All kinds of dental implants, or in other words, implants and implants, have firmly entered our lives and are no longer perceived as something unnatural. The invention of implantation - the implantation of artificial materials into the human body to replace lost organs - was a real breakthrough in medicine and science. Today, implants are used in many areas of medicine: these are artificial joints, silicone breast implants, and, of course, dental implants, which are available in almost every dentistry in Moscow.
History of the first patient
The first attempts to replace lost teeth with artificial ones were made by people in antiquity and even earlier. In the form in which we know dental implants now, they appeared in the second half of the 20th century. The first successful implantation was performed in 1965 on an ordinary carpenter, Gust Larsson, who lost all his lower teeth at the age of 34, had a cleft palate, a deformed upper jaw and chin, and experienced constant pain and significant difficulty eating and speaking. Larsson volunteered for a new study led by Professor Ingvar Brånemark at the University of Gothenburg, which Güsta had heard about by chance from his dentist. After the treatment, he was able to chew, eat and speak normally. The installed implants served Gust Larsson all his life. The experience of this brave man proved that installing dental implants is the most effective way to restore lost teeth.
Crowns supported by a core inlay
The stump tab is a structure that is fixed inside the root. It creates a support for further prosthetics without removing the root. The design has several pins installed in the root canals and a stump part, which is necessary for fixing the crown. Installation of a stump tab is possible only if there are indications:
- The crown is damaged by more than 60%;
- The upper part has a fracture;
- After caries treatment, the tooth walls have a suitable thickness.
If the conditions and requirements were not met when installing the stump inlay, the patient may be injured, damage bone tissue, adjacent teeth, and the root will need to be removed.
Contraindications:
- Inflammation of the gums near the root;
- Cyst, granuloma;
- Thin walls of the tooth;
- Short channels for installing pins;
- Allergy to materials.
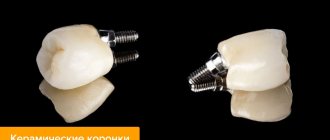
Stump inlays are made from metal alloys, metal-ceramics, ceramics, and zirconium. Crowns for them are selected accordingly - from metal, metal-ceramics, solid ceramics, zirconium. If you have an allergy to metal, the design is selected entirely from hypoallergenic materials - ceramics or zirconium.
Dental implants – what are they?
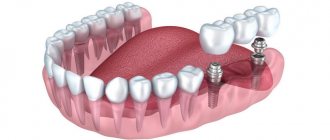
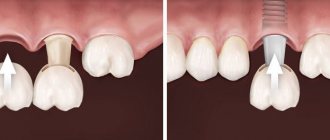
Dental implants, implants, implants are all artificial structures that replace missing teeth. They are firmly fixed in the bone tissue of the jaw and serve as a reliable support for fixed or removable dentures in the form of single crowns and bridges of varying lengths (you can see what dental implants look like in the photo above). There are several types of dental implants, but the most popular today are root-shaped dental implants, which have earned favorable reviews from both patients and leading implantologists around the world. Prices for dental implants depend on their quality, features of the installation system, the presence of special coating and other factors. Which implants are better is a topic for a separate article.
Photo of a dental implant
How to choose?
If you are healthy, under 50 years old, do not smoke, are willing to wait up to 6 months for the implant to survive and receive prosthetics, and want to restore a molar or premolar, you can get dental implants, which cost less. It is reduced by manufacturing from a titanium alloy with vanadium and aluminum, the absence of ultra-hydrophilic surfaces, acid etching and coating with phosphorus or other substances that accelerate healing.
If you smoke, have diabetes, osteoporosis, or are over 50 years old, you need implants made of pure titanium or its alloy with zirconium dioxide or bioceramics. After sandblasting and acid etching, the surface acquires hydrophobic properties that slow down implantation. Choose a design with an ultra-hydrophilic surface. Straumann implants have the best combination of characteristics. They produce several models, Roxolid has the highest survival rate. If you are confused about how much a Straumann dental implant costs, you can install Osstem or MIS. When implanting Osstem structures, prosthetics are postponed for 3-6 months. MIS has no such restrictions; healthy people with dense bone tissue can have a prosthesis installed after surgery or after 5-15 days.
