Concept and reasons for origin
The term “small lower jaw” in dentistry and orthodontics has several interpretations with significant differences:
- Micrognathia (also microgenia) is a pathology manifested in the form of defective or delayed development of the entire lower jaw, as well as its individual fragments;
- Prognathia is an intensive growth of the upper part of the jaw apparatus, which results in the visual effect of insufficient development of the lower jaw.
Both pathologies manifest themselves in both infancy and adulthood. Clinical manifestations of the anomaly make it possible to detect the presence of abnormalities at the primary stages of development, which provides the possibility of preventive treatment.
In children
In infancy, improper formation of the lower jaw is caused by various factors, the main one of which is a violation of the uniform process of fetal development in the prenatal period. At this stage, the relationship of jaw proportions is established, which can be influenced by:
- improper maternal diet;
- presence of genetic predisposition;
- consumption of nicotine and alcohol products;
- exposure to serious illnesses with complications.
In the early stages of a child’s life, factors influencing the development of pathology are:
- late formation of bite;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- early loss of baby teeth;
- bad habits (pacifiers, pacifiers);
- improper feeding.
The primary signs of small lower jaw syndrome in children are recession of the chin and lower lip, abnormal tooth growth and impaired sucking function. Timely identification of symptoms allows the anomaly to be stopped without the use of orthodontic treatment methods.
In adults
In older age, factors provoking the formation of pathology are:
- incorrect or incomplete treatment in childhood;
- receiving severe injuries to the jaw apparatus;
- disorders of the body's metabolic processes;
- pathologies formed in bone tissue (rickets, ostiomyelitis);
- abnormal development of the orbicularis oris muscle.
Characteristic manifestations of small lower jaw syndrome in adulthood are distortion of the patient’s facial features, deformation of the dentition, and problems with eating solid foods.
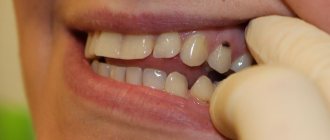
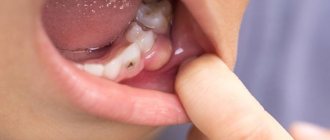
What is the type of malocclusion in children in the photo?
Experts divide all malocclusions into several large groups:
- Open bite (when a group of teeth does not close in central occlusion - that is, in the position of maximum closure). As a rule, this is an anterior open bite, less often observed on one or both sides.
- Mesial (the lower jaw moves forward further than the upper jaw).
- Distal bite (the upper row of teeth moves forward further than the lower one). This may be a consequence of excessive development of the upper jaw or underdevelopment of the lower jaw.
- Crossed (one of the jaws may be narrower than the other, and the lower jaw is generally shifted to the side). In this case, the child has facial asymmetry. Such a bite can be formed either unilaterally or bilaterally.
- Deep bite (when the mouth closes and the upper jaw overlaps the lower jaw by more than a third).
- Diastema (when a gap forms between the first incisors of one or both rows). This anomaly is often called the “London smile” or “London chic”, but it does not add health...
Treatment and prevention
The choice of treatment technique is determined by the clinical picture of the development of the pathology, as well as the age group to which the patient belongs. The main vector of therapy is to stimulate the development and growth of the lower jaw.
In childhood
The period of primary occlusion is one of the most favorable in terms of correction possibilities, since it allows the use of gentle treatment methods. The main methods used at this stage are:
- prosthetics for prematurely fallen milk teeth, ensuring the preservation of the normal shape of the jaw arch;
- sanitation of the oral cavity, accompanied by the restoration of individual damaged teeth and cleaning of defective roots;
- grinding of the areas of jaw closure - fissures - which allows you to eliminate malocclusion in the form of bumps on the chewing surface;
- normalization of breathing and tongue function, including by trimming the lingual frenulum and correcting the nasal septum;
- use of special corrective trays, plates or nipples.
Quite often, in order to stop the primary signs of pathology, it is enough to wean young children from bad habits.
As an adult
The treatment method during the period of permanent or mixed dentition is determined by the specifics of the anomaly.
To treat prognathia at the variable stage, special corrective orthodontic appliances, such as a Frenkel adjuster, a facebow or a Herbst device, can be used. Microdentia is treated with the help of distractors - devices that stretch the bone tissue and then replace it in the jaw with new bone.
