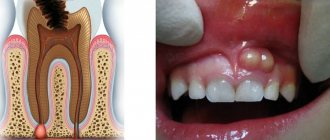
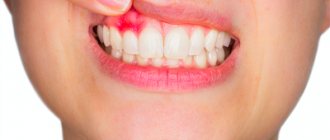
A periodontal abscess is an acute purulent inflammation of the gums. A complex pathology in which a purulent sac forms inside the periodontium, which in size can reach the size of a walnut. When a bladder filled with purulent contents ruptures, blood poisoning can occur and the infection can spread throughout the body. That is why it is important to promptly seek help from a specialist who will diagnose the disease, prescribe adequate treatment and prevent relapses.
The main causes of gum abscess
The main reason is the presence of an infection that affects the soft tissue of the gums and the periodontal pocket (the area between the root of the tooth and the gum itself). If no action is taken, the infection spreads throughout the body, affecting organs and systems.
The following pathologies of teeth and gums can provoke the development of infection:
- gingivitis;
- periodontal disease;
- periodontitis;
- deep caries.
Also reasons may be:
- incorrect installation of prosthetic systems or implants;
- mechanical injuries;
- chemical or thermal burns;
- unprofessional installation of braces;
- imperfect filling.
With an abscess on the gum, the inflammatory process develops in the periodontal pocket against the background of the active proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. At the site of inflammation, dead tissue accumulates in the form of pus, forming a serious abscess, which is accompanied by acute symptoms.
What is a tooth abscess and how to treat it?
Oral hygiene is the key to dental health, and if it is insufficient or irregular, infectious diseases may develop. One of these ailments is a tooth abscess, which is characterized by an acute course and localized development in the area of the roots of the teeth. Teeth that have chips and other defects are especially susceptible to damage. What is a tooth abscess and how to treat it? Let's consider the features of the disease.
What is an abscess and why does it occur?
A tooth abscess is an infectious disease accompanied by the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the soft parts of the teeth. Penetrating into the tooth area and developing there, pathogenic bacteria cause an inflammatory process with the formation of pus and swelling of the gums. Nerve endings located in the pulp relieve pain.
The main reasons for the development of dental abscess include:
- weakened immune system
- oral injuries
- gum disease
- neoplasms and cysts on teeth
The development of an abscess is quite spontaneous if timely measures are not taken. The disease can lead to damage to bone tissue, which jeopardizes the safety of the dental unit. Self-medication will not bring the desired results, although it can help relieve pain for a short period, which will only result in more serious consequences. The disease requires immediate seeking qualified help.
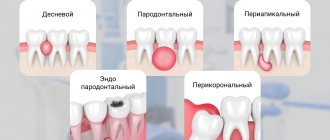
Types of tooth abscess
Depending on the characteristics of the disease, the following types are distinguished:
- peripical – the source of spread is the dental cavity. In this case, pus accumulates under the tooth root due to necrosis of the pulp
- gum – affects the soft tissues of the teeth without moving to the root
- periodontal – the disease occurs in the area between the tooth root and gum.
If pus accumulates in a small volume, it is like being in a kind of sac and is held in space. But with an increase in inflammation and the amount of pus, a fistula is formed, like a canal connecting the abscess with the external environment. Pus is released through the hole in the gum, and the gums become swollen.
Abscess symptoms
In the absence of emergency measures, suppuration may grow and spread to adjacent teeth. The onset of the disease is usually painful and there is swelling in the affected area. The pain subsides when taking painkillers, and then returns and becomes more intense. Also among the symptoms of an abscess:
- pain when pressing on a tooth or gum
- the appearance of a bitter taste in the mouth
- bad breath
- enlarged lymph nodes
- elevated body temperature
- headache
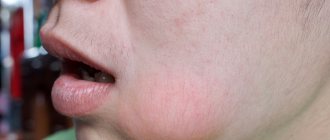
In some cases, facial asymmetry may appear. But if wounds begin to appear on the gums, this means that urgent dental care is required.
