- Facial neuritis is an inflammatory disease that causes partial, unilateral paralysis or paresis of the face.
The facial nerve is responsible for contractions of facial muscles and consists primarily of motor fibers. It is one of twelve paired cranial nerves. It begins in the brain and, branching, innervates the face. Its inflammation can occur both at the base (in the core area) and throughout, involving one or more branches. Depending on this, the symptoms of the disease vary.
In most cases, treatment of neuritis of the facial nerve is carried out using conservative methods, and only in the most severe cases (for example, with injuries with a complete rupture of the nerve canal), if therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment is used.
At the Tibet Clinic, treatment of neuritis of the facial nerve is carried out without surgery, using reflexology and physiotherapy. Positive results are achieved in 97 - 98% of cases.
As a result of treatment, contractions of the facial muscles and facial symmetry are restored, spasticity and other symptoms disappear, and the inflammatory process is stopped. These results are long-term and persistent.
Information about the disease
The facial nerve is responsible for ensuring the movements of facial muscles, the lacrimal gland, the tensor tympani muscle, and also innervates the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. It leaves the skull in a narrow canal located deep in the temporal bone. The slightest swelling in this area leads to compression of the fibers and the development of corresponding symptoms.
The pathology most often occurs in middle-aged people, who often neglect preventive measures due to the high pace of life. The peak incidence occurs in the cold season, since low temperatures are one of the provoking factors.
Make an appointment
Dermatillomania
Neurosis of the face and scalp can manifest itself in a behavioral disorder such as dermatillomania.
Its main manifestation is scratching the skin of the face and head, not because of itching, but because of dissatisfaction with its appearance. This also includes an obsessive zeal to squeeze out pimples, scratch off scabs, and pull out hair. Self-injurious actions cause a short-term feeling of pleasure, followed by feelings of shame, frustration, and dissatisfaction.
The face of such patients is covered with scars and scars due to constant trauma to the skin. This process is uncontrollable and can occur at any time of the day. But most often traumatic actions are carried out in front of a mirror.
Symptoms of the disorder also include the habit of biting the lips and mucous membranes of the cheeks. Patients are not deterred by the prospect of redness, bleeding, and scarring of the skin. They repeat the ritual day after day. It lasts from a few minutes to an hour.
Such actions can be provoked by feelings of fear, anxiety, and close examination of one’s skin because there is nothing to do.
Dermatillomania has been described as a state of addiction. It begins with concentrating on what the patient thinks is a skin defect. Gradually, attention is increasingly focused on this detail. A person begins to think that he is sick with something serious. This provokes irritability and nervousness in him, leading to obsessive actions.
The root cause of the disease is rooted in the psychological state of a person and lies in self-dissatisfaction, anger, feelings of shame and malice. Traumatic rituals are a way of punishment, self-flagellation.
Treatment of this pathology requires the intervention of a psychotherapist and a dermatologist.
The main method of treating addiction is psychotherapy, in particular cognitive behavioral therapy.
Yoga, physical exercise, relaxation procedures, as well as any hobby that absorbs a person and helps redirect attention will help reduce anxiety, distract and relax.
The help of a dermatologist is necessary to eliminate skin lesions in order to prevent infection and reduce the degree of dermatological defect.
Causes
Depending on the cause, the following forms of facial nerve neuropathy are distinguished:
- idiopathic: the cause of paralysis remains unidentified (the most common variant of the disease);
- infectious: pathology occurs against the background of infectious damage to nerve fibers due to herpes, tuberculosis, mumps, syphilis and some other diseases;
- otogenic: is a complication of inflammation of the middle ear or mastoid process;
- traumatic: neuropathy develops against the background of traumatic brain injury;
- ischemic: the disease is associated with impaired blood flow and decreased oxygen supply to nerve fibers.
The risk of pathology increases significantly in the following situations:
- for metabolic disorders, including diabetes mellitus;
- with advanced forms of arterial hypertension;
- during pregnancy, especially with severe toxicosis.
The triggering factor for the development of pathology is often hypothermia.
Prerequisites for the occurrence of neuritis
Causes of Bella's Palsy:
- Genetics. One of the reasons for the development of Bella syndrome is a narrow canal of the facial nerve, which is inherited.
- Alcoholism and drug abuse.
- Necrosis of facial tissue due to severe hypothermia.
