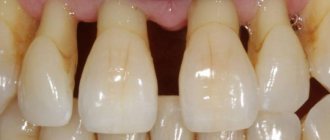
We have to admit that eliminating the consequences of periodontitis surgically is very problematic. However, there are several progressive techniques that allow you to get rid of this disease as painlessly as possible, reducing recovery time.
One such method is flap surgery. From a practical point of view, this type of surgery is based on making an incision in the gum, resulting in the formation of a flap through which the bacteria-affected area in the periodontal canal can be accessed.
The surgeon cleans and polishes the roots, removes bacterial deposits, and the gum flap is sewn into place.
One of the specialized areas of activity of the dental clinic “ManeClinic” is performing flap surgery.
The staff of our treatment center includes real professionals in their field: surgeons, anesthesiologists, prosthetists and implantologists. All these doctors are ready to provide emergency medical care in the most difficult clinical situations.
We guarantee our clients that all procedures will be painless and the cost of providing the service as reasonable as possible.
What is flap surgery in dentistry?
Surgery helps eliminate the pathological process in severe stages of periodontitis, when inflammation affects not only soft tissue, but also spreads to the bone tissue surrounding the teeth. In this case, there is a real threat of premature tooth loss. The problem cannot be solved using conservative methods; surgical treatment is required.
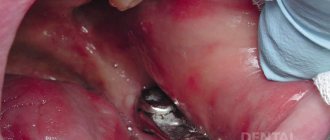
Flap surgery is one of the methods of surgical periodontology, aimed at stabilizing periodontitis. The name of the procedure is due to the tactics of accessing the roots of teeth to clean them of infected tissue. During the operation, using vertical incisions in the gums on both sides, a gingival flap is formed above the projection of the damaged teeth, which is folded back to access the tooth roots and clean them from pathological plaque, tartar and tissues atrophied due to a long-term inflammatory process.
If necessary, to restore hard tissue, bone material is transplanted to promote the formation of one’s own bone. To improve the regeneration of mucous membranes, a fibrin membrane is installed, which contains important cellular elements and increases the local immunological status in the area of surgery. After the manipulations, the flap is sutured back.
There are cases when a person does not have enough of his gums - due to a long pathological process, recession (loss) occurs. In such a situation, our periodontist decides to use transplant material - these are the patient’s own tissues, which are taken from the hard palate or the area behind the wisdom teeth.
The use of a microscope makes the procedure
minimally invasive.
Optical magnification allows the use of micro-instruments and the finest monofilaments. This ensures neat incisions and sutures, resulting in rapid healing and excellent aesthetic results.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich Chief physician and founder of the Doctor Levin center
Flap surgery is a tooth-preserving intervention. With its help, it becomes possible to stop the inflammatory process, stabilize the situation, reverse the manifestations of periodontitis - eliminate periodontal pockets, restore periodontal tissues, reduce tooth mobility.
Bone grafting and implantation
Bone tissue augmentation is resorted to in cases where there is insufficient internal volume to install an implant. This situation often occurs when implantation is performed a significant period after tooth loss. The bone on which it was located begins to dissolve and as a result the alveolar ridge decreases. To properly install the implant, bone augmentation will be required.
The timing of implantation after bone tissue augmentation directly depends on its volume. The more bone tissue has been built up, the longer the period required for its consolidation. Therefore, implantation is performed after complete healing of the bone graft, a period of which can reach six months.
Modern techniques and equipment allow the process to be as pain-free as possible and to carry out high-quality surgical intervention in the shortest possible time, which will result in healthy teeth. Regular, once every six months, visits to the dentist will help to detect the problem in a timely manner and eliminate it with minimal losses.
See also: Teleroentgenogram (TRG) in lateral projection, prices and description.
