Why can’t stomatitis be treated without the participation of a doctor?
Of course, the use of medicinal ointments and preparations, special lotions and rinses for the oral cavity does not require hospital conditions and strict supervision by doctors. Indeed, you can heal yourself.
However, your decisions and actions should always be in consultation with your healthcare provider. Do not take any action or purchase medications yourself.
One careless mistake can lead to a complicated course of the disease and an increase in the inflammatory process!
Who is a periodontist?
A periodontist is a highly qualified specialist involved in the diagnosis and treatment of periodontal diseases - the soft periodontal tissues that provide teeth with reliable fixation in the jaw.
The periodontist, as a highly specialized doctor, must have in-depth knowledge of the methods of treating various types of soft tissue diseases. In his practice, he uses antibiotics, special dental equipment, resuscitation agents and drugs to treat gums.
What can cause stomatitis?
One of the main reasons is a decrease in immune functions. Once the immune system weakens, it affects other systems of the body.
Ulcers with stomatitis are a common signal of problems with the immune system. You may need help from different specialists.
Sometimes stomatitis develops against the background of diabetes mellitus and some other disorders in the endocrine system. Often, ulcers appear after accidental mechanical damage to the mucous membrane (for example, due to careless handling of a toothbrush).
Another possible reason is intoxication of the body associated with poisoning with metal salts. In this case, urgent medical attention is required due to the threat to the patient’s health and life!
Advice from periodontists
In order to preserve the health of your gums, you need to use dental services twice a year and scrupulously follow the rules of hygiene.
Advice from doctors on oral care:
- Hygiene procedures must be carried out daily, morning and evening, without any exceptions. This is the main guarantee of periodontal health.
- During the day, after each meal, rinse your mouth; if you don’t have a special mouthwash on hand, you can use plain water. Any remaining food particles between the teeth must be removed using dental floss.
- The toothbrush should be chosen correctly; it should have a rounded end and medium-hard bristles, which will prevent damage to the gums during brushing.
- The toothbrush should be changed quite often, at least once every 4 months, otherwise it becomes an ideal place for the accumulation of dangerous bacteria.
- The choice of toothpaste should also be taken seriously, since it is its composition that determines how effective the cleansing of all components of the oral cavity will be. There are special pastes containing useful components and additives that will help eliminate problems with soft tissues.
Can stomatitis be a side effect after taking medications?
Rare, but still acceptable causes of stomatitis also include taking certain medications.
Some antibiotics, diuretics, and oral contraceptives affect the condition of the oral mucosa, causing increased dryness and other complications. If your mouth becomes very dry, cracks and ulcers may occur.
When is a visit to a gastroenterologist indicated?
Consultation with a periodontist is indicated for periodontitis, periodontal disease, and gingivitis. If gum inflammation and sensitivity are left untreated, you may lose your chewing organs. To prevent this from happening, you should contact your dentist. He will prescribe complex therapy.
It happens that you need to go not only to the dentist, but also to the gastroenterologist. Patients who have problems with the gastrointestinal tract should visit doctors. After all, gastrointestinal diseases often lead to stomatitis. If the disease is caused by duodenitis, stomach ulcers or gastritis, treatment should be prescribed by a gastroenterologist. Additional procedures include rinsing. The patient must observe oral hygiene rules. A balanced diet promotes recovery. Sweet, spicy, salty, and hot foods are excluded from the menu. It is easier to prevent a disease than to cure it. Strengthening the body has a positive effect on recovery. It is extremely important to get rid of ailments in a timely manner, especially if they are infectious.
What remedies are recommended for the treatment of stomatitis?
- Mouth rinses . You can prepare a solution based on boric acid (one teaspoon per 150 ml of water). Another option is a solution with hydrogen peroxide (add one teaspoon to a glass half filled with water).
- Oils for medicinal lotions . Use sea buckthorn oil and propolis tincture. Soak a sterile cotton pad (or gauze) with the product and apply to the ulcer for a few minutes.
- The use of antiseptics to treat ulcers and mucous membranes. Be sure to consult your doctor when choosing a product.
Stomatitis - symptoms and treatment
The main goal of treating stomatitis is to prevent the lesion from spreading throughout the entire oral mucosa and to prevent the disease from becoming chronic. First of all, it is necessary to determine the form and stage of the disease, since treatment tactics will depend on this. Treatment is complex: both local and general.
