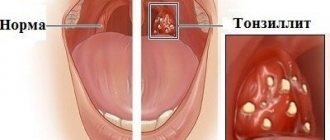
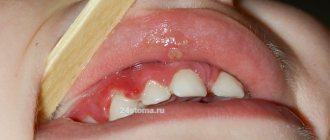
Symptoms of the disease
Angina:
- pain in the throat when swallowing;
- increase in body temperature;
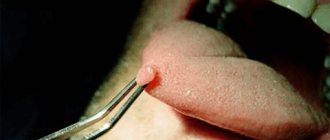
- the presence of purulent plugs on the tonsils;
- headaches;
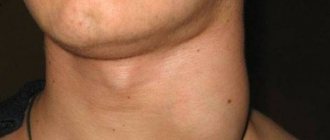
- enlarged lymph nodes and their pain;
- a state of general weakness.
Chronic stage of tonsillitis:
- discomfort and pain when swallowing;
- presence of bad odor from the mouth;
- excessive fatigue;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- sleep disturbance;
- enlargement and tenderness in the cervical lymph nodes.
Sore throat (acute tonsillitis)
Symptoms
The leading symptom is a sore throat, especially when swallowing and eating. The intensity of the pain syndrome can vary from quite tolerable to severe. The severity of symptoms of general intoxication (increase in body temperature from 37°C to 40°C or more, weakness, general malaise, headache, loss of appetite, sleep disturbances, enlarged and painful regional lymph nodes) and local inflammation in the tonsils also varies in different cases ( swelling, hyperemia).
The most typical, common manifestations of acute tonsillitis are listed above. Other symptoms may differ so significantly that this serves as the basis for identifying several relatively independent clinical forms.
Catarrhal sore throat is the most common and, fortunately, the least severe form. It manifests itself as a burning sensation, a “soreness” in the throat, drying out of the mucous membranes of the oropharynx, a coated tongue, and moderate pain when swallowing. As a rule, the syndrome of infectious intoxication occurring against the background of low-grade fever has an asthenic component. A mucopurulent coating may appear on the tonsils. With a sufficient immune response, symptoms are reduced within a few days.
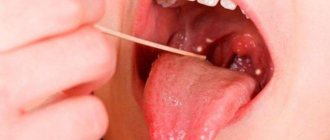
Follicular tonsillitis , also very common, usually manifests itself with high fever, sharp radiating pain in the throat, severe clinical intoxication, a feverish state (up to symptoms of depression of the central nervous system), gastrointestinal disorders, and vomiting. Multiple suppuration of small follicles gives the tonsils a characteristic “starry sky” appearance; spontaneous opening leads to accumulations of pus. The active phase of the disease lasts about a week.
Lacunar tonsillitis is, in fact, a more severe version of follicular tonsillitis. Muscle and joint pain and cardialgia are often added. Tonsils, as a rule, are covered with purulent plaque in the form of films.
Fibrinous tonsillitis , in turn, can be considered as the next phase in the development of lacunar tonsillitis: a continuous yellow-white coating forms, covering not only the tonsils, but also adjacent areas.
Phlegmonous tonsillitis is characterized by a widespread, diffuse purulent-inflammatory process in the parenchyma of the tonsil (usually one of the two). The muscles of the temporomandibular joint often spasm. The current is severe.
Gangrenous tonsillitis (Vincent's ulcerative-necrotizing tonsillitis, see above) is characterized by massive death of cells in the affected tonsil, putrid breath, deep ulceration with the formation of defects due to purulent melting of the tissue. Body temperature in most cases remains moderately elevated or normal.
Herpetic (viral) tonsillitis occurs more often in children, is distinguished by a particularly acute onset and high contagiousness, polymorphic severe symptoms (including from the gastrointestinal tract), which, however, are quickly reduced. The tonsils are covered with small red, inflamed blisters.
As is often the case in medical practice, the prevalence and fame of the disease does not at all guarantee against severe complications. The dynamics of acute tonsillitis can result in an intra- or peritonsillar abscess, trigger the start of a rheumatic process, glomerulonephritis; the rapid spread of infection in some cases results in meningitis or secondary inflammation of another localization, as well as life-threatening infectious-toxic shock or sepsis.
Possible complications of tonsillitis
- Rheumatism is the most dangerous complication, which, in turn, can affect the joints and lead to heart disease.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Peritonsillitis, peritonsillar abscess.
