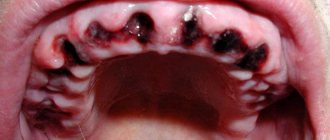
Characteristics of a blood bubble on the oral mucosa
The mucous membrane protects the entire body from the negative influence of the environment, from harmful microorganisms, various types of pollution, and also has a fairly high level of regeneration. If blood blisters regularly appear on the oral mucosa, then you should take this signal seriously and take action.
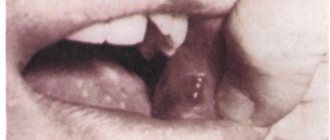
A bloody ball in the mouth is a hematoma (bruise), which is characterized by the accumulation of blood in a certain place in the oral cavity. The appearance of bloody blisters is a kind of hemorrhage that occurs due to trauma to the capillaries and thin vessels of the mucous membrane.
A blister on the mucous membrane may contain clear serous fluid without the presence of blood. This means that the vessels were not damaged and the resulting wound is superficial. Such blisters on the mucous membrane heal much faster. The presence of blood in the bladder indicates a deep injury and a longer period of healing and blood resorption.
Cheek structure
Many people do not think about the fact that the cheeks perform an important function. In addition to aesthetic value and participation in articulation, they also provide the most important function - chewing food. The cheeks are formed by muscles, mainly the chewing muscle. This is a fairly powerful bundle of skeletal muscles, which, when contracting, sets in motion the complex complex of the temporomandibular apparatus and the digestive system as a whole. The outside of the cheek is covered with skin, and the inside is lined with mucous membrane.
To understand the mechanisms of formation of pathological processes in the oral cavity, in particular on the cheeks, it is necessary to have an idea of the structure of the mucous membrane. The buccal mucosa consists of several layers:
- epithelium is the surface layer. This layer consists of a number of layers, the innermost one being the cambial layer, which is the source of stem cells, which, upon differentiation, participate in regeneration;
- The lamina propria of the mucosa is a section of tissue that nourishes the entire thickness; nerve and blood tissues are located here;
- the submucosa, which provides mobility and the ability of the mucosa to gather into folds, contains nerves and blood vessels;
- the muscular layer of the mucosa, represented by 2 layers - longitudinal and circular, which, when contracted, is involved in chewing and grinding food.
Also, the entire mucous membrane of the cheek is divided into 3 sections:
- maxillary - part of the department that is adjacent to the upper jaw;
- mandibular – adjacent to the lower jaw;
- intermediate - located along the line of closure of the teeth, serves as a location for the localization of pathological formations.
The main causes of a blood blister
The general condition and integrity of the oral mucosa usually indicates the level of health of the body. Often, by examining the appearance of the oral mucosa and blisters, the doctor makes a final diagnosis. After all, the symptoms of most infectious, bacterial, chronic, and acute processes that occur in the body are associated with changes in the integrity and color of the oral mucosa. Therefore, it is important to understand the main reasons that cause blood blisters to appear in the mouth.
Blood blisters are distinguished by the place of their occurrence - on the tongue, under the tongue, on the cheek. They can occur as a result of injury or be a signal of the presence of a serious disease in the body. Multiple blood blisters on the oral mucosa occur with stomatitis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system. The cause of the sudden appearance of a blood bubble in the mouth is damage to the mucous membrane.
There are the following types of injuries to the oral cavity:
- mechanical injury.
The cause may be various objects, solid food, biting the cheek; - chemical injury.
It occurs due to the consumption of spicy, salty foods, and exposure to chemicals on the mucous membrane. This irritates the delicate oral mucosa and causes injury; - thermal injuries.
Their appearance is provoked by too cold or hot food or drinks.
