Perforation of a tooth is a pathological hole of artificial origin between its root or crown part and the connective tissues of the periodontium. The latter are located in the slit-like space between the alveolar plate and the bone tissue of the cement, which covers the neck and root of the tooth. The problem arises during endodontic treatment and manifests itself as sharp, stabbing pain. The dentist can diagnose it either immediately (using a probe or endodontic file) or a little later (by referring the patient for an X-ray or CT scan).
The CELT Dentistry Department invites you to undergo treatment for tooth perforation in Moscow. Our clinic is multidisciplinary and has been operating in the paid medical services market for almost a quarter of a century. Our patients are treated by leading dentists who have decades of scientific and practical experience. They have a powerful diagnostic and treatment base, which helps them accurately diagnose and carry out treatment in accordance with international standards. You can view our prices in the price list by going to the “Services and Prices” tab. Although we update them regularly, we recommend checking the numbers with our information line operators or visiting your doctor.
Dentist consultation - 1,000 rubles.
Closing perforations (MTA) - RUB 6,500.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a consultation with a dental surgeon is 1,000
Make an appointment
What is perforation and its types
Perforation refers to tooth pathology, which manifests itself as a hole in the dental tissue that flows into the tooth cavity. A phenomenon such as perforation is rare, but the defect is quite serious and requires mandatory treatment. Depending on the location, the following types of perforation are distinguished:
- Bottom of the tooth cavity. This type of perforation is observed when the dental axis is displaced and can develop against the background of abrasion of the tooth surface. More often, the development of such perforation is caused by a strong expansion of the dental cavity, which can form during the treatment process.
- Tooth root. This type of perforation is the most common and requires immediate treatment, as it can cause the development of a destructive process in the periodontium. One of the main factors for perforation is incorrectly positioned or twisted roots. To find out the location of the hole in the canal, an x-ray is performed.
- Walls of the tooth. The formation of perforation in the area of the dental walls is caused by improper manipulations by the dentist. Its manifestation is the result of inaccurate strong impact on the tooth during its treatment. This pathology can be detected immediately, as gum bleeding and pain appear.
Depending on the time of manifestation of perforation, it can be fresh - it appears immediately after formation, and old, when the pathology has no symptoms for a long time, it becomes the cause of infection of dental tissues. If the defect is not corrected in time, the affected segment of the tooth, as well as the tooth as a whole, may be lost.
Diagnosis
At the time of a dental operation that led to perforation of the maxillary sinus, the doctor draws a conclusion about a new problem based on the signs described above. If perforation is questionable, the dentist's findings are rechecked using the following methods:
- probing with a thin probe;
- radiography - shows dark accumulations of blood, tooth root fragments and filling cement located inside the maxillary sinus, can be done with the preliminary administration of a contrast agent;
- CT scan;
- general clinical blood test - necessary when identifying an old problem to make sure there is an infection in the body.
Possible causes of pathology
Most often, tooth perforation is caused by incorrect manipulations by the doctor. Only in some cases does pathology develop against the background of other dental problems. The most common factors in the development of perforation include:
- Curved shape of root canals. When the canals are strongly curved, the process of tooth treatment becomes significantly more complicated. Narrowed and curved canals can be damaged if handled carelessly. A high risk of perforation is present during dental procedures aimed at eliminating infection that affects the internal dental tissues. Also, such a pathology often forms when the canals are greatly expanded or when preparing the tooth cavity for the installation of an inlay or pin.
- Injury to teeth. Mechanical impact on the dental cavity is one of the most common causes of perforation. Careless impact on tooth tissues with instruments can damage them, which leads to the subsequent formation of a hole. To exclude tooth perforation, you must carefully select a clinic and specialist.
- The result of caries complications. This perforation is caused by the destruction of the dental cavity by caries. Developing periodontitis not only causes perforation, but also leads to tooth loss.
Also, the risk of perforation of the tooth canal, its bottom or walls increases when the central dental axis is deviated from the norm. Perforation can be caused by severe abrasion of the chewing surface, thinning of the walls of the teeth, and dental procedures performed through an artificial crown.
Why does damage occur?
A patient may experience a perforation for several reasons.
- Mechanical injury. A blow or bruise to a tooth, as well as a medical error during treatment and filling of a canal, installing a crown or fixing an inlay, which indicates low qualifications or insufficient experience of the specialist.
- Anatomical and physiological features of humans. Narrowed or curved roots, incorrect position of canines, incisors and molars, jaw displacement, and bone atrophy can complicate the treatment process and lead to tooth perforation.
- Caries. The disease softens the dental tissue, in place of which a through hole appears from the top of the canal to the bottom of the crown.
What happens if you leave the problem without a solution?
Tooth perforation is a fairly serious problem leading to various dental problems. If a cavity forms in the root canal, root apex or tooth walls, immediate treatment is required. Lack of therapy can lead to the following consequences:
- the development of a granuloma - a cavity filled with pus, which can grow, gradually affecting nearby tissues;
- if left untreated, granuloma can develop into a cyst;
- if the tooth structure is severely damaged, root fracture may occur, which is difficult to detect without x-rays;
- development of inflammatory processes with severe painful symptoms that complicate chewing food;
- Aggravated tissue inflammation can affect speech, causing speech defects.
