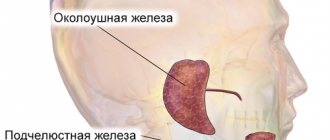
Salivary glands – increased salivation and dry mouth
There are a number of tips to help keep
your salivary glands healthy:
First, you need to drink plenty of water. Secondly, you should use chewing gum that does not contain sugar. And thirdly, it is necessary to suck on lollipops, which also do not contain sugar.
In certain cases, your dentist may recommend gargling with artificial saliva. The above drug is sold in spray or liquid form. You do not need a prescription to purchase it, but use it several times a day. However, artificial saliva does not contain proteins, minerals and other necessary elements that are contained in natural salivary fluid. Thus, the above drug will simply be useless for digestion.
Content
- Causes of nausea in a child Nausea due to “nerves”
- "Toxic" nausea
- Nausea caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Situations when a child complains of nausea are not uncommon, especially at an early age. Every parent has encountered this unpleasant phenomenon at least once.
Nausea refers to discomfort in the stomach and epigastric region. The logical conclusion of this condition is vomiting, that is, the “evacuation” of food and bile from the stomach. Usually accompanied by symptoms such as increased salivation, pale skin, decreased temperature and blood pressure, sweating and even fainting. It can be either episodic or permanent (depending on the reasons).
Excess saliva in the mouth
By and large, a large amount of saliva is not a problem if the condition is not systemic. Typically, the amount of saliva you produce depends on what you drink or eat. In a healthy person, the body easily eliminates excess salivation. In general, excessive salivation is caused by overactivity of the salivary glands, as well as if a person has a disturbed swallowing process.
If you eat a spicy dish during your lunch break, your body will begin to intensively secrete saliva. This is because the taste buds on the tongue help increase the volume of fluid produced. For a visual example, you can put something sharp on your tongue. After a few moments, you will be able to feel a rush of saliva into your mouth. Also, sour foods affect excessive salivation. Accordingly, you can reconsider your diet if you are concerned about excess salivary secretion. In addition, the above symptom may occur as a result of certain diseases and abnormalities, as well as due to the use of special medications.
The role of saliva
As experts explain, saliva performs several important functions at once: it washes away food debris from the teeth, softens food, facilitating its subsequent digestion, and even supplies teeth with calcium, strengthening them. Indeed, chronic dry mouth is often a harbinger of caries. However, our body must produce exactly as much saliva as is necessary to ensure these important processes, and not a drop more. Drooling and the need to constantly swallow saliva can be signs of increased saliva secretion, which can cause a lot of discomfort.
Diseases that cause increased salivation
Experts note a number of diseases that cause our salivary glands to work hard. Among them: central and peripheral paralysis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, mental development disorders, abnormally large tongue, Parkinson's disease, pregnancy (severe toxicosis), poisoning, stroke, rabies.
In addition, there are a number of drugs that cause excess salivary fluid. These include: drugs against schizophrenia, antiepileptic drugs, as well as medications prescribed to patients undergoing radiotherapy. The common medical term for excess salivation is sialorrhea or hypersalivation.
Nausea and vomiting with coronavirus
Severe complications and high mortality with COVID-19 force us to more carefully study the first symptoms of the disease. The difficulty lies in the fact that the virus rapidly mutates, and the clinical manifestations of the disease also change. In 2022, typical symptoms of coronavirus infection were fever, loss of smell and taste, muscle pain, and only then a cough. Only some patients experienced nausea and vomiting a little later. In 2022, the majority of cases are caused by the Indian strain of COVID-19, which is characterized by higher infectiousness and a “stomach” syndrome. Against the background of fever and catarrhal symptoms (runny nose, sore throat, cough), every third patient with coronavirus experiences nausea/vomiting and pain in the stomach. A little later, diarrhea and hearing problems appear, and the sense of smell disappears less often.
The "Delta" strain most often affects young people and children. And previously worked out treatment regimens give a noticeably less effect. This is why vaccination of the population, including those who have previously had coronavirus, is so important. Although a two-time vaccination does not completely eliminate infection, it will help avoid severe disease, complications and death. Among the sick, the percentage of vaccinated people does not exceed 1%.
Important! Nausea after vaccination against coronavirus occurs in every tenth vaccinated person. Vomiting is a rare side effect. All unpleasant consequences of the vaccine disappear within 3 days.
Excess saliva, or how to prevent it
By and large, there are three types of therapy that are used to treat increased salivation. These include Botox injections, surgical treatment and medications that are available only by prescription. It all depends on the factors that caused the disease. It is clear that the simplest thing will be to prescribe certain medications. Typically, the above drugs will include scopolamine and glycopyrrolate. Side effects include increased heart rate, trouble urinating, drowsiness, and blurred vision.
For severe forms of drooling, specialists resort to Botox injections into the salivary glands (one or more). The treatment is considered safe, but its effect only lasts for several months. And only in very severe cases do doctors resort to surgery. During surgery, the salivary glands are removed or the direction of the excretory ducts is changed.
With the help of surgery, you can permanently get rid of increased salivation. Salivary glands – increased salivation and dry mouth
Hypersalivation, treatment
To successfully eliminate hypersalivation, treatment must begin with a search for the true cause of the pathology - only an accurate diagnosis will allow one to prescribe effective methods of therapy. In the case where high salivation is caused by diseases of the oral cavity, treatment by a dentist will be necessary: examination and sanitation of the oral cavity, anti-inflammatory therapy.
