What is the trigeminal nerve
The human face has many muscles and nerve endings. Not only the mucous membranes of the nose, pharynx, and conjunctiva, but also the nerve endings can become inflamed. This is most often associated with neurological disorders that change the sensitivity of the fibers that conduct impulses.
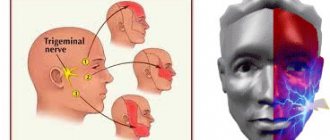
With neuropathy of the facial area, acute shooting pain occurs on the right or left. Mirror inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is extremely rare. It is located in the temporal region, near the base of the auricle. And from it there are branches along the entire half of the face:
- jaw nerve (upper and lower);
- optic nerve;
- infraorbital nerve.
The trigeminal nerve passes through the bone tissue in several places, which plays an important role in the occurrence of inflammation associated with pinching. Thus, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve can result in acute pain both in the upper and lower jaw, and in the forehead area, covering the eye sockets.
Location of the sciatic nerve
This nerve begins in the pelvis, in the lumbar spine. It is very long, due to which it covers a large proportion of the lower parts of the body. From the sacrum its branch exits through the infrapiriform foramen into the pelvis. Then it goes under the gluteal muscle, and is further divided into smaller parts that penetrate the muscles of the buttocks and thighs. The sciatic nerve simultaneously affects each joint of those located in this area.
The sciatic nerve provides sensation to the lower extremities
Descending to the popliteal fossa, it diverges into two branches: the tibial and fibular branches. Without these very branches of the nerve, not a single area of the skin of the legs would have sensitivity. Also, without it, the sensitivity of the muscles and joints of the legs is unthinkable.
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
There are several reasons leading to inflammation of the nerve ducts:
- Poor blood supply associated with physical compression of the nerve. First of all, this is swelling caused by diseases of the ENT organs. The resulting tumor can also pinch the nerves.
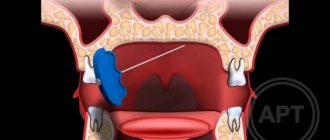
- Inflammation associated with dentistry. This includes gingivitis, periodontitis, caries, pulpitis, and eruption of wisdom teeth. Each of these diseases can lead to suppuration, abscesses, swelling and bacterial infections of tissues.
- Medical error by an anesthesiologist - if the injection was given unsuccessfully and the needle got into a nerve, pain cannot be avoided.
- Hypothermia causes muscles to lose their elasticity, which leads to pinching of the nerves passing between the fibers.
- Bacterial infections, in particular tetanus and polio.
- The cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, which is difficult to diagnose, is the psychological state of a person - frequent experiences, stress, and nervous disorders.
To determine the cause of inflammation, you need to consult a specialist.
Sciatica pain
The pain caused by sciatica is quite varied. There are burning and shooting ones. There are piercing and pulling. And there are also whining ones. But usually they come in fits and starts. In other words, unbearable pain and periods of relative peace follow each other.
Treatment methods
Depending on what caused the inflammation, a course of treatment is prescribed. For bacterial lesions, the emphasis is on antibacterial therapy through systemic administration of drugs.
However, regardless of the reasons, the doctor prescribes painkillers to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. It could be:
- ibuprofen;
- paracetamol;
- analgin;
- ketorol;
- diclofenac.
All of the listed drugs can be prescribed either in the form of tablets for oral administration, or prescribed in the form of solutions for intramuscular administration.
When conservative methods are not possible, the help of a surgeon may be needed. This primarily concerns abscesses due to the eruption of wisdom teeth, pulpitis or other dental diseases. In this case, the abscess will be opened, pus will be removed, the wound will be treated with antiseptic, and the tooth will be removed, if necessary. If a pinched nerve occurs as a result of pathologies in the structure of the skull, the surgeon will perform an operation to correct the situation and free the nerve bundles.
As a complex therapy, massage, heating or exposure to a magnetic field and electric current can be prescribed. You cannot massage or warm the inflamed area yourself, because this can lead to complications associated with rupture of the purulent capsule, blood poisoning and paralysis of the facial nerve.