Indications for use
Periodontitis is practically asymptomatic in the initial stages of development; with timely diagnosis, conservative (non-surgical) methods are usually sufficient. A direct indication for patch surgery is progressive periodontitis in advanced forms of clinical course (stages 3 and 4), which are diagnosed by a periodontist based on the following criteria :
- the presence of deep periodontal pockets of more than 4-5 millimeters
- significant damage to the tissues of the alveolar process
- more than half of the tooth root is exposed
- severe tooth mobility
- pathological changes in gum tissue - thinning, atrophy, appearance of fibrous structures
A person himself may suspect the development of a pathological process. In advanced stages of periodontitis, the quality of life deteriorates significantly; the symptoms are disturbing:
- Bleeding gums, which appears gradually - first with strong mechanical stress, then even with slight pressure with a toothbrush
- Unpleasant and persistent odor from the mouth, which is difficult to hide by rinsing, using mouth fresheners, and a metallic taste appears in the mouth
- Teeth become very sensitive to any irritating factors, for example, cold and hot drinks, sour or salty foods
- There is a feeling of tooth mobility, which worsens over time; chewing food develops into a real problem.
- The gums become uneven, with elements of white atrophy
- Temperature periodically rises, general weakness increases
These manifestations are a reason to immediately consult a doctor. It is important not to start the process - the sooner treatment is carried out, the greater the chances of a complete cure .
Open curettage of periodontal pockets –
The purpose of this operation is to remove all subgingival dental deposits, remove inflammatory granulation tissue from under the gums, eliminate periodontal pockets, and also stimulate the restoration of bone tissue (by means of “replanting” materials based on synthetic bone into bone defects).
Before the operation begins, careful preparation must be carried out - dental plaque must be removed, anti-inflammatory therapy must be carried out, and if there are indications, splinting of mobile teeth is carried out. The latter is very important, because Carrying out curettage without splinting mobile groups of teeth will lead to an even greater increase in their mobility, and will also increase the resorption of bone tissue around them.
Scheme of open curettage –
Description of the main stages of open curettage -
The operation is performed against the background of antibiotic therapy, under local infiltration and conduction anesthesia. During one operation, usually only one segment of 7-8 teeth is removed (usually this volume of intervention requires at least 2.5 hours of time). Next, we will focus on the main points of the operation.
1) Incision and detachment of flaps - open curettage means that after the onset of anesthesia, we make an incision in the gums around the necks of the teeth and peel off the mucoperiosteal flaps (on both sides of the dentition). Detachment of flaps from the necks of teeth and bone will allow us to expose the surface of the roots and bone tissue defects. Thus, we will obtain visual control over periodontal pockets and subgingival dental plaque (Fig. 9).
Clinical case No. 2 (Fig. 8-12) –
2) Removal of granulations and bone grafting – removal of granulation tissue is carried out using sharp curettes (in combination with an ultrasonic scaler or laser). The scaler softens granulations well and makes it easy to scrape them out of all the gaps and lacunae of bone tissue, as well as polish the root surface, removing a layer of necrotic cement from it. Next, antiseptic treatment of the wound is carried out. Next, chemical modification of the root surface is carried out, for example, with a suspension of tetracycline.
Next, the bone defects are filled with bone material, and ideally covered with special membranes. Bone grafting is effective precisely in the presence of deep periodontal pockets (when there is vertical resorption of bone tissue). If inflammatory bone resorption against the background of periodontitis occurs evenly and horizontally, bone grafting will not allow for an increase in bone volume. As a continuation of clinical case No. 2, you can see in this patient a partial restoration of bone volume in the interdental space (Fig. 11).
3) Suturing – sutures are placed in the area of the interdental papillae. At the end of the operation, a protective gum bandage is also applied, which will protect the operation area and promote speedy healing. Sutures are removed 10 days after surgery.
Open curettage: video
Preparation for flap surgery
Surgical manipulations on the gums require special preparation to avoid complications during surgery and in the postoperative period.