Diagnosis and treatment of tooth abscess in Minsk
When faced with the question of what a tooth abscess is and how to treat it, you should seek qualified help. During the appointment, the doctor examines the oral cavity, the affected tooth and adjacent tissues, after which he conducts an X-ray examination to identify the location and extent of the lesion. To determine the type of bacteria that caused the infection, laboratory tests are prescribed, after receiving the results of which, antibacterial therapy can be prescribed.
Treatment of an abscess involves minimizing the infectious process and involves opening it to neutralize the pus and washing the cavity with a special solution. Next, specialists from the Center for Family Dentistry remove the affected tissue and inject sealing compounds into the resulting cavities. As a rule, they make every effort to save the tooth.
Symptoms of gum abscess
- a painful tubercle on the gum, which upon palpation causes pain and discomfort;
- increased pain during chewing;
- loosening of one or a number of teeth;
- discharge of pus;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- smell from the mouth;
- weakness;
- elevated temperature;
- swelling of the cheek;
- sleep disturbance;
- lack of appetite;
- headaches and dizziness.
In the acute period, all signs of intoxication of the body are observed. When a purulent sac spontaneously ruptures near the gingival margin, a fistula is formed, through which purulent exudate is evacuated. Pus flows into the oral cavity, the pain becomes less. The wound can heal without medication, but in this case there is a high risk of infection of the tissues surrounding the lesion.
Clinic doctors
One of the services of the DentaBravo clinic is the treatment of periodontal abscess. Why is this disease dangerous? If left untreated, there is a risk of destruction and necrosis of periodontal tissue, the formation of a focus of chronic infection, loosening and tooth loss, the spread of inflammation to bone tissue and periosteum, osteomyelitis of the jaw, deformation of the jaw and distortion of the face, penetration of infection into other organs (for example, into the brain ).
What is a periodontal abscess?
This is a locally limited purulent inflammation of the gums (abscessus in Latin means “abscess”). It is a cavity filled with pus. Outwardly it looks like a rounded formation the size of a pea to a walnut.
What are the causes of periodontal abscess?
An abscess develops due to an infection that affects the periodontal pocket and gum tissue. The disease can be provoked by existing gum diseases (GINGIVITIS, PERIODONTITIS, PERIODONTOSIS, etc.). In addition, an abscess can appear as a result of mechanical, thermal and chemical injuries to the gums, as well as as a result of incorrect dental fillings or prosthetics.
What are the symptoms of periodontal abscess?
First, discomfort appears in the gum area. When chewing food or pressing on the gum with a finger, the patient feels pain. Gradually, the pain intensifies and leads to the inability to fully grind food with the teeth. After 1-3 days, a dense, reddened, spherical swelling forms in the area of inflammation. The tumor quickly increases in volume and is accompanied by pain radiating to the ear, jaw and cheek. The patient may also experience:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- increased body temperature;
- insomnia;
- loss of appetite;
- decreased performance.
Sometimes a spontaneous opening of a periodontal abscess occurs, and then the pus flows into the oral cavity, and the pain and inflammation gradually subside. After this, the wound can heal, but without antiseptic treatment there is a high risk of re-infection of surrounding tissues.
How is a periodontal abscess diagnosed?
An experienced dentist can diagnose a periodontal abscess based on a visual examination. If the abscess is large and the gums are severely inflamed, an X-ray examination will be required to help determine whether the bone tissue is affected.
How is periodontal abscess treated?
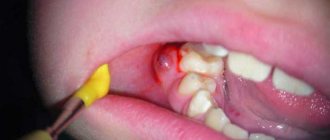
Exclusively surgically. After local anesthesia, the doctor makes a precise cut in the gum and drains the abscess. The affected area can also be cleaned through the gum pocket, but this is not possible in all cases. Treatment of periodontal abscess includes the complete removal of pus and dead tissue, after which the wound surface is treated with antiseptic solutions. In case of significant inflammation, a course of antibacterial therapy is recommended, and in case of severe pain, analgesics are recommended.
