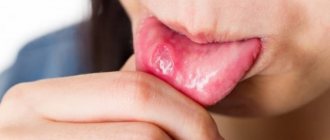
If on child's language bubbles appear, do not try to get rid of them yourself. Surely there were reasons for their occurrence, and only a specialist can accurately determine them. First, the doctor must find out what exactly triggered the formation of painful blisters on the child’s tongue. The reasons vary. Most often, white blisters appear due to a fungal infection or thrush. Also, their occurrence could be detected by severe dysbacteriosis or as an allergy. It should be noted that most allergic reactions manifest themselves in the form of urticaria, diathesis or dermatitis.
Stomatitis: features of the disease
Stomatitis is a disease related to dental pathologies in which inflammation of the oral mucosa occurs. Infection of the tongue with stomatitis in adults is also called “glossitis.”
The inflammatory process affects the mucous membrane and causes severe symptoms:
- redness and swelling of the tongue;
- formation of white plaque;
- severe pain;
- the formation of many small blisters and ulcers.
Due to severe sensitivity and soreness of the tongue, the patient cannot eat food, fever, insomnia and irritability are possible.
Stomatitis under the tongue in adults, as in other parts of the oral cavity, is classified into two types.
- Aphthous. A form of inflammation in which the tongue becomes covered with papules and ulcers that turn into erosions (aphthae).
- Herpetic. The inflammatory process is manifested by swelling and redness of the tongue. Small bubbles are localized in groups.
Prosthetic stomatitis and ulcerative-necrotic form of pathology are extremely rare.
Without treatment, the signs of stomatitis completely disappear, but this does not mean that the patient is cured of the pathology. The inflammatory process becomes chronic and when the immune system is weakened or exposed to an irritant, a relapse occurs.
What not to do with blisters in your mouth
When blisters appear in the baby’s mouth, it is necessary to adhere to certain rules, which will ensure a positive outcome of treatment. It is strictly forbidden to use iodine, brilliant green and other means for treating the tongue, which are prohibited for treating the mucous membrane.
When using these products, wounds, bleeding, and severe pain may occur.
When to see a doctor
If blisters appear in large quantities on a child’s tongue, it should be shown to a doctor. If several small bubbles appear, it is recommended to provide first aid to the child.
If after a few days the bubbles go away and new ones do not appear, then there is no need to worry. Otherwise, you need to take your baby to see a doctor.
Blisters cannot appear without a reason. They are determined by the doctor, which allows him to prescribe effective treatment.
Causes of stomatitis
Stomatitis under the tongue in adults is a reaction of the immune system to certain types of irritants, which are any substances. The causes of stomatitis have not been clearly identified; presumably, the body exhibits an individual reaction to certain substances or microorganisms.
Possible causes of stomatitis on the tongue in adults:
- bacteria and infections of the oral cavity (caries, gingivitis, periodontitis, etc.);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract of an infectious or viral type;
- respiratory diseases (ARVI, influenza, etc.);
- frequent injury to the tongue by orthopedic or orthodontic structures;
- damage to the tongue due to a chipped tooth;
- fungal infection;
- bad habits (smoking or alcoholism);
- burning the tongue or eating “spicy” foods.
In addition to the listed causes of stomatitis on the tongue in adults, inflammation of the mucous membrane can be caused by the herpes virus (herpetic stomatitis).
Treatment Basics
If an adult has a swollen tongue, the surface is covered with plaque, or has severe hypothermia, you should consult a dentist. Even in the absence of neoplasms in the oral cavity in the form of papules, ulcers or erosions, a specialist will be able to determine the development of the inflammatory process. With timely treatment, the risk of pathology becoming chronic is minimal.
Treatment of stomatitis on the tongue in adults is carried out exclusively conservatively. Depending on the causes of the disease and the clinical picture, the doctor will determine a treatment regimen and prescribe effective drugs of systemic and local action.
The dentist’s task is not only to eliminate symptoms and inflammation, but also to identify the cause. If the provoking factor has a constant impact, then stomatitis under the tongue will constantly recur.
Treatment of stomatitis on the tongue in adults begins with the relief of concomitant diseases - the root causes.
