The condition of the oral mucosa is one of the indicators of human health. It is involved in most pathological processes occurring in the body and reacts even to minor changes in the microbial composition of the oral cavity. Therefore, many people have experienced red dots on their gums and palate at least once in their lives. This is a natural reaction to mechanical and temperature stimuli. Redness may be caused by:
- consumption of hot and spicy foods and drinks;
- damage to soft tissues with a hard brush, toothpick, bones and pieces of hard food;
- Using the wrong toothpaste or mouthwash;
- wearing prostheses, braces, retention caps.
However, red spots can also indicate various diseases. Let's look at the most common cases.
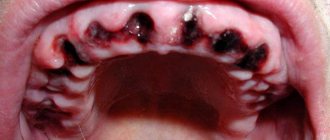
Characteristics of a blood bubble on the oral mucosa
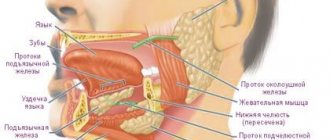
The mucous membrane protects the entire body from the negative influence of the environment, from harmful microorganisms, various types of pollution, and also has a fairly high level of regeneration. If blood blisters regularly appear on the oral mucosa, then you should take this signal seriously and take action.
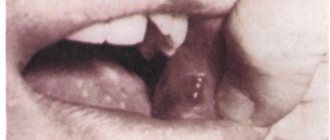
A bloody ball in the mouth is a hematoma (bruise), which is characterized by the accumulation of blood in a certain place in the oral cavity. The appearance of bloody blisters is a kind of hemorrhage that occurs due to trauma to the capillaries and thin vessels of the mucous membrane.
A blister on the mucous membrane may contain clear serous fluid without the presence of blood. This means that the vessels were not damaged and the resulting wound is superficial. Such blisters on the mucous membrane heal much faster. The presence of blood in the bladder indicates a deep injury and a longer period of healing and blood resorption.
Angina
Herpetic sore throat is also a fairly common cause of the formation of red dots in the throat on the roof of the mouth. The disease is characterized by high fever that lasts for several days, pain when swallowing, discomfort in the abdomen, and enlarged lymph nodes.
Streptococcal sore throat is accompanied by general malaise, headache, and high body temperature. The tonsils become loose and covered with plaque. In this case, antibiotic therapy is used, but the treatment regimen must be drawn up by a qualified specialist.
The main causes of a blood blister
The general condition and integrity of the oral mucosa usually indicates the level of health of the body. Often, by examining the appearance of the oral mucosa and blisters, the doctor makes a final diagnosis. After all, the symptoms of most infectious, bacterial, chronic, and acute processes that occur in the body are associated with changes in the integrity and color of the oral mucosa. Therefore, it is important to understand the main reasons that cause blood blisters to appear in the mouth.
Blood blisters are distinguished by the place of their occurrence - on the tongue, under the tongue, on the cheek. They can occur as a result of injury or be a signal of the presence of a serious disease in the body. Multiple blood blisters on the oral mucosa occur with stomatitis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system. The cause of the sudden appearance of a blood bubble in the mouth is damage to the mucous membrane.
There are the following types of injuries to the oral cavity:
- mechanical injury.
The cause may be various objects, solid food, biting the cheek; - chemical injury.
It occurs due to the consumption of spicy, salty foods, and exposure to chemicals on the mucous membrane. This irritates the delicate oral mucosa and causes injury; - thermal injuries.
Their appearance is provoked by too cold or hot food or drinks.
Herpetic stomatitis
With stomatitis, spots in the throat range from light pink to red. Areas with the rash may merge or be located far from each other. There are several types of stomatitis, among which herpetic stomatitis is especially common.
This disease is accompanied by headache, high fever, and red dots form on the upper palate, tongue, lips, and cheeks. These points turn into bubbles and explode to form red erosions. The herpes virus remains in the body for life. With strong immunity, it is in an inactive phase, and will manifest itself in the following cases:
- With exacerbation of chronic inflammatory processes.
- After a course of corticosteroids.
- In case of trauma to the mucous membrane.
- During emotional turmoil, allergies, vitamin deficiency.
- When the immune system is weakened.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis should be prescribed by a qualified dentist.
The mechanism of formation of a blood bubble on the oral mucosa
Bloody blisters in the mouth in most cases are not life-threatening. They are formed as a result of mechanical damage to the mucous membrane. When microtrauma occurs, harmful microorganisms attack the damaged area.
