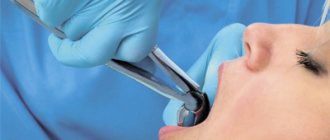
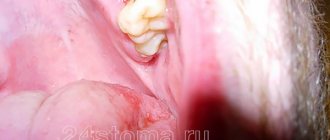
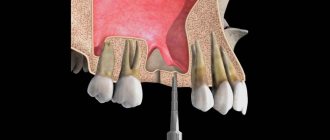
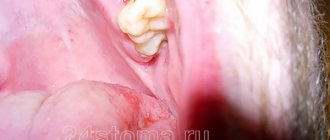
Bleeding gums in children and adults is a fairly common phenomenon. Someone will say that this is a small thing - bleeding from the gums. But this is not true; bleeding may be a sign of a serious oral disease or infectious pathology. If this is not the first time you have seen blood when brushing your or your child’s teeth, you should contact your dentist.
By the way, many girls and women’s gums begin to bleed during pregnancy. The main reason, as a rule, is hormonal changes in the body. 2-3 months after giving birth, the situation will change for the better, you will no longer feel the unpleasant taste of blood in your mouth.
Self-help: ways to stop bleeding
When blood bleeds for a long time after the removal of a wisdom tooth, it brings discomfort on a physical and emotional level. If you can't get to the dentist, use gauze swabs. Fold a small piece of bandage into several layers, apply it to the hole and bite firmly. Keep for 20 minutes. To disinfect, you can soak a swab in hydrogen peroxide. Bleeding after wisdom tooth removal can be stopped by this method both day and night. Another option is to use ice. Apply to your cheek and apply for 5 minutes with short pauses. If the patient has a history of hypertension, a high blood pressure pill should be taken.
Causes
The most common factors that lead to bleeding gums are:
- Improper oral hygiene:
using a brush with hard bristles, strong pressure when brushing, inaccurate use of dental floss, picking with toothpicks and other objects, improper installation of dentures. Due to frequent trauma, gum pockets form, which provoke inflammation.
- Tartar.
With irregular and improper brushing of teeth, plaque forms, which gradually hardens. The stone moves the gum away from the tooth, the tissue becomes inflamed and begins to bleed.
- Dental procedures.
Bleeding may occur after professional cleaning, tooth extraction, or the installation of a filling or implant. A poorly manufactured or fitted structure constantly injures the edge of the gum. In addition, filling material and dentures can cause an allergic reaction.
- Diseases of gums and teeth:
gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease. Inflammatory processes are accompanied by swelling, swelling, exposure of the neck, abrasion and loosening of teeth.
- Infections and viruses.
Herpes, fungus, tonsillitis, influenza, ARVI, tuberculosis, HIV lead to the destruction of the periodontal structure and provoke inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
- Hypovitaminosis.
Bleeding from the gums occurs when there is a deficiency of vitamins B, K, C, E. A monotonous and unbalanced diet, frequent diets, and inducing vomiting lead to pathology. With a lack of vitamin C, scurvy can develop. During the disease, teeth become loose and begin to fall out.
- Hormonal disbalance.
The problem is observed during pregnancy and puberty, with diabetes. Due to an imbalance of biologically active substances, tissues swell and become looser. In this case, bleeding from the gums occurs not only when brushing teeth and eating solid food, but also from the slightest touch.
- Taking a number of medications.
Blood thinners, including Aspirin, Heparin, and Warfarin, can lead to the problem. Some nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have similar side effects.
- Blood diseases.
Bleeding disorders often lead to gum pathology: hemophilia, thrombocytopenia. The condition of the mucous membranes also worsens with tumor processes - leukemia and leukemia.
General rules of first aid for bleeding
If the victim has lost a significant amount of blood, try to lay him down and elevate his legs.
Do not touch the wound with your hands or remove glass shards from it.
If sand and rust get into the wound, do not wash the damage, as this will increase the bleeding.
If the wound becomes dirty, you need to carefully remove the dirt in the direction from the wound, then treat the cleaned edges with an antiseptic.
When treating the edges of a wound with an iodine solution, do not allow the antiseptic to get inside the wound.
Depending on the type of blood loss, try to stop the bleeding using a tourniquet, twisting, or squeezing the damaged vessel.
First aid for capillary bleeding
Bleeding from the capillaries is not accompanied by large blood loss and stops relatively quickly. A sign of capillary damage is the appearance of a gentle stream of blood on the wound.
