Ear pain is a fairly common symptom. Painful sensations in this case give the patient a lot of unpleasant moments, and it is very difficult to simply “endure” such pain. It is noteworthy that pain in the ear is not always associated with diseases of the hearing organ. Such painful sensations can also be caused by other organs that radiate, that is, “giving off,” to the ear. A condition in which the ear hurts, but there is no inflammation in it, is called otalgia.
Otalgia can be caused by many reasons:
Temporal arteritis
The disease is an inflammation of the vessels of the temporal artery.
If the inflammatory process spreads to the ear artery, the patient will also experience pain in the ears. This disease is typical for older women. It causes blurred vision, headaches, pain in the temples, and increased fatigue. Make an appointment right now! Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
Along the branches of the vagus nerve, pain can radiate to the ear from the esophagus, thyroid gland, and organs of the cardiovascular system.
If you have ear pain, you should definitely consult with an otolaryngologist, since this condition may signal the presence of serious diseases in the body. If the ear is healthy, no abnormalities have been identified, and the pain does not go away, it is necessary to diagnose the nose, larynx, pharynx and, if necessary, other organs to identify the cause of otalgia. Further treatment will depend on the diagnosis.
Common diseases that cause pain in the throat and ear
| Pathology | What is it characterized by? |
| Diphtheria | An acute infectious disease that develops as a result of exposure to bacterial agents. It is manifested by the development of fibrinous inflammatory processes in the area where the latter is introduced. Most often these are the upper respiratory tract, bronchi or oropharyngeal mucosa. |
| Measles | An acute infectious viral disease, manifested by the appearance of a rash on the skin, fever and pain in the throat, radiating to the ear. Its complication is often otitis media, which also causes pain. |
| Scarlet fever | Acute infectious processes that begin with a sore throat and are characterized by primary damage to the oropharynx, as well as pronounced intoxication. |
Antiviral agents
With the help of traditional medicine, it is possible to reduce ear pain and improve the effect of drug therapy.
Garlic
Use the product as drops, sending them into the ear in case of severe pain. You can do without oil if you drip garlic juice into your ear. This article explains how to use onions and garlic for colds.
This budget option effectively relieves ear pain. At the same time, onions also have an antiseptic and antibacterial effect. During therapy, it is possible to stop the inflammatory process.
You need to take one onion, remove the husk and crush it. Wrap the pulp in gauze. Apply the compress to the affected ear for 20 minutes. This procedure can be performed 2-3 times a day. You can take onion juice in an amount of 20 ml, heat it and add 2 drops.
You need to fill a plastic bottle with thermal water. Place it on the affected ear and place a towel on top. The duration of the thermal procedure will be 5 minutes. This therapy option can relieve pain when swallowing in the ear.
Ginger root
With the help of this plant it is possible to have an anti-inflammatory effect. In addition, ginger root perfectly relieves pain. It is necessary to extract the juice from it and then send it to the affected ear. You can also combine 20 g of fresh ginger juice and combine with 50 ml of warm sesame oil. Apply the resulting mixture to the affected ear when it has cooled. This article explains how to use ginger against flu and colds.
Bishop's weed
To relieve ear pain, use the oil of this plant. You need to combine 20 ml of bishop oil with 40 ml of sesame oil. Place 3-4 drops of the product into the affected ear. Be sure to warm the mixture before use.
Camphor oil
This product can be used in the treatment of ear pain in two ways:
- Compress. You need to take 20 ml of the main product, warm it and dip gauze in it, folded in several layers. Apply the compress to your ear for 30 minutes. Then place a cotton swab in your ear.
- Drops. You can drip 4 drops of camphor oil into the affected ear, and then apply a cotton swab. Lie like this for 10 minutes and leave the tampon overnight. But this article will help you understand how to use oil for dry throat.
Pain in the ear when swallowing is an unpleasant symptom that may indicate the presence of an inflammatory process. Most often this occurs with otitis and injury to the eardrum. Each case is assigned its own treatment regimen, the essence of which is to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and the underlying factor.
| A drug | Photo | Price |
| Arbidol | From 162 rub. | |
| Kagocel | From 212 rub. | |
| Teraflu | From 161 rub. | |
| Tsitovir | From 242 rub. | |
| Remantadine | From 71 rub. | |
| Anaferon | From 206 rub. | |
| Coldrex | From 192 rub. | |
| Amiksin | From 593 rub. | |
| Tamiflu | From 1276 rub. |
They destroy viruses, reduce throat swelling, and increase the body's immune defense. Release forms for children are syrups, for adults - capsules, tablets.
Plant decoctions have an analgesic effect:
- mint,
- oregano,
- fragrant rue,
- bloodroot,
- caraway,
- meadow lumbago.
A teaspoon per 150 ml of water, leave for 15 minutes in a thermos.
If you have a sore throat, or if there is pain in the hearing organs, you need to prepare drinks from medicinal herbs that have anti-inflammatory, bactericidal, and sedative properties for gargling:
- chamomile,
- elecampane,
- calendula,
- St. John's wort,
- oak bark,
- sage.