After this, a number of responses are activated in the human body:
- The immune system is activated. Monocytes and leukocytes, as well as macrophages, instantly arrive at the damaged area, attacking the harmful pathogen and quickly destroying it.
- Immune cells die. This is a signal for other cells and substances are released in the affected area that are mediators of inflammation of the mucous membrane - serotonin, histamine and bradykinin.
- These substances cause a strong spasm of the circulatory system and the outflow of blood is hampered. After the spasm is relieved, all accumulated blood immediately flows to the site of inflammation. It moves at high speed and under pressure. A detachment of the mucous membrane occurs in the mouth, and a bloody blister appears.
Associated symptoms
If you find red spots in your mouth, you should consult a specialist. As a rule, most of the listed diseases are also accompanied by the following manifestations:
- local pain,
- itching and burning,
- bad breath,
- swelling and inflammation of the gums,
- local temperature rise,
- discomfort when chewing, swallowing, communicating.
If these symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
Pediatric infectious diseases
Many infectious diseases that manifest as a rash on the palate are known as “childhood” diseases. But this does not mean that adults are not susceptible to infection. Having suffered from such diseases once, a person receives lifelong immunity. But if you do not get the same chickenpox in childhood, there is a risk of contracting this infection in adulthood.
Rubella
With rubella, red spots may first appear on the child's palate, and only then on the face and body. Rubella usually resolves easily and without complications in childhood, with the exception of infants up to one year old. These babies endure the disease very hard, so scarlet specks in the mouth, which quickly merge into specks, should alert parents: this may be the first symptom of rubella. This disease is also dangerous for adults who did not have it in childhood, especially for pregnant women.
Measles
As with rubella, with measles a rash in the mouth may appear earlier than on the body - sometimes within a day or two. But the nature of the rash is very different: with measles, the rash looks like dots of white or pale gray color, reminiscent of semolina. Their accumulations on the upper palate, tonsils and back of the throat are surrounded by a pinkish border, this phenomenon is called Belsky-Filatov syndrome.
Chicken pox
With chickenpox, a red rash in the mouth should alert you, as it indicates a complicated course of the disease. Bubbles filled with liquid can shed the gums, tongue, inner surfaces of the baby’s lips and cheeks, and are often found at the top - on the hard and soft palate. Breaking through, they form ulcerations in the oral cavity.
Scarlet fever
With scarlet fever, a small red rash covering the child's body may also appear on the upper palate. The mucous membranes of the pharynx with scarlet fever are bright red, the regional lymph nodes and tonsils are enlarged, the tongue becomes crimson in color and is covered with a white coating - see photo.
Speckled rashes are usually accompanied by a very high fever and vomiting, and in severe forms of the disease - convulsions and clouding of consciousness.
- Causes of rashes in children
Roseola
Since the disease begins with a high fever, and after a couple of days, when the temperature subsides, a rash appears, roseola is often mistaken for ARVI and an associated allergy to medications. Small red spots and blisters in the throat and palate precede the appearance of similar rashes on the body. Their presence is accompanied by redness of the pharynx and pain when swallowing.
The difference between a rash in the mouth and on the body with roseola and any other is that it disappears when pressed.
Causes of herpangina
Herpangina can be caused by about 70 serotypes of enteroviruses. Most often these are Coxsackie B, Coxsackie A17 viruses and enterovirus 711.
Since the only carrier of enteroviruses is humans, you can become infected through contact with a sick person or with a virus carrier who has no symptoms of the disease1. According to the literature, the number of virus carriers can be up to 46% of people2.
The virus is released into the external environment with feces and droplets of saliva. It is also contained in bubbles that appear in the patient’s throat. Enterovirus infections most often affect children, although the disease also occurs in adults5.
The patient or virus carrier excretes viruses from the upper respiratory tract within 3 weeks after infection, and with feces - up to 8 weeks. In the first two weeks, herpetic sore throat is most contagious1.
You can become infected in the following ways:
- through dirty hands, objects and food if they are exposed to the virus;
- drinking contaminated water from a reservoir;
- upon contact with a patient or virus carrier.
The herpangina virus is also transmitted transplacentally - from mother to fetus3.
Up to contents
Diagnostics
The success of any treatment process directly depends on the accuracy of diagnosing the problem. If you notice red spots on the roof of your mouth, you should consult a physician. You will also need to undergo an examination by a dentist and otolaryngologist. If there is a suspicion of an infectious disease, the specialist will refer you for a scraping to identify the pathogen.
Drug treatment involves taking antibiotics and antiviral drugs. Among other things, local treatment of the throat and oral mucosa is prescribed through regular rinsing procedures. Regardless of the disease, it would be appropriate to use a vitamin complex to strengthen the body’s protective properties.
