- home
- Useful articles
- Oral abscess: causes, symptoms, treatment
The development of an abscess in the oral cavity is associated with infection entering the pulp and its further spread throughout its entire structure. An inflammatory process begins, leading to tissue swelling and accumulation of purulent deposits. If the infection is not stopped and timely treatment is not started, then it will penetrate through the dental canals into other organs of the body, causing various diseases.
What is an oral abscess?
An oral abscess is an acute inflammatory disease characterized by the formation and accumulation of pus in the tissues of the gums, tongue or cheeks. The abscess is accompanied by local swelling and hardening of soft tissues, severe pain on palpation, fever and general weakness. The disease is diagnosed by a dentist after a visual examination of the tissue, after which immediate surgical intervention is required: opening the abscess, followed by cleaning and taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
Oral abscess is one of the most common complications in the practice of dental surgery. It can be observed in patients of different ages. Untimely treatment can lead to the transition of inflammation to the chronic stage. Against this background, sepsis and phlegmon can develop. That is why, if the slightest symptoms of an abscess occur, you should immediately visit a dentist.
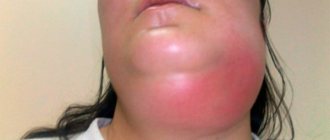
Cheek abscess
The main danger of a cheek abscess is that it can spread to neighboring organs and parts of the face. Such an abscess can appear on both the outer and inner sides of the cheek. In addition to redness and hyperemia of the inflamed area, the swelling can be expressed by moderate pain, which intensifies when opening the mouth.
When formed on the inner mucous membrane of the cheek, such inflammation, in case of spontaneous opening, can infect the oral cavity in the presence of microcracks. In any case, you should not delay visiting a doctor, since even an open abscess can lead to many negative consequences.
Self-medication in such cases is dangerous, but before visiting a specialist, rinsing with antiseptic solutions, herbal decoctions at room temperature, as well as applying a cold bandage to the inflamed area will help relieve pain and stop the development of inflammation. It is important not to overheat the source of infection to avoid its further spread.
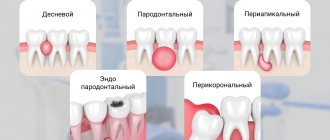
Types of abscess by location
An abscess is classified based on the location of the inflammation. The following types of pathology are distinguished:
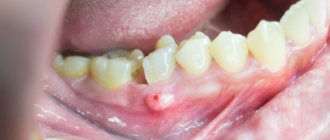
Gum abscess The most common type, inflammation forms near a specific tooth. If left untreated, an abscess can provoke: leakage of pus from the formed fistula, putrid odor from the mouth and intoxication of the body. Abscess of the floor of the mouth Forms under the tongue, which causes severe pain and discomfort during communication or eating. When the abscess spontaneously opens, the infected fluid pours into the oral cavity and can provoke a new outbreak in the pharynx and neck. Abscess of the palate Occurs against the background of uncured or previous periodontitis of the teeth of the upper jaw. In the future, inflammation can spread to the peritonsillar region and other tissues of the palate, leading to osteomyelitis of the palatal plate. Cheek abscess The depth of damage to this area of the mucosa determines the localization of inflammation, which can sit inside the cheek or extend to the outer surface. Such abscesses are extremely dangerous, because the infection can affect nearby facial organs and tissues. Tongue Abscess Obvious signs include a swollen tongue, pain during meals, and difficulty communicating and breathing. This type of abscess, according to doctors, is the most dangerous and requires immediate treatment.
Periodontal abscess
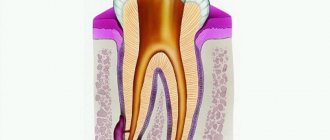
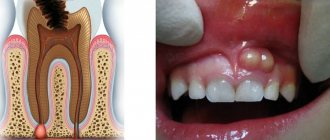
The causes of gum abscess (periodontal) are most often the gaps between the gum and teeth, the so-called periodontal pockets, into which the infection enters. Externally, the source of infection resembles a small red ball, painful when touched. Pockets can form for various reasons, in particular due to diseases of the oral cavity, constant injury from incorrectly installed dentures or fillings, mechanical damage (trauma, bruises, burns).
