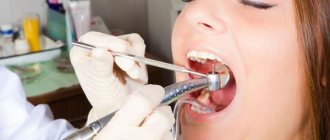
Any treatment in dentistry begins with an examination by a specialist - this is the first and most important stage in the diagnosis of dental diseases. The doctor talks with the patient and finds out his complaints. Then he examines the oral cavity and teeth, palpates soft tissues, masticatory muscles and the area of the temporomandibular joint. This makes it possible to detect pathological processes such as caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontitis, and muscle-articular dysfunctions associated with bite pathology at a very early stage. It is recommended to undergo a preventive examination by a dentist every six months, even if a person is not bothered by pain, bad breath or other unpleasant symptoms.
Inspection process
If the patient comes to the clinic without any complaints about his health, the doctor conducts an examination according to the classic scenario. First of all, a visual assessment is necessary: hard and soft tissues, existing crowns and implants, mucous membranes, palate, etc. are carefully examined. This allows you to detect excessive accumulation of plaque, tartar and other deposits. If a stone appears, this may indicate that a person does not pay enough attention and time to oral hygiene.
Professional cleaning using an effective method such as Air Flow may be required to remove stone and hard deposits. The doctor must also examine the enamel, determine the presence of changes in its color, density, and identify the presence of chips and cracks on the surface. When tissue demineralization occurs, strengthening therapy using fluoride-containing drugs may be prescribed.
After this, you can move on to studying the gums: you should check the tissues for the presence of compactions, foci of inflammation, ulcers, etc. The appearance of the tongue, palate, and cheeks is also important. If there are signs of mechanical damage or injury, the doctor may recommend changing your toothbrush and other hygiene devices to more gentle ones.
X-ray (digital) examination
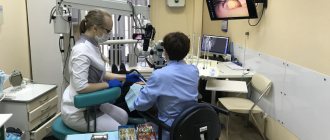
The initial consultation with a dentist includes not only a visual examination, but also an examination of the oral cavity with a special apparatus. He takes a photo of the jaws and sends it to the computer. The specialist analyzes the information, makes an assessment and draws up a plan for further treatment. The tooth can be seen from all sides and angles. Defects in both soft and bone tissue are immediately detected. Using an x-ray, you can evaluate the filling of the root canals (if the tooth has already been filled).
Doctors can also use a dental microscope, designed to identify microcracks on the surface of teeth. In dentistry there is a device called an apex locator. It measures the length of the root canals, for example if the patient complains of gum inflammation. Thanks to the indications, the specialist will select the instruments of the required length, which will affect the successful course of treatment.
Orthopantomogram (panoramic image)
You come for an initial consultation with a dentist and voice your complaints. He sends you for an orthopantomogram. The image shows close-up carious changes and inflammation in the soft tissues.
When should you schedule an initial dental consultation?
- You feel discomfort and soreness of the enamel. The surface of the tooth has become more sensitive to hot or cold food. There is a feeling that the tooth is sticking out and getting in the way. The gum or crown is sore.
- You experience a persistent unpleasant odor from your mouth.
- The gloss and color of the enamel began to change. You have found tartar on the surface.
- Mechanical injury to the mucous membrane, gums, and tooth occurred.
Current reasons for seeking an initial examination
- The gums began to bleed, became swollen, and looked pale.
- Acute pain in teeth.
- Visually you see the exposed neck of the tooth.
- Curvature and other abnormalities of teeth.
- Lack of teeth. You will receive an initial consultation with a dentist on prosthetics or implantation.
After an initial consultation and examination, treatment is prescribed and the cost is announced.
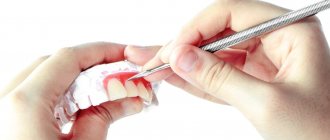
Probing
This research method can be carried out to evaluate the reliability and density of the enamel of real teeth and artificial crowns. To do this, the dentist uses an instrument called a probe. With its help, it is possible to determine the presence of carious cavities and the stage of tissue damage. The method is also actively used for the diagnosis of other non-carious diseases, for example, hypoplasia, erosion, fluorosis, etc.