Separately, you may need to consult a neurologist who will determine the cause of the inflammation if other specialists have not found obvious foci of infection and abscesses.
Traditional methods of treatment are permissible only as an addition to the main therapy. For example, rinsing with chamomile decoction will relieve inflammation and reduce swelling. But you can resort to such procedures only with the permission of the attending physician.
Why does sciatica begin to develop?
Inflammation of this nerve may well be caused by the following factors:
- uncomfortable ambient temperature;
- stressful situations;
- pathologies of the spine, due to which the nerve can become inflamed or pinched;
- spinal injuries;
- diabetes;
- infections;
- lifting too heavy loads;
- lack of physical activity;
- pregnancy;
- drinking alcohol;
- poisoning with any heavy metal;
- gout.
There are many reasons for inflammation of the sciatic nerve
Moreover, sciatica does not necessarily begin because of just one single factor.
There are professions in which the likelihood of getting this pathology is slightly higher than in other jobs. Eg:
- farmer;
- machine operator;
- driver.
It is also exceeded among those whose workplace is not comfortable enough, as well as among smokers.
Also, sciatica can either appear suddenly, for example, due to an injury, or develop gradually, which results from difficult work and/or complications from other pathologies.
Possible complications
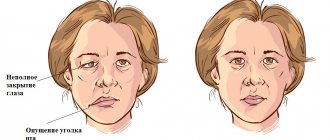
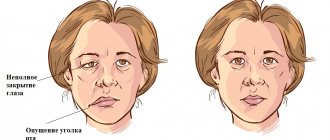
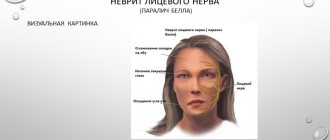
Doctors call facial paralysis the first complication that appears in the absence of adequate treatment. This means that a person who does not receive medical care in a timely manner is deprived of the opportunity to express his emotions through facial expressions on one side of his face. This condition can no longer be corrected, which will certainly affect the quality of life. Distortion of facial expressions will lead to the development of depression and constant dissatisfaction with one’s appearance. Not every patient can come to terms with irreversible changes in their appearance without deep distress.
One of the most unpleasant manifestations of paralysis is the inability to close the eyelids on the injured side of the face. In this case, the eye will have to be regularly instilled with artificial tears to prevent the cornea from drying out, since natural hydration through blinking becomes unavailable for this eye.
Symptoms
The following symptoms of inflammation of the facial nerve are distinguished:
- partial or complete impairment of facial muscle movements;
- the corner of the mouth lowers, the nasolabial fold on one side is smoothed out;
- the face becomes asymmetrical;
- the eyelid does not close completely;
- the eyeball protrudes and turns upward;
- pain in the ear, taste disorder;
- watery or dry eyes;
- hearing loss or sensitivity to loud sounds;
- the patient cannot whistle or stretch out his lips with a straw.
Prevention of inflammation
To prevent the risk of developing inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, it is recommended to follow a number of measures:
- monitor oral hygiene and consult a dentist in a timely manner;
- do not stay in the cold for a long time or protect your face from freezing with a scarf;
- do not self-medicate otitis media.
At the first manifestations of pain on the face, you should immediately consult a doctor. This will stop the development of inflammation. In addition, early diagnosis allows for conservative treatment methods.
Sciatica therapy
When treating sciatica, medicinal and non-medicinal methods can be used. How it is carried out is determined by the degree of pathology, as well as the original cause - that is, the nerve is inflamed or pinched. If necessary, doctors may resort to surgery. But the operation is performed only as a last resort, when other methods of combating the disease have been found to be unsuccessful.
Here is a list of non-drug treatments for sciatica:
- physiotherapy;
- hydrotherapy;
- massage;
- exercise therapy;
- visiting the gym.
