Bleeding gums after tooth extraction is a natural process that usually does not require medical intervention. But in some cases, this phenomenon indicates serious tissue damage or other pathologies, and it will be almost impossible to stop the bleeding on your own. What to do if there is severe bleeding from the socket and when should you consult a specialist?
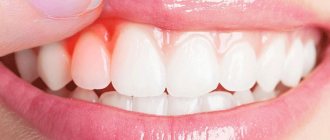
Gums bleed after tooth extraction
How long does it take to bleed after surgery?
Any surgical intervention, including tooth extraction, is associated with tissue trauma and damage to blood vessels - the teeth “hold” tightly to the tissue with their roots, so the doctor has to separate them using physical force. For this reason, it is simply impossible to do without blood during the procedure.
If your gums bleed after tooth extraction while you are at the dentist, the surgeon will help you on the spot
Normally, bleeding stops within 10-30 minutes after surgery - during this time the blood clots, and a clot forms in the socket, protecting it from infection. When removing teeth in the lower jaw, which dentists often call difficult, bleeding may take a little longer. After the initial bleeding stops, ichor may be released from the wound (do not mistake it for blood), so the saliva will be colored pink.
Removal of a wisdom tooth on the lower jaw
It should be noted that in some patients bleeding does not occur at all - this is due to the fact that adrenaline, which is released in the body or contained in anesthetics, causes temporary vasospasm. In such cases, there is a serious risk of developing alveolitis or the “dry socket” effect, since a protective clot does not form in the wound.
If the bleeding is strong enough and does not stop after using simple remedies, you should contact your dentist - you may need medical help to stop the bleeding.
There are many different reasons that lead to prolonged bleeding from a wound.
Professional assistance at the Berezka clinic
A dentist in a clinical setting stops bleeding in several ways, depending on the severity of the condition and the individual characteristics of the patient. It should be noted that each of the methods will be effective only if you seek medical help in a timely manner.
Stitching
The damaged vessel is ligated over the hole or soft tissue is sutured. The boas of the method stop bleeding with equal effectiveness.
Electrocoagulation
The manipulation is performed under local anesthesia. They resort to this procedure if several capillaries are damaged. The tissues are dissected using a special tool, after which they are soldered, facilitating rapid healing of the wound.
Application of fibrin film
A fibrin film is applied to the place where the tooth was removed. In addition to the hemostatic effect, the film also has an anti-inflammatory, disinfecting and healing effect.
Tamponation
In this case, the dentist uses iodoform turunda. It is inserted into the hole in the same way as a gauze swab, but to a greater depth.
Hemostatic tube
The method is relevant for patients suffering from high blood pressure. The tube is carefully inserted into the hole and held until the AT is brought back to normal.
You can also use gelatin and collagen sponges to stop bleeding.
The dentist makes a decision on the need for additional treatment procedures based on the results of examining the condition of the wound after extraction.
Why is bleeding from a socket dangerous?
Intense bleeding from the gums often frightens patients - they fear dying from blood loss. However, the risk of death after tooth extraction surgery is minimal - this happens in isolated cases, and only with people who suffered from serious illnesses, alcoholism or drug addiction. But problems with internal organs and systems as a consequence of severe bleeding from the gums are quite likely, so it is not recommended to ignore severe bleeding.
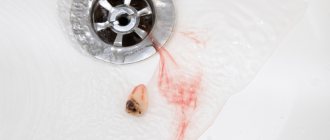
Blood clot after tooth extraction
Signs of normality
It is quite normal that after you have a tooth pulled out, the wound that forms in its place begins to bleed. This is natural, because the doctor performed a surgical operation, during which he acted on living tissues penetrated by many vessels and capillaries. As a result of the injury, a physiological reaction such as bleeding occurred.
Immediately after removing the root, a hole forms in its place, which should fill with blood. The oozing blood should not be spit out; you must wait until it thickens and stops. The resulting clot is necessary for our body, as it performs a protective function and prevents infection from entering damaged tissues.
Important! Don't confuse blood with ichor. Ichor is a yellowish liquid with a slight admixture of blood, which is released from damaged tissues and promotes their healing. You may notice how saliva is stained with it within 1-3 days after extraction (removal), which is also a sign of normality.