Causes of sore throat:
- various viruses;
- bacteria;
- hypothermia of the body;
- decreased immune system functions;
- tonsil injury;
- violation of nasal breathing;
- various inflammations in the oral cavity.
Causes of chronic tonsillitis:
- frequent sore throats and ARVI;
- diseases of teeth and gums;
- nasal breathing disorder.
- weakened immune system;
- presence of allergies.
Causes of chronic tonsillitis
In fact, inflammation occurs constantly in the tonsils - this is their function. But sometimes the protective resources of the tonsils are unable to cope with the infection, and then the inflammation, which gets out of control, turns into a serious disease - tonsillitis.
The acute form of tonsillitis is tonsillitis. Untreated tonsillitis often develops into chronic tonsillitis. Conversely, exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis leads to an outbreak of tonsillitis. If a person gets tonsillitis every year or several times a year, then he most likely has chronic tonsillitis.
Sometimes chronic tonsillitis can develop even if a person has not had a sore throat. This is possible if there is a source of infection that can affect the tonsils for quite a long time, for example, untreated caries or chronic sinusitis.
Treatment of tonsillitis in the clinic
To prescribe high-quality and effective ENT treatment, the doctor must accurately determine the nature of the inflammation (acute, chronic), its type (with or without purulent content), and the type of pathogen (virus, fungus). If tonsillitis is chronic, it is important to determine whether conservative treatment will be sufficient or surgery is indicated.
Conservative treatment involves washing the tonsils, removing plugs with pus, gargling, drinking plenty of warm fluids, and taking anti-inflammatory drugs.
In no case should you self-medicate - it is better to consult a specialist who, after an examination, will prescribe you the correct treatment.
WHAT SYMPTOMS SHOULD YOU CONSULT AN OTOLARINGOLOGIST?
Symptoms of diseases of the ENT organs cannot be ignored. You should consult an otolaryngologist if you are concerned about the following symptoms:
- breathing complications;
- whistling when breathing;
- pain when swallowing;
- redness of the throat;
- enlarged lymph nodes under the jaw;
- hoarseness and sore throat;
- fatigue, dizziness;
- cough;
- pain in the ear when swallowing;
- sensation of a foreign body in the larynx;
- hemoptysis;
- pain in the throat area.
Diseases associated with chronic tonsillitis
There are quite a lot of them. Such diseases may be directly or indirectly associated with chronic inflammation of the tonsils. First of all, these are collagen diseases (rheumatism, systemic lupus erythematosus, periarteritis nodosa, scleroderma, dermatomyositis), a number of skin diseases (psoriasis, eczema, polymorphic exudative erythema), nephritis, thyrotoxicosis, peripheral nerve damage (plexitis, radiculitis). Long-term tonsillogenic intoxication can contribute to the development of thrombocytopenic purpura and hemorrhagic vasculitis.
Chronic tonsillitis often causes a prolonged increase in low temperature (low-grade fever), pathological auditory sensations (tinnitus), worsens the course of vasomotor dysfunction of the nose, vegetative-vascular dystonia, vestibular dysfunction, etc.
Chronic tonsillitis has serious complications - these include difficulty breathing due to constant swelling of the nasal cavity and its mucous membrane. It has been established that during the night, about 200 ml of pus enters the stomach, which disrupts the normal functioning of the stomach and intestines. Such patients are at risk of developing a sore throat, which often leads to a peritonsillar abscess. A peritonsillar abscess often develops into cellulitis of the neck, a disease that can be fatal. In total, up to 55 diseases can be identified that arise as a complication of chronic tonsillitis.
Methods for treating symptoms of acute and chronic tonsillitis
Treatment of acute tonsillitis is carried out taking into account its cause. For bacterial tonsillitis, antibiotics are selected, for Candida - antifungals, as well as medications that help alleviate symptoms: antipyretic, local anesthetic, etc. [1].
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis of the throat can be:
- conservative - prescribing antibiotics, washing the tonsils to eliminate the source of infection, physiotherapeutic methods;
- surgical - removal of tonsils using a laser, excision, cryotherapy, etc. It is recommended in case of ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, frequent exacerbations, and severe toxic-allergic form [1].
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis in adults
It can be conservative or surgical, and the choice between these two types depends on the form of the disease, which the doctor determines during the diagnostic process.
Treatment of compensated form of chronic tonsillitis
For acute symptoms of the disease, treatment is the same as for ordinary sore throat.
