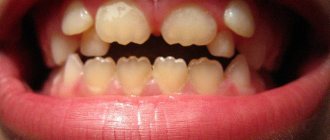
Enamel hypoplasia is the most common non-carious lesion. Its varieties are Hutchinson, Fournier, Pfluger and Turner teeth. They represent changes in the anatomical structure of the coronal part.
Histologically, the violations are also quite significant, so the teeth remain practically functional, but require certain treatment.
Crown anomaly in primary occlusion
What is tooth enamel hypoplasia?
Literally, the term “hypoplasia” can be translated as “little enamel.” This formulation fully reflects the situation, since the disease is characterized by underdevelopment or absence of areas of enamel. The opposite of hypoplasia is enamel hyperplasia, when pathological growth of tooth tissue occurs, most often manifested in the form of enamel drops. Due to phonetic similarity, confusion often arises. Hypoplasia often develops on baby teeth, which, by default, have thinner and more vulnerable enamel, but the disease can also affect molars.
Attention!
The risk of hypoplasia of the enamel of permanent teeth increases many times if at the milk stage the pathology was not corrected in time and transferred to the rudiments of the molars. Enamel hypoplasia in adults occurs much less frequently and, as a rule, is a consequence of pathologies that developed in childhood.
Elimination of hypoplasia, reliable methods and immediate measures
It is advisable to preserve the teeth of Hutchinson, Pfluger, and Fournier with the placement of an artificial crown. Minor changes can be corrected by using modern filling agents. Moreover, tissue preparation should be minimal. Help with hypoplasia has not only physiological significance, but also psychological significance. This is especially true for children and adolescents.
If there are stains on the enamel, remineralizing therapy is indicated. So if the size of pigmentation is 4-5 mm, then the procedures must be carried out within 1 year on average. In this regard, it is necessary to prepare the child for a long period of treatment.
In fact, complex remotherapy gives positive results for everyone. In addition, it is shown even in the absence of color change.
To strengthen hard tissues, the following drugs are prescribed:
- calcium gluconate solution for applications;
- sodium fluoride in the form of varnish;
- vitamins;
- antioxidants;
- natural biologically active substances.
The doctor prescribes all medications in courses every 3 months. Applications can be carried out both at home and in the clinic. Treatment is prescribed for the whole year. Systematic monitoring and conscientious implementation of all therapeutic recommendations are necessary.
Great importance is paid to personal oral hygiene. The use of fluoride toothpastes is required.
Dentists often recommend the following brands:
- President Classic;
- Silka;
- SPLAT Arktikum;
- Elmex - protection against caries;
- New pearls;
- Arbat;
- Children's pearls.
Toothpastes can be used as an application. They can be applied for 15 minutes. 2 times a day.
In case of severe changes in Pflueger’s teeth, it is possible to eliminate the anomaly by preparing and applying composite filling materials. They must have not only aesthetic qualities, but also have good adhesion, and also withstand mechanical stress.
Hypoplasia is much less common than carious lesions. However, it requires no less attention, both from the person himself and from dentists. With timely assistance, it is possible to preserve the dentition for a long time. When there is no treatment, this leads to complete destruction of the crown part and eventual loss of the dental unit.
Causes of hypoplasia
Treatment of dental enamel hypoplasia in children is complicated by the fact that this disease has a very extensive etiology. Enamel hypoplasia occurs under the influence of a number of factors that are formed both at the stage of intrauterine development and after birth.
Causes of enamel hypoplasia before birth
- Heredity is one of the main factors. Enamel hypoplasia is inherited as a dominant (X-linked) trait. Women have two X chromosomes, so a mother's hypoplasia can be passed on to her children, regardless of their gender. In men, hypoplasia is inherited only by daughters. If both parents have hypoplasia, the chances of transmitting the pathology to children increase.
- Viral and chronic diseases in the mother.
- Severe forms of toxicosis during pregnancy.
- Lack of vitamins and microelements.
- Bad habits, drug addiction and alcoholism.
Reasons for the development of hypoplasia after birth
- Prematurity and traumatic birth.
- Metabolic disease.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system in children.
- Hemolytic disease.
- Infectious diseases.
- Anemia.
- Complications after taking antibiotics.
- Dental diseases.
- Damage to the rudiments of permanent teeth. This factor provokes the development of hypoplasia of the enamel of molars in children.
- Vitamin deficiency and unhealthy diet.
Not all of the above factors are the root cause of hypoplasia, but each of them contributes to the development of the disease to varying degrees.
Damage to primary occlusion
Diagram
Pathology is formed during the prenatal period. The main factor here is the serious illness of the pregnant woman. Baby teeth suffer much less often than permanent teeth. However, nowadays such cases have become more frequent. This is associated with a significant reduction in perinatal mortality.
Even in the first weeks of life, the occurrence of systemic diseases in a child can provoke the occurrence of hypoplasia. Abnormalities are more common in the incisors and canines of the upper jaw. This is why such anomalies as Hutchinson, Fournier and Turner teeth are so common.
