Good teeth are more than just an attractive smile. This is also an opportunity to live without major prosthetics for a long time. However, sometimes anomalies in the shape of teeth occur during growth, and the identification of these developmental anomalies is more important for early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Below you will find out what violations of the correct shape of teeth are, and what methods are used for their diagnosis and treatment. You can also find out how to treat your teeth quickly and painlessly in Odessa.
What is pathology
Hutchinson's teeth are a pathology of tissue development that can occur in adults after illnesses when infection penetrates into the tooth buds, be a consequence of trauma or congenital. With this disorder, the crowns of the teeth have a screwdriver shape with a semilunar notch. This area may be covered with enamel, but sometimes it is only at the corners of the tooth, and in the middle part the dentin remains uncovered.
“The shape of the crowns of the upper lateral incisors is most often disrupted.
More often, cone-shaped, spade-shaped, T- and Y-shaped, barrel-shaped incisors are identified - Hutchinson’s teeth.” Dedova L.N., Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor [1]
The most common cause is considered to be incomplete development and even absence of tooth tissue. Initially, the pathology manifests itself as minor changes in the appearance of the teeth. Depigmented areas, depressions, and grooves appear on them. Here are some features of the violation:
- The main symptom is pain in response to stimuli.
- Hypoplasia leads to the development of pulpitis, deep caries, and the formation of malocclusion.
- The cause of the problem is congenital defects and metabolic disorders in the fetus. The laying of embryonic cells occurs incorrectly due to exposure to harmful factors. If the mother suffered from rubella, ARVI, toxoplasmosis, or the pregnancy proceeded with severe toxicosis, then the risk of dental hypoplasia in the baby increases. Negative factors are also prematurity, trauma during childbirth, rickets, calcium metabolism disorders, and encephalopathy.
- Enamel hypoplasia is diagnosed on primary and permanent teeth, but more often on permanent teeth [2, 3].
In addition to the aesthetic disadvantage, Hutchinson's teeth create difficulties when eating. This affects the functioning of the digestive tract and the condition of the entire body as a whole. Non-standard-looking teeth often cause the development of psychological complexes, for example due to the ridicule of others. A qualified doctor will help you get rid of the psychological and physical discomfort associated with dental abnormalities.
Types of dental anomalies
| View | Characteristic |
| Size pathology | Macrodentia. The crown is significantly enlarged. The developmental anomaly is associated with the fusion of several rudiments into one due to hormonal imbalance. Defective units are more often located in the upper row of the smile zone. Microdentia. Excessively small units. Pathogenesis is associated with genetic predisposition. The violation affects the incisors, mainly the upper ones. |
| Anomalies of dental structure | Hyperplasia. “Pearls” are formed on the crown - formations of enamel of various shapes, 1.5 - 3.5 mm in diameter. Droplets are most often localized near the neck of the segment, or in the bifurcation zone of the root. Dysplasia. The surface of the unit is heterogeneous, thinned in places, and gray spots are present. There are many serrations on the incisors. Chipping and increased sensitivity may occur. Hypoplasia. The enamel layer is sharply thinned, sometimes absent (aplasia). Leads to premature development of inflammatory diseases of hard tissues (caries, pulpitis). Dentinogenesis imperfecta. Units are amber in color, opalescent. Enamel and dentin are fragile, susceptible to abrasion and destruction. Insufficient amelogenesis. It manifests itself as thinning of the enamel, the appearance of brown spots, and hyperesthesia to stress factors. |
| Form defect | Spine-shaped (in the form of a thorn or awl). The segments are wide at the base and sharply taper towards the periphery. Possible combination with microdentia. The surface is uneven and spotty. The pathology is characteristic of segments of the smile zone. Barrel-shaped (Hutchinson's teeth). The neck is thickened, the cutting surface has a recess in the center of which there is no enamel layer. Molar segments with a shortened surface and enamel hypoplasia, etc. |
| Growth disorder | Anomalies in tooth growth are associated with their abnormal spatial arrangement: vestibular displacement (outward); oral (inside); high or low localization; trema, diastema (gaps between units); tortoanomaly (rotation of a segment around an axis); crowding; transposition (change of place). |
| Pathology of numbers | Supernumerary (hyperdentia). Extra units. Hypodentia (insufficient quantity). Adentia (complete absence of units in the mouth). |
| Impaired eruption | Retention (retention of a unit in the jaw or alveolar process). Late eruption of incisors. Impaired eruption of paired segments. Premature eruption. |
| Abnormalities of tooth roots | Characterized by a change in the number of roots (downwards or upwards), their curvature |
Common symptoms that occur with most developmental anomalies are: discomfort in the mouth (sometimes soreness), problems with chewing food, and speech defects. Such pathologies are often accompanied by other genetic defects (cleft palate, lips, etc.).
Etiology
The development of pathology can occur for the following reasons:
- Different Rh factors in the blood of the mother and fetus, which come into conflict with each other.
- Viral, infectious diseases suffered by a woman at the beginning of pregnancy or a child in the first six months of life.