For all types of stomatitis, professional oral hygiene . It is the removal of dental deposits such as tartar and soft pigmented plaque.
Effective drugs for the treatment of stomatitis in adults
Next, it is necessary to eliminate chronic foci of infection and predisposing factors. For painful ulcers, anesthesia of the oral mucosa :
- applications of a 2% solution of procaine (Novocaine);
- applications of 2% lidocaine solution [7].
The affected mucous membrane is treated with antiseptics (0.02% Furacilin solution; 0.06% chlorhexidine solution; 0.1% Dimexide solution).
Applications of collagen films with various medicinal substances, for example, corticosteroid drugs, Diphenhydramine, and anesthetics, are also used. This film attaches to the erosion and has anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects, after which it dissolves on its own. To accelerate the healing of the mucosal epithelium, an oil solution of vitamin A, rosehip oil, and dental adhesive paste with solcoseryl are used.
How can you rinse your mouth for stomatitis?
When treating stomatitis, it is very important to identify the cause and eliminate it. Rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions (0.02% Furacilin solution, 0.06% Chlorhexidine solution) or herbal decoctions will reduce swelling and inflammation, but this is not the main method of treatment.
General treatment
Includes adherence to a diet (it is not recommended to consume spicy, spicy, rough foods, alcoholic beverages), as well as the use of antihistamines, antivirals, antibacterial, antifungal drugs (depending on the form of stomatitis) and sometimes glucocorticosteroids (GCS) - analogues of natural hormones of the adrenal cortex [6 ].
Desensitizing therapy : orally “Tavegil”, “Diphenhydramine”, “Suprastin”, 1 tablet 2 times a day for a month.
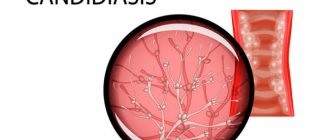
Antifungal therapy is carried out for candidal stomatitis: tablets “Nystatin”, “Nizoral”, “Diflucan” [9].
For viral stomatitis, antiviral drugs are prescribed: Lavomax, Valtrex, Bonafton. In severe forms of stomatitis, corticosteroids can be prescribed: prednisolone 15-20 mg per day, the dose of the drug is reduced by 5 mg per week from the moment of epithelization of erosions and ulcers.
For stomatitis, restorative therapy . Vitamins of group B, C, PP. Imudon tablets have an antiseptic effect, normalize microflora, and increase local immunity [11].
From the first day of the patient’s treatment until complete epithelialization, physiotherapy : ultraviolet irradiation, helium-neon laser, laser biostimulation of blood.
Laser treatment of stomatitis
Laser in the treatment of stomatitis is especially effective if the oral mucosa is affected by bacteria, viruses or fungi. The laser beam is targeted specifically at the affected area of the mucous membrane without damaging healthy tissue. The method allows you to destroy microbial cells, reduce pain and swelling, improve microcirculation, which promotes healing. The procedure is painless and safe.
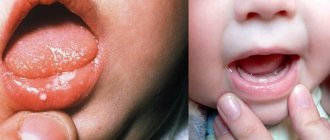
How to cure stomatitis in a child
The principles of treating stomatitis in children and adults are similar, but it is important for the doctor to take into account the age of the child and correctly calculate the dosage of drugs. Another feature is that young children will not be able to rinse their mouths or use mouth baths. Therefore, antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity is carried out by parents with a finger wrapped in several layers of gauze and soaked in an antiseptic solution.
Treatment of stomatitis at home
If symptoms of stomatitis appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Self-diagnosis and treatment with folk remedies often aggravate the disease.
What should you not do if you have stomatitis?
While you are treating stomatitis, never eat too hot food. Mouth rinse solutions should also be at a moderate warm temperature.
Temporarily avoid ice cream and cold drinks, do not eat spicy, sour, overly salty or sweet foods to avoid increased irritation.
Do not try to remove the ulcer yourself. If necessary, such manipulation will be performed by a doctor on an outpatient basis. If you open an ulcer yourself, you may accidentally introduce an infection into the wound.
Who should adults contact?
The disease is treated by a dentist who specializes in problems of the lining of the mouth. After the examination, the doctor will refer the patient for examination to determine the exact cause of the anomaly. If necessary, the oral cavity is cleaned. Besides:
- If the patient suffers from allergies, you should contact an allergist. Irritating food additives provoke the development of the disease.
