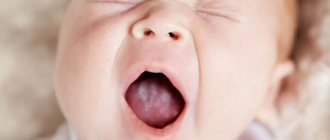
Causes of stomatitis
In children, as in adults, stomatitis can be caused by viruses, fungi, bacteria, allergies and injuries. About six months after birth, the child loses the immunity received from the mother, the protective power of the immune system changes, and the child’s body becomes more susceptible to infections. The oral mucosa in children is more delicate and easier to injure; children also more often “bite” their cheeks after dental treatment due to a temporary loss of sensitivity after anesthesia, which causes traumatic stomatitis.
Children are not always motivated to brush their teeth, so poor hygiene can also cause stomatitis.
With the following diseases, stomatitis is observed in children much more often: chronic tonsillitis, diabetes mellitus, heart defects, chronic hepatitis.
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
Classification of HRAS (chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis)
| CLASSIFICATION | A COMMENT | ||
| classification: | According to the degree of damage to the mucous membrane: | a comment: | 1) Superficial (catarrhal, fibrinous) 2) Deep (ulcerative, necrotic) |
| classification: | According to the clinical course: | a comment: | 1) acute 2) chronic |
All types of stomatitis occur in children, but the most common are: herpetic, candidal and traumatic stomatitis.
Acute herpetic stomatitis
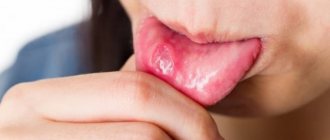
It occurs most often, and mainly affects children from 10 months to 3 years.3 The appearance of rashes is preceded by inflammation of the lymph nodes.
With a mild form
In acute herpetic stomatitis, the temperature rises to 37-37.5°C, the general condition is satisfactory, slight swelling and redness may occur on the gums, then up to six blisters appear, which burst with the formation of painful aphthae surrounded by a red rim.
Afta is a round-shaped erosion. Aphthae may merge together. The rash appears once, and after 1-2 days the erosion gradually heals.
Moderate form
Acute herpetic stomatitis is characterized by deterioration of the child’s well-being, weakness, and headache. The child is capricious, has no appetite, the lymph nodes are enlarged and painful, the temperature rises to 38-39°C, the symptoms resemble ARVI. The oral mucosa is swollen, reddened, rashes appear (bubbles, then erosions) of 10-15 pieces, and often there are rashes on the face. Salivation increases, and gingivitis appears (inflammation of the gums, accompanied by bleeding). The rash may appear several times, i.e. after the old ones heal, new ones appear. Healing of erosions takes up to 4-5 days. Bleeding gums and swollen lymph nodes persist for some time after the erosions have healed.
Severe form
It begins as an acute respiratory viral infection, there is pain in the muscles, joints, tachycardia and bradycardia (increased and slow heartbeat), and nosebleeds may even be observed. In this form, the temperature is high up to 40°C, gingivitis is pronounced, the mucous membrane is bright red, swollen, the child’s lips are dry, the mucous membrane of the eyes is swollen, reddened. The rashes constantly appear again, their number can reach 100. Rashes often appear around the mouth, on the eyelids, on the mucous membranes of the eyes, between the fingers, on the earlobes. Simple gingivitis turns into ulcerative (a more severe form of gum inflammation, with the formation of ulcers), salivation increases, and bad breath appears. Recovery is long and hospitalization is often required.
Enteroviral vesicular stomatitis (arm - leg - mouth)
Caused by enteroviruses. It also occurs in adults, but in 95.7% of cases children are affected.6 It is characterized by seasonal occurrence (summer - autumn) and group incidence.4 It is observed mainly in children under 10 years of age. Vesicular stomatitis is contagious, so it is recommended to use separate utensils and hygiene products. Characteristics for this disease: temperature 37.5-38, weakness, headache, muscle pain, rash on the palms, soles, as well as blisters on the hard palate and pharynx, which then turn into erosions that are almost not painful.
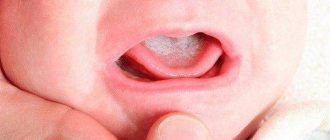
Acute pseudomembranous candidal stomatitis (thrush)
Acute pseudomembranous candidal stomatitis (thrush) occurs:
- Light shape
- Medium-heavy forms
- Severe form
The main symptom of the disease is a white or yellow coating.