If there is insufficient jaw bone tissue, it is better to install a basal type implant (manufactured by the Swiss company ROOTT). It is inserted deeper into the jaw bone and is more stable. This operation is indicated for elderly people, smokers, patients with diabetes, and osteoporosis.
How do dental implants take root?
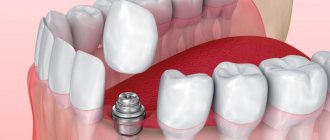
What material are dental implants made of? The answer to this question will help us understand why they take root well. Almost all of the newest dental implants are made from titanium. This unique material is ideal for the manufacture of artificial tooth roots, since it is not perceived by the human body as something foreign and is not itself subject to the destructive effects of the surrounding biological environment. But the most important thing is that it can reliably fuse with the jawbone. These unique properties of titanium solved the problem of rejection and made implantation a reliable and durable technique. However, in very rare cases when a patient is allergic to titanium dental implants, zirconium dioxide is used as a base to make the prosthesis.
How long does it take for a dental implant to take root? Experts believe that the survival of dental implants is an individual process. The timing of osseointegration depends on the area of the dentition in which the implantation was performed, as well as on the quality of the bone tissue. In general, the healing of dental implants lasts from three months on the lower jaw and up to six months on the upper jaw. If the implantation is successful, then removal of the prosthesis becomes almost impossible, which proves the reliability of the structure. What is the survival rate of dental implants that worries many patients? It varies among different manufacturers, but in general it does not exceed 5%. In addition, the success of the operation is also influenced by the skill of the implant surgeon, so the choice of dentistry should be approached with special care.
I heard that a titanium implant often does not take root, the probability of success is 50/50. Is it so?
This is probably the most common misconception among patients. The same reasoning is used by unscrupulous doctors who do not know this technique and try to persuade the patient to do what they know how to do (bridges, removable dentures). In fact, dental implantation has already become a safe and well-predicted manipulation. The problem of “whether it will take root or not” and “what to do so that the implant takes root” is no longer discussed among advanced doctors at dental congresses, symposiums and other professional “get-togethers”. The success of this manipulation in the hands of a good surgeon is estimated at approximately 95-98%. This is a very high figure for medicine. It is noticeably higher, for example, the probability of successful canal retreatment in the presence of any additional problems (broken instruments in the canal, perforations, large cysts and granulomas on the roots), even by the hands of a well-equipped, experienced endodontist. Of course, there are contraindications for implantation, but recently their list has been significantly narrowed.
It’s no longer worth going to a fortune teller to find out if your “screw” will take root...
Lifespan of dental implants
Although implantation is significantly more expensive than traditional prosthetics, with a long-term calculation the costs are equalized. This is due to the fact that traditional bridges, crowns, clasp or nylon dentures need to be replaced on average every 5 to 7 years, and the supporting teeth will have to be ground down again each time. How long does a dental implant last? The minimum service life of a dental implant is about 30 years, and if all the doctor’s instructions are followed, the implant will last you a lifetime. Most manufacturing companies, including world industry leaders, who invest considerable funds in the latest developments, provide a multi-year or even lifetime warranty on their products. This applies to the part of the structure that is located inside - that is, the root (base plate, etc.) and the abutment. A crown installed on an abutment has a more limited service life, but it is also significantly longer than that of a traditional prosthesis installed on ground natural teeth. This is on average 10 – 15, sometimes 20 years. If we are talking about implantation for a young person, then, of course, he will be interested in what happens to implants in old age. With proper care and preventive examinations, nothing should happen to the artificial root.
What warranty is there for a titanium implant?