Treatment
It is not necessary to treat blood blisters that form on the buccal mucosa. But if they bother you a lot, then you can puncture such blisters. It is better not to carry out such punctures on your own, especially if you are not sure of the diagnosis, so as not to harm yourself. In addition to punctures, you can rinse the mouth with antiseptic solutions - for example, chlorhexidine, furatsilin; You can use oral baths with decoctions of chamomile herbs or oak bark - these solutions will relieve local signs of inflammation. In addition to all this, it is believed that the development of such blood blisters occurs due to the weakness and fragility of the blood vessels. To strengthen the walls, you can use B vitamins, vitamin A, E, K, C inside. It will not hurt to stimulate and maintain the immune system, especially in the off-season, when the supply of micro- and macroelements to the body is reduced. Complex multivitamin preparations, which already contain all the necessary substances in the required quantities, are perfect for such purposes.
The mechanism of formation of a blood bubble on the oral mucosa
Bloody blisters in the mouth in most cases are not life-threatening. They are formed as a result of mechanical damage to the mucous membrane. When microtrauma occurs, harmful microorganisms attack the damaged area.
After this, a number of responses are activated in the human body:
- The immune system is activated. Monocytes and leukocytes, as well as macrophages, instantly arrive at the damaged area, attacking the harmful pathogen and quickly destroying it.
- Immune cells die. This is a signal for other cells and substances are released in the affected area that are mediators of inflammation of the mucous membrane - serotonin, histamine and bradykinin.
- These substances cause a strong spasm of the circulatory system and the outflow of blood is hampered. After the spasm is relieved, all accumulated blood immediately flows to the site of inflammation. It moves at high speed and under pressure. A detachment of the mucous membrane occurs in the mouth, and a bloody blister appears.
Blood blisters
The cheeks, due to their vital importance, are well protected, this is how it happened evolutionarily. Therefore, the muscle and mucous tissue of the cheeks are well innervated and richly vascularized, that is, supplied with blood. However, it also happens that this seemingly useful process becomes a problem. Many people are faced with the fact that a blood ball appears in the mouth on the mucous membrane of the cheek. Often such formation does not foreshadow anything dangerous. A blood bubble that forms in the mouth on the cheek is just the result of a mechanical injury. Most likely, the cheek area was bitten by the teeth while eating or talking. Since the oral cavity is a complex biological system in which a huge number of microorganisms live, it is natural that when such a microtrauma occurs, it becomes contaminated with various kinds of pathogens. As a result, a whole cascade of body responses is activated:
- since the pathogen is a foreign substance in the inner layer of the cheek, the immune system is immediately activated. Leukocytes, monocytes and macrophages quickly arrive at the site of infection, capture the pathogen and destroy it, and often die themselves;
- due to the death of immune cells that have absorbed pathogenic microflora, their internal contents are released into the environment. These biologically active substances are chemotaxis factors, that is, they signal to other cells, as a result of which substances such as histamine, serotonin, bradykinin - inflammatory mediators - are released in the area of inflammation;
- inflammatory mediators cause spasm of the circulatory system, which makes blood flow difficult; and after some time the vessels relax, and all the blood that has accumulated at the site of narrowing immediately flows into the source of inflammation. Since such blood flows at high speed and under high pressure, it forms a detachment of the mucous membrane - a bubble - and a blood ball appears in the mouth.
Thus, the blood blisters that form in the mouth are just part of the body's defense mechanism, which has been formed over centuries. When such a pathology appears, you should not panic too much. Regular blood blisters reorganize on their own within 3-4 days. But if the blood bubble does not self-destruct within a week, consult a dentist to rule out the diagnosis of unwanted neoplasms. The doctor will not only prescribe a pain reliever (since the appearance of a neoplasm on the mucous membrane is sometimes accompanied by pain), but will also take a sample of the epithelium for histology analysis.
Causes of a blood ball in the mouth
Most often, a blood ball in the mouth is formed under the influence of external irritants and periodically, less often, is chronic. If there is an infection (viral or bacterial), the mucous membrane in the oral cavity also changes, which can lead to the formation of a ball. If it is present, depending on the size, a person feels acute pain when eating food with acid, drinking juices or plain water.