- Hutchinson's teeth may be a sign of congenital syphilis. Most often, pathology appears when the disease is hidden or asymptomatic. Late congenital syphilis is registered in children over two years of age, is rare and almost always in combination with specific symptoms (deafness and parenchymal keratitis).
- Severe, long-term late toxicosis.
- Child dystrophy, rickets (poor appetite, lack of vitamins).
- Metabolic disorders.
There are 3 degrees of development of Hutchinson's teeth:
- initial - small dark spots of pigmentation on the enamel layer of the teeth;
- middle - the surface of the enamel is covered with convex grooves and depressions;
- severe - visible deformation of the teeth.
Types and classification of malocclusions
Bite is the position of the segments at the moment of tight closure of the jaw bones. Occlusion is assessed in 3 planes:
- by crown height (vertical);
- lateral arrangement of segments relative to the jaws (transvesial);
- ratio of the length of the row and the jaw (sagittal plane).
Malocclusion can be of 2 types: skeletal and dental. In the first case, the cause of pathological closure of the elements is the non-standard size of the jaws or their position in the mouth. Dental abnormal bite is formed due to dental defects (number, size, shape, etc.).
Classification of dental malocclusions:
- Open: the segments of the top and bottom rows do not meet each other vertically. The mouth remains slightly open. Due to the defect, speech, breathing, and chewing are impaired.
- Deep. The lower crowns are significantly (more than ½ covered by the upper ones). The face takes on a flattened shape. Often leads to injuries to the mucous membrane, rapid abrasion of teeth, and defects of the temporomandibular joint.
- Distal (prognathic). Occurs due to disproportionately developed jaws (overdevelopment of the upper or underdevelopment of the lower).
- Mesial: the lower row overlaps the upper segments.
- Crossed: on one side of the jaw, the teeth are located without pathology, and on the other, the lower crowns protrude above the upper ones.
Treatment
Elimination of the consequences of the disorder is carried out in different ways depending on the patient’s age, stage of development of hypoplasia, medical history and a number of other factors:
- Prosthetics after the final formation of the permanent bite: veneers, half-crowns, crowns.
- Dental restoration using light-cured composite fillings using the direct method in one visit.
In the early stages, remineralization is an effective method, so doctors often resort to this procedure. The destructive effect of hypoplasia stops careful dental care.
Diagnosis of hypoplasia
At a late stage, the symptoms of hypoplasia become pronounced, which makes the diagnosis easier. In the initial stage, its symptoms are very similar to the development of caries - its initial and superficial types.
| Symptom | Caries | Hypoplasia |
| Location of spots | A single white spot appears near the neck of the tooth. | Numerous spots ranging from white, yellow to light brown appear throughout the tooth. |
| Condition of tooth enamel | The surface of the enamel layer remains even and smooth. | Sometimes there may be no enamel layer at all or partially; grooves and depressions are spread over the entire surface. |
| Shape of teeth | Remains unchanged. | In some types of the disease, the shape of the teeth changes, becoming barrel-shaped, the cutting edge is bent in the shape of a crescent moon. |
When the first symptoms of hypoplasia appear, you need to contact a dentist, who will clarify the diagnosis, determine the stage and form of the disease, and prescribe adequate treatment.
Preventive actions
The following measures will help reduce the risk of developing dental hypoplasia:
- Ensuring the normal intrauterine development of the child (healthy diet, giving up bad habits, caution with the use of medications, since many negatively affect the fetus, etc.).
- Timely correction of endocrine system disorders, treatment of infectious and chronic diseases in a child.
- Reducing the amount of sour and sweet foods in the child’s diet.
- Using toothpastes correctly selected by your dentist.
- Premature detection of syphilis in mothers and its effective treatment.
- Regular visits to the dentist for the prevention and timely diagnosis and treatment of dental development disorders.
Hutchinson's teeth are a pathology of dental tissue, characterized by thinning or complete absence of enamel. In the early stages it looks like caries, in the later stages it has a specific, easily recognizable barrel shape. Only a qualified dentist can diagnose such a dental anomaly. The treatment plan is drawn up individually, taking into account the specifics of the anomaly and the individual characteristics of the patient.
List of sources:
- Leus P. A. Non-carious diseases of hard dental tissues. Educational method. allowance, 2008 // URL: https://www.bsmu.by/downloads/kafedri/k_1_terstom/nekar.pdf (access date: 12/25/2020).
- Petrin A. N. Congenital and hereditary dental diseases. Medical and clinical genetics for dentists: textbook for universities, 2009 // URL: https://vmede.org/sait/?page=8&id=Genetika_stomat_yanushevish_2009&menu=Genetika_stomat_yanushevish_2009 (access date: 11/02/2020).
- Excessive number of teeth (hyperdentia, supercomponent teeth), Ran-Dent magazine: treatment and prevention of diseases of teeth and gums // URL: https://ran-dent.ru/detskie-zuby/getchinsonovy.html (access date: 11/02/2020 G.).