In general, we can talk about guarantees in medicine very conditionally. Can a doctor give a guarantee for your health? Therefore, this issue can be approached not from a medical position, but only from a legal and commercial one. And this issue is resolved differently in each clinic. Somewhere, in case of failure, you will be offered to reinstall the implant again without any additional payments, somewhere you will pay for the repeated intervention without taking into account the cost of the implant, somewhere - all financial responsibility will be placed on you. This is a reason to question the doctor more carefully and carefully read the contract for the provision of medical services, as well as the informed consent. If you have not seen these papers before starting treatment, then after treatment you can only count on the integrity of the clinic or a specific doctor. This is not the worst option, only if you are 100% confident in the man in the white coat, in his professionalism and decency at the same time (let's not pretend - this is not such a common case nowadays). At the same time, the pieces of paper do not protect you at all, since they usually describe everything in a way that is beneficial to the medical institution, and not to you. This is quite understandable. And with all cash receipts, contracts, in case of problems and lack of mutual understanding with the clinic, you need to remember what country we live in and what prospects there are for going to court if you are not a professional lawyer. So you still need to try not to make a mistake when choosing a doctor... Think 10 times before you sit in the chair.
What else can be said about guarantees? You shouldn’t fall for some advertising hype like “only we have a 10…15…100 year guarantee on implants.” You need to carefully read what is behind this marketing ploy. As a rule, zilch. Either it turns out that in your specific case such a guarantee cannot be given, or you will be forced to undergo various preventive procedures at an inflated cost within strictly specified periods (by analogy with buying a new car and having to undergo the entire warranty period of maintenance strictly at the dealer). This is actually not bad, but as you understand, for this seemingly luxurious guarantee you will pay extra out of your own pocket. Actually, this is precisely why such promises are most often made.
General and specific contraindications
Who is contraindicated for dental implants? Implantation is a surgical operation and, like any other operation, it has contraindications. They are divided into two types: general for any type of implantation and specific dental ones.
The following concomitant diseases are common to all types of implantation (and to surgical interventions in general):
- violation of coagulation (blood clotting), diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, chronic rheumatism - these diseases complicate wound healing and implant placement;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- childhood and adolescence – children and adolescents continue to grow, and this is fraught with displacement of implants or their rejection, or slowdown in the growth of individual organs as a result of the installation of dental implants in them;
- diseases of bone tissue that reduce its regenerative abilities;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- cancer during exacerbation, HIV and AIDS, specific diseases of the immune system that weaken the body as a whole and do not allow it to recover after operations.
The following can be considered specific contraindications to dental implantation:
- when installing implants in the upper jaw, it is necessary to take into account such factors as the proximity of the sinuses (aka the maxillary sinuses), as well as the width and density of the bone at the point of contact of the jaw with the sinuses; in some cases, the implantation procedure may be preceded by a sinus lift;
- chronic, including inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa;
- patient's failure to comply with oral hygiene;
- insufficient height and density of bone tissue at the site of proposed implantation (this applies to both the upper and lower jaws) - in such a case, bone grafting can correct the situation.
It is worth noting that diabetes and advanced age are not currently included in the list of contraindications for dental implantation.
Dental implants in the upper jaw
Understanding the terminology - what is right and what is wrong
Before dwelling on the difference between an implant and an implant, it is worth learning more about the origin of the terms. It all started with the word “implant”. It comes from the combination of the Latin root plantatio - “transplant”, and the prefix im (in) - “in”, “inside”, and appeared in domestic dentistry at the end of the 19th century. In 1891, Doctor of Medicine, Professor of Moscow University Nikolai Znamensky proposed the terms “implantation” and “dental implant” in his work “Implantation of Artificial Teeth”[1]. Where did the words “implant” and “implantant” come from, and is there a difference between them?
Let's take a closer look at the term “implant”
The word “implant” arose later as a tracing paper from the English word implant, derived from the same Latin root, and means “to implant.” Both words, implant and implant, are equivalent, but the latter, despite its later appearance, is used more often - perhaps due to its short form and greater euphony. The only difference is in pronunciation, there are no semantic differences between a dental implant and an implant.
Is there a term "implant"?
Practicing dentists use various terms in their work, which are often incomprehensible to patients due to difficulties in pronunciation or the lack of consonant synonyms in the Russian language. Therefore, you need to figure out which is correct - a dental implant or an implant.
You need to know that using the word “implant” is a mistake. There is no such term in dentistry, or in medicine in general. Therefore, the difference between an implant and a dental implant is that the first is simply a made-up word (or better yet, mispronounced). Whereas an implant is a really existing concept (read more about what it is below).