There are many methods for treating sciatica
There are also non-traditional, but still effective therapeutic methods:
- acupressure;
- ozone therapy;
- manual therapy;
- mud therapy;
- cupping massage;
- acupuncture therapy;
- leech treatment.
Drug treatment methods for sciatica
When treating sciatica, the main focus is on medication. Let's talk about the main groups of medications that are used to cure sciatica.
Despite the fact that the purposes of using glucocorticosteroids coincide with NSAIDs, the methods of their use are quite different. Any steroids should only be used to relieve symptoms if carefully supervised by a specialist. As well as using any narcotic drugs designed to relieve pain, for example, morphine and tramadol.
Sometimes the patient is prescribed medications belonging to different categories.
Typically, topical medications are used, produced in the form of ointments and creams. There are also vitamins and medications for pain and inflammation that can be used in the form of inhalations or injections during exacerbations and/or severe pain.
The patient may be prescribed NSAIDs
If you need medication in tablet form, it is recommended that you first consult a specialist. There are quite a few NSAIDs whose side effects override their beneficial effects or at least make them less attractive from this point of view. For example, some tablets disrupt the gastrointestinal tract and also cause bleeding and ulcers. Moreover, the risk is greatest when using such products for a long time. So NSAIDs are used only during exacerbations, which require effective pain relief techniques. Tablets should not be taken for more than 5-14 days, which is determined by the drug itself.
Treatment of optic neuritis
Treatment must be carried out in a hospital setting; it should begin as early as possible, in order to avoid the disease becoming chronic and developing complications. Source: Modern view on the problem of optic neuritis (systematic review). Krivosheeva M.S., Ioileva E.E. Saratov Scientific and Medical Journal, 2022. p. 602-605. For patients with optic neuritis, diet No. 15 is indicated - a general table, in the absence of indications for other types of therapeutic diets.
The basis of treatment is etiotropic therapy aimed at eliminating the primary disease that caused optic neuritis. Until the etiology of the disease is clarified, remedies are used to reduce the symptoms of inflammation, remove swelling, allergic manifestations, and improve metabolism. For this purpose:
- glucocorticosteroid drugs, if they are intolerant - non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (prescribed in rare cases);
- antibacterial or antiviral therapy;
- antifungal agents to prevent fungal infection due to a long course of antibiotics;
- detoxification therapy – intravenous drip administration of saline solutions;
- antihistamines;
- diuretics;
- products that improve microcirculation;
- neuroprotectors;
- vitamins.
In addition to medications, physical therapy may be used to treat optic neuritis.
With papillitis, as well as the infectious-toxic etiology of the disease, the prognosis is more favorable than with other types of optic neuritis - in 75-90% of cases, with proper treatment, vision is completely restored. When the optic nerve is damaged due to autoimmune, demyelinating diseases, collagenosis, sarcoidosis, and specific infections, relapses often occur, incomplete restoration of vision, and nerve atrophy is possible. Source: Results of treatment of optic neuritis. Latypova E.A. Saratov Scientific and Medical Journal, 2022. p. 875-879.
Which specialist can help with sciatica?
In the treatment of sciatica, the help of a neurologist is needed. It may also be necessary to consult other doctors:
- vertebrologist;
- neurosurgeon;
- vascular surgeon.
The “main” doctor to contact for sciatica is a neurologist, but he can also refer you to other specialists
During the treatment process, you also need the help of a physiotherapist, exercise therapy and massage specialist. The services of an osteopath may be helpful.
Occipital neuralgia
The article was prepared by a neurologist, the chief physician of our clinic, Pavel Dmitrievich Kovzelev. In this article, in addition to a description of occipital neuralgia and the principles of treatment, you can watch a video with a clinical case from our patient, as well as a video of how an occipital nerve block is performed - one of the most effective methods of treating this pathology.
Anatomy of nerves.
The occipital nerves, 3 in number, are formed at the level of the 2-3 cervical vertebrae, then exit to the posterior surface of the spine and are located between the deep and superficial muscles of the neck.