First aid for this bleeding includes treating the edges of the wound with an alcohol antiseptic (iodine), on which an aseptic gauze bandage is applied. Please note that the bandage is not tight. Usually, with capillary bleeding, there is no need to go to the hospital, with the exception of situations where the damage is extensive.
1 First aid for bleeding
2 First aid for bleeding
3 First aid for bleeding
First aid for venous bleeding
A sign of venous bleeding is rapidly flowing dark blood. Its flow is uniform, without gushing or pulsating.
With venous bleeding, blood clots may appear; they cannot be removed, since in this case blood loss may increase.
To stop bleeding, apply a pressure aseptic bandage to the wound. If blood loss continues, it is necessary to apply a tourniquet below the damaged area. To reduce injury to soft tissues and skin, a soft pad is placed on them (under the tourniquet). It is necessary to make a note indicating the time of application of the tourniquet. The maximum time for wearing a tourniquet is 2 hours in warm weather and 1 hour at sub-zero temperatures. The tourniquet cannot be held longer than this time, otherwise the bloodless tissue will begin to die. If you don’t have a tourniquet, you can make twists from available materials: a bandage, a belt, a towel, a piece of fabric using a handle and a short stick. The time frame for the spins is the same. Try not to use any hemostatic drugs without a doctor's prescription.
First aid for arterial bleeding
Arterial bleeding is one of the most dangerous. The main sign of arterial damage is bright scarlet blood flowing out in a pulsating stream at high speed. If large arteries are damaged, the blood begins to flow intermittently, like a fountain.
First aid for this bleeding is to apply a hemostatic tourniquet above the level of the wound. You can also use a twist. Time restrictions are the same.
If there is no tourniquet or twist, you can stop the bleeding by pressing the artery above the damaged area with your finger, i.e. at the pulsation point.
In case of bleeding from the brachial, ulnar, femoral or popliteal artery, you can fix the arm or leg as bent as possible in an elevated position.
Gastrointestinal bleeding
Blood from the mouth may be accompanied by vomiting
Bleeding can occur in a variety of parts of the gastrointestinal tract. The main symptom is the appearance of blood in a person’s stool or vomit. It can be hidden and detected only with the help of specially conducted tests. In situations where blood from the mouth is caused by some kind of disease of the digestive system, it often goes along with vomiting.
In some cases, vomiting accompanied by slight bleeding may indicate a burst vessel in the throat or esophagus. But most often bleeding indicates the following diseases:
- stomach or duodenal ulcer
- erosion of the mucous membrane of the stomach or esophagus
- liver cirrhosis in severe stages
Ulcers provoke up to eighty cases of bleeding occurring in the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, due to bleeding, diseases such as enteritis, colitis, polyps, gastritis, duodenitis and others become aggravated. It also causes complications of cancer in any part of the digestive system.
The most severe form of blood effusion in the gastrointestinal tract is considered to be its loss through the veins of the esophagus, which occurs with portal hypertension. Sometimes severe bleeding occurs as a result of hemorrhoids. The use of certain medications in some situations causes the development of bleeding.
Why shouldn’t bleeding gums be ignored?
Firstly, you will be haunted by bad breath, which will repel both those around you and those close to you. You will become more complex and less sociable.
And secondly, if you refuse treatment, you can lose healthy teeth. Bleeding gums can be caused by periodontitis, periodontal disease, stomatitis and gingivitis.
Gums bleed when brushing teeth
With all of the listed diseases and health problems, this symptom may appear. But in some cases, bleeding is caused by using a toothbrush that is too hard. Doctors usually recommend that this hygiene item should not be soft, otherwise it will not be able to effectively cope with plaque that settles on the teeth and oral tissues.
However, if it is too hard, it is capable of causing mechanical damage to the latter, even scratching them until they bleed. They are especially susceptible to this, being too sensitive. To avoid this, you should consult your doctor about which brush is right for your case.
If your gums bleed when brushing your teeth, you may be performing this procedure incorrectly - you are making too intense, pressing movements, which cause tissue injury.
In both cases, an incorrect approach to hygiene measures can lead to gums receding over time and the necks of teeth becoming exposed. The main symptoms of this phenomenon are that the latter visually lengthen, their root part, which has a darker color than the crown part, is revealed to the eye. Their sensitivity increases, as the problem progresses, they become looser and subsequently fall out.
Treatment methods
If you find that there is bleeding from your gums, you should immediately contact your dentist. The doctor will determine the cause and prescribe adequate treatment. The most effective ways to combat bleeding gums are:
- Professional teeth cleaning and ultrasonic calculus removal.
Waves completely eliminate plaque. During pregnancy, methods that are safe for the fetus are used.