Main reasons:
- mechanical - biting the cheek or hard food can disrupt the integrity of the oral cavity, and since there is a large number of bacteria in the mucous membrane, a ball forms or this place becomes inflamed
- thermal - burn from hot or cold food
- chemical - food that is too salty or seasoned with spices disrupts the mucous membrane in the oral cavity, which can lead to the formation of a ball in different places
- pathological - stomatitis, thrush, tumor, hemangioma, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or endocrine system - in the case of such pathologies, the mucous membrane is damaged, or rather its protective properties for the oral cavity decrease and wounds, pustules and blood globules form in it
Treatment or what to do if a blood ball appears in the mouth
A blood ball in the mouth, as a reaction to external or internal irritants, goes away on its own within seven days. If this does not happen, then you should contact a specialist who will diagnose and prescribe treatment. It is important to determine its nature, fullness, size and location.
Most often, conservative therapy (less often surgical intervention) is carried out with the help of antiseptics (Chlorhexidine or Miramistin), which prevent the spread of bacteria, heal the wound and the blood ball resolves.
If the formation on the gum causes discomfort
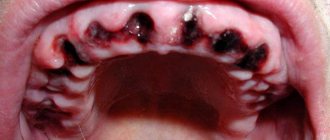
If a bubble near a molar causes pain, this indicates an infectious inflammatory process. Discomfort is also typical with gum injuries and hematomas. Painful formations can be caused by a cyst, cancer, fibroma, periostitis, periodontitis.
Gingivitis - the disease affects only one gum, and the periodontium near the molar remains uninjured. The main symptoms of the pathology are swelling, bleeding, and peeling of the epithelium. Gingivitis often occurs against the background of halitosis. Sometimes pathology develops as a result of endocrine and metabolic disorders.
When treating, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of gingivitis. Professional oral hygiene, diagnosis and treatment of metabolic disorders are performed. To eliminate inflammation and prevent further spread of bacteria, antibiotic therapy is administered. For pain and severe discomfort, analgesics are prescribed.
Periodontitis - purulent bumps on the gums appear as a result of degeneration of the alveolar process, through which the tooth root is held in the alveolus. Tissues can be destroyed due to poor oral hygiene and internal pathologies.
In the initial stages, periodontitis is treated by teeth cleaning at the dental clinic and further proper care. An advanced form of the disease, in which the teeth become loose, pus accumulates, requires surgical intervention - restoration of the alveolar processes or removal of molars.
Periostitis or flux is a dense formation near a problematic molar with carious lesions. Patients complain of pain radiating to the temple, chest, neck, ear. The condition gradually worsens and the temperature can rise to 38 degrees. In the oral cavity, lesions due to periostitis are hyperemic. A purulent fistula forms. When the discharge is removed, the discomfort decreases.
Causes of periostitis: trauma, periodontitis, osteomyelitis, weak immune system, infectious pathologies occurring in the body and vitamin deficiency.
Treatment of neoplasms in the oral cavity
A lump under the jaw or on the gum can be detected upon examination. For an accurate diagnosis, a biopsy or x-ray is prescribed. Treatment is selected taking into account the cause of the formation of a bubble in the oral cavity. It will be necessary to stop the further spread of infection and eliminate discomfort.
The doctor will determine how to remove the lump after a complete diagnosis, but the main measures include:
- fistula - pus is removed by rinsing with a disinfectant solution;
- epulis - surgical intervention (removal using diathermocoagulation, cryodestruction or a scalpel);
- periodontitis - removing fillings, cleaning canals, removing pus, rinsing with herbal decoctions and soda solution;
- periostitis - placement of special drugs under a temporary filling (if there is no result, the tooth will have to be removed);
- gingivitis - cleaning of periodontal tubules, antiseptic and antibacterial therapy, removal of lumps.
When a formation appears on the gum, you can rinse your mouth with vodka, diluted alcohol or juice from fresh Kalanchoe leaves.
Timely diagnosis allows you to prevent further spread of infection and save teeth.
Only an experienced dentist will help you get rid of a lump in your mouth, minimizing the risk of developing serious complications. At the first signs of pathology, you should immediately consult a doctor. The doctor's consultation