- Oncology.
- Plastic surgery.
The following prerequisites will help determine the development of pathology:
- Noticeable weakening of the facial muscles, inability to control one or another muscle.
- Difficulty closing the eyes completely. This pathology is called lagophthalmos.
- Increased sensitivity to loud noises.
- Dulling of taste buds.
- Unreasonable tearing of the eyes or, conversely, their excessive dryness and redness.
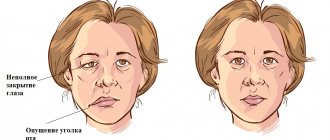
- There is noticeable facial asymmetry.
- Paralysis of parts of the face or individual muscles.
- Swelling of the face.
- Difficulty controlling salivation.
- Jaw dropping.
Paralysis of the facial nerves, or so-called Bella syndrome, is characterized by slow progression, thanks to which it is possible to determine the development of the pathology and take the necessary treatment measures in a timely manner.
Symptoms
Symptoms of facial neuropathy make it possible to immediately suspect the disease. Signs arise from the affected nerve. Patients note:
- acute pain: it usually begins in the ear area and gradually spreads throughout the face and begins to radiate to the occipital region;
- intense lacrimation, less often dry mucous membranes of the eyes;
- discomfort or ringing in the ear due to sharp sounds;
- disturbance of the sense of taste in the anterior parts of the tongue.
As the disease progresses, signs of damage to the motor fibers of the nerve appear:
- smoothness of skin folds, especially nasolabial folds;
- swelling of the cheek when exhaling or trying to pronounce a consonant sound;
- lack of complete closure of the eyelids, rotation of the eyeball upward and outward (lagophthalmos);
- leakage of fluid from the corner of the mouth;
- food getting stuck between the gum and cheek when eating;
- limitation of facial expressions: the patient cannot frown or smile.
If the cause of neuropathy is an infectious process, the characteristic signs are accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication:
- high body temperature;
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- weakness.
Symptoms of neuralgia
- Facial pain (prosopalgia). A characteristic sign of neuralgia. Sharp and sudden, reminiscent of an electric shock. Usually lasts from 5 to 15 seconds, is paroxysmal in nature and can occur at any time. During periods of remission, the number of attacks decreases. Most often, pain occurs in the area of the cheekbones and lower jaw (both right and left), and can be localized in almost all areas of the face.
- Impaired sensitivity. A severe form of neuralgia can lead to partial or complete loss of sensitivity of the skin.
- Nervous tic of the eyelid (nystagmus), spasms and twitching of facial muscles.
- Loss of coordination and motor skills are rarer manifestations of severe forms of the disease.
- Headaches, fever, chills and weakness are syndromes caused by viruses and infections.
Diagnostics
Neurological disorders characteristic of facial neuropathy can also occur with other diseases, in particular with stroke. That is why, if any similar symptoms occur, you should urgently consult a neurologist.
Diagnosis of pathology includes:
- collection of complaints;
- taking an anamnesis, during which the doctor clarifies the time and circumstances of the onset of symptoms, records previous and chronic diseases, injuries and other important details;
- neurological examination, during which a specialist checks skin sensitivity, motor function, muscle strength, quality of reflexes, functioning of the central nervous system, etc.;
- tests: general blood and urine analysis, biochemical blood test with mandatory determination of glucose levels, determination of antigens and antibodies to infectious diseases if their presence is suspected;
- X-ray of the chest organs: allows you to diagnose tuberculosis, tumors;
- MRI or CT scan of the brain: helps visualize tumors, areas of acute ischemia, hemorrhages, consequences of injuries and strokes;
- CT scan of the temporal bone;
- electroneuromyography: assessment of the speed of impulse transmission along nerve fibers and muscles, allows you to determine the level of damage and severity of the disease;
- consultations with specialists: therapist, otorhinolaryngologist, endocrinologist, infectious disease specialist, if necessary.
The list of studies can be adjusted depending on the specific clinical situation.
Diagnosis of the disease
Modern medicine has in its arsenal many diagnostic techniques that make it possible to determine the type of neuralgia and the cause of its occurrence:
- visual examination and questioning of the patient;
- X-ray of the jaw;
- MRI of the brain and blood vessels;
- laboratory analysis of urine and blood;
- electromyography.