What are the measures to prevent periodontal abscess?
The most effective methods of prevention are timely treatment of teeth and gums, high-quality oral hygiene care, prevention of gum injuries and treatment of oropharyngeal diseases.
How much does it cost to treat a periodontal abscess?
Prices for the services of the DentaBravo clinic can be viewed in the table below or in the price list. And if you need specialist advice, call us or fill out a special form by clicking on the “Make an appointment” button.
Main forms of periodontal abscesses
- Acute – characterized by pronounced clinical manifestations and a sharp increase in pain. Deep periodontal pockets are diagnosed in the oral cavity, individual teeth become mobile, and the person feels a general malaise.
- Chronic – the disease occurs with “erased” symptoms. The gums begin to bleed, the ulcers become more voluminous and dense, and the roots of the teeth become exposed.
Note! Sometimes a periodontal abscess may go away on its own, but this does not mean that the patient has cured on their own. The process can become chronic, poisoning the body with decay products of soft tissues.
Depending on the location of the purulent sac, the following types of abscesses are distinguished:
- basal;
- apical;
- cervical.
Causes of dental inflammation
Bacterial damage to dental tissues can occur due to poor oral hygiene and insufficient patient attention to dental health issues. Among the common reasons:
- gum pathologies (periodontitis, periodontal disease, gingivitis);
- spread of caries;
- dental cysts, granulomas;
- cracks, chips on the tooth surface;
- oral injuries (for example, while eating);
- untimely change of toothbrush;
- poor quality teeth cleaning;
- weakening of the immune system.
However, the source of infection can be located in other parts of the body, and bacteria are carried into the gums by the bloodstream. Therefore, close attention should be paid to the treatment of any infectious diseases (especially ENT diseases) and increasing immunity.
Diagnosis and treatment of periodontal abscess
To diagnose the disease, it is enough for the dentist to perform a visual examination with palpation of the inflamed area. Based on the data obtained, the doctor makes a decision on further therapy.
It is important! Periodontal abscess does not need to be heated! Exposure to temperature will only worsen the process and the patient’s condition. The main right decision in this case is to seek qualified help from a dentist.
Basically, the following actions apply:
- surgical opening of periodontal gum abscess with preliminary local anesthesia;
- abscess drainage;
- taking painkillers;
- antibiotic therapy;
- regular rinsing of the mouth with antiseptic compounds;
- vitamin therapy;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
Causes of gum abscess
The human oral cavity contains about 30 strains of microorganisms, represented by more than 700 species of bacteria. Under normal conditions, microbiocenosis does not harm its owner. A dental abscess occurs only in the presence of certain factors:
- traumatic disruption of the periodontal junction;
- infectious dentogingival pathologies;
- transmission of microorganisms through the bloodstream from other infectious foci (meningitis, pneumonia, tonsillitis, etc.);
- gum damage during segment therapy;
- trauma to the crown or root of the unit;
- peri-implantitis (inflammation around the implanted tooth root).
The likelihood of developing the disease increases with poor oral care, hypothermia, accumulation of tartar inside deep periodontal pockets, and smoking. Professional hygiene and gum treatment in Moscow is carried out by doctors of the North-Eastern Dental Center No. 1. A timely visit to the clinic will reduce the risk of the formation of a purulent formation.
METROGYL DENTA® for periodontal abscess
METROGYL DENTA® has antibacterial activity and helps relieve inflammation caused by pathogenic microorganisms. The gel can be used to treat periodontal abscess in the postoperative period. Before using the drug, you must brush your teeth. Then a small amount of gel is carefully applied to the affected area of the gum using a cotton swab. The duration of action of the drug is 30 minutes; during this period you should refrain from drinking and eating. The duration of treatment is on average 7-10 days. Before using METROGYL DENTA®, we recommend consulting with your dentist.