- Consultation with an immunologist is required when external irritants affect systems and organs. In this case, the body's defenses are activated. But when they are weakened, relapses often occur.
- You may need a referral to an endocrinologist for hormonal imbalances.
Therapy is prescribed according to indications. Complex treatment measures may be required. It is important to eliminate provoking factors. A gentle diet and vitamin supplements are prescribed. Mucous tissues should be irrigated with antiseptics and lubricated with antiviral or antifungal agents.
Types of disease
Based on external symptoms, nature of manifestation and cause of occurrence, the disease is divided into several types, each of which has characteristics and requires a special approach for effective treatment. The most popular types of disease:
- Aphthous. This type occurs in 10-40% of adult patients and manifests itself in the form of a large number of aphthae - white-yellow ulcers. Accompanied by itching and pain, which interferes with talking and eating. The cause is weak immunity due to diseases, lack of vitamins, allergic reactions. Treatment of this type of stomatitis requires an integrated approach; recurrence of the disease is possible.
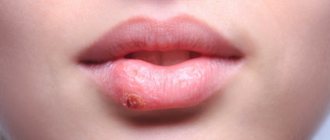
- Herpetic. This species is caused by a herpes virus that penetrates cells and remains there forever. When contacted with the mucous membrane, bacterial cells actively divide, damaging the epithelium, which leads to the development of ulcers. The most popular places of occurrence are the mucous membranes of the lips and cheeks, the outer border of the lips. It often takes a chronic course, so periodically treatment of stomatitis in adults will require resumption. The doctor will tell you in more detail how to treat stomatitis in the mouth after examining the clinical picture.
- Catarrhal. The most common reason for its appearance is insufficient hygiene and injury to the oral mucosa. In addition to painful inflammation, swelling of the palate is observed, and a high temperature may rise. This type cannot always be recognized at the initial stage, since ulcers do not appear immediately.
- Allergic. It manifests itself due to the body’s high sensitivity to various food and non-food allergens. It can arise from intolerance to certain foods, oral hygiene products, medications, pollen, and so on. It is considered one of the most complex forms of the disease, since identifying the cause is often problematic - it is necessary to undergo tests and tests for allergens. It has standard symptoms in the form of ulcers, to which is added sleep disturbance and nervousness.
Causes
The mechanism of the disease has not been fully studied, but it is generally accepted that it is a reaction of the immune system to various types of irritants. Stomatitis can develop independently or be a sign of systemic pathology.
External reasons:
- neglect of personal hygiene rules (unwashed hands, dirty vegetables and fruits);
- oral injuries (chemical, mechanical or thermal origin);
- unbalanced diet with a lack of vitamins and microelements;
- alcohol abuse;
- stress;
- poorly performed dental prosthetics;
- use of certain medications;
- using toothpaste or mouth rinses containing sodium lauryl sulfate;
- burns from hot food or drinks.
Internal reasons:
- parasite infection;
- streptoderma;
- systemic scleroderma;
- diabetes;
- allergic reaction;
- bronchial asthma;
- exudative erythema multiforme;
- changes in hormonal levels (during pregnancy, menopause);
- anemia;
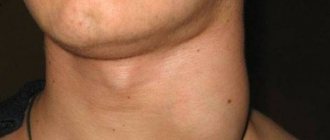
- malignant neoplasms of the nose, neck, pharynx.
Symptoms
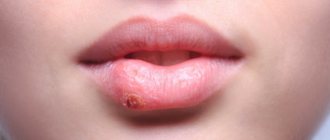
The first manifestation of stomatitis is the appearance of small redness. Subsequently, the affected area swells, swells, pain and itching are noted.
The bacterial form is characterized by the formation of an ulcer with smooth edges. Its center is covered with a thin white film.
Other signs:
- bad breath;
- bleeding gums;
- discomfort and pain in the oral cavity;
- increased salivation.
If the course of the disease is acute, then the body temperature rises and the lymph nodes enlarge. Typically, this clinical picture is typical for children, since their immunity has not yet fully developed. Also, the child may sleep poorly, refuse to eat, and be capricious.
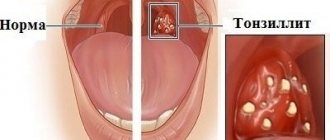
Typical localization of spill elements:
- sky;
- tonsils;
- inner side of lips;
- tongue, sublingual area.