At the permanent stage of occlusion, the most effective method is jaw surgery, which involves removing part of the dentition and excision of the alveolar-ridge area. It is also possible to use a radical technique - plastic surgery, in which the lower jaw is broken off from the main bone and moved forward, and in its place new bone material is placed, fixed with special plates.
The easiest way to avoid orthodontic intervention and stimulate the normal development of the lower jaw is in childhood - to do this, it is enough to follow simple preventive measures, prevent the development of bad habits and contact specialists at the first signs of pathology.
Consequences of malocclusion
In addition, a formed malocclusion can negatively affect appearance, which entails a number of psychological problems, such as the development of an inferiority complex, low self-esteem, inability to communicate with others - in addition, it also negatively affects a person’s health in general.
What is its danger?
- An incorrect bite increases the risk of periodontal disease. Teeth wear down faster, lose enamel and become less strong.
- The temporomandibular joint also suffers from malocclusion, which leads to surges in blood pressure, migraines, ringing in the ears or a feeling of “stuffed” ears.
- An incorrect bite affects the digestion process. Chewing and swallowing with it can be uncomfortable for the child, which can lead to the baby either swallowing unchewed food or switching to something easier to eat (chocolate and sweet water, for example). And this definitely will not have a positive effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, or on health in general. In addition, if the baby experiences pain when chewing, he may refuse to eat altogether.
- With an incorrect bite, changes in diction occur, for example, a lisp and other abnormalities in speech. This, of course, will not add self-confidence to the child. In addition, speech disorders can cause mental retardation in the baby. Moreover, until the bite is corrected, even the best speech therapist will not help to cope with the problem.
- With an abnormal bite, the process of hygienic treatment of the oral cavity of children becomes more complicated - plaque accumulates between the teeth, bacteria begin to multiply, which can cause bad breath and lead to the development of caries and other oral diseases. To facilitate oral hygiene in case of malocclusion, use ASEPTA BABY dental napkins. They effectively cleanse gums and teeth of plaque and disinfect the mucous membrane.
Another consequence of a developed malocclusion in a child can be a problem with the ENT organs, their more frequent diseases compared to other children, as well as problems such as the appearance of polyps, snoring, and voice changes.
Trembling of the chin in a newborn is a physiological norm
Tremor caused by immaturity of the nervous system is considered a physiological norm. When a child cries and his chin trembles, it is enough to simply calm the baby. In newborns, such conditions are not treated. 3 months will pass and all phenomena will disappear. Don't worry if you notice your chin shaking while breastfeeding, bathing, or changing clothes. With any load on the nervous system, the baby begins to twitch. Trembling can be caused by:
- Overwork.
- Fright.
- Paradoxical (rapid eye movement) sleep.
- Hunger.
- Painful sensations.
- Uncomfortable air temperature.
- Bright lights and loud sounds.
- Sudden change in body position.
For obvious reasons, when the mother understands what is causing the trembling of the chin, there is no need to worry. If twitching is observed in other situations, occurs for no reason and in complete rest, the child should be examined by a doctor.
What is tremor in newborns
The term “tremor” is commonly used to describe systematic trembling of the legs, arms, chin and head. Involuntary muscle movements can be triggered by both positive and negative emotional experiences. During infancy, especially in the first weeks after birth, babies experience a lot of stress. Light, smells, sounds, bathing, hunger, sudden movements - all this is new and incomprehensible to the baby’s body and imperfect nervous system. It is not yet able to work correctly and control the functions performed. It is the high excitability and activity of muscle tissue that causes trembling and convulsive movements.
Chin tremor in a newborn or infant is a common occurrence. Symptoms are observed in every second child. Normally, this state lasts a few seconds. Until the age of two months, infant tremor does not require correction or treatment, but parents should closely monitor the condition of the newborn and not forget about the existing problem.
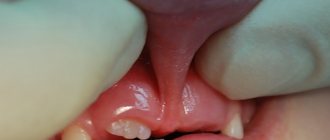
Signs
External signs are immediately visible. The oval shape of the face and mouth is changed, there are functional impairments. The upper jaw is pushed forward and the facial profile is changed. Because of this, the chin has an underdeveloped shape. Often the upper incisors protrude far forward and prevent the lips from closing completely. To make a diagnosis, the orthodontist only needs to conduct an examination. Occlusal anomalies form a certain facial expression. The person seems to be constantly surprised and frowning. Another sign is the presence of a sagittal fissure.