Forms of the disease
Experts divided hypoplasia into 6 forms:
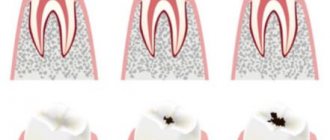
- Spotted. On the surface of the teeth (usually the incisors are the first to be affected), whitish or light brown spots become noticeable. In these places the structure of the enamel changes
- Erosive (cup-shaped). Round or oval defects of different sizes appear on the enamel, similar to a cup. Such erosion usually occurs in pairs and simultaneously affects symmetrically located teeth. In places of defects, the enamel becomes thinner in the direction of the depression or disappears completely. When the color of the spot is yellow, this means that dentin is already visible in this place
- Furrowed. The tooth is gradually covered with parallel grooves. Then the pathology spreads further to the teeth adjacent to the affected unit. The depth of the grooves depends on the severity of the disease, in the end, they appear on all teeth, the upper incisors are most damaged
- Linear and wavy shapes. Expressed by vertical grooves mainly on the vestibular part of the teeth. It seems that the enamel has become wavy
- Aplastic. Complete absence of enamel on the teeth or a very small amount of it. This is the most severe form of hypoplasia
- Mixed. With this form of the disease, all the manifestations described above are observed, which affect several teeth in the mouth. Cup-shaped and spotted forms are most often present.
Prevention
To prevent enamel hypoplasia from developing in an adult, preventive measures are necessary. These are quite simple rules, following which you can completely avoid the disease. But you will have to pay attention to prevention in advance.
Nutrition
Proper diet and hygiene are the essence of preventing hypoplasia
A large role in the prevention of hypoplasia is given to proper, nutritious nutrition. A woman should pay close attention to her diet, starting from the planning stage of pregnancy. It is necessary to ensure that the child eats fully and correctly. After switching to complementary feeding, instead of breast milk or formula, the baby’s diet must include:
- Products containing fluorine and calcium (cottage cheese, milk, cheese and others);
- Vitamin D in the form of a ready-made preparation or exposure to the sun for a sufficient time;
- Products containing vitamin C (oranges, tangerines, broccoli, spinach, cranberries);
- Foods containing vitamins A and B - seafood, legumes, carrots, poultry.
Hygiene
From the age of one, your baby should begin to be taught daily oral hygiene. At first, it may just be a game, morning and evening, especially if the baby doesn’t like brushing his teeth at all. Here parents will need imagination, and, of course, they need to set a personal example. You need to teach your child to rinse his mouth after every meal. It is necessary to visit the dental office twice a year in order to identify problems at an early stage.
Let's sum it up
What to do if the lower front teeth or upper teeth are worn out, pain and other unpleasant symptoms appear? First of all, you need to go to the dentist to conduct a thorough diagnosis and identify the exact causes of the pathology. The longer the patient ignores the presenting signs, the more severe the consequences for him. In order not to encounter this phenomenon, it is necessary to take preventive measures, especially for those at risk.
Sometimes the enamel wears away due to age-related changes. In this case we are talking about a natural process. Which group should the problem be classified into, and whether treatment should be prescribed, should be decided solely by the doctor.
Basic terms in dentistry: names and causes of inflammatory diseases of the teeth and oral cavity
It plays a vital function in the digestion process: it is responsible for grinding food and influencing its subsequent breakdown by enzymes. In addition, there is a huge number of microorganisms that create natural microflora, but are considered opportunistic. This nuance determines the fact that any dental disorders progress extremely quickly.
Among the key factors in the occurrence of dental diseases are:
- poor hygiene;
- mechanical injuries and damage;
- chronic illnesses;
- metabolic disorders and abnormalities;
- the presence of thermal irritants in the body;
- bad environment;
- hereditary predisposition.
The branch of medicine that studies the emergence and development of pathologies is called etiology. It is partially correlated with diagnostic procedures, as it helps in determining pathogenesis.
Reviews
If a child is found to have Turner teeth, his parents have no reason to panic. This is a relatively mild form of hypoplasia that can be corrected with appropriate treatment.
If your child has been diagnosed with MGE, please share your personal experience with us. How severe was the destruction of the enamel, what treatment method was used, what was the result? The feedback form is at the bottom of this page.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: enamel destruction
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
How effective are braces for diastema and are they always necessary?
Next article
What filling materials are used in pediatric dentistry?
Preventive measures
It is hardly possible to talk about a guaranteed possibility of preventing any types of hypoplasia, including Turner’s teeth.
The most common root cause of the disease - an inflammatory process in the “milk jug”, which transmits the infection to the embryo of the permanent unit - can begin in the prenatal period.
However, the risk can be minimized by regular preventive visits to the dentist, timely treatment of dental caries, and monitoring of the child’s general health, his immunity, and nutrition.
It has been established that children with weakened immune systems, who often suffer from colds and other diseases, are more susceptible to enamel hypoplasia. Therefore, strengthening the child’s general health and nutritious nutrition have a beneficial effect on the condition of his jaw apparatus.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
How to adjust sizes
Treatment of such anomalies is directly related to its specific type and severity. If the dimensions slightly deviate from the norm and the bite is not disturbed, if there is no serious aesthetic defect, you can leave everything as is. In other cases, the size of the crowns can be restored using photopolymer composites, prosthetic crowns or the installation of veneers. Sometimes the doctor has to remove one to several large teeth and then replace them with fixed dentures on implants.