About the term "transplant"
It is also worth distinguishing an implant from a transplant, which in turn is a living (and not artificial) donor organ or tissue - for example, bone tissue, transplanted to the place of the lost one.
Caring for Dental Implants
Many patients who have had artificial teeth installed are concerned about the question: how to care for dental implants? In fact, caring for artificial teeth is practically no different from regular oral hygiene. The same few basic rules apply here: regularity, thoroughness, correctness. That is, you need to brush your teeth at least twice a day - in the morning and before bed, and preferably after every meal, especially after eating carbohydrates; this must be done for at least three minutes, and also use additional hygiene products: dental floss, irrigator, etc.; You need to brush your teeth correctly - with sweeping movements away from the gums. The same brushes that are used for cleaning natural teeth are suitable for cleaning dental implants, but you can purchase a special toothbrush for implants.
Selecting implants for the anterior teeth
Crowns are placed on rods that are implanted into the jawbone. They are not visible; outwardly they do not differ from living teeth.
When implanting teeth, the beauty of your smile depends on the type and price of the structure. When metal or bioceramic rods are installed in the jaw, the bone sags. This is not noticeable in the first year. The normal amount of atrophy is less than 1 mm per year for the first four years after prosthetics and 0.2 mm per year after 4-5 years. As the bone settles, it exposes the head of the rod; it is covered only by gum tissue. With constant contact with metal, it changes its color and acquires a bluish tint, which is clearly noticeable.
In order for the smile to remain beautiful and the gums to look healthy, when implanting incisors and canines, it is necessary to install structures that provide a minimum amount of atrophy: AstraTech (0.25 mm over 5 years) or Straumann (0.45 mm over 5 years). Most manufacturers do not indicate this indicator in the technical specifications. Independent studies were conducted, but not all models were included in them. And their performance from one manufacturer can vary greatly.
But it will not be possible to avoid atrophy when installing any model. To prevent gums from changing color, install a dental implant made of bioceramics to restore an incisor or canine.
If there is insufficient bone volume, implantologists recommend installing modern basal type dental implants ROOTT or Straumann.
Dental implants – pros and cons
As for expert opinions, the majority of specialists are inclined to argue for dental implants, and those who are usually against are either very elderly doctors or dentists who do not have sufficient qualifications to carry out such procedures. If we consider the pros and cons of dental implants, then among the undeniable advantages we can note durability, the absence of the need to grind adjacent teeth, in contrast to the installation of bridges, as well as the preservation of all the functions of a natural tooth, such as: full participation in chewing and speech, prevention of tooth loss bone tissue and changes in facial features. As for the disadvantages, the price becomes a significant difficulty for most patients, however, as mentioned above, this is an adequate cost of solving the problem once for a lifetime. As for an alternative to dental implants, it does not exist as such, since traditional prosthetics is inferior to it in all respects.
Dental implants make it possible to improve the quality of life, restore the full functionality of the dentition, restore the attractiveness of the smile, and also protect yourself from the loss of bone tissue in the place of the missing tooth, and therefore from the possibility of losing neighboring teeth. But, in any case, only an implantologist can confirm the need for this operation; he will also help you draw up a treatment plan and choose designs that suit you personally.
Make an appointment:
1. Dental clinic on the street. 50 Let Oktyabrya, 24, office 2/2: Tel 2. Dental clinic on the street. Permyakova, 73: +7 3452 51-40-47
Dental implants: types and prices in Moscow in 2022
The cost of a turnkey dental implant in Moscow includes the price of the design, surgery and abutment with a crown. It may differ in different clinics by 20-30%. When calculating how much it costs to install a dental implant, sometimes you need to add the costs of bone grafting and sinus lifting. They are done if the jaw bone does not have enough volume to accommodate an implant. But sometimes, instead of bone grafting, basal-type structures can be installed. Prices for turnkey dental implantation also depend on the type of prosthetics (removable, fixed) and crown material.
Premium designs include:
- Straumann - the price for a dental implant in Moscow starts from 65 thousand rubles when installed with a metal-ceramic crown, and from 90 thousand rubles if you choose a crown made of zirconium dioxide.
- Astra Tech - from 70 thousand rubles with a metal-ceramic crown, from 80 thousand - with a zirconium dioxide crown.