At the level of the occipital bone, the nerves pierce the superficial muscles and exit under the skin, breaking up into small terminal branches that innervate the skin of the occipital region.
It's best to look at the picture.
Causes of neuralgia/neuropathy of the occipital nerve.
Why occipital neuralgia (also known as neuropathy) occurs is not completely clear.
The most popular hypothesis is that the nerve becomes trapped between the muscle and the fibrous tissue at the exit site and is pinched.
In people who have undergone surgery on the cervical/occipital region, people with Arnold-Chiari malformation, problems in the cervical spine, as well as those who have recently suffered a whiplash injury to the neck, NLDs are more common, which, in principle, fits into the “trap” hypothesis.
Symptoms of occipital neuralgia.
- The pain is severe, shooting, like electric shocks.
- Has a paroxysmal character: from several seconds to several minutes.
— The pain is localized in the back of the head, usually on one side and rarely on both sides.
- Between attacks, a dull, low-intensity pain may persist.
An attack can be provoked by touching certain points of the head, turning the head and any mechanical stimuli.
Sometimes patients note a decrease in sensitivity in these areas, and sometimes patients note dizziness and nausea.
IMPORTANT: Pain with occipital neuralgia can reach the fronto-ocular region through the connections of the occipital nerve with the trigeminal nerve at the level of the spinal cord.
The clinical picture may vary among patients. There are diagnostic criteria that I took from the 3rd International Classification of Headaches.
Let's look at them, but they are more important to me or your doctor.
- Unilateral or bilateral pain in the distribution of the greater, lesser and/or third occipital nerves and fulfillment of BD criteria
- Pain has at least two of the following three characteristics:
- repeated paroxysmal attacks lasting from several seconds to minutes
- heavy in intensity
- shooting, stabbing, or sharp pain
- Pain is associated with both of the following:
- dysesthesia and/or allodynia, manifested during painless stimulation of the scalp and/or hair (this is when normal touch is perceived as painful)
- one or both of the following: a) tenderness when pressing over the affected nerve branches
- b) trigger points at the origin of the greater occipital nerve or in the distribution of the C2 root.
- Pain is temporarily reduced by applying local anesthesia to the affected nerves. (i.e. when performing a blockade).
- Does not fit other diagnoses of the 3rd International Classification of Headaches.
Diagnosis of neuropathy of the occipital nerves. The diagnosis of NMN is made clinically (i.e., upon examination by a doctor), but for this it is necessary to exclude other causes. Taking into account the fact that many pathological processes in the posterior part of the brain and skull, as well as in the cervical spine, can produce similar pain in the occipital region, it is necessary to carry out:
- MRI of the brain
- MRI of the cervical spine, ultrasound examination of the vertebral arteries.
- In our clinic, ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck is performed by a doctor with extensive experience, Irina Alekseevna Romadova, using an expert-level ultrasound device.
Treatment of neuralgia of the occipital nerves Treatment usually begins with a diagnostic blockade, which often gives a lasting positive result. I prefer to perform this block under ultrasound guidance for more precise and, more importantly, safe insertion. If necessary, the blockade can be repeated, but not more than once every three months. This is what it looks like schematically
This is how everything is visible with ultrasound navigation. I circled the nerve itself and its signature in red. It is very small, it literally looks like a dot. (Image clickable)
Drug therapy (standard drugs for neuropathic pain): gabapentin, tricyclic antidepressants, pregabalin, baclofen, carbamazepine.
of reflexology has proven itself well , which in this case is additional to stabilize and consolidate the effect.
If all of the above methods do not help, then you can: try botulinum toxin.
Also, one of my patients noted the effect of using Cefaly , a device for the treatment of migraines, which can be rented at our clinic to evaluate its effectiveness.
Neuralgia of the occipital nerves is an uncommon but extremely painful pathology. Sometimes people suffer for decades without a diagnosis or adequate treatment. At the same time, neuralgia has relatively clear diagnostic criteria and treatment approaches.