Diagnostics
Aimed at determining the stage of periodontitis and choosing treatment tactics. The periodontist conducts:
- examination - to assess the depth of periodontal pockets and the amount of deposits on the teeth.
- Anamnesis collection To obtain information about the duration of the inflammatory process, the presence of systemic diseases of the body.
- Bakposev Sowing the contents of the gum pockets - for microflora and sensitivity to drugs.
- Tests Prescribes blood tests - general and sugar, if necessary - for the level of hormones and vitamins.
The most important and informative diagnostic method is computed tomography (CT).
A CT scan is performed to assess the degree of bone tissue destruction, depending on which the surgical tactics and the need to use bone materials and gum grafts are determined.
Complex events
In our Center, flap operations are performed only in combination with other procedures that precede surgery and provide high-quality preparation to avoid complications:
- Hygienic cleaning Removing deposits from the visible part of the teeth from plaque and tartar to prevent infection of the surgical area.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity Treatment of dental diseases (caries, pulpitis, periodontitis) to eliminate all foci of inflammation in the oral cavity.
- Splinting Stabilization of teeth with splinting structures in case of severe mobility in order to prevent their loss.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy Taking antibacterial drugs to prevent possible infectious complications.
Medvedeva Tatyana Alexandrovna
Dentist-periodontist, 6 years of experience
Specialist in the diagnosis and treatment of gum diseases. Conservative, surgical, regenerative treatment. Microsurgical operations without pain under sedation.
More about the doctor
Surgical results
A few days after the flap surgery, the doctor will remove the stitches or they will dissolve on their own (depending on the suture material used). Based on the results of surgical intervention, the following tasks can be implemented:
- complete removal of pathogenic microflora;
- elimination of periodontal pockets;
- osteoplasty;
- recession plastic;
- correction of gum shape.
Doctor's opinion: very rare, but complications do occur in patients. What can happen: bleeding, inflammation, rejection of integrated bone material. When these phenomena appear, you should not panic; all this can be stopped. You should not delay your visit to the doctor in the hope that it will “go away on its own.” Only a specialist can provide qualified assistance.
Stages of the procedure
The procedure is performed by a periodontist at our Center. Lasts from one to three hours.
The duration depends on the scale of the operation (in the area of one tooth or a segment of several teeth), complete or partial detachment of the flap is performed, whether bone regeneration or gum augmentation with grafts is performed.
In general, the course of the operation is as follows:
- Formation of the flap Treatment of the oral cavity with special antiseptic solutions. Making two vertical incisions from the crease to the edge of the gum and a horizontal incision along the lower edge. Formation of a periosteal flap, instrumental provision of access to the root zone.
- Root cleaning Removal of infected tissue, removal of tartar and grinding of tooth roots. If there is a clear deficiency of bone tissue, the doctor fills it with bone materials.
- Suturing After completion of all planned manipulations, the flap is returned to its original place or shifted to increase the size of the gum. When there is a deficiency of mucous tissue, gum grafts are used. Sutures are placed in the spaces between the teeth.
- Treatment The postoperative surface is carefully treated with an antiseptic, an antiseptic napkin and a periodontal bandage are applied.
After the operation, the doctor gives mandatory recommendations for oral care, which will allow you to maintain the results for many years.
After 7-10 days, the doctor removes the sutures or they dissolve on their own, which depends on the suture material used.
Is it painful to have flap surgery?
The operation is completely painless as local anesthesia is provided through injections around the surgical area.
But for patients with phobias who experience an overwhelming fear of dental treatment, as well as for people with a low pain threshold, or in the case of long-term large-scale interventions, we offer the operation during sleep.
This is not general anesthesia. Ultra-short-acting sedatives are used, which are completely eliminated from the body after 30-40 minutes and do not cause adverse reactions such as nausea, dizziness and clouding of consciousness. Sedation provides absolute psycho-emotional and physical comfort, without worries or pain.