Causes of bleeding after tooth extraction
Bleeding after dental surgery is usually divided into primary and secondary - in the first case, blood flows immediately after the procedure, and secondary bleeding can develop several hours, sometimes several days after the visit to the clinic.
Bleeding after tooth extraction
There can be several reasons for primary bleeding, most of them are associated with pathological conditions of the body.
Table. Causes of primary bleeding after tooth extraction.
| Causes of bleeding | How to prevent |
| High blood pressure | Before going to the dentist, you need to measure your pressure and also take a sedative that will reduce the risk of it (pressure) increasing during the operation |
| Poor blood clotting in certain diseases (leukemia, hepatitis, hemophilia) | People with serious pathologies and hematopoietic diseases should report their problem to the doctor, who will choose the safest method of performing the operation |
| Taking medications | 2-3 days before tooth extraction, refrain from taking aspirin, heparin and other blood thinning drugs, as well as oral contraceptives (increased concentrations of estrogen in the blood in women can also cause bleeding) |
| Severe stress | If a person has a strong fear of dental procedures, a surge of adrenaline in the body can provoke bleeding - to prevent it, before visiting the dentist you need to try to calm down, and if necessary, take a sedative |
| Anatomical features of the dentofacial apparatus (large blood vessels on the surface of the gums) | Closely monitor the condition of the socket after surgery, avoid physical activity and follow the doctor’s recommendations |
- Why do my gums hurt after tooth extraction?
Another common cause of severe gum bleeding after tooth extraction is medical errors during extraction. Careless or too rough operation causes severe tissue trauma, which causes intense bleeding, and this situation is especially dangerous when large branches of the arteries are damaged.
Severe bleeding may be the result of a medical error
The main cause of secondary bleeding is patients’ failure to comply with the dentist’s recommendations: drinking hot drinks, solid foods, exposure to other traumatic factors, smoking, etc. In addition, blood from the socket can ooze in the event of complications developing - suppuration, alveolitis, the presence of cysts or granulomas. They impair coagulation at the site of inflammation, which leads to large blood loss both during and after surgery.
Alveolitis in the tooth socket
Prevention of complications
In order not to encounter such an unpleasant problem as alveolar bleeding, for 3-5 days after surgery it is necessary to refrain from actions that increase blood pressure, a rush of blood to the head and the operated area, and contribute to damage to the protective clot.
| What's prohibited | What is possible |
|
|
If you are going to have a tooth removed, be sure to tell your doctor about any medical conditions you have. The day before your scheduled surgery, do not take blood thinning medications under any circumstances. After extraction, strictly follow all the specialist’s recommendations, and then the risk of complications will be reduced to zero.
When should you see a doctor?
In most cases, bleeding can be stopped using simple measures, but sometimes it requires immediate consultation with a doctor. You need to contact an emergency dental clinic if:
- the blood flows too intensely (the oral cavity fills with blood literally every few seconds);
- along with bleeding, a person experiences weakness and dizziness;
- the affected area is very swollen and painful;
- bleeding is accompanied by fever, difficulty breathing or swallowing;
- the patient experiences a severe headache and numbness in the areas adjacent to the affected area.
Phlegmon - acute extensive (spread) inflammation of fatty tissue
A variant of the norm is considered to be mild or moderate bleeding, which lasts no more than 24 hours; after the removal of third molars, this period increases to three days.
Photo of holes after tooth extraction
What could be the consequences?
If the bleeding does not stop flowing for too long, it is necessary to seek help as soon as possible from the medical staff of the clinic where the operation took place. Don’t be needlessly nervous and stress yourself out; perhaps this phenomenon has a completely logical explanation.
Prolonged bleeding can lead to the following unpleasant consequences: severe weakness and exhaustion of the body, poor health, drowsiness, drop in blood pressure and headaches. Also, such patients have pale skin and may lose consciousness. However, we are only talking about a large loss of blood.
Also among the complications is the so-called “dry” socket. In the absence of a clot covering the entrance to the tooth bed, it becomes very vulnerable. Food particles, dangerous microbes and bacteria can get into it, which over time will lead to the beginning of the rotting process.
Against the background of incessant bleeding, a serious inflammatory process can develop: alveolitis, phlegmon, osteomyelitis, etc. If the patient notices a strong increase in body temperature, increased pain, and the appearance of purulent discharge, this with a 99% probability indicates an infection in the wound.
previous post
How to choose toothpaste?
next entry
What can a doctor do?
