Various strange and unusual tastes that appear in the mouth are alarming and make you wonder if everything is okay with the body. For example, what does the taste of salt in your mouth indicate? Doctors note that the feeling of excess salt cannot be considered normal.
Cardiologist, therapist, endocrinologist Tatyana Romanenko told AiF.ru about what diseases such a taste in the mouth indicates and what needs to be done .
When we talk about the taste of salt in the mouth, we must first of all exclude the most important, serious and dangerous causes of this pathological phenomenon.
Blood in the mouth
One of the most important and yet common causes of this phenomenon is bleeding. Naturally, since we are talking about the mouth, then most often it arises from the gums. But increased gum bleeding can be caused by a number of factors.
Question answer
What causes the bitter taste in the mouth? One of the most common problems is inflammatory infectious diseases of the oral cavity. The reason may be either untreated, not fully sanitized teeth, or inflammatory diseases of the gums and tonsils themselves. These could also be neoplasms. That is, the problem lies in all local processes.
Another fairly global problem that we should always remember is bleeding gums due to changes in blood clotting. These are various types of thrombophilia, for example. Of course, there will be not only a salty taste in the mouth, but also other symptoms of hemorrhagic syndrome.
Another rather serious reason is blood disease, in particular those that are accompanied by bleeding. This could be thrombocytopenia, anemia, etc. That is, in this case, salty in the mouth is the taste of blood, and such a condition always requires prompt differential diagnosis and initiation of treatment.
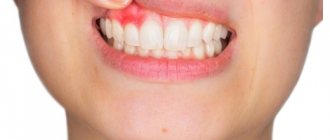
Bleeding gums
There is a taste of salt and you don’t know what could be causing it? The cause of this phenomenon could be bleeding gums. It could arise against the background of trauma to the mucous membrane or as a result of the development of gingivitis or periodontitis.
Blood is close in its ionic composition to sea water. It contains sodium and chloride ions, due to which people with a similar pathology experience a salty taste.
Your mouth may also feel salty due to the fact that you recently had a tooth removed. After all, after this procedure, a wound has formed, which first bleeds, and then ichor is released from it for a long time. Damaged tissues need time to heal, after which the unpleasant symptom will no longer bother you.
Oral hygiene
A common cause of a salty taste in the mouth is poor oral hygiene. If a person does not brush his teeth well enough, if plaque forms, all this contributes to the development of pathological microflora, the waste products of which will give this unpleasant salty taste.
Also, the appearance of taste is influenced by the presence of an infectious process in the oral cavity - the formation of tartar, fistulas, chronic tonsillitis.
Taste of illness. How to determine your diagnosis by the taste in your mouth Read more
Taking medications
All medications affect metabolism to one degree or another. This may manifest itself as foreign tastes in the mouth - this side effect is safe, but sometimes irritating to the patient. This feature is usually indicated in the instructions if you carefully read the section on side effects. Most often, a salty taste is caused by: Unflavored lozenges; Sprays and solutions for rinsing the mouth and throat; Antibiotics; Antihistamines (antiallergic) drugs; Some hormonal medications; Chemotherapy drugs used in oncology; Antidepressants. Particular attention should be paid to diuretics. The salty taste may be due to the characteristics of the active substance or to incipient dehydration. When treating with them, you cannot change your drinking regimen without permission; this will reduce the effectiveness of therapy, so you need to consult a doctor and pay attention to the presence or absence of other signs of dehydration.
Excess salt on the menu
A similar symptom may appear when we eat excessively salty foods. For a long time now, scientists, doctors, as well as adherents of a healthy lifestyle have noted that salt in large quantities is dangerous for the human body. And its main danger is the load on the cardiovascular system, urinary system, and kidneys. It also increases blood pressure. Therefore, to some extent, modification of diets can lead to the fact that taste perception is restored and excess salt begins to be felt.
Why does it occur in women?
If the specific taste in the mouth and lips in women does not cause a cough due to problems with the ENT organs or other listed problems, then the unpleasant symptoms are associated with the menstrual cycle or hormonal imbalance. Pregnant women especially often complain about this condition. Temporary restructuring of the body during childbearing followed by breastfeeding contributes to changes in taste buds.
Salinity also occurs due to dehydration caused by toxicosis. A woman may complain of constant nausea, vomiting, weakness, dry mouth, and dizziness. In this case, it is advisable to eat natural food with a minimum amount of dyes, drink drinks that alleviate the condition, and eat sour fruits that smooth out the symptoms of nausea and strange taste in the mouth.
Dysgeusia often develops in pregnant women. This is a taste disorder under the influence of hormones. This phenomenon is temporary and disappears without a trace after delivery.
