stomatolog-minzdrav-smertnost (access date: 05/22/2020).
Teeth brushing methods
Pakhomov method G.N.12
- All teeth are conventionally divided into several sections (chewing left and right, and front)
- They start brushing their teeth with the chewing right teeth, then move on to the front teeth and end with the chewing teeth on the left.
- The anterior (labial) and posterior (lingual) surfaces are cleaned with sweeping movements from the gums to the edge of the tooth, the brush is held at an angle of 45°
- The chewing surface is cleaned with back and forth movements.
Fones method12
- When brushing your teeth using this method, you need to close your teeth together and smile broadly, the front surface of all teeth is brushed in a circular motion.
- Next, with the mouth slightly open, the inner (lingual and palatal) surface of the teeth is cleaned in a circular motion.
- The chewing surface is brushed in a circular motion
Baas method12
- The toothbrush is held like a pen
- Use circular movements to clean each tooth one at a time, without applying too much pressure. This cleanses the outer and inner surfaces of all teeth.
- When cleaning chewing teeth and the inner surface of all teeth, some of the bristles must be placed on the gum, and some on the enamel.
- The chewing surface must be cleaned in a circular motion, the bristles should fit snugly against the tooth, but not bend.
Types of hygiene
Measures to maintain the microflora of the oral cavity are divided into 2 types:
- Personal hygiene.
This is the basis for maintaining healthy teeth, preventing gum inflammation, caries and enamel destruction. High-quality and effective personal hygiene is not only about brushing your teeth. And it is advisable to know the basic measures to maintain “order” in the mouth from childhood.
- Professional cleaning.
It is performed by a dentist in a medical office.
It is important to note that these points do not exclude, but complement each other. It is necessary to undergo a preventive examination (2 times a year), observe the rules of personal hygiene and periodically resort to deep cleaning. All this will help prevent oral diseases and maintain the attractiveness of your smile.
Professional hygiene
Professional oral hygiene should be carried out every 6 months. For brace wearers, hygiene is mandatory every quarter.
Stages of professional hygiene: 11
- ultrasonic treatment (scaling) - removal of hard dental plaque
- Air Flow cleaning – removing soft plaque
- polishing with a brush and abrasive paste
- fluoridation, calcination – if necessary
The Skyler is used for ultrasonic cleaning of plaque and tartar from the surface of the tooth and under the gum. Scaling can be performed under local anesthesia.
The second stage is Air Flow - teeth cleaning with a special device using fine powder, air and water supplied under high pressure.
Benefits of Air Flow:7
- cleaning hard-to-reach areas from plaque
- polishing the enamel surface
- decreased adhesion (sticking) of bacteria
- whitening effect
After cleaning, polishing is carried out using a rotating brush and a special paste. It is very important. By making the surface of the teeth smooth, the doctor prevents bacteria from attaching to the enamel.
At the end of the procedure, a mineralizing gel containing fluoride and calcium salts, necessary for the prevention of caries and increased sensitivity of the gums, is applied to the teeth. The gel is applied only when necessary.
Symptoms and their manifestation
Oral diseases can be diagnosed independently at home. It is only necessary to notice changes that have characteristic signs of a pathological process:
- The appearance of itching, burning or pain;
- Swelling;
- Formation of ulcers and pustules;
- Bleeding gums;
- Damage to tooth enamel;
- The appearance of an unpleasant odor;
- Weakness and sickness.
Popular questions
Can I lighten my teeth with Air Flow?
Yes, but you need to understand that hygiene is not a substitute for bleaching. After brushing, your teeth will become 2-3 shades lighter due to the removal of plaque. But there are pigmentations that have penetrated deeply into the teeth and cannot be removed. This requires special whitening procedures.
Recommendations: what to do after hygiene?
It is necessary to adhere to the “white diet” to maximize the whitening effect. You should change your toothbrush. Do not eat anything hot or cold for at least 4 hours after hygiene.
What is the “white diet”?
“White diet” is a special type of nutrition in which a person eats light, non-coloring foods, that is, without pronounced pigment.
Is blood after professional hygiene normal?
Yes, a small amount of blood may appear after the procedure. After some time it should go away on its own.
Can teeth sensitivity increase after hygiene?
Yes, sensitivity may persist for several days after cleansing. If the sensitivity does not go away, you need to contact your dentist to prescribe treatment.
Can regular dental floss be used to clean children's teeth?
Yes, children can use adult dental floss. The main thing is that the taste suits the child, so it is recommended to choose fruity or tasteless threads.
What to do if after hygiene there is still bad breath?
Home hygiene needs to be adjusted. If hygiene measures do not help, then it is worth checking the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system and endocrine system.
Treatment of teeth and gums in Moscow dentistry
During the pandemic, many people refuse to visit the dentist, believing that solving dental problems can be left “for later.” This opinion is erroneous, since the health of the entire body depends on the health of the teeth.
We offer the right solution to the existing problem with the health of teeth and gums - immediate treatment of dental diseases in a specialized center for family dentistry in Moscow - “Aesthetics”. To make your visit to the doctor as safe as possible for you, be sure to follow all preventive measures recommended by WHO.
In turn, specialists will do everything possible to protect their patients from any risks of contracting the coronavirus. Disinfection of work rooms, equipment and instruments used in treatment and diagnosis is carried out regularly. To minimize contact with strangers, we recommend making an appointment with a doctor by calling +7 (495) 66-574-55 for a specific day and time.
In our center you can receive professional dental care provided by qualified doctors. We have set affordable prices for all treatment and diagnostic procedures, and provide discounts on prosthetics and dental implantation to citizens of preferential categories.
All patients who leave their reviews on the site also receive a guaranteed 3% additional discount (in addition to the main one) on all dental services. Share your opinion, leave your reviews and don’t miss the opportunity to save your personal budget on dental treatment and prosthetics at the Aesthetics family dentistry center.