Deciduous incisors undergo changes most often if a pregnant woman has suffered from diseases such as toxoplasmosis, rubella, or suffered from toxicosis. Hypoplasia is also observed in premature babies who have a history of birth trauma, congenital allergies or hemolytic jaundice.
Anomalies develop in utero at approximately 25-30 weeks of pregnancy. Sometimes this process occurs within 1 month of life.
Forms of enamel hypoplasia
Hypoplasia is divided into two types: systemic and local. They differ in both symptoms and etiology.
Systemic enamel hypoplasia
With systemic enamel hypoplasia in children, a large area of the dentition is affected. It is often called congenital and genetic, since it occurs immediately with the appearance of baby teeth. May cause changes in tooth shape, especially in the incisal area. The disease has several forms and varieties.
- Spotted.
Light spots appear on the enamel, but its structure is not damaged. - Erosive enamel hypoplasia.
A more severe form, in which round-shaped depressions appear on the surface of the enamel. - Furrowed.
Depressions in the form of large or small grooves, in some cases may resemble waves. - Mixed.
The simultaneous manifestation of two or more forms is observed.
Local enamel hypoplasia
Local enamel hypoplasia is localized, that is, it affects one or two teeth. Most often acquired and occurs against the background of inflammation and damage to the buds of the teeth. It appears in the form of spots of various shapes, pits and grooves. If left untreated, the disease affects the deeper tissues of the tooth and provokes the development of caries.
Aplasia or absence of enamel
The most severe form of the disease, which some experts distinguish separately. It can be either local or systemic (less commonly).
Dental hyperplasia in children: causes and treatment
Dental hyperplasia externally looks like small growths on the enamel, formed due to excessive tissue formation.
In children, the defect is detected during examination by a dentist or by radiographic methods. Tubercles measuring 3-5 mm are located in the neck of the tooth, near the roots and are often covered by the gums. There is also localization on the crown. The causes of hyperplasia are not fully understood. Among the possible options for the formation of an enamel defect:
- improper development of the rudiments of mammary and permanent units;
- pathologies of dental tissue growth;
- metabolic disorders;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- heredity.
The incidence of hyperplasia in children is less than 1%.
The defect does not bother the patient and therefore does not require special treatment. If there are “enamel drops” on the surface of the chewing teeth, the doctor will recommend fissure sealing to reduce the risk of caries.
If the localization of the anomaly is unsuccessful and the gums are injured, the pediatric dentist will carefully remove the tubercles with special burs, treat the enamel with remineralizing compounds, and return the dental crown to its anatomically correct shape.
Diagnosis of enamel hypoplasia
- Visual inspection. Hypoplasia always has external manifestations, so the first conclusions can be drawn.
- Anamnesis collection.
- Analyzes and studies to identify the root cause.
Differential diagnostics are carried out separately in order to make the correct diagnosis and exclude diseases with similar symptoms. For example, to exclude suspicion of caries, vital staining with methylene blue is performed (areas with hypoplasia are not stained, unlike carious ones). Fluorosis and enamel hypoplasia can also have similar symptoms, but the nature of these diseases is different. Fluorosis occurs due to excess fluoride in the body. Spots may appear on the surface of the enamel, but unlike hypoplasia, they have a characteristic brown tint.
Composition and structure of tooth enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the strongest substances in the human body and completely covers the crown of the teeth. Under the layers of enamel there is dentin and a pulp chamber with a neurovascular bundle. A mixture of increased hardness made from collagen and calcium fibers (also called dental cement) covers the entire surface of the root system.
Composition of tooth enamel:
- 96% minerals, mainly calcium phosphate in the form of hydroxyapatite crystals
- 2% organic matter
- remaining 2% water
Strength of tooth enamel:
- Surface layers are the most durable and provide protection
- Cervical area and sides - density decreases
The average density on the chewing surface is 1.5 - 1.6 mm.
Treatment of enamel hypoplasia
Treatment of dental enamel hypoplasia in children is carried out in two directions. Firstly, it is necessary to eliminate or correct the main factor that provoked the development of the pathology. Of course, if the disease was inherited, it is difficult to do anything about it, but in most other cases it is necessary to minimize the influence of concomitant diseases and pathologies. The treatment method for manifestations of hypoplasia depends on the form and severity of the disease.
- Hypoplasia of the enamel of primary and molar teeth in the stained stage, when the enamel structure is not damaged, is treated conservatively. Remineralization, fluoridation, resurfacing and whitening are the main procedures that restore the aesthetics of a smile.
- Erosive and grooved hypoplasia affecting dentin is treated with filling with composite materials.
- Severe cases of hypoplasia, in particular aplasia, require orthopedic treatment. The most effective methods for treating enamel hypoplasia of permanent teeth are the installation of crowns and veneers.
Damage to permanent dentition
The higher the incidence rate in childhood, the greater the possibility of dental anomalies. Half of the children who had chronic diseases, especially of the endocrine system, subsequently experienced anatomical changes in the crowns.