A gingival abscess that is not drained in a timely manner can damage one or even several teeth, which subsequently leads to their loss. Among other things, periodontal inflammation grows quite quickly and can increase to the size of a walnut, which not only deforms the jaw and facial contours, but also leads to severe intoxication of the body.
Treatment for this type of inflammation is standard: the abscess is opened with a scalpel, the pus is drained out, the cavity is drained and cleaned. Sutures are rarely used during such operations, since the size of the incision is usually quite small. However, if the tumor has reached an impressive size before the operation, the process of drainage and further recovery may be delayed. In some cases, doctors prescribe a number of physiotherapeutic procedures to speed up the patient's recovery.
Causes of development of abscess in the oral cavity
An abscess in the oral cavity occurs as a complication of advanced periodontal disease and periodontitis. These diseases are characterized by damage to the teeth and gums with the subsequent formation of pockets in the periodontium. They accumulate pathogenic microorganisms that provoke inflammation. Among other things, an abscess can occur due to infection in a damaged area of soft tissue (trauma, syringe needle, instrument). The cause of the disease is often staphylococcal and streptococcal sore throats, as well as boils on the face.
Inflammation in the oral cavity also appears as a complication after suffering from influenza or ARVI, which weaken the immune system, as a result of which the body is not able to fight infection.
We know how to cure ORAL ABSCESS
In the near future, a medical coordinator will contact you and advise you on the conditions and cost of treatment, select a doctor and make an appointment for you.
| Make an appointment | Or call us +375 29 699-03-03 +375 33 319-03-03 |
Causes
The main reasons for the development of a tooth abscess:
- exacerbation of chronic periodontitis;
- accumulation of bacterial infection in the tooth pulp;
- violation of sterility conditions during root canal treatment;
- root cyst;
- vertical fracture of the tooth root.
The bacterial microflora of the oral cavity is represented not only by beneficial bacteria. It is also inhabited by streptococci, staphylococci, cocci, lactobacilli, bacteroides, and spirochetes. The inflammatory process begins with the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms beyond the root apex. Hypothermia, colds and infectious diseases predispose them to increased reproduction.
Symptoms
The abscess is characterized by rapid development. At first, the patient may be bothered only by minor attacks of pain, similar to the sensations that arise during caries or periodontitis. Subsequently, the pain is localized in one place and gradually increases. In a specific place there is swelling, sometimes a new formation on the gum, sometimes reaching the size of a walnut. If the inflammation is localized closer to the outer surface, then swelling and redness can be observed with the naked eye. If you notice the first symptoms, we recommend that you consult a dentist.
An abscess of the tongue is characterized by an increase in the organ's volume, difficulty swallowing, chewing, and even suffocation. Any abscess is accompanied by fever, deterioration and general weakness, insomnia, and loss of appetite. The progression of the disease leads to a breakthrough of the abscess, which is manifested in a decrease in temperature, a decrease in swelling and an improvement in overall well-being. However, there is no reason to stop treatment, since inflammation can continue and develop into a chronic form. This can lead to tooth loss, sepsis and phlegmon.
Symptoms
A developing tooth abscess causes the following symptoms:
- throbbing pain in the area of the affected tooth, aggravated by chewing;
- inability to fully open the mouth (if the process occurs in the lower jaw);
- exposure of tooth roots;
- pathological mobility of teeth (typical of periodontal abscess);
- painful swelling of the gums and cheeks;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- increased body temperature;
- headache;
- weakness.
A change in general condition is usually associated with an acute course of the abscess. At the same time, the process can be chronic. For example, with a periapical abscess, a fistula can form - a canal lined with granulation tissue. As a rule, the fistula opens on the mucous membrane of the gums - in the projection of the apex of the tooth root. Less commonly, the fistula opens into the nasal cavity or maxillary sinuses. The fistula serves to remove purulent discharge, therefore, with chronic abscesses, the clinical picture of the disease can be blurred.
Pediatric dentists are faced with abscesses of primary teeth. Its symptoms are the formation of a lump on the gum filled with pus, aching pain in the tooth.
The appearance of symptoms of a purulent abscess requires an emergency visit to a dental surgeon. Otherwise, the risk of complications increases - for example, phlegmon. This is the name of the purulent process in the subcutaneous fat. Unlike an abscess, it is diffuse, i.e. has no clear boundaries. Cellulitis leads to necrotic damage to the jaw bones, and then to infection of the entire body. This process is life-threatening.