With a mild form
The plaque is located in islands, most often on the tongue and cheeks. Children are restless, sleep poorly, and suck the breast sluggishly. Older children may complain of a burning sensation. The plaque is easily removed; underneath there is a bright red mucous membrane. The disease lasts no longer than 7 days.5
Moderate form
The plaque is located on the cheeks, tongue, hard palate, and mucous membranes of the lips. Under the plaque, erosions form, which sometimes bleed. The plaque is more difficult to remove. Lymph nodes are sometimes enlarged and painful. The duration of the disease is 10-15 days, there are relapses.
Moderate form
The plaque is dirty gray, almost cannot be removed, and is located on the tongue, cheeks, soft palate, tonsils, pharynx, and mucous membranes of the lips. Cheilitis appears in the corners of the mouth - inflammation of the lips. The oral mucosa is dry and inflamed. The child’s health is impaired, the child refuses to eat, and the temperature rises. Lesions in the genital area, neck folds, and between the fingers are also common. The disease is long-term, with frequent relapses.
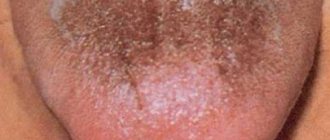
A red or pale tongue is not the norm!
Both options indicate pathological changes occurring in the child’s body:
- A crimson-red tongue always indicates the presence of an infection (viral, bacterial or fungal). Most often it is tonsillitis, scarlet fever, stomatitis or glossitis.
- A red and shiny tongue is a sign of anemia, exhaustion and severe stomach disease;
- A cherry tint is a sign of influenza and measles, as well as general intoxication or kidney dysfunction;
- A bluish color indicates a lack of oxygen; there is reason to suspect disorders in the cardiovascular system or lungs;
- Purple color may indicate blood and lung diseases, heart failure.
- A too pale tongue, being penetrated by blood vessels, a priori cannot be lighter than blood. In most cases, this sign indicates exhaustion, deficiency of folic acid or vitamin B 12.
Let us remind parents that very often there may be a coating on the surface of the tongue, the color of which also has its own characteristics.
Bacterial stomatitis in children
Necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis is more common in weakened children and is caused by fusobacteria and spirochetes. May be a sign of periodontal disease (progressive destruction of periodontal tissue). It is characterized by the appearance of painful ulcers, weakness, gingivitis (inflammation of the gums), enlarged and painful lymph nodes, difficulty eating, speaking, and bad breath.
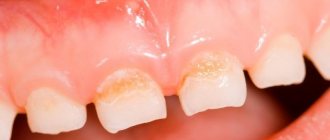
Often, erosions in traumatic stomatitis can become infected through dirty hands, toys and other objects, then bacterial stomatitis develops, so it is important to pay attention to antiseptic treatment.
Should I worry?
At first glance, this problem seems trivial to some. But we must not forget that the tongue is an important organ. With its pathology, a person is reluctant to communicate with others, and the full process of eating is disrupted. Therefore, if a symptom such as discoloration or soreness appears, the tongue is covered with a white coating or it stings, such discomfort and unpleasant sensations cannot be tolerated.
What does a healthy organ look like? Firstly, it is medium in size. It is pale pink in color. His papillae are not enlarged, they are of normal size. As for humidity, it should be moderate. There are no films or ulcers. Its lower part has a thin mucous membrane. By the way, by her condition you can always find out whether the patient has negative changes in the body.
If the tongue is covered with a dense white coating, and besides, it cannot be cleaned off, this is an alarming sign. In this case, as a rule, sensitivity increases and functionality is impaired. Dense plaque can be a sign of chronic infections and pronounced development of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Visit a doctor when the deposits are constantly present and there is an unpleasant odor. Do not delay your visit if standard hygiene measures do not clean your tongue, tooth marks and swelling have appeared on it, and the color has become grey, yellow or white. Make an appointment with your dentist if your papillae become enlarged and you experience dry mouth, burning sensation, and loss of taste sensitivity.
Traumatic stomatitis in children
A specific form of traumatic stomatitis in children is Bednar's aphthae . This is a traumatic erosion of the oral mucosa. In children, unlike adults, the mucosal epithelium consists not of four layers, but of two, so it is easily injured. The cause may be early teething, a rough nipple from the mother, or a long nipple on the bottle. Erosion is most often located in the middle of the palate or opposite the cutting edge of the teeth. The child begins to refuse food, cries, and sleeps poorly.
