Causes
The exact causes of the pathology are not fully understood. The disease is not an independent disease; it appears against the background of other diseases. Most often, this phenomenon occurs in men over 40 years of age, but is sometimes observed in women. This disease is very rare in children.
The pathology is most often observed in people with gastrointestinal dysfunction, ulcers and gastritis. The development of the disease is greatly facilitated by poor oral hygiene, smoking habits and excessive coffee consumption.
The main causes of the development of the disease are considered:
- long-term use of medications, especially antibiotics;
- fungal infections;
- dehydration;
- chemotherapy;
- metabolic disease;
- weakened immune system;
- Regular rinsing of the mouth with solutions containing astringents.
The risk group also includes people with dental defects and the absence of a large number of teeth, since in this case they are forced to eat only soft food, which does not have the proper abrasive effect on the surface of the tongue.
Geographical language. What kind of disease is this and how to deal with it?
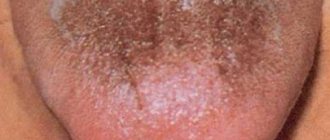
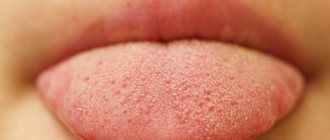
Geographic tongue (benign migratory glossitis) is an inflammatory disease that manifests itself as lesions on the back and sides of the tongue.
Typically, the affected tongue has a "bald" red area of varying sizes that is partially surrounded by an irregular white border.
The appearance of the affected part of the tongue is the result of the loss of finger-shaped projections (papillae) that cover the surface of the tongue. From time to time, similar lesions appear in other parts of the mouth - the palate, cheeks, under the tongue or on the gums. This is called geographic stomatitis or erythema migrans.
Geographic tongue can vary in color, shape and size - hence the name. Manifestations can persist for different periods of time - days, months and even years. They often disappear completely on their own. But they may appear again later.
What causes geographic language?
The causes of this disease are not fully known. Factors suspected include emotional stress, bad habits, allergies, diabetes and hormonal imbalances. An association between geographic tongue and psoriasis has been reported. However, none of these factors have been conclusively linked to geographic language.
Who gets geographic language?
Geographic tongue is a fairly common condition. Some reports in the medical literature indicate that geographic tongue affects women slightly more often than men. This can happen at any age, including in childhood. It is estimated that it may occur in 1-2.5% of the population.
Is it possible to get infected with it?
No, geographical language is not contagious. There is no evidence that the disease is transmitted in any way.
How is geographic tongue diagnosed?
Based on clinical examination and detailed history.
Are there any complications?
Geographic tongue is a disease that does not pose a threat to general health.
Does geographic tongue require treatment?
In most cases, there is no need to treat this condition.
Apart from appearance, geographic language in most cases does not manifest itself in any way. Sometimes it can cause unpleasant sensations: burning, tingling of the tongue, most often associated with eating spicy or sour foods.
If discomfort persists, your pediatrician may recommend anti-inflammatory medications (topical corticosteroids, such as triamcinolone in toothpaste applied several times a day as needed) or pain medications (local analgesics) applied directly to the affected areas. Antiseptics and anesthetics may also be effective.
Some authors have reported that the use of cyclosporine, topical and systemic antihistamines, and topical retinoids can sometimes produce beneficial results.
Can geographic tongue transform into cancer?
There are no documented cases of geographic tongue causing cancer.
Should you see a doctor if you suspect geographic tongue?
Geographic tongue is an uncomfortable condition but does not cause health problems. However, tongue damage can be a sign of other serious illnesses.
If you or your child has tongue lesions that do not go away within 10 days, be sure to contact your primary care physician/pediatrician or dentist.
Symptoms
Pathology is immediately detected during a visual examination by a dentist. In the initial stages of the disease, the presence of a foreign object in the mouth is felt, other unpleasant signs gradually appear, then the upper part of the tongue noticeably turns black. In advanced cases, the affected area occupies two-thirds of the tongue. The disease is accompanied by unpleasant odor from the mouth, changes in taste sensations, a metallic taste appears in the mouth, a feeling of tickling and soreness on the surface of the tongue, as well as causeless nausea. In rare cases, there is a burning sensation and severe itching.
Differentiation of plaque in gastritis from other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
A thick, grayish coating is characteristic of dysentery.
It is important to suspect the onset of a dangerous disease in time. To take action and prevent complications from occurring. Differential diagnosis by tongue of gastritis from other diseases and conditions:
- A thick, grayish coating is characteristic of dysentery. In this case, the tongue looks cracked, and less saliva is produced than usual.
