Who is the study for?
The main indication for ultrasound examination of the salivary glands is the presence of any complaints in the patient. Most often, patients come to the doctor with the following problems:
- sharp pain in the submandibular or parotid area;
- local or general hyperthermia (increased temperature directly in the area of the lesion or in the entire body as a whole);
- increase in the size of the salivary glands;
- dry mouth (xerostomia);
- the presence of compactions (tumors, stones) near the salivary glands.
If the above symptoms are present, as well as after a visual examination, palpation examination and history taking, the doctor, in addition to laboratory tests, refers the patient to an ultrasound scan. The method is used if it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis for such pathologies as:
- inflammatory diseases of the salivary glands (acute and chronic sialoadenitis, viral and bacterial);
- adenoma;
- salivary stone disease;
- tonsil damage;
- tumor neoplasms (malignant and benign);
- individual anatomical anomalies;
- enlargement of nearby lymph nodes;
- dystrophic lesions of organ tissue.
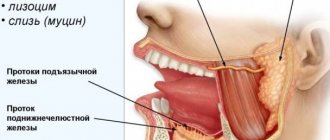
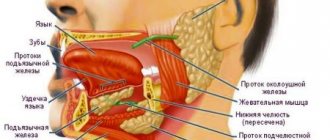
During the study, specialists can assess the condition of the group of large salivary glands: parotid, sublingual, submandibular.
Treatment
Having established the causes of inflammation of the tongue, the specialist prescribes treatment. In case of inflammation of the salivary glands, the purulent contents are initially removed, then antibacterial agents are injected into the ducts, and the patient is also prescribed antibiotics or sulfonamide drugs orally.
As a rule, therapy is accompanied by rinsing (in each case the doctor selects the optimal solution) and physiotherapy: UHF, Sollux and others. For fever and general malaise, paracetamol or ibuprofen is prescribed.
Surgical treatment methods are used extremely rarely. The operation is performed if there are stones in the duct and they cannot be removed in any other way.
If you experience unpleasant symptoms or discover inflammation or swelling under your tongue, do not look for what it might be. Go to a qualified dentist, he will examine the oral cavity, make a diagnosis, and prescribe adequate therapy. Perhaps pain in the sublingual space is a symptom of another serious disease and consultation with an appropriate specialist will be required.
Monitor the condition of your teeth and mucous membranes, visit the dentist regularly, promptly treat inflammation of the ENT organs and ARVI - such preventive measures will minimize the possibility of inflammation and pain.
How to prepare for the procedure
Ultrasound of the salivary glands is an absolutely safe and painless manipulation, for which the patient does not require special preparation. Patients of almost any age tolerate the procedure well, without showing any anxiety before and during its implementation, and therefore it does not require premedication (pre-administration of sedative medications) even in children.
On the eve of the visit to the specialist (about 3-4 hours in advance), the patient is advised to refrain from eating, and immediately before the examination he needs to thoroughly clean the oral cavity.
ALL-RUSSIAN CENTER FOR EYE AND PLASTIC SURGERY
On the pages of this site you can get acquainted with the scientific and medical center of federal significance, located in a picturesque corner of the city of Ufa. The basis for the creation of the Center was the development in Ufa of an innovative technology for tissue transplantation, protected by the Alloplant trademark. This is one of the rare cases when a fundamentally new treatment method has led to the opening of a federal scientific institution. The Center received All-Russian status in 1990. Since 1983, our team has been known as the Republican Laboratory of Tissue Conservation. The first Alloplant biomaterial transplantation operation was performed in 1973.
The All-Russian Center for Eye and Plastic Surgery today is a well-known scientific institute of regenerative surgery in the country and abroad. As is known, methods of regenerative surgery are being developed in various scientific and medical centers on the basis of cell, tissue and organ transplantation. Our institution creates and implements methods for the regenerative restoration of anatomical structures based on tissue transplantation. Donor tissues subjected to deep physical and chemical processing are commonly called biomaterials. Tissue transplantation fully meets the requirements of Russian and international legislation, is much cheaper than cellular technologies in terms of costs and can be implemented in both multidisciplinary and specialized medical institutions.
Our Center has all the necessary structural units in the field of transplantology from experimental development to clinical implementation.
It includes a scientific department of morphologists with laboratories of electron and laser microscopy, immunohistochemistry; a multidisciplinary tissue bank with a tissue conservation laboratory, a radiation sterilization unit for biomaterials and a laser modeling complex. The clinical divisions of the Center include specialized ophthalmic surgery departments, associated services of otorhinolaryngology and plastic surgery. Services for neurophysiological and psychological rehabilitation of patients are separated into a separate complex.
It is necessary to dwell separately on the systemic effect of transplants, first noticed by Academician V.P. Filatov and called biostimulation. Our studies have shown that Alloplant biomaterials, acting through the immune, nervous and endocrine systems, make it possible to rehabilitate patients with severe damage to the musculoskeletal system, peripheral and central nervous system, etc. For the clinical implementation of this area, a special department of biophysical methods of diagnosis and treatment “Aura” has been created.
All presented laboratories and departments form a single scientific, medical and production complex within the Center, within which the treatment and rehabilitation technologies created here are constantly being improved.
More detailed information about each service can be found on the corresponding pages of the site.
To quickly find the necessary sections of the site, use the Navigator - a visual menu. it is available on all pages of the site - just click on the Navigator icon.