Traumatic stomatitis also occurs in children when wearing braces. Erosions have uneven edges, are painful, and are usually located on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and lips, less often on the tongue.
What does diagnostics include?
Recognizing a “hairy” tongue is not difficult. All changes can be easily seen with the naked eye. Clearly elongated, dark-colored filiform papillae directly indicate the development of pathology. However, it should be noted here that in medical practice there is also such a concept as “false hairy tongue,” and in this case we will be dealing with simple pigmentation of its surface.
Usually the cause of the so-called false phenomenon is a malfunction of the intestines or, for example, a lack of proper hygiene and acute inflammatory processes in the oral mucosa. As part of the diagnostic examination, the doctor will conduct a thorough visual examination and may also suggest a bacterioscopic examination for the presence of leptotrichium bacteria.
Only a dentist can diagnose the disease
Drug-induced stomatitis
Occurs when there is an allergy to a drug. Often, allergies can occur to antibacterial, antimicrobial drugs, vaccines, iodine. The mucous membrane is red, swollen, the lips and tongue also often swell, blisters appear, which burst, leaving erosion. The gums are inflamed and bleed when touched. General manifestations are possible, such as urticaria, nausea, vomiting. In severe cases, anaphylactic shock occurs (an emergency condition manifested by decreased blood pressure, shortness of breath, fainting, suffocation), Quincke's edema (an atypical reaction of the body, manifested by rapid and severe swelling)
Both conditions are extremely dangerous and require immediate action and calling an ambulance!
Prevention of stomatitis in children
In children's groups, infections spread especially quickly. Therefore, if a child is infected with the herpes virus, he needs to stay at home until he recovers. Children who have been in contact with sick people should use antiviral ointments for 5 days.
If a pregnant woman has herpes or candidiasis, she should treat it before giving birth. If you have the herpes virus during the period of illness, you should use separate utensils, do not kiss children, and wear a mask.
Kindergartens and other preschool institutions must be cleaned and objects, including toys, must be treated with disinfectants.
To avoid allergic reactions, you should seek help from an allergist to identify existing allergies.
It is worth preventing a decrease in immunity; hardening works especially well in childhood. It is worth limiting your intake of fast carbohydrates, because... they create a favorable environment for the development of candidiasis. An important point is the proper nutrition of the child; regular intake of vitamins, especially vitamin C, is essential.
Tantum® Propolis
For children over 14 years of age , you can use Tantum® Propolis lozenges; they contain a lot of vitamin C, which will strengthen the immune system, and propolis has an anti-inflammatory effect, preventing the occurrence of infections.7
Find out more
Prevention of Bednar's aft is preparing the breasts for feeding, using special creams to soften the skin, prevent cracks, and it is also worth choosing the right bottle. In case of injury due to braces, you need to use orthodontic wax; here it is important to prevent the wounds from becoming infected, so it is better to treat them with antiseptic solutions and sprays.
Tantum® Verde spray will relieve pain at the site of injury and its antiseptic effect will prevent infection.8,9
How to treat pathology
Since the appearance of dark hair-like growths on the tongue is not a full-fledged independent disease, the help of a therapist or gastroenterologist may well be needed to treat the root cause of this symptom. As for symptomatic therapy, the patient can be offered tissue restoration using the following methods:
- application therapy: applications soaked in a keratolytic agent are applied to the darkened area - it has a mild effect on dead cells and stimulates metabolic processes in tissues. This method is good because its use does not damage the mucous membrane, but at the same time it gives only a short-term effect,
- injection: the patient is given an injection of 2% novocaine and calcium chloride directly into the source of the lesion. The procedure is usually carried out twice a week. This method is considered less traumatic and the most effective,
One of the treatment methods is injection - cryodestruction: in this case, the keratinized areas are irrigated with liquid nitrogen, which leads to the gradual death of the deformed papillae. This procedure makes it possible to quickly get rid of the defect, but it is not carried out in all clinics.
As part of the treatment, the patient is also prescribed medications. Otherwise, the main emphasis is on eliminating the original source of the problem, which is dealt with by highly specialized specialists.