Salt in the mouth of women can appear as a result of sudden mood swings, crying, or tears. In older representatives of the fairer sex, a salty taste appears during menopause, when hormonal changes occur intensively. It is often accompanied by dry mouth, inability to swallow food, burning, and itching.
Related posts:
- The whole truth about real depression Depression is not just a bad mood, but serious changes...
- Benefits of Stress Stress is a normal defense mechanism that the human body needs...
- Constant fear and anxiety in children It is common for every person to experience fear, anxiety, and anxiety. But, unlike...
- Mysophobia is a pathological fear of dirt and germs. Mysophobia is a mental illness, the symptom of which is a strong, irresistible fear...
The reason is tears
Another interesting reason may be related to the pathology of the tear ducts. It would seem, how are the eyes and the salty taste in the mouth connected? In fact, if there is a disruption in the functioning of the tear ducts, increased secretion of tears may occur; on the other hand, the normal passage of this tear content is also disrupted. As a result, the tear enters the nose, then it flows down the back wall of the throat, and a feeling of saltiness occurs in the mouth. Pathology of the lacrimal glands (ducts) can provoke a salty taste in the mouth.
Why does a metallic taste appear in the mouth? More details
Allergy
An allergic reaction is accompanied by the release of a whole cascade of substances. There are several mechanisms due to which salty taste develops. It is caused by mucus and tear fluid entering the mouth during allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, a decrease in the concentration of fluid in saliva, and the ingress of substances involved in the development of an allergic reaction. This is not the most striking symptom of an allergy, and there is no need to specifically fight it - the salty taste in the mouth will go away on its own after the allergic reaction is over.
Rare reason
Quite rarely, but it still happens, the reason lies in the pathology of the nervous system, when a change in taste perception is noted. In particular, such sensations can occur after suffering traumatic brain injuries, acute cerebrovascular accidents, chronic cerebral circulatory disorders and, of course, infectious diseases. Any viral infections can provoke a perversion of taste disturbance, and this can contribute to the appearance of such a salty taste in the mouth.
Hormones are acting up
Hormonal problems, particularly diabetes, can also lead to dry mouth. Sometimes it may additionally be a taste of acetone, since diabetes mellitus is often accompanied by damage to the kidneys and central nervous system.
Brain pathologies This is the rarest cause of the symptom. Receptors on the tongue respond to the chemical composition of food, but the concept of taste is formed in the cerebral cortex. This means that with normally functioning receptors and nerves, a healthy oral cavity and neighboring organs, the functioning of the part of the cortex responsible for the perception of taste may be disrupted. Such disorders can be observed in brain tumors, epilepsy, and a number of mental illnesses. If the patient does not have such a diagnosis or a history of head injuries, the doctor is unlikely to immediately think about such a cause of the salty taste - it is very unlikely.
Gastrointestinal tract and dehydration
A salty taste in the mouth often occurs with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Such a common pathology as gastroesophageal reflux disease causes a similar problem. First of all, of course, this is the appearance of a feeling of acidity, but some people may also complain of saltiness in the mouth.
Often, the taste of salt can be felt when the body is dehydrated, for example after some kind of infection. The effect is especially enhanced if, against the background of a lack of moisture, there is an excess of alcohol and caffeine-containing drinks. A characteristic aftertaste may arise here. Fluid imbalance causes more sodium chloride to appear in saliva. Hence the taste of salt in the mouth. Any loss of fluid and blood thickening are accompanied by this symptom.
Symptoms of the disease
Food allergies often appear within a few minutes of consuming the product. There is a rash, itching, redness, swelling of the skin of the hands, face and neck. Many people complain of a sore throat, heartburn, and bloating. Children and adolescents are at high risk of anaphylactic shock, acute urticaria, eczema, and asthma.
In adults, the following symptoms most often develop:
- chronic urticaria;
- atopic dermatitis;
- rhinitis and conjunctivitis;
- gastritis;
- migraine;
- dermatitis.
According to statistics, skin manifestations are observed much more often. The rash is usually erythematous in nature. Elements of the rash can be located on any part of the skin. Dermatological manifestations persist from several hours to several days, then disappear on their own provided there is no further contact with the allergen.
When it enters the body again, the allergy develops again. There is a possibility that each episode will be more severe and intense.
Food allergies cause gastrointestinal problems within the first hours. The following symptoms are usually noted:
- stool disorders;
- abdominal pain, bloating;
- vomiting
With high allergic readiness, these symptoms develop already at the time of consumption of the allergen. It happens that dyspepsia is accompanied by immediate swelling of the mucous membranes of the mouth, lips, and tongue; nasal congestion.
Some varieties of fish, strawberries, and peanuts cause the most severe systemic reactions - angioedema, anaphylactic shock.
People suffering from bronchial asthma or food allergies often experience an attack that develops as a cross-allergy. Headaches, fatigue, and weakness appear after eating potentially dangerous foods.