An exceptional property of the Alloplant biomaterials we created was the ability to stimulate the regeneration of various tissues and anatomical structures. The development of the described biomaterials required solving a whole complex of scientific, organizational, technological and production problems. These include the technology of physical and chemical processing of donor tissues, which makes it possible to reduce the immunogenicity of the final biomaterial and achieve its decontamination while maintaining bioplastic properties. The technological equipment of our production was created through integration with the Russian Federal Nuclear Center (Sarov). Today we actively cooperate with this wonderful and highly respected scientific institution, constantly improving methods of selective radiation sterilization of biomaterials and their laser modeling. By creating biomaterials of various biochemical composition, spatial structure and biomechanical properties, the Center’s team solved many applied problems of regenerative medicine.
In particular, it was possible to achieve regeneration, both experimentally and in the clinic, of various types of epithelial cover, connective structures, blood and lymphatic vessels, peripheral nerves, optimize osteogenesis, etc.
As a result of many years of scientific and innovative activity of our Center, the technology of regenerative medicine based on Alloplant biomaterials was created and introduced into industrial and clinical practice.
Over 95 types of Alloplant biomaterials are used in clinical practice in more than 600 clinics in all regions of the Russian Federation and CIS countries.
The center cooperates widely with a number of scientific and medical institutions and universities in Russia, which ensures the introduction of biomaterials into various fields of medicine. One of the important activities of the team is training doctors in Alloplant transplantation technologies under postgraduate professional education programs.
With best wishes, Chief Scientific Consultant of the All-Russian Center for Eye and Plastic Surgery, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Professor Ernst Muldashev
How to do an ultrasound of the salivary gland
The examination can be carried out in 2 ways: from the oral cavity and from the external surface. The procedure does not take much time (it usually takes no more than 20-30 minutes to complete). During an ultrasound scan of the salivary glands, the patient does not feel any pain or other discomfort.
During the examination, the patient takes a supine position, places his head on a specially prepared pillow and tilts it slightly back (or turns it to the left or right, depending on the location of the gland being examined).
If the parotid gland is being examined, the device's sensors are placed on the parotid area. When studying the sublingual and submandibular glands - into the oral cavity (sometimes the extraoral method can be used).
Parotid gland
Parotid gland
(lat.
glandula parotidea
) - paired salivary gland. Along with the submandibular and sublingual glands, the parotid glands belong to the so-called major salivary glands. The parotid glands are the largest of all the salivary glands. The mass of the parotid gland is approximately 20–30 g. The parotid glands are grayish-pink in color and irregular in shape. The parotid glands are located on the lateral surface of the lower jaw and the posterior edge of the masticatory muscle, under the skin, in front and below the auricle. From above, the parotid gland approaches the zygomatic arch, from below - to the angle of the lower jaw, from behind - to the anterior edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the mastoid processes of the temporal bone. Behind the lower jaw, the parotid gland reaches the stylopharyngeal, stylohyoid and styloglossus muscles, starting from the styloid process. Secretes mixed saliva.
The excretory duct of the parotid gland (stenon duct) opens on the side wall of the vestibule of the oral cavity at the level of the second upper molar.
The parotid gland is surrounded by the parotid-masseteric fascia. The density of this fascia is uneven: mostly dense, it has loosened areas covering the upper and medial surfaces of the gland.
Sometimes there is an accessory parotid gland above the Stenon duct, the excretory duct of which merges with the Stenon duct.
On the GastroScan.ru website in the “Literature” section there is a subsection “Oral diseases associated with gastrointestinal diseases”, containing publications for healthcare professionals on this topic.
Parotid gland The Nomenclature of Medical Nomenclature of Medical Services approved by Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated October 13, 2022 N 804n provides for the following services:
- Removal of formations of the parotid salivary gland with isolation and preservation of the branches of the facial nerve, service code A16.07.064
- Removal of the salivary gland, service code A16.07.067
- Removal of the parotid salivary gland with isolation and preservation of the branches of the facial nerve, service code A16.07.067.005
- Subtotal resection of the parotid salivary gland, service code A16.07.067.006
- Resection of the parotid salivary gland, service code A16.07.080
- Resection of the parotid salivary gland with a reconstructive plastic component, service code A16.07.080.001
- Resection of the parotid salivary gland with neurolysis of the trunk and/or branches of the facial nerve using microsurgical technology, service code A16.07.080.002
Figure used under CCA3.0 license, taken from “Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014”. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436. Adapted. Back to section
Ultrasound of the submandibular salivary gland
The norm for an ultrasound examination of the salivary submandibular gland corresponds to the following parameters:
- Fine-grained homogeneous structure.
- The edges of the glands are smooth.
- The excretory duct is well visualized, small in size, without signs of blockage.
Determining the normal size of the submandibular glands is not particularly difficult precisely because of its clear contours. During inflammation (sialoadenitis), the organ increases in size and its edges become blurred.
Ultrasound of the sublingual salivary gland
Normally, the sublingual salivary gland has smooth, not very clear contours. They have a homogeneous structure, but echogenicity (the ability to reflect ultrasound) may be slightly increased. In the absence of any diseases, the device will not show the ducts of this organ.
The shape of the sublingual salivary glands displayed on the device screen changes depending on where the sensor is placed. When located in the chin area, the glands have oval contours. If the device is applied parallel to the body of the lower jaw, the glands will be slightly elongated.