Kovzelev Pavel Dmitrievich
Chief physician, neurologist, vertebrologist
Why does pathology occur?
Doctors consider primary and secondary neuropathy. The primary cause is injuries, infectious diseases and hypothermia. The list of reasons that can cause a secondary type of illness is much more extensive. These include:
- disc displacement;
- neoplasms of any nature;
- osteochondrosis;
- protrusion;
- osteophytes;
- spasmodic muscles;
- curvature of the ridge;
- tunnel syndrome;
- intervertebral hernia;
- post-injection suppuration.
Diagnosis of the disease
As a rule, patients who have the first symptoms of optic neuritis turn to an ophthalmologist. The disease is considered an interdisciplinary pathology; an ophthalmologist or neurologist must take part in its treatment. If neuritis develops against the background of other pathologies, it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis and carry out specific therapy for the primary diseases. Source: Visualization of the optic nerve in the diagnosis and monitoring of retrobulbar neuritis. Yuryeva T.N., Burlakova E.V., Khudonogov A.A., Ayueva E.K., Sukharchuk O.V. Acta Biomedica Scientifica, 2011. p. 133-136. Then the appropriate specialists are involved in the treatment - an immunologist, an otolaryngologist, an infectious disease specialist, a phthisiatrician.
The first step in diagnosing optic neuritis is collecting anamnesis, external examination of the patient, and palpation. During the medical history, the doctor will clarify the presence of concomitant pathologies, the time of onset of the disease, what complaints the patient has (pain, decreased visual acuity, changes in color perception, the appearance of “blind” spots), how quickly the symptoms developed and how severe they are, whether one eye or both is affected.
External examination and palpation may often not provide additional data. Pain, forward displacement of the eyeball, and limitation of its movements may occur with retrobulbar neuritis, but are not obligatory.
Next, the doctor proceeds to an ophthalmological examination. It includes:
- determination of visual acuity;
- the study of color perception is carried out using Rabkin’s polychromatic tables;
- study of pupil reaction to light;
- measurement of intraocular pressure, which can be a symptom of glaucoma and other diseases that provoke the development of neuritis;
- biomicroscopy – examination of the anterior segment of the eye to exclude its pathology;
- ophthalmoscopy (examination of the fundus of the eye) after instillation of drops that dilate the pupil;
- computer examination of visual fields at 120 points;
- study of visual fields using kinetic perimetry.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following methods are used:
- electrophysiological diagnostics - study of the threshold of electrical sensitivity of the retina and visual evoked potentials;
- ultrasound examination of the eyes, MRI of the orbit of the eye and brain;
- coherence tomography of the optic nerve;
- fluorescein angiography of the retina.
Laboratory diagnostics:
- general blood analysis;
- blood for HIV, syphilis, rheumatoid factor;
- blood culture for sterility;
- PCR studies;
- histological, immunochemical analysis.
If the patient has concomitant diseases, he is prescribed consultations with specialists.
Disease prevention
To prevent optic neuritis, it is recommended to give up bad habits, promptly treat infectious diseases, avoid eye and head injuries, and visit specialized doctors in the presence of chronic pathologies.
Article sources:
- Retrobulbar optic neuritis. Kukhtik S.Yu., Popova M.Yu., Tantsurova K.S. Bulletin of the Council of Young Scientists and Specialists of the Chelyabinsk Region, 2016
- Visualization of the optic nerve in the diagnosis and monitoring of retrobulbar neuritis. Yuryeva T.N., Burlakova E.V., Khudonogov A.A., Ayueva E.K., Sukharchuk O.V. Acta Biomedica Scientifica, 2011. p. 133-136
- Modern view on the problem of optic neuritis (systematic review). Krivosheeva M.S., Ioileva E.E. Saratov Scientific and Medical Journal, 2022. p. 602-605
- Results of treatment of optic neuritis. Latypova E.A. Saratov Scientific and Medical Journal, 2022. p. 875-879