The use of sedation also has a beneficial effect on the healing rate - the pressure does not increase, and the risk of bleeding, hematomas and postoperative edema is correspondingly reduced. The body does not produce a stress hormone, which causes a response from the body in the form of decreased immunity.
Types of contraindications
Dental surgeons classify all contraindications for surgery into relative (surgical intervention is possible, but there is a high risk that it may adversely affect the patient’s health; the patient’s recovery process must take place under the continuous supervision of the attending physician) and absolute (surgical intervention is strictly prohibited, as how the consequences can seriously threaten the patient’s life).
List of relative contraindications:
- colds/viral ailments;
- poor oral hygiene;
- presence of malocclusion;
- incomplete closure of the teeth of the upper and lower jaw (due to pathology);
- presence of carious cavities.
To eliminate these problems, the patient is forced to undergo a certain course of treatment, after which permission to perform an operation can be obtained.
Absolute contraindications include:
- oncological diseases;
- weak immunity;
- heart disease and poor circulation;
- serious damage to the crown of the tooth;
- diabetes mellitus;
- open tuberculosis.
Be that as it may, before hospitalization and surgery, the patient must undergo a thorough diagnostic examination and pass the necessary tests (general urine test, blood biochemistry, test for syphilis, HIV, certain categories of hepatitis). Only after deciphering the results, and if they are satisfactory, can a flap operation be prescribed.
Recovery after surgery
Gum healing takes 10-14 days. On the 4-5th day after the intervention, pain disappears and swelling decreases.
Accelerated rehabilitation
For those who want to prevent problems that are inevitable after any surgical operation, our Center provides a complex of accelerated rehabilitation:
Recommendations of the periodontist in the postoperative period
In order to preserve and consolidate the result obtained after flap surgery, it is important to strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations, both immediately after the procedure and in the long-term period.
After operation:
- In the first 7-8 hours after surgery, you should not brush your teeth or rinse your mouth.
- After 8 hours, regular rinsing with antiseptic solutions or decoctions of anti-inflammatory medicinal plants every 4 hours is recommended.
- On the first day, apply cold to the projection area of the operated gum, from the outside, to reduce tissue swelling.
- Food should only be soft and not irritate the postoperative wound; salt, pepper, and acidic foods should be excluded.
- Visiting saunas, swimming pools and gyms is prohibited.
- Smoking after surgery may cause bleeding, so abstinence is recommended.
- Active physical activity should be limited for several weeks.
- From the beginning of the 2-3 days of the postoperative period, you can begin to carefully brush your teeth, but only with a soft brush using a desensitizing paste.
- In case of severe pain, you can take analgesic drugs taking into account the recommended dose and frequency of use.
- To prevent the development of postoperative complications, the doctor prescribes a course of antibacterial drugs for 5-7 days.
Such easy-to-follow recommendations will help you avoid various complications and consolidate the results obtained.
To avoid relapses of periodontitis, it is important to avoid accumulations of subgingival deposits, so visiting a doctor every 3-6 months for professional oral hygiene and monitoring the situation is strictly necessary!
It is important not to neglect the recommendations in order to avoid complications. You will be required to be highly involved and motivated, to follow all the doctor’s recommendations for oral care.
In our clinic, your operation will be performed by highly qualified doctors using the latest equipment and medications, which guarantees the maximum effect of treatment.
The name of the procedure is due to the formation of a flap of gum tissue with vertical incisions on both sides above the projection of damaged teeth, which, after all manipulations, is sutured back, thereby ensuring maximum fit and aesthetics. The operation gives the doctor maximum access to periodontal tissues and roots, which must be cleaned of pathological plaque, tartar and atrophied tissues due to a long-term inflammatory process.
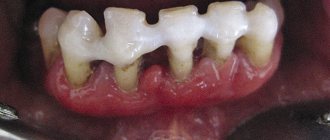
What is periodontitis?