To gargle and gargle in case of purulent inflammation of the throat, teeth, or if the ear hurts when swallowing, it is necessary to use solutions with salt; it, by changing the osmotic pressure of the cells, draws out all pyogenic bacteria from them. Mix a teaspoon into half a glass of water.
After a cold, tea, rose hip drink, black currant, and lemon are useful to boost immunity.
Treatment of tubootitis: disinfection of the ear cavity at home is done with hydrogen peroxide 3%.
- mint;
- oregano;
- fragrant rue;
- bloodroot;
- caraway;
- meadow lumbago.
- chamomile;
- elecampane;
- calendula;
- St. John's wort;
- oak bark;
- sage.
Traditional healers recommend gargling with a solution of salt and iodine, decoctions of chamomile and calendula. Warming up is possible (if the body temperature does not exceed 37 degrees) - vodka or alcohol compresses on the neck. Inhalation is the procedure of inhaling steam from solutions of medications, herbs or just potatoes.
Laryngitis
Laryngitis is a disease in which the mucous membrane of the larynx becomes inflamed. In most cases, pathology is caused by various viruses, leading to hyperemia and swelling of the inner layer of the respiratory tract. If left untreated, laryngitis, especially in preschool-age patients, can lead to the development of false croup, a disease during which the movement of air masses in the larynx becomes difficult or impossible.
Acute laryngitis rarely occurs as an independent pathology; in most cases it develops against the background of a severe form of acute respiratory viral infection, measles, scarlet fever, etc. The chronic form of the disease is formed due to improper treatment of acute laryngitis or as a result of prolonged harmful effects on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract of various pathogenic factors: dust, chemicals, smoke.
The disease manifests itself as a dull pain and burning sensation in the throat, while the unpleasant sensations can be localized on one side of the larynx. Patients often also complain of discomfort in the ears, difficulty swallowing, and dry mouth and throat. When diagnosing laryngitis, you should pay attention to other symptoms of the disease:
- hoarseness or hoarseness of the voice;
- sensation of a foreign object in the throat;
- dry cough in acute laryngitis or wet in chronic.
A patient with uncomplicated laryngitis does not require hospitalization, so treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. In this case, bed rest is necessary only for patients whose pathology has developed against the background of ARVI. Other patients can lead their normal lives, but try not to talk or whisper to reduce the strain on the vocal cords.
Patients are prescribed ultraviolet treatment, magnetic therapy, quartz procedures, alkaline or oil inhalations. To relieve pain and stop coughing, it is recommended to drink plenty of warm drinks and use lozenges with eucalyptus, sage or chamomile extract.
Other causes of sore throat and ear pain
In addition to sore throat and ear pain, all of the above inflammatory pathologies have one more common symptom: increased body temperature. However, there are other reasons for which pain symptoms occur, and they are not associated with inflammation. Therefore, there is no elevated temperature with them or occurs only when the process is neglected.
| Initiating factor | What is it characterized and manifested by? |
| Traumatic injuries to the mucous membrane | Pain can occur due to a burn (thermal or chemical), ingress of a foreign body, or mechanical impacts. |
| Neoplasms of benign and malignant etiology | Benign and malignant neoplasms of the larynx are a fairly rare phenomenon that can make it difficult to eat and cause pain. Requires seeking professional medical help. |
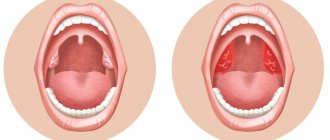
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is a disease in which the epithelial lining of the back wall of the pharynx becomes inflamed. Pathology can be non-infectious, bacterial or viral in nature. The disease in most cases is combined with tonsillitis, accompanied by lacrimation and a feeling of congestion in the nose and ears.
Non-infectious pharyngitis develops due to the patient inhaling excessively hot or cold air, toxic vapors, prolonged contact with substances that irritate the mucous membranes: coal, chalk, wood or stone dust, etc. The infectious form of the disease occurs when a streptococcal, staphylococcal, pneumococcal, fungal or viral infection develops in the human body. In this case, pharyngitis is usually caused by a pathology that has spread beyond the source of inflammation: sinusitis, otitis media, etc.
In case of infectious pharyngitis, it is necessary to identify the nature of the causative agent of the disease. Otherwise, treatment may not be effective.
With pharyngitis, patients experience characteristic signs of the disease:
- Pain
. The pain syndrome is dull and localized in the throat. When swallowing, the discomfort increases, causing unilateral discomfort in the ear area. - Sore throat
. The patient constantly has a desire to cough; patients often complain of a painful dry cough. - Hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membranes of the pharynx
. In rare cases, upon examination, small papules or ulcers may be noted on the surface of the epithelium. - Low-grade fever
with an increase in body temperature to 37.5-38°C.
Pharyngitis therapy is aimed at relieving the symptoms of the pathology and eliminating the factor that caused the disease. The patient is prescribed antibacterial or antiviral agents: Doxycycline, Ampicillin, Acyclovir
etc.
Taking these drugs is necessary in the treatment of infectious pharyngitis. It is also recommended to use sprays with local anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects: Hexoral, Strepsils, Chlorophyllipt
.
To treat a disease of a non-infectious nature, the patient should stop smoking, use personal protective equipment when working with irritating substances, and avoid eating spicy or excessively hot foods.