Probing is an absolutely painless and safe process. To check your teeth, the doctor simply needs to run the blunt end of his instrument over the surface of the enamel. This allows you to find irregularities and defects, determine density and hardness. This device can also be used to detect the presence of gum pockets.
Additionally, the dentist can check for gaps between the gum and the crown (or between healthy areas of enamel and the filling material). If there is a severe gap, the filling will need to be reinstalled.
For all ages:
- Treat visiting the dentist as an ordinary, everyday matter; Do not attach great importance to the visit, turning it into a whole event. And most importantly, don’t be nervous yourself, don’t give your children a reason to think that you’re worried about the upcoming appointment;
- Do not discuss the negative experience of visiting the dentist in front of your child, do not scold the doctors, and especially do not analyze the “unsuccessful” treatment of one of the family members;
- On the day of the reception, talk with your children about abstract topics - all preparatory work must be carried out before day “X”;
- Avoid deception by promising your child that he won’t feel anything at all, that there won’t be an injection, that the doctor will just take a look, especially if you know for sure that a single examination is not enough in your case;
- Feed your child before the appointment, even before the examination. The optimal time to eat is 1.5 hours before the visit.
Palpation and percussion
This technique is used to assess the health of periodontal tissues. To do this, the specialist carefully moves the tooth to the right and left using medical tweezers, checking its mobility and ability to move. If the coronal part moves easily, this indicates the presence of serious inflammation or indicates tissue swelling.
Such consequences can occur due to severe injuries to the jaw, as well as diseases such as periodontitis, periodontitis or periodontal disease. Using palpation, the doctor assesses the degree of pain of the procedure for the patient, because pain can be of varying intensity depending on the complexity of the pathology and its location.
Percussion is a method in which the doctor gently taps the surface of the tooth crowns with a probe or other device. If unpleasant sensations occur with horizontal impacts, this indicates the development of periodontitis; if with vertical impacts, then this indicates an inflammatory process in the pulp chamber. Based on the data obtained, the specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis and send the patient for further examination. Sometimes, during the general examination, an x-ray is prescribed; this is necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
The course of mother's pregnancy and the formation of teeth in children - is there a connection?
Scientific research has proven that the mother's health during pregnancy, its course and intrauterine development of the fetus can affect the dental health of children after birth.
Some diseases of the mother during pregnancy can be considered as a predisposing factor for violation of the timing of teething in children, various disruptions in the process of enamel formation and malformations of its development (hypo- and aplasia).
Complex maternal illnesses, stress, and even the negative effects of certain medications or bad habits can be considered as the cause of abnormalities in the development and differentiation of teeth.
By the way, bad habits of the mother are considered as factors of increased risk of disorders in relation to the intrauterine development of the maxillofacial region and the birth of children with cleft lip and palate.
Studies have shown that risk factors may include not only maternal smoking, but also passive smoking. Moreover, the latter is considered the most dangerous.
In addition, the mother's oral health can also affect the children's dental health. It is known that caries is an infection caused by representatives of streptococci. An adult’s body is quite capable of coping with bacteria, restraining their growth and development, but a child’s body does not yet have this ability. And, if infection occurs in infancy, this can threaten the development of caries at an early age.
Considering the vulnerability of children to various oral diseases, predisposition to them, as well as the connection between diseases of the oral cavity and internal organs, parents should understand the importance of preventive examinations and timely visits to the dentist.
When should you undergo a general examination by a dentist?
Experienced dentists and orthodontists strongly recommend visiting a dental clinic for a preventive examination at least once every 6 months. This should be done even if there are no complaints. If you have any unpleasant sensations, you should not delay your visit to a medical facility for even a minute.