"Chlorhexidine": instructions for use for mouth rinse
This is a cheap and universal antiseptic. Bottle with 100 gr. The product costs about twenty rubles. You can buy it at any pharmacy without a doctor's prescription. True, pharmacists often offer Miramistin, which is more expensive, but do not fall for the assurances that the effect of these solutions is completely identical. They differ from each other only in cost.
Instructions for use for “Chlorhexidine” for mouth rinse indicate that the drug has the following properties:
- stopping the development of infection;
- reducing the activity of pathogenic microorganisms;
- pain relief after tooth extraction;
- disinfection of the oral cavity;
- healing of pimples, inflammations, ulcers;
- acceleration of healing after damage to the tongue, gums, cheeks;
- treatment of sore throat and inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- reduction of swelling;
- accelerated tissue healing after oral surgery;
- reduction of hyperemia.
To rinse, dilute the concentrated preparation in a ratio of 1:5 with clean water. The first rinse should be a test: if the child does not experience excessive burning, then the procedure can be continued. Otherwise, the solution should be diluted by another third.
How is the treatment carried out?
Treatment for stomatitis is comprehensive.
- Anesthesia. To eliminate pain, the dentist may prescribe topical medications containing lidocaine or analgesics.
- Antiviral therapy. If the disease is caused by a herpes virus, the doctor prescribes antiviral drugs of the appropriate group of effects.
- Antibacterial therapy. In case of bacterial stomatitis, local treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions and dental ointments with antibacterial action is mandatory.
- Antifungal therapy. Stomatitis can be the result of fungal activity in the mouth. This form is more common in children, but is not excluded in adults. The specialist prescribes the patient a strict regimen of antifungal drugs.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy. It is carried out in cases of severe inflammation. The dentist recommends taking anti-inflammatory systemic drugs that have a targeted effect depending on the pathogen or cause of tongue stomatitis.
- Diet. Patients with stomatitis are prescribed a diet that excludes foods that can aggravate irritation of the mucous membrane and tongue. So dentists recommend avoiding hot, spicy, sour and salty foods. Smoking and drinking alcohol should be avoided.
Together with the treatment of stomatitis, treatment of diseases of the respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, inflammation of the gums, caries, etc. can be carried out.
Causes of blisters on the root and body of the tongue
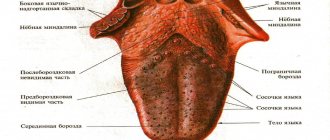
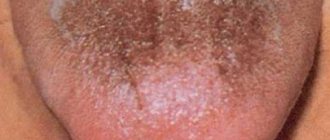
A healthy person's tongue is pale pink; its structure is symmetrical, its surface is velvety. If there are infectious agents in the body, the signs change, and a dense coating with numerous blisters appears on the mucous membrane, localized on different parts of the unpaired outgrowth.
Visually, the rashes look like group (less often single) translucent neoplasms with liquid inside. The color of the blisters varies from white to bluish-red, often they are outlined by an inflamed edging of pink shades.
The most common causes of white blisters on the tongue are second-degree thermal burns caused by excessively hot food and drinks. If acids (alkalis) accidentally come into contact with the oral mucosa, chemical burns occur, also accompanied by rashes.
White blisters on the tongue appear in smokers. Rashes can develop into cancer.
Infectious lesions of the body, accompanied by the appearance of blisters (near the throat, on the body of the tongue), are classified into several groups. Among the reasons for the formation of bubbles are pathologies of the respiratory system, dental diseases, and diseases caused by viral infectious agents.
Candidal stomatitis
Manifestations of candidal stomatitis
The disease develops against the background of dysbacteriosis, more often during long-term use of antibiotics with a wide range of effects on microorganisms. Manifests itself in the form of thrush:
- mixed form;
- fungous type.
It begins with the appearance of whitish pinpoint formations on the mucous membranes, which after 48 hours merge into a cheesy white coating tightly fused with the tissues of the oral cavity. A detailed examination reveals small bubbles around the perimeter of the tongue.
The pathological condition is accompanied by a burning sensation and difficulty in eating.
It is diagnosed in both an adult patient and a child (including a newborn).
Dermatological diseases
Manifestations of atopic dermatitis
Blisters on the tongue quite often indicate that the patient has such ailments as:
- atopic dermatitis;
- lichen.