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammation of the soft and hard tissues of the periodontium, which is practically asymptomatic in the initial stages of development, but poses a real threat of premature tooth loss. The etiology of the disease is determined by insufficient oral care, impaired circulation of the gums due to smoking and chronic deficiency of vitamins and minerals.
Obvious signs of the disease appear already at advanced stages of the pathological process and are expressed by the following symptoms:
- bleeding gums, which appears gradually, that is, first with strong mechanical impact, and then with slight pressure from the toothbrush;
- unpleasant and persistent odor from the mouth, which is difficult to hide with anything;
- teeth become very sensitive to any irritating factors, for example, cold and hot drinks, sour or salty foods;
- tooth mobility is felt, worsening over time;
- chewing food develops into a real problem;
- the gums become uneven, with elements of white atrophy;
- swelling of the gums periodically increases;
- a metallic taste appears in the mouth;
- quality of life deteriorates significantly.
If these symptoms are present, doctors diagnose stage 3 or 4 periodontitis, with the presence of deep periodontal pockets and significant damage to the tissue of the alveolar process. Advanced stages of inflammation of the root tissues of the tooth are a direct indication for surgical treatment using flap surgery.
To prevent the development of advanced stages of periodontitis, it is necessary to undergo regular preventive examinations and pay due attention to oral hygiene using high-quality toothpaste and an antiseptic rinse. Also important is the technique of brushing your teeth, the duration of this manipulation and the frequency, at least twice a day. At the first pathological signs in the form of streaks of blood while brushing your teeth, you should definitely consult a dentist.
Indications for flap surgery
Surgical intervention aimed at stabilizing periodontitis is not a cheap method, but its effectiveness guarantees long-term remission of the pathology, which will save financial resources that would have to be spent on endless trips to the dentist if the patient, for example, turned to a doctor who practices outdated non-invasive treatment methods.
Manipulations of the last century can become expedient only in the treatment of initial forms of inflammation of periodontal tissue. For flap surgery, doctors determine the following indications:
- progressive periodontitis in advanced forms of clinical course (stages 3 and 4);
- the presence of gingival pockets with a depth of more than 4-5 millimeters;
- presence of bone tissue destruction;
- pathological changes in gum tissue caused by thinning, atrophy and the appearance of fibrous structures;
- tooth root exposure;
- severe mobility of the teeth, which poses a problem when chewing food;
- formation of large gaps between teeth.
With the help of an incision in the gums, it becomes possible to stabilize the situation, reverse these manifestations and preserve the vitality and functionality of the teeth for many years.
Contraindications
Like any surgical intervention on the human body, patch surgery also has a number of contraindications that should be taken into account. Thus, treatment of periodontitis using flap surgery may be impossible for the following reasons:
- immunodeficiency conditions (AIDS, hepatitis B and C);
- extreme degree of destruction of bone tissue, which accounts for more than half the volume of the alveolar processes;
- a pronounced tissue defect at the junction of the tooth root and the crown;
- advanced degrees of cardiovascular pathologies;
- congenital heart defects;
- the presence of artificial joints;
- diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation;
- acute and chronic blood diseases;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- infectious processes in the oral cavity;
- a burdened allergy history, which calls into question the possibility of using anesthesia during surgery, which is impossible to do without.
If there are contraindications, periodontitis is treated using non-invasive methods, which does not guarantee a stable effect and long-term remission. The pathological changes in the body themselves, characteristic of the pathologies listed above, can provoke an exacerbation of periodontal inflammation.
Preparatory stage
Surgical manipulations on the gums require special preparation to avoid complications during surgery and in the postoperative period. After the patient has received a referral for flap surgery, he will undergo thorough preparation, which consists of the following aspects:
- clinical examinations (general blood count, urine test and glycemic indicators);
- determination or confirmation of blood type;
- elimination of all foci of inflammation in the oral cavity;
- ridding the visible part of the teeth of plaque and tartar;
- performing splinting if there is severe tooth mobility;
- general anti-inflammatory therapy with the use of antibacterial drugs is used to prevent possible complications of an infectious nature;
- Patients with a phobia may need to consult a psychologist before the upcoming treatment process.