- Rinse with antiseptics.
Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Rotokan, Chlorphyllipt, Furacilin, Tantum Verde, etc. are prescribed as a solution for sanitation. It is acceptable to use decoctions of sage, chamomile, calendula, and oak bark. The procedure is carried out in the morning, before bed and after each meal. The course lasts no more than 10 days.
- Dental gels and ointments.
The most effective drugs are Metrogyl Denta, Asepta, Dental, Cholisal, Parodium, Stomatofit, Solcoseryl, Salvin. The composition quickly penetrates the mucous membrane, has an antimicrobial effect, relieves inflammation, pain and bleeding. The products are applied twice a day, after rinsing and drying with a cotton swab.
- Additional medications.
For concomitant diseases of the oral cavity, antibiotics, painkillers, “Parodontocid” spray, lozenges Septolete, Faringosept, Grammidin, etc. are prescribed.
- Physiotherapy.
Gum restoration is accelerated by procedures such as ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis, current treatment, oxygen treatment, balneo-, light- and vacuum therapy. Various types of massage are effective: water, hardware, manual. As a rule, a course of physiotherapy includes 5 procedures.
- Proper oral care.
It is necessary to brush your teeth twice a day. Dentists recommend using only soft brushes marked Soft and pastes for bleeding gums: Parodontax, Lacalut, ROCS, BlanX, Mexidol Dent. After eating, you need to carefully remove food debris with dental floss and use an alcohol-free mouth rinse: Silca, Lacalut, PresiDent, Forest Balm. You can also use a solution of water with salt or hydrogen peroxide.
- Taking vitamin complexes and immunomodulators.
Popular drugs are “Dentovitus”, “Alphabet”, “Vitrum”, “Immunal”, “Calcinova”, “Calcium D3 Nycomed”, and lemongrass tincture. To reduce the fragility of capillaries, Ascorutin is additionally prescribed.
- Nutrition correction.
It is recommended to avoid sugar, bread, spicy, sour and salty foods, carbonated drinks and alcohol. The diet should include fresh juices, vegetables and fruits, foods rich in protein, vitamins C, B, K, E. As a result, periodontal tissue will be strengthened, and the mucous membranes will recover faster. Spices are also useful: ginger, wasabi, sesame, cinnamon. Spices stop the proliferation of bacteria and relieve inflammation.
There are also emergency measures. If there is bleeding from the gums, it is necessary to apply a swab soaked in ice water to the tissue. This will quickly soothe the gums and stop bleeding.
The best treatment is prevention. Visit your dentist twice a year. A specialist will detect and eliminate all problems with teeth and gums in a timely manner. If you follow your doctor's recommendations, you will forever forget about bleeding gums.
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details! Ask your doctor about contraindications and side effects.
Folk recipes
Of course, herbal decoctions and juices are not able to completely cure gums that bleed when brushing your teeth. However, natural compounds can become excellent therapy assistants, reduce pain, reduce bleeding, and most importantly, significantly speed up treatment.
The most popular remedies for bleeding gums are:
- A decoction of blueberries will help quickly get rid of even severe bleeding.
- A decoction of oak bark is effective for almost all gum diseases.
- Sage decoction provides antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Chamomile has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. A decoction of this plant helps with gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontal disease, and for the prevention of gum inflammation.
- Lemon and black radish will provide reliable protection of teeth from plaque and gums from inflammation.
- An effective means of preventing gum inflammation is water pepper tincture. This healing composition increases the density of the walls of blood vessels, increasing blood clotting.
- Onion and aloe juice are also used to prevent and treat inflammation. These plants (in equal parts) can be applied as applications to the gums twice a day.
To prevent bleeding and inflammation of the gums, it is necessary to eat raw carrots, apples, celery, pears, radishes and other hard fruits and vegetables. Such food will not only enrich the body with vitamins, but will also provide excellent natural massage of the gums and cleanse the enamel of plaque.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
- Clinical studies of antisensitive toothpaste “Asepta Sensitive” (A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, S.B. Ulitovsky) A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist O.V. KALININA, dentist S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
Why do my gums bleed?
They are a mucous membrane that covers the alveolar part of the lower jaw and the alveolar process of the upper. This shell wraps around the teeth in the area of their neck, protecting dental tissues from various damages, and the teeth themselves from falling out.
Bleeding of this mucous membrane, as a rule, is a symptom of some disease of the oral cavity or body. Under the influence of various factors, the tissues are weakened, and, as a result, the gums bleed. These are the reasons why this problem appears. They will be discussed in more detail below.