Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
The grinding of teeth at night brings horror to a person's family and friends. Agree, you can hear a creaking sound in a dark room. Neurologists call unconscious short-term teeth grinding bruxism, and dentists advise not to delay the treatment of this problem. Let's look at the causes of nighttime grinding and determine ways to eliminate it.
Causes of Bruxism
Parents often wonder why their child grinds his teeth in his sleep. Unfortunately, no doctor knows the exact causes of bruxism in children. Experts correlate the occurrence of the disease with factors such as:
- teething pain;
- psychological factors: stress, anxiety, abnormal emotional development;
- neurological factors: epilepsy, enuresis, etc.;
- dental factors: malocclusion and dentition (extra teeth, adentia), improper orthodontic treatment (incorrectly selected braces, etc.);
- dehydration of the body;
- allergy;
- helminthiasis (worms);
- intoxication due to various diseases;
- endocrine disorders, etc.
Indications and contraindications for botulinum therapy of masticatory muscles
Indications
- pain in the temporomandibular joint area,
- limited mouth opening,
- clicking, crunching, discomfort when moving the lower jaw,
- pathological abrasion of enamel,
- overstrain of the masticatory muscles, their soreness and heaviness,
- preparation for implantation, classical prosthetics (especially veneers), orthodontic treatment.
Contraindications
- pustular skin lesions, ulcers, acute infection in the area of the masticatory muscles,
- viral and infectious diseases in the acute stage,
- neuromuscular diseases (myasthenia gravis),
- constant use of certain medications and antibiotics,
- pregnancy and lactation period,
- bleeding disorders,
- diabetes,
- allergic reactions to the components of the drug,
- oncology and severe mental disorders.
Dangerous symptoms: when should you see a doctor?
The question of when to start treatment for bruxism in children worries many parents.
As a rule, the disease goes away on its own, without any consequences, by the age of 12–13 years. This is due to the fact that by this period the formation of molars is completed. No treatment is required for this form of bruxism. However, there are times when the picture is not so rosy. You should contact your doctor immediately if your child exhibits the following symptoms:
- headache and/or toothache in the morning;
- rapid wear of teeth;
- long and intense attacks at night (more than 10 seconds).
Complicated bruxism in children leads to quite unpleasant consequences, including gum disease and significant tooth wear.
Minor defect?
Grinding of teeth in a child may seem like a minor deviation from the norm only at first glance. It’s good when this phenomenon is temporary and at the age of 5–6 years, bruxism in a child goes away on its own. But if your first-grader continues to grind his teeth at night, don't hesitate to seek medical help. Otherwise, even the permanent teeth that will replace the milk teeth will be at risk.
Psychological help
The psyche of children and teenagers is unstable. Therefore, psychological factors, including anxiety, often lead to the development of bruxism.
In an anxious state, other symptoms may be observed: the habit of pulling and twisting hair, biting nails, etc.
The trigger for bruxism can be changes in a child’s life: moving, changing schools, parents’ divorce, various conflicts, etc. In such cases, a psychologist will help.
What should the mother do and how to help the child?
You can help your child cope with teeth grinding at home. The task of parents is to relax the child, especially in the evening. Suitable for relieving tension:
- massage;
- exercise therapy;
- correct daily routine;
- walks in the open air;
- drinking enough water;
- exclusion from the diet of foods that excite the nervous system: chocolate, coffee, tea, Coca-Cola, Pepsi, etc.;
- last meal – an hour before bedtime;
- hot bath before bed;
- refusal of active games, quiet activities in the evening: drawing, listening to lullabies, etc.
In addition, heart-to-heart conversations with your child can help. If the child does not speak out, he will go to bed with anxious thoughts. This will trigger an attack.
The following techniques will help reduce facial muscle tension:
- heat compresses (including for pain in the morning);
- chewing solid food;
- giving up chewing gum.
Treatment
The diagnosis is made based on interviews with relatives and the patient himself. The main points are:
- experience of regular alcohol consumption;
- time of the last binge and the onset of hangover;
- what alcohol-containing substances were used.
New psychoses can be successfully treated. Intensive therapy includes cleansing the blood of toxic substances and influencing the brain with drugs from the group of antipsychotics. Clarification of consciousness during the fight against psychosis motivates the patient to undergo treatment for alcohol addiction. No one has the right to place him in a clinic without the patient’s consent. But he must clearly understand one thing: a repeated attack is a direct path to dementia.
Bruxism in adults: causes
Bruxism also occurs in adults, and the disease appears in both sexes with equal frequency.
The question of why teeth grind in their sleep remains open: the exact reasons have not been established. Various factors can lead to the disease:
- psychological: fatigue, stress, depression, anxiety neurosis, complexes, a special type of personality (vulnerable or hyperactive nature);
- neurological: epilepsy, cervical osteochondrosis, lesions of the trigeminal nerve, apnea, somnambulism (sleepwalking), nightmares;
- dental: malocclusion, jaw defects (over-row teeth, their absence or incorrect location), joint pathology, uncomfortable braces or dentures, incorrectly installed fillings, etc.;
- hereditary factor;
- other factors (not recognized by all doctors): acid reflux into the esophagus, helminths, snoring, impaired nasal breathing (enlarged adenoids, frequent rhinitis or deviated septum in the nose), lack of vitamins.
In 70% of cases, teeth grinding is the result of psychological problems.
What happens if hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles is not treated?