The main aids in making a diagnosis are laboratory tests of blood and urine. Characteristic symptoms and test results indicate a particular problem.
Possible complications.
More often, the disease passes without dangerous consequences for the patient. But with weak immunity, especially in young children, severe herpes sore throat can lead to serious complications caused by the spread of the virus to other organs:
- serous meningitis
- heart pain, myocarditis
- pyelonephritis
- encephalitis
- conjunctivitis.
To exclude the development of serous meningitis, you need to consult a neurologist; if you have heart complaints, you need to contact a pediatric cardiologist. If there are changes in the general urine test, you must make an appointment with a pediatric nephrologist.
With proper and effective treatment of herpes sore throat complicated by meningitis, the prognosis is usually favorable. But at the same time, the treatment of the youngest patients requires careful attention. With myocarditis the situation is more severe. Any complications of herpetic sore throat require the intervention of specialists!
Pharyngitis - symptoms and treatment
Treatment of acute pharyngitis begins with organizing a regimen and nutrition :
- gentle regime with enough sleep;
- creating conditions for the normal functioning of the mucous membrane - cool, moist air, eliminating active and passive smoking, contact with dust and irritants;
- diet excluding spicy and rough foods;
- warm drinks, alkaline rinses and inhalations [12].
Sometimes these measures already lead to an improvement in the condition. As prescribed by a doctor, to reduce the symptoms of pharyngitis caused by inflammation, complex products are used in the form of tablets, aerosols, rinses :
- antiseptics (chlorhexidine, hexetidine, benzydamine, iodine preparations, plant extracts, etc.);
- sometimes antibiotics (gramicidin);
- anti-inflammatory drugs (ketoprofen);
- local anesthetics (lidocaine, tetracaine, menthol) [13].
The choice of drugs is large, but excessive use can lead to suppression of the normal microflora of the pharynx, decreased local immunity, allergic reactions, damage to the mucous membrane; in addition, their effectiveness in viral infections has not been proven [7].
To reduce the temperature, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, paracetamol) are prescribed.
Treatment of bacterial pharyngitis
Specific treatment of acute and chronic pharyngitis in adults with bacterial pathogens, especially with GABHS (group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus) is systemic antibiotic therapy. The drugs of choice are antibiotics from the group of semisynthetic penicillins (amoxicillin). Often sick children who have a variety of pathogenic flora on their mucous membranes are prescribed protected aminopenicillins (amoxicillin + clavulanic acid). When mycoplasma or chlamydia is detected, antibiotics are prescribed when the process descends into the bronchi and lungs or the disease becomes protracted [7]. Macrolide antibiotics (azithromycin, clarithromycin) are used.
Viral pharyngitis does not require antibiotic therapy.
Treatment of fungal pharyngitis
For mycoses, local antimycotic agents are used (co-trimoxazole, pimafucin, 2% alkaline solution). If local therapy does not help, antifungal antibiotics (amphotericin B) or special antifungal agents (ketoconazole, mycoheptin, fluconazole) are prescribed.
Treatment of chronic pharyngitis
Treatment of chronic pharyngitis during an exacerbation is no different from treatment of the acute form of the disease. It includes symptomatic therapy, proper organization of daily routine and food intake.
Purulent pharyngitis is not isolated, so there are no separate recommendations for its treatment.
Treatment of pharyngitis at home
Mild acute viral pharyngitis, if you follow a home regimen and regular warm drinks, goes away within seven days. However, the disease can occur not only due to a viral infection, but also for another reason. Therefore, without making a diagnosis, you should not self-medicate.
Physiotherapy
For obsessive dry cough and dry throat, you can use inhalations with saline solution as directed by your doctor.
Surgery
Surgical treatment consists of correcting the nasal septum and removing nasopharyngeal polyps. Surgery is necessary if the cause of chronic pharyngitis is constantly difficult nasal breathing. Removal of adenoids and tonsils is carried out according to strict indications. The decision on the need for surgery is made by an otolaryngologist after a thorough diagnosis.
Treatment of herpes sore throat in children
There is no specific antiviral treatment. Treatment of the cause of herpetic disease should be carried out according to the following scheme:
- isolation of the patient
- drinking plenty of fluids, bed rest
- actions aimed at relieving and alleviating symptoms.
At the moment, no drug has yet been invented that can kill the causative agent of the disease. You can only alleviate or remove the symptoms. A person recovers completely only when the body develops immunity to the virus. Usually the body takes a week to do this.