In addition, a special role is played by:
- gastrointestinal problems;
- toxic dyspepsia;
- congenital syphilis;
- acute infectious diseases;
- rickets;
- brain disorders.
It is noted that 40-60% of hypoplastic changes occur already in the first 9-10 months of life. During this period, the protective properties of the body are still weakly expressed. The child’s adaptive and compensatory capabilities are not able to withstand aggressive factors of the internal and external environment.
Hypoplasia in permanent dentition
In permanent teeth, the first molars are the first to suffer. The lesion is observed primarily on tubercles and convex surfaces. By 8-9 months, canines and incisors are formed.
If before this period the child suffered from some serious illnesses, then the risk of hypoplasia in the form of Hutchinson’s and Fournier’s teeth is quite high.
Characteristic symptoms
The main symptoms of the pathology include a change in the color of the enamel: white spots appear on the outer surface. Such changes do not cause unpleasant feelings. In addition, the surface of the teeth in the affected areas is smooth and non-pigmented.
More severe forms of hypoplasia are characterized by the presence of pronounced depressions. At the initial stages, the lesions have a natural shade, but over time they become pigmented. Sometimes on such teeth you can notice deep grooves located horizontally or vertically. Despite the hyperpigmentation of certain areas, the integrity of the enamel is not compromised.
Aplasia (complete absence of enamel) is characterized by pain upon contact with any irritant. In addition, aplasia is associated with underdevelopment of dentin. This leads to the fact that the teeth gradually begin to change shape.
Signs
Clinical symptoms of the development of pathology are:
- the appearance of pigmentation, changes in shade to yellow-brown;
- pinpoint depressions on the surface of the coronal part;
- absence of enamel (complete or partial);
- curvature, incorrect course of development of the unit.
Patients complain of the development of defects, violation of external aesthetics, increased sensitivity to temperature and other stimuli. The changes are irreversible and can only be eliminated using various restoration methods. Treatment is mandatory, as it leads to worsening of the condition, development of caries, tooth decay and malocclusion.
Deep fluoridation of tooth enamel
Deep fluoridation involves saturating tooth enamel with various minerals that prevent the development of caries. Fluoride-containing substances prevent the destruction of tooth enamel.
Main indications for the procedure:
- To prevent caries
- After installing the filling (to increase its service life)
- High sensitivity of teeth
- General strengthening of tooth enamel
- The need for bleaching and stain removal
- Caries in the active stage
Contraindications:
- Individual intolerance to fluoride-containing components
- Epidemic fluorosis
The procedure is completely safe and painless, but fluoride oversaturation is possible. To avoid this, stop using fluoride-containing medications, including toothpastes, before the procedure.
Main stages of deep fluoridation:
- Complete cleaning of teeth from tartar and plaque (professional cleaning of the oral cavity)
- Using special preparations, the oral cavity is dried with a warm air stream.
- A special sealing agent is applied and dried after a few minutes.
- Teeth shading is carried out - surface treatment of tooth enamel with a solution of copper and calcium hydroxide
Deep fluoridation of tooth enamel is an effective procedure, but its quality is inferior to enamel implantation with Innodent.
Professional methods for restoring tooth enamel
In most cases, damaged enamel requires professional restoration at a dental clinic. There are many methods, we will look at the most popular ones, as well as an innovative method of restoring teeth using the drug Innodent Repair .
Remineralization
Remineralization ensures restoration of the structure of tooth enamel by stabilizing the balance of minerals present in tooth enamel. Professional remineralization in a dental clinic is carried out using products and preparations containing fluoride and calcium.
Main indications for the procedure:
- Loss of natural shine on teeth
- Lack of surface mineralization
- Development of carious enamel damage affecting the internal tissues of the tooth
- Toothache when eating high or low temperature foods, as well as sweet and sour foods.
The remineralization procedure occurs by coating the enamel with a special preparation containing the necessary complex of minerals necessary to maintain the integrity of the teeth’s incisors.
As a rule, it includes: ionized fluorides, components that increase the protective properties of enamel, phosphorus, zinc and calcium.
Erosion
This is the most destructive type of tooth enamel disease. Erosion is a constantly ongoing process of tooth destruction, when first the enamel itself is destroyed, then the gum tissue. Over the years, the depth of erosion increases, the affected area darkens and the tooth changes color. Erosion can develop rapidly or last for several years.
Causes of erosion:
- using hard brushes to clean your teeth;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- the use of medications that destroy the layer of tooth enamel;
- consuming foods and drinks with excess amounts of vitamin C.
Treatment of enamel erosion is long-term and requires patience and perseverance from the patient. The course of treatment involves demineralization of the enamel and filling of the affected teeth, so at the very first signs it is best to go to specialists who will provide proper assistance.
A timely visit to the Family Dentistry Center clinic for the treatment of tooth enamel diseases will allow you to provide professional dental care without pain. And may your teeth be healthy!