The masseter muscle, which moves the lower jaw, is the most powerful in the group of facial muscles. By contracting, it is capable of creating a force of up to 80-100 kg (compare - in order to chew food efficiently, we use barely 10% of this force).
Chronic spasm and overstrain of such strong masticatory muscles creates excess pressure on the teeth, periodontal tissues and temporomandibular joints. From here, many unpleasant consequences for the jaw system and health in general develop along the chain:
- abrasion of enamel and reduction in tooth height,
- chips and cracks, various enamel defects,
- frequent caries,
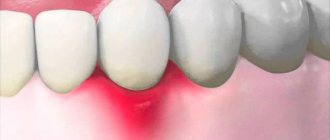
- overload of periodontal tissues and the development of gum diseases - in particular, dangerous periodontitis,
- failure of fillings, crowns and dentures,
- threat to implants, the possibility of their overload and loosening,
- swelling and inflammation of the masticatory muscles,
- dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, pain and discomfort when chewing,
- deterioration of blood circulation and tissue nutrition in the area of muscle spasm,
- increased headaches, dizziness, noise and pain in the ears,
- overstrain of the neck and back muscles, development of posture problems,
- violation of facial aesthetics: angular jaw, deep wrinkles around the nose and lips, haggard face and reduction of the lower third.
People suffering from bruxism complain of:
- pain of various origins: headache, ear, tooth, face, jaw and neck;
- increased sensitivity and mobility of teeth;
- erasing enamel;
- damage to teeth, crowns, etc.;
- inflammatory processes of the gums;
- insomnia, irritability, etc.
Symptoms worsen under stress. Most of these symptoms are short-term and correctable. However, if left untreated, there can be more serious consequences: facial asymmetry, hearing loss, severe wear and tear and broken teeth. In some cases, teeth are worn down almost to the roots.
With regular grinding at night, the mental health of the patient and those around him suffers. People don't get enough sleep and experience fatigue, anxiety and depression.
You can identify the symptoms of bruxism yourself by external examination in the mirror. Upon inspection you will find:
- worn teeth, cracks and chips on them;
- teeth marks on the cheeks and tongue;
- change in bite;
- damage to prostheses;
- thickening of the jaw bones.
There may also be a crunching/clicking sound when moving the jaws. Sometimes patients have difficulty opening/closing their mouth.
Important! At rest, the teeth of the upper and lower jaws should not touch each other.
Treatment
Bruxism in adults does not go away on its own. A dentist can help determine whether the problem is serious and requires treatment.
The main goal of treating nocturnal bruxism is to relax the masticatory muscles. Moreover, the treatment method directly depends on the severity and cause of the disease. Accordingly, you may need the help of the following specialists:
- dentist, orthodontist;
- neurologist;
- psychologist, psychotherapist.
The most effective dental treatment methods are:
- plastic splints and individual night guards - linings that protect the dentition from abrasion;
- Mandibular thrusters: also used for snoring;
- teeth grinding: the method eliminates jaw defects;
- prosthetics: the method is used for severe abrasion.
Medications may also be part of complex therapy:
- muscle relaxants: administered before bed to relax facial muscles;
- Botox: Injected in extreme cases to reduce the force of muscle contraction.
Since psychological factors most often lead to teeth grinding, you may need the help of a psychologist and psychotherapist. The psychotherapist will prescribe medications to normalize sleep and relieve anxiety, antidepressants.
Psychological treatment of bruxism in adults requires an individual approach. A psychologist will help identify and understand the conflict, and also stabilize the emotional state. Ultimately, the patient will learn to relax his jaws and get rid of the habit of clenching his teeth under stress.
The main task of the patient is relaxation. Methods such as:
- massage, including face and neck;
- light exercise, sports;
- yoga, meditation;
- evening walks;
- listening to pleasant music or reading before bed;
- baths with aromatic oils or herbs (chamomile, lemon balm, special mixtures, etc.);
- soothing teas and mixtures;
- exclusion from the evening diet of foods rich in caffeine (coffee, tea) and carbohydrates: this excites the nervous system;
- giving up bad habits: smoking, alcohol;
- full sleep.
To relieve muscle hypertonicity, you need to:
- take medications with magnesium, potassium and B vitamins;
- make warm compresses, herbal lotions, apply a heating pad (including at night);
- chew solid food (apples, carrots, crackers);
- give up chewing gum, do not chew a pencil/pen, or nails.
Try to relax your face and keep your jaws open while at rest. If you find it difficult to do this, use the following practice: purse your lips and hold the tip of your tongue between your teeth. Remember! Self-medication will not help with advanced or severe forms of bruxism.
Be sure to consult a dentist: the doctor will determine the causes of bruxism and prescribe adequate treatment. If medical recommendations are followed, the prognosis is favorable.
Conditions for treating alcoholism in the clinic
Comprehensive treatment and constant medical supervision are the main things that clinical conditions can provide to a person who has become dependent. Factors for successful treatment in a drug treatment hospital are:
- selection of an individual course taking into account concomitant diseases;
- attention to each patient, round-the-clock monitoring for violent behavior;
- anonymous stay in the center;
- recovery from psychosis followed by recovery from addiction.
Alcohol psychoses show that it is almost impossible to free yourself from addiction on your own in the later stages of alcoholism. Relatives and friends should be careful in their demands on a drinking relative. Abrupt abstinence from alcohol can cause enormous harm to his psyche. In this situation, you need qualified medical help and comprehensive treatment.