Diagnosis is carried out by a neurologist, but additional examinations by other specialists are often required: dentist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist. Particular attention is paid to differential diagnosis, since neuralgia may resemble other diseases in its symptoms, in particular glaucoma, otitis media, ethmoiditis, Slader syndrome, etc.
Treatment of facial nerve neuropathy
A combination of drug and non-drug methods is used for treatment. As a rule, doctors prescribe medications from these groups:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): ibuprofen, meloxicam, nimesulide, diclofenac and other drugs; necessary to relieve pain and inflammation, eliminate swelling; used for mild to moderate neuropathy;
- glucocorticosteroids: prednisolone, hydrocortisone, dexamethasone; have an anti-inflammatory effect, relieve swelling; used for severe forms of the disease, as well as when NSAIDs are ineffective;
- diuretics: furosemide, lasix; necessary to eliminate tissue swelling;
- vascular drugs: pentoxifylline, nicotinic acid, cavinton; stimulate active blood flow in the affected area, improve tissue nutrition;
- metabolic agents: actovegin; necessary to stimulate metabolism and regenerate damaged structures;
- antiviral and antibacterial agents for the infectious nature of the pathology;
- anticholinesterase drugs: neuromidin, axamon; improve the transmission of excitation from nerve to muscle, help to quickly get rid of paralysis of facial muscles;
- B vitamins: milgamma, combilipen; stimulate nerve regeneration and improve impulse conduction.
If neuropathy has become chronic and muscle paresis has given way to spasm, muscle relaxants are prescribed: mydocalm, carbamazepine, baclofen. They replace anticholinesterase drugs and promote muscle relaxation. If these remedies are ineffective, injections based on botulinum toxin are used.
Drug treatment is complemented by physiotherapy. In the acute period the following are used:
- UHF;
- exposure to alternating magnetic field;
- phonophoresis with hormones.
After one and a half to two weeks from the onset of the disease, these methods are added:
- electrotherapy (diadynamic currents, etc.);
- electrical stimulation of muscles;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- Darsonvalization.
An additional effect is provided by mud applications, therapeutic baths, and acupuncture.
During the acute period it is also recommended:
- sleep only on your side (affected side);
- tie a scarf around your face to prevent stretching of paralyzed muscles;
- carry out muscle taping: tighten the muscles using an adhesive plaster (duration from 30-60 minutes to 2-3 hours);
- tilt your head in the direction of the lesion several times a day and support the muscles with your palm; The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes.
After acute inflammation has subsided, it is recommended to perform therapeutic exercises to develop the affected muscles:
- frown and raise your eyebrows;
- open and close your eyes wide;
- widen the nostrils;
- puff out one's cheeks;
- smile with your mouth open and closed;
- stretch out your lips, blow out an imaginary candle, whistle;
- stick out tongue, etc.
The more the patient grimaces, the faster the muscles will recover. During the same period, a light therapeutic massage to stimulate blood circulation is acceptable.
If treatment does not bring effect within 2-3 months, doctors recommend using surgical treatment methods. Two types of operations are used:
- restoration of impulse transmission along the nerve: decompression of the nerve fiber when it is compressed in the canal of the temporal bone;
- reinnervation: replacement of the affected area with a donor nerve (segment of the hypoglossal, phrenic or accessory nerve, as well as healthy branches of the facial nerve);
- partial suturing of the eyelids (tarsophasia);
The choice of a specific treatment method depends on the form of the disease, its cause, severity and level of damage.
Make an appointment
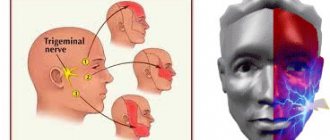
Trigeminal neuralgia
This is another lesion of the nerve fiber structure, which is often chronic and accompanied by periods of exacerbation and remission.
It has several causes, which are divided into idiopathic - when a nerve is pinched, and symptomatic.
The main symptom of neuralgia is paroxysmal sensations in the form of pain on the face and in the mouth.
Pain sensations have characteristic differences. They are “shooting” and resemble an electric shock; they arise in those parts that are innervated by the n.trigeminus. Having appeared once in one place, they do not change localization, but spread to other areas, each time following a clear, monotonous trajectory.