- NobelBiocare - from 80 thousand rubles with a metal-ceramic crown, from 90 thousand - with a zirconium dioxide crown, with fixed prosthetics for a toothless jaw - from 370 thousand (four implants are installed, a fixed prosthesis is attached to them), the dentition is completely restored.
Among budget designs, implantologists recommend:
- Roott-Form - how much does implantation of 1 tooth cost depends on the material of the crown, with a metal-ceramic crown - from 54 thousand, with a zirconium dioxide crown - from 63 thousand rubles.
- Roott - used to restore a group of adjacent teeth, installed when there is insufficient volume of jaw bone without bone grafting; how much dental implantation costs depends on how many implants need to be placed. Installation of 1 basal component costs from 35 thousand rubles. For fixed prosthetics of a toothless jaw (6-10 basal components and a bridge) – 230-325 thousand rubles, depending on the type of bridge.
- AlphaBio - from 35 thousand rubles with a metal-ceramic crown, from 50 thousand - with a zirconium dioxide crown.
- MIS – from 35 thousand rubles with a metal-ceramic crown, from 50 thousand – with a zirconium dioxide crown.
- Osstem - from 35 thousand rubles with a metal-ceramic crown, from 40 thousand - with a zirconium dioxide crown.
What else does the success of dental implantation depend on?
You can name the best dental implants in Moscow based on the totality of their characteristics. But the significance of the indicators for patients who are or are not included in risk groups, who are restoring incisors or molars, who are ready to wait three months for prosthetics, or who want to complete treatment in 1-2 weeks, is not the same. And if you also take into account how much a dental implant costs, then it will not be possible to give recommendations on the choice in absentia and in general terms. Discuss this issue with the dentist who will perform the operation.
It takes into account one more factor: the implantation technique:
- The classic two-stage method - having installed the rod, the doctor completely sutures the mucous membrane above it and creates sterile conditions for the implant to heal. When pathogenic bacteria multiply in the oral cavity, they will not enter the surgical field and will not cause inflammation. When the rod fuses with the jaw bone, the surgical damage heals, the second stage of the operation is carried out - opening the gum mucosa above it, removing the plug screw and installing the gum former. This method is recommended for smokers, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems. But prosthetics are done after 3-6 months.
- One-stage - after installing the rod, the gum above it is not sutured, but a former is immediately placed. The gum contour is formed from the first days after surgery, but oral fluid enters the surgical field. The immune system of healthy people controls the growth of unwanted bacteria, and inflammatory processes do not develop. But, if the immune system is weakened, saliva contains carcinogenic substances obtained by inhaling tobacco smoke, the risk of inflammation and rejection of the implanted structure increases. Using this technique, a permanent bridge can be installed within 2-6 weeks. But it is not used if the patient is over 50 years old, smokes, has osteoporosis, diabetes, is prone to inflammatory processes on the skin, and frequent colds.
- Without delaying prosthetics - a temporary plastic crown is installed on the rod on the day of surgery, a few hours after implantation. It is used if one incisor or canine is missing in the dentition, and the patient experiences severe discomfort when communicating, or if his appearance is directly related to his ability to work.
- In case of complete absence of teeth, when installing basal structures in the deep layers of the jaw bone, a permanent bridge can be placed on the rods 1-3 days after the operation. The number of basal components is determined for each patient.
Installation methods
The classic method of implantation is surgery, followed by a long period of osteosynthesis. Modern techniques make this process easier and faster.
Types of dental implantation:
- Traditional – carried out in 2 stages. The crown is installed six months after implantation.
- One-stage – the crown is installed immediately after implantation.
- Basal – pins are installed in the basal bone; sinus lift surgery is not required.
- Translingual - the artificial root is inserted through small punctures. The technique is considered minimally invasive. The crown is fixed after 3–4 days.
The method of installing dental structures is chosen by the doctor. It depends on the patient’s diagnosis and associated factors.