The perforation options don't end there. Various inflammatory and destructive processes can develop, which lead not only to dental diseases, but also to their loss.
Prevention
When carrying out endodontic treatment, preventive measures play a significant role in preventing perforations:
- mandatory x-ray examination of the curvature of the root canals in all patients;
- changing the shape of hand tools according to the curvature of the roots;
- good visualization of the working field;
- control of the movement of the working tool;
- reduction of pressure when even minor obstacles arise in the advancement of instruments.
Symptoms of pathology
In the first stages of perforation development, symptoms are absent or mild, so the patient does not consult a specialist. Pronounced symptoms appear as a result of complications of perforation. In rare cases, signs of a problem can be recognized in the early stages. These include:
- the appearance of sharp pain in the oral cavity;
- swelling, redness, inflammation of the gums;
- headaches and weakness;
- bleeding that appears from the resulting wound;
- periodic aching pain (with old perforation).
The difficulty in identifying perforation is due to the fact that it cannot be recognized visually. The formation of a cavity in the dental canal in the root area occurs within the structure of the teeth. Sometimes the dentist can immediately detect the formation of a perforation when the position of the instrument in the canal changes suddenly.
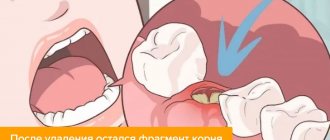
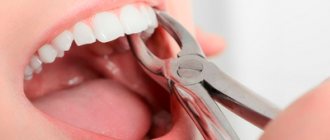
In what cases is a tooth removed?
In the previous section, we looked at what it is to close a tooth root perforation and how effective this treatment method is. But it is not always possible to use it and sometimes you have to resort to a last resort - tooth extraction. The need for it arises in the following cases:
- significant destruction of the tooth root;
- tooth mobility 3-4 degrees;
- development of purulent inflammation;
- inability to close the perforation due to technical difficulties or anatomical features of the tooth.
After tooth extraction, treatment continues for some time and includes taking antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Diagnostic methods
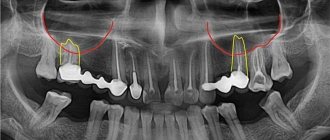
Diagnosis of tooth perforation is based on patient complaints and visual examination of the oral cavity. In most cases, perforation in the crowns of teeth can be recognized using an x-ray. If there is a suspicion of perforation localized in the area of the bottom of the dental cavity, an X-ray with contrast is performed. In any case, an image is taken that allows you to determine not only the presence of perforation, but also to identify complications caused by the pathology.
When holes form in the dental canal, additional equipment and tools are required to identify them. It is easier to diagnose perforation when there are already symptoms: sharp pain, mild bleeding, changes in the movement of the instrument during dental treatment.
With old perforation formed in the canal, symptoms appear, which in their manifestations resemble periodontitis. It is diagnosed along with inflammation, which affects the tissues located near the roots of the teeth. In the presence of such perforation of dental units, characteristic pain in the tooth is observed, which appears when pressing on the damaged segment, swelling of the gums, concentrated in the area of inflammation.
Tooth perforation, localized in the root of the teeth, is diagnosed using a paper pin by immersing it in the canal. The location of the perforation is determined by the trace of blood that remains on the paper.
Diagnostics
Timely detection of perforation and timely elimination of pathology is the best solution to the problem. An undetected hole in a tooth leads to the development of pathology in the tissues or an increase in the size of mechanical damage.
The nature of the pathology can be determined using hardware diagnostics:
- X-ray using a contrast agent;
- vital staining of units;
- electroodontic diagnostics;
- light fluorescence;
- laser diagnostics.
An X-ray with contrast is performed precisely, in 2D format. A targeted X-ray differs from a panoramic X-ray in the small volume of the image - a pair of adjacent units next to the one being examined. In the picture you can see the focus of root inflammation, and also analyze the condition of the sealed canals.
With the help of vital staining of the molar crown, you can see the smallest cracks in the enamel. However, the method does not allow determining deep tissue damage.
Electroodontodiagnosis was used back in Soviet times, when there was no MRI and CT. This method allows you to determine the condition of the pulp after injury or other adverse processes with a molar. The dentist directs the electric current and determines the condition of the internal tissues of the tooth by assessing the excitability of the nerves. Diagnostics answers the questions: is it possible to cure the unit under study, is there a cyst on the root?
Light fluorescence allows you to assess the depth of tissue damage. The method involves illuminating the molars with a special lamp. The diagnostic picture is displayed on the monitor at the same moment. The doctor can see any damage that may be located both in the root system and at the bottom of the tooth, and on the surface of the crown.