In cases where it was not possible to stop the bleeding on your own, you should call an ambulance or go to the dental office. Doctors will examine the sore spot and prescribe one of the procedures aimed at stopping the bleeding:
- packing or suturing;
- cauterization of blood vessels;
- taking medications that improve blood clotting.
Tamponade bleeding
If the bleeding was not stopped in a timely manner, inflammation may begin in the hole - blood stops oozing from the wound, but the soft tissues begin to swell and hurt. If such symptoms appear, it is necessary to clean the hole, then fill it with a special anti-inflammatory agent and undergo a course of antibiotic treatment. If all of the above measures are ineffective, the patient is indicated for hospitalization.
After tooth extraction
Why you should entrust your treatment to the ENT Department of Dentistry
ENT dentistry combines two areas of medical services and treatment options - otolaryngology and dentistry . This is a modern format for the clinic’s work on comprehensive rehabilitation in the treatment of traumatic and inflammatory processes in the upper jaw, penetrating into the maxillary sinus or passing along its borders.
The Center for Private Dentistry “Doctor Levin” has been specializing in providing care to patients with combined ENT and dental pathology for many years. Medical and surgical treatment programs are carried out by candidates of medical sciences, maxillofacial surgeons with ENT training.
Statistics for the 20 years of work of the Center and for the last 10 years of work of the Department, unfortunately, are inexorable. The main providers of patients with complications are our colleagues who are caught in the dead end of an unsuccessful treatment plan. We are grateful to our colleagues who do not hesitate to send us patients with ENT complications, despite the reputational damage. It is always possible to avoid a dramatic outcome if you stop treatment in time.
How to prevent bleeding?
To avoid postoperative bleeding, you must refrain from the following actions:
- eat hard, rough, hot and cold foods;
- rinse your mouth intensively, especially with hot water;
- take a hot bath or visit a sauna;
- engage in heavy physical labor;
- actively use facial expressions (open your mouth wide, etc.);
- clean the affected area with a toothbrush, touch the wound with your tongue, fingers or foreign objects;
- smoke, drink alcohol;
- apply warm compresses to the cheek.
Normal socket healing
The above conditions must be observed for at least 24 hours (ideally 3 days) - this will help avoid not only bleeding, but also serious postoperative consequences.
In most cases, bleeding after tooth extraction is a normal physiological phenomenon that can be eliminated with simple home remedies, and if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the pain, fear and blood that accompany any operation will soon be left behind.
- What medicine is put into the hole after tooth extraction?
Features of the maxillary sinus
The maxillary sinus (its other name is the maxillary sinus) is located in the thickness of the bone tissue of the upper jaw. It is separated from the oral cavity by the alveolar process of the upper jaw, which forms its bottom. The volume of such a sinus is quite large, and in adults it can reach 10 cubic centimeters.
This sinus, or sinus, is not airtight. It communicates with the nasal cavity through a narrow slit.
Typically, perforation of the maxillary sinus occurs in the area of its bottom. Some of its features contribute to this:
- Close proximity of the roots of molars and premolars. In some cases, the thickness of the bone layer between the tooth roots and the bottom of the maxillary sinus can be relatively large - up to 1 cm, but in some people the bone border between these formations is very thin - no more than 1 mm.
- Sometimes the roots of the first and second molars are located in the sinus cavity itself, separated from it by just a layer of mucous membrane.
- Rapid thinning of the bone layer in the presence of acute or chronic inflammatory diseases: periodontitis, periodontitis, cysts.
- Relatively thin bony trabeculae in the tissue of the upper jaw.
All this predisposes to the occurrence of perforation during dental procedures, even if the treatment technique was not violated and the doctor did not apply significant traumatic force.
Preventive actions
Prevention of perforations of the floor of the maxillary sinus consists of:
- in a full examination of the patient before complex dental procedures;
- in the correct assessment of the anatomical and topographical characteristics of each person;
- in strict adherence to the technology of therapeutic manipulations.
Timely detection of signs of perforation and its adequate treatment is the key to a favorable outcome for the patient. Incorrect therapeutic tactics or self-medication can aggravate the course of such a complication and cause the development of severe negative consequences.