If the pathology is caused by disturbances in the functioning of other systems (digestive, nervous, endocrine), joint supervision of the dentist and related specialists - gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, neurologist will be required. In any case, even if the problem is caused by some kind of systemic failure in the body, successful therapy will require high-quality sanitation of the oral cavity with the elimination of all infectious and inflammatory foci.
In some cases, hypersalivation is treated with drugs that reduce salivation. You can take such drugs only on the recommendation and under the supervision of a doctor; moreover, you need to remember that sometimes they cause unwanted side reactions. In addition, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures, massage and facial gymnastics, rinsing - all these methods are usually used in combination. In particularly difficult situations, surgical intervention to remove large salivary glands is possible, but surgical treatment is used only as a last resort.
How to reduce salivation with folk remedies
If the examination does not reveal serious diseases, traditional methods can be used to reduce salivation. In this case, it is necessary to stop smoking and maintain oral hygiene. An important component of treatment is a diet with the complete exclusion of fatty, smoked, fried, canned foods, and a decrease in carbohydrate intake.
You can temporarily combat increased salivation with lozenges or sugar-free chewing gum. Rinsing the mouth after eating until symptoms disappear with the following mixtures, infusions and decoctions is very effective:
- 1 tablespoon of water pepper extract per 1 glass of warm water;
- 25 drops of shepherd's purse tincture per 50 ml of boiled water;
- Brew 2 tablespoons of mashed viburnum berries with 1 glass of boiling water, leave, strain;
- Pour 2 slices of lemon into 1 glass of warm water and leave.
Causes of nausea in a child
Based on their origin, the causes of nausea can be divided into several categories.
Nausea in a child due to “nerves”
The central nervous system is involved here. The condition occurs when:
- head injuries and concomitant concussions;
- hypertensive or hypotensive crisis (sharp increase or decrease in blood pressure). This phenomenon is not uncommon in children during adolescence, when the body experiences hormonal overload, and surges in blood pressure occur quite often. Vomiting may provide relief, but not for long;
- encephalitis (inflammation of the membranes of the brain);
- the presence of benign neoplasms in the brain (slowly progressing and not metastasizing);
- meningitis (inflammation of the brain);
- malignant tumors of the brain, cerebellum;
- "sickness" in transport. This condition is associated with weak functioning of the vestibular apparatus. It may disappear completely with age. If your child is prone to such conditions, you should not travel long distances, and you should always have antiemetics with you. The peculiarity of this type of nausea is its suddenness. Vomiting does not bring relief, after it the condition may even worsen. Source: Lilenko S.V. Motion sickness in children and adolescents: pathogenesis, symptoms, prevention and treatment // Russian Pediatric Journal. 2016; 19 (1):49-54. DOI 10.18821/1560-9561-2016-19 (1)-49-54
If a child experiences repeated nausea without fever (or with low temperature) and diarrhea or without vomiting, there can be a variety of reasons. Such conditions are reasons to immediately consult a doctor. With timely treatment, the prognosis is generally favorable.
"Toxic" nausea
It is associated with the presence in the body of toxins of various origins that circulate through the circulatory system:
- The most common cause of this ailment is poisoning from stale foods that contain E. coli. You can also be poisoned by various poisonous plants (mushrooms) or by exceeding the permissible dose of medication. Poisoning in a child, in addition to nausea, causes fever and abdominal pain, diluted stool; Source: E.O. Komarovsky Handbook of sensible parents. Part 2. Emergency care. Eksmo-Press, 2011
- renal failure. It can be caused by a number of diseases - from congenital insufficiency to acquired pathologies. If the kidneys do not perform their function properly, an excess amount of toxins appears in the body, causing permanent nausea;
- liver failure. The liver, like the kidneys, performs the function of removing toxins. Liver cell destruction (which can be acute or chronic) also causes occasional nausea in children;
- various types of benign and malignant tumors;
- thyrotoxicosis (associated with dysfunction of the thyroid gland) - poisoning of the body with hubbub.
Nausea caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
- gastritis – inflammation of the mucous membranes of the stomach. Nausea appears after eating and may also be accompanied by a burning sensation and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, heartburn;
- taking certain medications (for example, antibiotics). You should carefully study the side effects of the medicine, and if such symptoms appear, ask your doctor to prescribe another drug;
- duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum);
- pancreatitis – inflammation of the pancreas. The child experiences nausea after eating. May be accompanied by bitterness in the mouth, a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium, bloating;
- appendicitis. One of the signs of inflammation of the cecum, in addition to pain in the side, is periodic nausea. If you suspect appendicitis, you should immediately call an ambulance;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum - the formation of wounds on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract;
- cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) and cholelithiasis. Accompanied by a feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- tumors of the gastrointestinal tract;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract (natural movement of food and feces through the digestive system). It often occurs due to a foreign object swallowed by a child;
- congenital pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
If a child periodically experiences nausea, this is a serious reason to contact a pediatric gastroenterologist, who will prescribe tests. The sooner treatment is started, the more favorable the medical prognosis will be.