Up to contents
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.
Prevention
- Thorough dental hygiene: brushing your teeth in the morning and evening, rinsing your mouth after every meal, using various devices: dental floss, brushes. If there are dentures in the mouth, it is recommended to clean them of food debris using an irrigator - a special device that supplies water under pressure.
- Timely treatment of diseases of teeth and gums.
- Preventative dental examinations are necessary at least 2 times a year to assess the condition of the teeth and oral cavity. If there is hard dental plaque, use hardware teeth cleaning.
Kinds
Dental inflammatory disease, accompanied by swelling and accumulation of purulent exudate, is divided into two categories according to its nature and course.
- Spicy. The disease has a pronounced clinical character. Pathological mobility of elements of the dental system and the formation of deep periodontal pockets are diagnosed. The patient experiences severe pain, malaise, fever, and deterioration in general health.
- Chronic. Painful condition of the gums, bleeding, filling of pockets with a purulent component with a certain frequency. When diagnosing, exposure of the roots of the molars and swelling of the gums may be detected. The patient experiences increased sensitivity to external stimuli.
When opening a periodontal abscess, the localization can be established both in the cervical area and in the apical part of the molar or canine. At this clinic, deep pathological pockets and hard subgingival deposits are recorded. In case of a chronic disease, exacerbation is observed in the autumn-spring period with a sharp change in temperature and immunodeficiency.
Treatment
Surgery.
During the operation, the inflamed periodontal tissues are dissected, purulent exudate is removed from the periodontal pocket, and the gum cavity is drained. The procedure can be performed in two ways:
- through the periodontal pocket (the surgeon finds the hole and gently stretches the tissue to ensure the drainage of pus);
- through a traditional gum incision (gingivotomy).
Drug therapy.
After the operation, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving drugs. Most often, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution at least 3 times a day. Antibiotics are prescribed only when a periodontal abscess is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. For local treatment, preparations in the form of ointments and gels can be used.
Up to contents
Which clinic in Moscow performs the opening of a periodontal abscess?
The DemoStom clinic provides all necessary consultations and diagnostic measures in these cases. The treatment plan is coordinated with a number of specialists. Our dentistry is equipped with innovative equipment; materials and instruments meet the requirements of sterility, and therefore safety. Painless surgery at the DemoStom clinic. Without treatment, the situation can only worsen, leading to serious impairment and even death. Timely contact with dentists helps restore the health and beauty of your smile.
Diagnostics
The examination includes:
- patient interview,
- inspection,
- dental radiography,
- laboratory and instrumental methods.
During the examination, the doctor sees a painful local bulge and altered mucous membrane. There is no transitional fold from the periodontium to the tooth. The depth of the pockets is at least 3 millimeters.
X-ray shows:
- enlargement of the periodontal gap,
- destruction of the cortical plate,
- uneven resorption of spongy substance.
A blood test indicates nonspecific inflammation:
- high level of leukocytes,
- increase in ESR,
- shift of the leukocyte formula to the left.
PCR allows you to accurately determine the composition of the microflora of the gum pockets. With an abscess, the number of bacteria increases 100 times. During the examination, doctors exclude:
- acute periodontitis or exacerbation of the chronic form,
- cyst with suppuration,
- periostitis,
- osteomyelitis.
What are the symptoms of the disease?
On the gum in the alveolar region, where the roots of the tooth connect to the jaw bones, a formation appears on the gum side. Symptoms include:
- Edema mucous membrane;
- Loosening of the tooth;
- Pain when chewing and biting;
- Pus coming from under the gums.
If you do not consult a doctor, an abscess can lead to the formation of a fistula, changes in bone tissue, or tooth extraction. Even if you spontaneously open a periodontal abscess, you should visit a dentist as soon as possible. Otherwise, a relapse may occur.