The preparatory stage before flap surgery usually lasts 5-7 days.
Progress of the operation
The course of the operation is determined by the following sequential actions of the dental surgeon:
- treatment of the oral cavity with special antiseptic solutions;
- providing local anesthesia through injections around the surgical area;
- making two vertical incisions from the fold to the edge of the gum and a horizontal incision along the lower edge;
- a so-called periosteal flap is formed from tissues;
- instrumental provision of access to affected periodontal tissues;
- removal of pathological areas from the alveolar bone (cleaning the periodontal pocket);
- removal of tartar and grinding of tooth roots;
- after the cleaning stage, the surface is again carefully treated with an antiseptic;
- if there is a clear deficiency of bone tissue, the doctor fills it with transplantation materials, which usually take root well and contribute to the formation of one’s own bone;
- after completion of all planned manipulations, the flap is returned to its original place, where it is sutured in the spaces between the dental units;
- The doctor applies an antiseptic napkin to the postoperative surface and covers it with a periodontal bandage.
After 4-5 days, the doctor removes the stitches or they dissolve on their own, which depends on the suture material used. The doctor gives mandatory recommendations for oral care, which will allow you to maintain the results for many years.
Recommendations in the postoperative period
In order to preserve and consolidate the result obtained after flap surgery, the patient must strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations from the end of the procedure and for a long period of time.
The dentist's instructions will be as follows:
- pressing the tampon applied after surgery with teeth for 3-4 hours;
- on the first day, cold should be applied to the projection area of the operated gum, from the outside, to reduce tissue swelling;
- in case of severe pain, you can take analgesic drugs, taking into account the recommended dose and frequency of use;
- sometimes the doctor may prescribe the administration of narcotic painkillers;
- to prevent the development of postoperative complications, the doctor prescribes a course of antibacterial drugs for 5-7 days;
- in the first 7-8 hours after surgery, you should not brush your teeth or rinse your mouth;
- after 8 hours, the doctor recommends regular rinsing of teeth with salted water, antiseptic solutions or decoctions of anti-inflammatory medicinal plants every 4 hours;
- from the beginning of the 2-3 days of the postoperative period, you can begin to carefully brush your teeth, but only with a soft brush using a desensitizing paste;
- food should only be soft and not irritate the postoperative wound (exclude salt, pepper, acidic foods);
- active physical activity should be limited for several weeks;
- visiting saunas, swimming pools and gyms is prohibited;
- Smoking after surgery can cause bleeding, so the doctor recommends abstinence.
Such easy-to-follow recommendations will help you avoid various complications and consolidate the results obtained.
Possible complications during and after gum surgery
Typically, surgical intervention for the treatment of periodontitis is well tolerated by patients, which is ensured by modern equipment and fully equipped dental offices. However, the possibility of complications is always present, since the reaction of the human body to the action of any factor can be unpredictable. The following facts about possible complications are described from the practice of leading dentists:
- the development of bleeding during and after surgery, which is successfully controlled by appropriate measures;
- the risk of postoperative inflammation is always present, but in practice it is no more than 5-10%;
- rejection of bone material, which is introduced to compensate for the deficit in the volume of the alveolar process of the tooth, which is considered an indication for repeated surgery with a change of prosthetic material;
- allergic reaction to drugs used for anesthesia;
- severe swelling of tissues in the area of manipulation;
- severe pain that lasts 5-7 days;
- discomfort during brushing your teeth, when eating and during normal conversation lasts no more than 2-3 weeks and goes away without a trace.
The likelihood of complications developing is quite low and often depends on the thoroughness of the preparatory stage and compliance with postoperative recommendations.