Signs are divided into:
- Intraoral. During the examination, the doctor discovers a violation of the relationship between the projections of the antagonist teeth on the two jaws. The frontal teeth, protruding forward, form a gap, the size of which is larger than with an orthognathic bite.
- External. Distal occlusion is easy to recognize by its appearance. The lower third of the face is smaller. The upper teeth or lip are pushed forward. With severe pathology, the lips are always open and cannot close. The anomaly is also reflected in the spine. A person with pathology has a posture with the body tilted forward. Doctors at our clinic notice that patients with long-term occlusion have a stooped posture, a protruding abdomen, and a characteristic bird-like facial profile.
- Functional. Due to the underdevelopment of the mandibular bone, it is difficult for a person to swallow and chew, he cannot breathe through his nose, and diction is impaired. Anomalies develop from childhood. Therefore, an adult person already fully adapts to them.
Often patients with distal occlusion have other anomalies. This may be an open bite, the presence of large gaps in the dentition. The risk of caries and periodontal diseases increases. When the dental system has already been formed, correction of distal occlusion is possible only with the help of braces, mouth guards or surgery. Our clinic provides orthodontic treatment for adults and children. There is no point in refusing the correction. Prognathia leads to serious problems in the future.
Correction of distal occlusion in adults
It is better to treat prognathism in childhood or adolescence, because later, to correct the distal bite, surgical intervention may be necessary - orthognathic surgery, which is also called genioplasty. It consists of correcting the shape of the chin. This is a rather complex operation, and many orthodontists prefer to mask the pathology by correcting the position of the teeth with braces or special mouth guards. In most cases, several teeth have to be removed. As a rule, these are premolars or molars. Thanks to masking treatment, doctors correct the patient's profile. However, in case of severe pathology, it is unlikely that it will be possible to achieve the desired results in this way.
After treatment for prognathia is completed, orthodontists prescribe wearing a retainer, a bite former, and performing myogymnastics. This is done in order to consolidate the result obtained, since at first the teeth will tend to return to their usual abnormal position.
Treatment of malocclusion in children
It is advisable to begin treatment of malocclusion in children as early as possible. It is ideal if parents notice the problem and begin to take measures to eliminate it before the baby turns 5 years old.
Depending on what period of life a person sought help in correcting malocclusion, different technologies are used:
Thus, to correct the bite of children who do not yet have permanent teeth, experts recommend using removable appliances that stimulate the growth of the jaw bones and correct the functioning of the jaw muscles. These include:
- various pacifiers (special anatomical shape; influence the correct position of the child’s jaws and tongue; used up to 2 years of age);
- lip bumpers (metal arches placed between the lips, cheeks and teeth; reduce the pressure of the muscles of the neck and lips on the teeth\lengthen the dental arch\ change the inclination of the first, just forming teeth; used up to 7 years);
- trainers (made of silicone and are universal, i.e. they do not require a special impression. With their help, the cause of malocclusion and bad habits that contribute to its formation are eliminated, and the tongue muscles and chewing muscles begin to work correctly. For children 6- For 8 years old it is better to choose a soft pre-orthodontic trainer, for children 8-12 - a harder model);
- plates (made of a plastic base, which is placed near the palate and follows its structure and metal arches, which correct the position of the teeth. Their use corrects the position of still growing jaws and teeth. Designed for children under 12 years of age and, as a rule, do not require constant wear , and a maximum of 4 hours a day, but they will have to be changed as the child ages and adjusted to changes in the bite).
To correct malocclusion in adolescents, fixed appliances or braces are used. They are fixed only on permanent teeth. Such a system can be in a child’s mouth for up to 3 years. At the same time, in the first week they will cause some discomfort: interfere with eating, speaking and even breathing. The child will also have to get used to his reflection in the mirror. When using braces, you will need to pay more time and attention to oral hygiene. And after removing the brace system, retainers will be needed to consolidate the achieved result. Braces, in turn, are:
- metal;
- plastic;
- sapphire (almost invisible in the mouth);
- ceramic