Sometimes the difference between implantation and crown installation is only a couple of thousand rubles
Sometimes the difference is only a couple of thousand rubles due to the need for preliminary treatment before installing an orthopedic structure. If the tooth is severely damaged, additional costs will be required - strengthening with a pin or inlay. The patient pays for depulpation and root canal treatment. In addition, caries often develops under the denture. Even with good treatment, the root with the removed nerve is vulnerable to infection and is fragile, it can break even under light load.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich
Chief physician, Ph.D.
Implants come with a lifetime warranty. The most that will need to be replaced is a prosthesis. As research has proven, the service life of orthopedic structures based on artificial rather than living roots increases by 30–40%. With daily careful hygiene, the service life coincides with the implants.
Rehabilitation and rejection after the procedure
Installation of a titanium pin does not require hospitalization and is performed under local anesthesia. After the procedure, the patient goes home. Survival rate and the absence of complications depend on the quality of oral care and compliance with the dentist’s prescriptions.
Recommendations for nutrition for 3 days after surgery:
- do not eat for 3 hours after the procedure;
- the first day - soft, warm, non-acidic and non-spicy food;
- chewing load - only on the healthy side;
- Alcohol and smoking are prohibited;
- It is advisable to exclude coffee and tea; the best option is herbal tea, unsweetened compote;
- observe the drinking regime.
Attention! Alcohol after implantation is completely and categorically prohibited. It promotes the destruction of bone tissue and slows down the healing process. In addition, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics. Alcohol intake is dangerous for the patient's life.
Hygiene rules:
- there is no place for hands in the mouth;
- 3–4 days – only oral baths with prescribed medications, rinsing is strictly prohibited;
- 3–5 days after examination by a doctor, you are allowed to use a toothbrush;
- 2 weeks after implantation, start using an irrigator.
After surgery, buy a new toothbrush. This way you will reduce the risk of wound infection by pathogenic flora.
After implantation it is strictly prohibited:
- using electric toothbrushes;
- brushing teeth with floss;
- carry out hygienic cleaning without a doctor’s referral - the dentist must know and be able to work with implants. Therefore, only as prescribed by the implantologist;
- chew nuts, pencils, bite any hard objects.
Smokers should give up cigarettes at least until the stitches are removed. Then after each smoking session you need to do a mouth bath with chlorhexidine.
Pin or implant? What to choose?
What is an implant
What is a pin and how is it different from an implant?
How does a pin differ from an implant?
Pin or implant? This question worries many who decide to restore lost teeth. To make a decision, it is important to understand the difference between these designs. Both the post and the implant support the crown. However, they perform different tasks and are installed in different clinical situations. Let's take a closer look at each of them.
What to put on a dead tooth
A dead tooth is pulpless, without a nerve. A root without pulp becomes brittle and may not withstand heavy loads. If the root breaks, the prosthesis will need to be changed urgently. It will not be possible to preserve the old design; you will have to make a new one, and this will be an unforeseen expense. In the case of implantation, there are no such risks.
In addition, in case of severe damage, the dental unit must be strengthened and a pin installed in the root. But even with a positive prognosis, there is no guarantee that a crown with a pin will last at least 10 years. In case of critical damage, stump inlays are installed, which are made according to casts to order. The recovery process becomes longer and more expensive.
In difficult cases, there is no guarantee that the structure will last long. Therefore, it is necessary to assess the condition of the tooth and predict the duration of its functioning. If the prognosis is unfavorable, it is better not to spend money, remove the problematic molar or incisor, and install an implant that will last a lifetime.
If the cost of restoration with a crown with preliminary treatment is comparable to implantation, preference is given to the latter. You will receive a warranty from the manufacturer and from the clinic for the implant, and a 1-year warranty for treatment and prosthetics.
Profession: implanter or implantologist?
An implanter, or implantologist, is a doctor who restores single teeth or a full row of them.
An implanter is sometimes confused with a prosthetist. Their functions are not the same, but are interconnected. Thanks to the implantologist, a support for bridge-type or removable prostheses is created.
Before starting work, the doctor determines a detailed treatment plan, which indicates the timing of the screw’s healing. If a person decides to seek help from an implant, then preference should be given to the method of dental restoration proposed by Dr. Dante. Its peculiarity lies in the absence of any surgical intervention: the implant is simply screwed into the canal where the molar was previously located.