Treatment of oral abscess
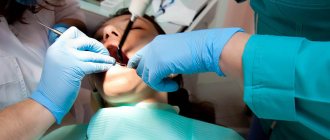
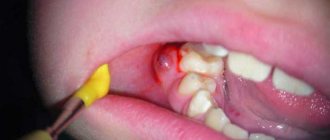
Treatment of an abscess requires surgery. In order to eliminate the source of infection and stop the spread of inflammation, the dental surgeon step by step:
- opens an abscess;
- drains the cavity;
- cleans the pocket;
- Rarely applies stitches if the size of the incision is large.
After removal of the pus, the patient’s well-being improves, and facial geometry is restored. Taking antibiotics, antihistamines, immunostimulants and a vitamin complex significantly speeds up the healing process. Sometimes the doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures (UHF therapy and fluctuarization).
For some time, the patient needs to exclude solid foods from the diet and adhere to healthy eating rules.
General principles of treatment of the disease
The doctor who treats phlegmon of the maxillofacial area is an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Each doctor, when starting to treat an odontogenic process in the maxillofacial area, is guided in his actions by the following principles:
The tooth that caused the development of phlegmon is removed. Timely diagnosis is very important due to the characteristics of this area, from where the infection can spread, causing severe consequences (in particular, mediastinitis). It is necessary to eliminate the spread of the infection, that is, promptly open the lesion and eliminate the inflammatory exudate, relieve tissue tension. The rate of subsidence of inflammation depends on the quality of evacuation of all decay products from the wound, that is, careful postoperative treatment of the wound is necessary. Comprehensive treatment of pathology using all means and methods available in this medical institution. Friendly management of the patient with colleagues from other areas, timely appointment of consultations with all specialists for combined lesions. Visible external changes often occur, which are not always pleasant for the patient, which is especially painful in the face area. Therefore, there is an urgent need to organize work with patients by a medical psychologist in the early stages after surgery, especially if there is a significant visible defect. Correct stage-by-stage treatment, organization of medical rehabilitation, referral to the appropriate department with complete information about the patient. Fully informing relatives and the patient about the violation of significant functions of the maxillofacial area, if any. Upon leaving the hospital, the patient should have clear further recommendations, especially if it is necessary to continue treatment on an outpatient basis.
Prognosis and prevention of oral abscess
The success of treating oral abscesses depends on at what stage of the disease the patient seeks help and how strong the body’s defense mechanism is. With timely treatment, the prognosis for eliminating inflammation is quite favorable. In the absence of complications, strong immunity and a high-quality opening of the lesion, an oral abscess can be cured in a couple of weeks.
Prevention of the disease consists of following the following recommendations:
- regular teeth cleaning and professional oral hygiene at least once every six months;
- minimizing the risk of injury to the mucous membrane;
- timely treatment of caries and periodontal diseases;
- visiting a dentist for a preventive examination once every 6 months.
Diagnostics
To diagnose a tooth abscess, the dentist must conduct an examination of the oral cavity and take an x-ray of the tooth. An X-ray image reveals signs of an inflammatory process (widening of the periodontal fissure, thinning of the spongy substance of the alveolar process).
A visual examination reveals swollen, bright red areas of the gum mucosa and increased tooth mobility. With periodontal abscess, periodontal pockets up to 6 mm deep and higher, filled with purulent discharge and granulation tissue, are noticeable.
The purpose of diagnostic measures for a tooth abscess is to differentiate the pathology from an exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, cysts, periostitis, osteomyelitis.
Possible complications
Possible complications: when opening a peritonsillar abscess, complications may develop, as with any surgical intervention:
- incomplete outflow of pus;
- wound infection;
- allergic reactions to medications used;
- increased swelling of the pharyngeal mucosa (as a reaction to intervention).
In terms of examining the patient, it is necessary to prescribe clinical blood tests over time, a general urine test, in order to determine the severity of the body’s general reaction to the infectious-inflammatory process, and electrocardiography. Bacteriological studies of throat cultures and studies of the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibacterial drugs are carried out.
Since paratonsillar abscesses usually develop in people suffering from chronic tonsillitis, it is recommended to remove the tonsils during a quiet period.