Laser diagnostics is carried out using a diode laser with red radiation. This method is the most advanced, as it allows you to detect hidden pathological cavities in hard-to-reach places.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment method for perforation depends on its type and degree of neglect, location, size, presence or absence of complications. The specialist carefully studies the patient’s clinical picture and the data obtained during the diagnosis. Perforation can be treated by two methods: therapeutic and surgical. The first includes the following activities:
- When a tooth is perforated, it is necessary to close the resulting hole using special materials. When small cavities are formed, they resort to filling. The procedure is possible for perforations located close to the crown of the teeth.
- If a hole is found in the teeth, localized in the root canals, it must be eliminated using a microscope. This allows you to minimize the risk of errors and ensure high quality results. When performing this work, biocompatible materials are used.
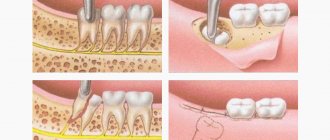
If the perforation of a tooth is advanced and its elimination is impossible with the help of a therapeutic method, they resort to surgery. It provides the following manipulations:
- Resection of the apex of the tooth root is performed. The specialist removes a section of the root that is no longer viable. Along with the tooth perforation fragment, the source of infection, which is located in the peri-root tissues, is also removed.
- Resection is effective not only in case of perforation, but also in eliminating complications that develop against it. After such a procedure, the tooth can last for many years, provided that there is no high load on it.
Tooth perforation can also be eliminated by combining the first and second methods. It is indicated for the old form, when therapeutic treatment has not yielded results. The doctor makes an incision in the gum to gain access to the hole, seals it, uses osteogenic materials, and then sutures the gum tissue.
How we treat
Treatment is carried out only comprehensively and strives to be carried out in one visit , simultaneously:
- Hygienic cleaning and dental treatment We prepare the oral cavity for sterile surgical work. We treat compromised roots. Operations are performed only in a sanitized oral cavity to avoid re-infection.
- The operation is carried out in the surgical department, subject to all conditions of sterile operating rooms. Ultrasound removes inflammatory processes, removes roots that provoked or supported inflammation, eliminates all inflammatory elements, removes cysts, polyps, mucoceles, and foreign bodies.
- Orthopedics Temporary crowns or any other orthopedic elements are fixed to mask the work performed. We do everything to avoid sending the patient home without teeth!
We do not welcome radical and punitive surgery!
Rest assured that after surgery we will never keep you in the hospital unless absolutely necessary.
Levin Dmitry Valerievich Chief physician and founder of the Doctor Levin center
Features of the maxillary sinus
The maxillary, or maxillary, sinus is a cavity inside the skull, bounded on all sides by bone tissue. In adults it is quite voluminous, sometimes reaching 10 cm3. Its shape and location in the bones determine the unique pronunciation inherent in humans. The cavity, resonating, forms the timbre of sound.
The paranasal sinuses are lined from the inside with a thin mucous membrane and are connected to the nasal cavity by thin tubules for drainage of mucus and ventilation. If the holes become clogged, inflammation develops - sinusitis.
There are a number of known features that explain the appearance of a hole in the bottom of the maxillary sinuses:
- The size and thickness of the walls separating the maxillary sinuses from the oral cavity are individual for each person. With thinned bone (up to 1 mm thick), the sinus is easily perforated when the dentist works. This is also facilitated by the proximity of the roots of the front teeth.
- It happens that the roots of distant teeth penetrate into the sinus area and are separated from it only by a thin film of mucous tissue. As long as the tooth is healthy, everything is fine. If the doctor begins to manipulate the canals of such teeth, the mucous membrane breaks through and penetration occurs.
- Even healthy bone can atrophy and become thin and weak with persistent periodontal and periodontal diseases. Or the trabeculae of the upper jaw - the plates that form its skeleton - are insignificant from birth. It is easy to perforate such an obstacle with sharp instruments.
Therefore, it cannot be unequivocally stated that the doctor is always to blame for the development of complications.
What factors are taken into account by the dentist when performing an intervention?
The likelihood of sinus perforation increases when the tooth root is located in close proximity to it at the time of extraction. Therefore, surgical treatment should be carried out with extreme care and subsequent X-ray monitoring of the tissue condition after surgery. The dentist also monitors the condition of tissues when using pins for implantation or when treating root canals for filling purposes, since there is a high risk of filling material and root fragments penetrating into the maxillary sinus.
If the process occurs at the time of implantation into bone tissue or when filling canals, then this is a direct mistake that is made by the doctor during his therapeutic tactics. The only way to control manipulations is X-ray control and the experience of the dentist, who, when working, must take into account the anatomical structure of the patient’s upper jaw. In this case, damage to the bottom of the sinus is fraught with serious complications that are difficult to eliminate. Especially if this happens during the implantation of artificial roots. The bone tissue in the upper jaw quickly undergoes degenerative changes, and this leads to a decrease in the height of the alveolar process.
When performing root resection to eliminate cystic formations, as in the above cases, the dentist must fully examine the patient. If the history is insufficient, perforation may occur in a situation where the doctor does not know the exact size of the bone plate that separates the bottom of the sinus from the wall of the cyst itself. In this case, the prognosis worsens if it is necessary to remove a large volume of bone tissue.