There are several main causes for concern: increased sensitivity of the enamel, pain in the gums under the denture, swelling, redness and any other visible tissue changes. Also, one of the symptoms of developing pathology is a strong smell from the mouth, which does not disappear even after brushing.
Abundant accumulation of plaque and tartar, changes in the shade and transparency of the enamel, bleeding - all this is a good reason to visit your doctor. Also, consultation and examination are required before orthodontic treatment.
previous post
Why are my teeth numb?
next entry
Changeable bite in a child - what to pay attention to?
The beginning of the mixed dentition is marked by the appearance of the first permanent teeth - the first permanent molars; their eruption begins at 5-6 years. Then the loosening begins, and then the loss of the front group of teeth - the central and lateral incisors, which changes to permanent ones.
The process of transition from a mixed dentition to a permanent dentition is long, it lasts for years, and the main task of dentists and parents is to prevent complications. The main danger is premature loss of baby teeth.
Advanced caries and its complications are the main cause of premature tooth loss and the subsequent development of bite pathologies.
Milk teeth retain space for their permanent “descendants.” If they are missing, then the permanent teeth are in the wrong position. As a result, teeth begin to appear in the oral cavity, like a picket fence. The teeth become dystopic - that is, they erupt outside the dentition.
During this period, it is necessary to be especially careful about the health of baby teeth. Caries in baby teeth spreads to permanent teeth.
Let us remember that newly erupted teeth are extremely vulnerable to caries-forming bacteria; the enamel is not yet perfect and is still continuing the stages of its mineralization.
In mixed dentition, bite pathologies are most often diagnosed, which can be quickly and painlessly corrected - as they say, “with little bloodshed.”
By the way, it is during the period of mixed dentition, when the anterior central incisors appear, that the frenulum is surgically corrected - that is, it is trimmed. Otherwise, children will develop cavities between their teeth.
Another reason for the formation of malocclusion is a violation of the timing of tooth loss: baby teeth have not yet fallen out, but the eruption of permanent teeth has already begun. Simply put, these children’s teeth grow in two rows, and dentists affectionately call them “shark babies.”
This clinical picture requires immediate help, namely, surgical removal of baby teeth. This usually happens when the process of resorption of the roots of baby teeth is disrupted, which is common.
If you do not intervene in this process and do not remove baby teeth, then various occlusion pathologies can form: crowding of teeth, the appearance of dystopic teeth when they extend beyond the dentition - and much more.
How to make an appointment at the clinic
A consultation with an implantologist is carried out after making an appointment with a doctor - through personal contact or remotely (by phone, through the website or the clinic’s messengers). Some institutions have 24-hour support - you can call or make an appointment at any time. You can contact others only during business hours from 9 a.m. to 6 p.m. When contacting, be sure to tell us about the purpose of the future visit so that an appointment can be made with the right specialist – a dentist-implantologist.
“I was looking for an implantologist based on reviews on the Internet. I re-read the forums and found several good doctors. Then I started looking at the websites of the clinics where they work. Even in the chat on the sites I asked what interests me. Because it’s a front tooth, and I know that they don’t put a crown on just one tooth at once. But they quickly made an appointment for me, literally within a day. And the doctor, after a consultation and x-ray, told me what and how best to do in my case. Everything is very clear and accessible (by the way, the crown can be placed right away).”
Irina P., review from gidpozubam.ru
What does a dental consultation in Moscow include?
An initial visit to a specialist may have a preventive, diagnostic or therapeutic purpose. Primary medical appointment includes:
- Taking anamnesis;
- Thorough inspection;
- Completing medical documentation;
- Development of an individual examination and treatment plan.
A consultation with a dentist will allow you to:
- Identify the pathological process in a timely manner long before the appearance of clinical symptoms;
- Carry out the necessary treatment quickly;
- Prevent further development of the disease.
This is why it is recommended to visit the dentist at least twice a year!