Long-term simple inflammation of the tonsils in remission requires conservative therapy, including:
1. Local therapy: gargling and rinsing lacunae, while local use of antibiotics is not recommended1,3.
- Lacunae rinsing is a medical procedure during which a solution is injected into the lacunae using a conventional injection syringe or a special device under pressure, which flushes out the pus and plugs that have accumulated in them. Preparations with antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects are used as washing solutions3. A total of ten procedures are carried out once every 2-3 days.
- Gargling complements the procedure for rinsing the lacunae, but does not replace it and cannot be used as monotherapy2,3 for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis at home. Antiseptic solutions are also used for gargling, for example, HEXORAL®, approved for use in adults and children over 3 years of age5. The main active ingredient of the drug HEXORAL® is hexetidine. It is a broad-spectrum antiseptic, active against most bacteria (including group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus), some viruses and fungi that are aggressive against the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils5. HEXORAL® helps clear the tonsils and reduces throat discomfort. To do this, it is enough to rinse it twice a day - the drug can act for 12 hours5.
2.Physiotherapy
It includes UHF on the area of regional lymph nodes and a quartz tube directly on the tonsils1.
Antibiotics for chronic tonsillitis are prescribed only if the disease is streptococcal in nature. In addition to it, in cases of sharply reduced immunity, immunocorrective drugs are used 2,3.
The course of therapy is repeated 2-3 times with an interval of 3-4 months1. If there is no effect or it is insufficient, sore throats continue to recur, and the picture in the pharynx does not change for the better, the doctor recommends removal of the tonsils1,5 - tonsillectomy.
Treatment of decompensated form of 1st degree of severity
As in the case of the simple form, they begin with conservative therapy: washing the lacunae of the tonsils, gargling and physiotherapy. If after 1-2 courses (or more often within two weeks) of such treatment the doctor does not see any improvement, a tonsillectomy is performed5.
Long-term inflammation in the stage of decompensation, that is, its toxic-allergic form of grade 2 , is an absolute indication for tonsillectomy1-5.
Up to contents
Prevention of tonsillitis
There are individual preventive measures aimed primarily at strengthening the immune system.
A healthy lifestyle and the absence of bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol play a key role. Don’t forget about hardening the body, doing physical exercise, regularly spending time in the fresh air, and consuming enough vitamins with food.
In the modern world, special attention is paid to the use of various biologically active additives (BAS) to improve health, including for the prevention of colds and strengthening the immune system.
The composition of such supplements is very diverse and rich, including various vitamins, minerals, nutrients, and substances of plant origin.
They come in the form of tablets, lozenges, dragees, drops, etc. But you shouldn’t count on “magic”; such supplements will not cure all diseases, but they will really help direct the body to work in the right direction and improve the effect of the main treatment. It is also important to choose the right biological supplement, focusing on the body’s needs and its problem. For example, lozenges can help strengthen the immune system.
Tantum® Propolis 13
Propolis is a valuable substance that has been used for medicinal purposes since the times of Hippocrates, Discorides, Avicenna and others, and is used in modern medicine to this day.
Plants from which bees collect and carry resinous substances have bactericidal, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulating, and antiviral properties.14 Find out more
Not being a medicine, Tantum® Propolis can support the patient’s immunity during seasonal ARVI and influenza, reduce pain, irritation and itching in the throat, and also replenish the lack of vitamins in the patient’s body.
In preventing complications, it is very important to consult a doctor on time, follow the prescribed treatment regimen and recommendations, and avoid self-medication.
A little anatomy and physiology
The palatine tonsils are located on the side walls of the pharynx and are shaped like large almond kernels. The second name - “tonsils” - tonsils received due to their resemblance to acorns, which are called “glandulae” in Latin. Since the Latin word for tonsils is “tonsilla,” their inflammation is called tonsillitis.
The palatine tonsils belong to the organs of the immune system and are small accumulations of lymphoid tissue 2. The part of the tonsils protruding into the pharynx has depressions (lacunae), in the walls of which there are numerous slit-like pockets (crypts)1. The surface of the crypts is the “working area” of the tonsils. Basic physiological processes take place here: immune cells, phagocytes, absorb microbes that have penetrated the tonsils, “study” them, send the received information to higher departments of the immune system, and then kill the infection1. If the microbes are very aggressive and there are a lot of them, and the immune system is weakened, an infectious inflammation of the tonsils develops - tonsillitis.
Up to contents