The diseases affect both the skin and the oral mucosa. They are characterized by the appearance of red blisters on the tongue, located closer to the throat. The bubbles are filled with colorless liquid and can spread from the oral cavity to the surface of the face (wings of the nose, lips).
Both children and adults can suffer from these diseases.
Herpetic infection
A sharp increase in colonies of the herpes virus in the body is the cause of plaque on the tongue. When immunity is reduced, cheesy deposits are accompanied by the appearance of neoplasms. To correctly identify the blisters located at the very root of the tongue, you should familiarize yourself with the photo:
Herpes on the tongue
When the blisters burst, they release watery contents into the oral cavity, which contributes to the further spread of pathogens. An ulcer forms at the location of the blister.
Additional symptoms of the disease are high fever, general weakness, chills, suppressed appetite and pain in the mouth. Both adults and children can get the disease.
A child infected with the herpes virus experiences disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea) and enlarged lymph nodes. A white, dense coating appears on the root of the tongue, and later rashes are discovered.
Pathologies of the respiratory system
Blisters on the throat with sore throat
Diseases of the upper respiratory tract accompanied by inflammatory processes in the mouth include:
- angina;
- chronic pharyngitis.
Blisters on the root of the tongue that occur with the above diseases do not cause much discomfort in humans. Visually, the bubble near the throat looks like a conical red neoplasm (you can see it in more detail in the photo).
The red color of the bubbles at the very root of the tongue has one peculiarity: they interfere with speaking, but do not cause pain
All age categories of patients can get sick.
Dental diseases
Diseases such as gingivitis and caries also cause blisters on the root of the tongue (the latter are accompanying symptoms of the disease). The main signs of the disease are: pigmentation of the enamel, defects in the hard tissues of the teeth, bleeding gums.
Photo of blisters located on the tongue closer to the throat
Chicken pox, scarlet fever
Blisters on the tongue with scarlet fever, chicken pox
Blisters on the root of the tongue are the first signs of the infectious diseases in question. Small bubbles are filled with gray-yellow exudate. New growths that appear on the tongue cause pain and burning during swallowing movements. The illnesses are accompanied by general weakness and fever. With scarlet fever, swelling of the larynx occurs.
Chickenpox is more often diagnosed in a small child than in an adult, but in clinical practice there are frequent cases of re-infection at an older age (patients who suffered from the disease in the first few years of life are ill).
General recommendations
For stomatitis in adults, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. The dentist can perform initial treatment of the oral cavity, then the patient will need to perform all the manipulations independently at home.
Antiseptic treatment of the entire oral cavity is a prerequisite for the successful treatment of stomatitis and the rapid recovery of the affected mucosa. For “disinfection”, solutions containing chlorhexidine, furatsilin or metronidazole are used. Dentists also recommend rinsing with a soda solution every 2-3 hours.
Locally in the affected areas, it is necessary to remove heavy plaque using gauze and apply anti-inflammatory and regenerating gels or ointments to the areas where ulcers accumulate. The procedure is unpleasant, but significantly speeds up recovery.
Treatment of stomatitis on the tongue in adults, subject to all prescriptions and recommendations of the dentist, takes no more than 10 days. Symptoms of the disease disappear after 3–5 days; a few more days are required to restore the affected tissues.
Traditional methods of treating blisters on a child’s tongue
Many children are afraid to rinse their mouths with medicinal products. But the herbal infusion, which tastes like regular tea, is received with a bang. Some dry crushed herbs have excellent antiseptic and astringent properties.
- One tablespoon of dry crushed calendula should be boiled in 0.5 liters of water. Rinse your mouth with the resulting infusion for one minute three to four times a day. It is recommended to do this after eating. At the same time, you cannot give up brushing your teeth and usual hygiene procedures.
- Mix chamomile, calendula and yarrow in equal proportions - one tablespoon each. Boil for five minutes in 0.5 liters of water. The child should rinse his mouth with the resulting decoction for one to two minutes daily. The more often the procedure is performed, the better.
- A decoction of dry oak bark has excellent astringent properties. Able to alleviate pain in the presence of ulcers and blisters in the child’s mouth. The infusion should be prepared in the proportion of two tablespoons per half liter of water, boil for two to three minutes.