First of all, it is advisable to isolate the child from other family members - separate dishes, linen and towels - the disease is contagious. For herpetic sore throat, children are prescribed antihistamines to relieve swelling and irritation. "Claritin", "Suprastin" and others are suitable. To reduce the temperature, use antipyretics: Nurofen, Efferalgan, Paracetamol, etc. To relieve pain in the throat, gargle with decoctions of sage, chamomile, calendula, salt or soda solution. Rinsing should be done every hour. You can use special sprays and aerosols: Hexoral, Ingalipt, Tantum-Verde. Tablets and lozenges relieve pain. It is advisable to use the antiseptic agents Miramistin and Chlorhexidine.
For successful recovery it is necessary to create favorable conditions for the child. It is necessary to provide conditions for sleeping in a well and frequently ventilated room. The diet should consist of soups, purees, and cereals. Food should not be hot so as not to irritate a sore throat. Don't forget about drinking plenty of warm drinks. The patient can be given rosehip decoction, tea with jam or honey.
Note to parents! In case of herpes sore throat, do not inhale, warm up or apply compresses under any circumstances. Such measures will only activate viruses, and the disease will drag on.
Some parents mistakenly lubricate the bubbles in the larynx with iodine or brilliant green. This measure is absolutely ineffective, does not bring any practical benefit, but causes severe pain to the baby.
There is no need to give your child antiherpetic drugs such as Acyclovir and its analogues. As we have already mentioned, the course of the disease has nothing to do with the herpes virus.
Sources
- Corsino CB, Ali R, Linklater DR. Herpangina. 2022 Jun 23. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan–. PMID: 29939569. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507792/
- Ter-Baghdasaryan L.V., Ratnikova L.I., Stenko E.A. Clinical and epidemiological aspects of enterovirus infection // Infectious diseases: news, opinions, training. 2022. T. 9, No. 1. P. 88-93. doi: 10.33029/2305-3496-2020-9-1-88-93 https://infect-dis-journal.ru/ru/jarticles_infection/672.html?SSr=2601343bdb01ffffffff27c__07e4040b011a36-9772
- Alacheva Z. A., Rybalka O. B., Kulichenko T. V. Should everyone escape from Coxsackie?! Or fear has big eyes. Issues of modern pediatrics. 2017; 16 (4): 286–290. doi: 10.15690/vsp.v16i4.1774) https://vsp.spr-journal.ru/jour/article/viewFile/1787/713
- Herpangina Brenda L. Tesini. University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry // MSD Handbook - 2019 https://www.msdmanuals.com/ru/professional/infectious-diseases/enteroviruses/herpangina
- Kozlovskaya O.V., Katanakhova L.L., Kamka N.N., Evseeva A.N. Epidemiological, clinical and diagnostic features of enterovirus infection in children and adults. Bulletin of Surgu State University. Medicine. 2018;(2):56-60. https://surgumed.elpub.ru/jour/article/view/140/141
- Kuo KC, Yeh YC, Huang YH, Chen IL, Lee CH. Understanding physician antibiotic prescribing behavior for children with enterovirus infection. PLoS One. 2022 Sep 7;13(9):e0202316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202316. PMID: 30192893; PMCID: PMC6128467. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30192893/
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® SOLUTION:
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® AEROSOL:
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS:
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA:
Up to contents
If it's tonsillitis
The disease occurs in an acute form, affects the palatine tonsils, and the causative agent is streptococcus. During the development of the disease, a large number of toxins and antigens are released, which destabilizes the functioning of the joints, heart muscle, and kidneys.
Characteristic symptoms:
- pain in the larynx, radiating to the neck and ears;
- increase in body temperature (slight);
- headache, brittle bones;
- tonsils become covered with plaque, the surface becomes loose;
- lymph nodes enlarge.
For drug treatment, antibiotics of the penicillin group (Augmentin, Amoxiclav) or macrolides (Sumamed, Azithromycin) are recommended. Local agents are also prescribed (Lugol's solution, antiseptics, antibacterial spray).
To increase the effectiveness of treatment, namely to eliminate red spots, traditional medicine recipes are also used:
- gargling solution made from warm water (200 ml), soda (tsp), salt (tsp), iodine (5 drops);
- decoctions and infusions of plants (calendula, raspberry leaves, peppermint, oak bark, wormwood, plantain leaves, etc.);
- teas from black currant, honey, linden blossom, rose hips, marshmallow, etc.;
- chewing propolis;
- warm compresses on the neck.