The nature of the pain is paroxysmal, lasting up to 2 minutes. At its height, a muscle tic is observed, that is, small twitching of the facial muscles. At this moment, the patient has a peculiar appearance: he seems to freeze, but does not cry, does not scream, and his face is not distorted from pain. He tries to make a minimum of movements, since any of them increases the pain. After the attack there is a period of calm.
Such a person performs the act of chewing only with the healthy side, at any time. Because of this, compaction or muscle atrophy develops in the affected area.
The symptoms of the disease are quite specific, and its diagnosis is not difficult.
Therapy for neuralgia begins with taking anticonvulsants, which form its basis. Their dose is subject to strict regulation and is prescribed according to a specific scheme. Representatives of this pharmacological group can reduce agitation and the degree of sensitivity to painful stimuli. And, therefore, reduce pain. Thanks to this, patients have the opportunity to freely eat and talk.
Physiotherapy is also used. If this treatment does not give the desired result, proceed to surgery.
Prevention
Compliance with the rules for the prevention of facial nerve neuropathy can reduce the likelihood of pathology occurring. This is especially true if there is an increased risk of developing the disease. Doctors recommend:
- avoid hypothermia and facial injuries;
- observe safety precautions at work to prevent eye damage;
- consult a doctor in time for infections and otitis media;
- control blood sugar levels;
- promptly diagnose and treat chronic diseases.
Complications of the disease
Neuritis of the facial nerve can lead to contracture of the facial muscles. It appears 4-6 weeks after the onset of the disease due to incomplete restoration of the motor functions of the facial muscles. Contracture is a contraction of the muscles of the affected half of the face. At the same time, it seems that it is not the diseased part of the face that is paralyzed, but the healthy one.
To avoid complications of inflammation of the facial nerve, you need to consult a doctor in time. For prevention, we recommend doing facial exercises. You will find examples of exercises at the end of the article.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Facial nerve neuropathy requires the fastest and most accurate diagnosis and comprehensive, comprehensive treatment. Only in this case can a rapid restoration of impaired functions be achieved. Neurologists at the Energy of Health clinic use the most effective techniques:
- modern drug regimens that affect the cause of the disease and relieve symptoms;
- physiotherapy courses for tissue restoration;
- massotherapy;
- training in facial gymnastics techniques;
- taping the affected areas;
- observation throughout therapy, adjustment of dosages and medications if necessary;
- a full range of measures for quick and complete rehabilitation;
- organization of sanatorium-resort treatment for the most complete recovery.
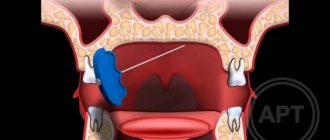
Surgery
Surgical treatment of facial nerve neuritis is usually carried out to restore its integrity, damaged by injury (rupture of nerve fibers). For this purpose, the nerve is sutured.
In addition, surgery may be performed if the cause of nerve inflammation is compression by a tumor, aneurysm, scar tissue, or other neoplasm. The cause of the compression is removed (an example of such an operation is neurolysis - removal of connective tissue proliferation).
Another type of surgical treatment is replacing the damaged portion of the facial nerve with a graft. Such operations are usually performed for injuries. The section of nerve to be transplanted is taken from the leg. The volume of plastic surgery is determined by the surgical plan. In particular, the transplant can be sutured to the facial nerve on the healthy half of the face. In this case, the signal from the brain will arrive to the facial muscles simultaneously on the right and left sides.
Surgical treatment is indicated in cases where conservative therapy does not bring results. It can be carried out within 12 months from the onset of symptoms of neuritis. Carrying out the operation later does not make sense, since by this time the facial muscles have time to atrophy.
Advantages of the clinic
The Health Energy Clinic provides each visitor with medical care of the highest level, regardless of his age and reason for visiting. We offer:
- screening diagnostic programs to assess health status;
- accurate and quick diagnosis of obvious and hidden pathologies;
- modern methods of drug therapy, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, massage;
- minor surgical operations within the walls of the clinic;
- course treatment of chronic diseases in comfortable day care wards;
- organization of hospitalization in a specialized hospital if necessary;
- preparation of documents for sanatorium-resort treatment, selection of sanatorium;
- remote consultations with foreign doctors to obtain an alternative opinion;
- modern rehabilitation programs.
Facial nerve neuropathy is a fairly common pathology. To prevent it from leading to irreversible facial asymmetry, contact a specialist as soon as possible. Neurologists at the Energy of Health clinic will always come to the rescue.