- Desquamative glossitis - this type of inflammation of the tongue is characterized by such symptoms as red spots of complete absence of epithelium or several altered taste buds on the tongue, covered with a white coating.
- Galvanic stomatitis is a form of inflammation of the tongue that arises as a result of a reaction to metal prostheses, manifested by spots in the form of pimples, and subsequently by the appearance of erosions against a background of white plaque.
- Infectious diseases - sore throat, scarlet fever, diphtheria, HIV infection can cause the appearance of a white coating on the tongue, but almost all of these infections are accompanied by high fever and skin rashes.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels - plaque is located on the anterior third of the tongue.
- Kidney disease - plaque on the tongue is localized at the back along the edges.
- Endocrine disorders - under the plaques of white plaque there are ulcers and erosions.
- Anemia is not a coating on the tongue, but blanching of the entire surface of the organ. Diseases of the respiratory system are often indicated by the localization of white plaque on the front and along the edges of the tongue.
- Diseases of the salivary glands - the appearance of a white coating is accompanied by the appearance of an unpleasant odor.
- Diseases of the liver and gall bladder - the color of the plaque is not white, but has a yellowish or brown tint. A white coating on the tongue can be caused by the consumption of dairy products, as well as the proliferation of bacteria and fungi in those who abuse sweets. Unlike plaque during gastritis, such layers are easily removed and do not form further.
Treatment
It is necessary to contact a dentist or maxillofacial surgeon with such a problem. To obtain a complete clinical picture, it is necessary to undergo examination by a gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, endocrinologist and neurologist. Since the pathology develops against the background of other diseases, a comprehensive treatment regimen is used.
Only treatment of concomitant diseases, professional cleaning and treatment of the oral cavity, taking multivitamin complexes, antifungal medications and, if necessary, sedatives will help eliminate this unpleasant defect. Removal of heavily overgrown papillae can be carried out by cryodestruction (exposure to the pathological focus with liquid nitrogen). It is also necessary to adjust your diet, enriching it with foods with fiber, vitamins and minerals.
The prognosis for black hairy tongue is usually favorable. Elimination of causative factors, as well as appropriate comprehensive treatment of the disease, leads to complete restoration of the surface of the tongue.
Which doctor should you contact?
Few people know which specialist to contact if their tongue becomes stained. In fact, a whole group of doctors can help establish the cause of the disease and get rid of it: a dermatovenerologist, an ENT doctor, a surgeon, a dentist, a pulmonologist, a gastroenterologist and others. The first thing the patient should do is visit a therapist or dentist, who, if necessary, will refer him to a more specialized specialist.
Any pathology, be it small red dots or redness of the entire surface of the tongue, requires timely consultation with a competent doctor.
Prevention
As such, there is no prevention of black villous tongue. Even with good oral hygiene, you can encounter a similar phenomenon, but with timely treatment of diseases that lead to the development of such a complication, you can minimize the likelihood of the disease occurring.
The following rules must also be observed:
- thoroughly brush your teeth, gums and tongue with a soft brush;
- It is necessary to drink enough water, because if there is a lack of hydration in the oral cavity, it begins to develop; bacteria;
- reduce coffee consumption and quit smoking and alcoholic beverages.
The disease recurs quite rarely. During an exacerbation, the patient is advised to follow a gentle diet; food should be warm and soft in consistency.
What changes can there be in the language?
Every morning and evening, after brushing your teeth, it is necessary to examine the oral cavity for pathological changes. The procedure, which only takes one or two minutes, helps to avoid serious illnesses. If a red spot appears on the tongue, it may indicate the development of an allergic reaction, internal or local infectious pathology. With such a symptom you should consult a doctor.
The tongue of a healthy person should be uniformly pink in color, without changes in relief, moist, clean, not enlarged, painless, and moderately sensitive. Pathological changes can be very diverse - from simple redness to ulceration. Here are the main ones:
- neoplasms;
- itching;
- plaque;
- color change;
- ulcers;
- dashes;
- spots of various colors;
- wounds;
- plaques.
It must be remembered that many changes in the language appear for serious reasons and may not be very noticeable at first. Some, such as plaque or discoloration, may not cause discomfort to a person, but this is not a reason to let the situation take its course. The most common problem is stains.
What color is the pathological plaque?
By the color of the coating on the tongue, you can determine which organ malfunction caused it:
| White | A light whitish coating that can be easily cleaned with hygiene procedures is the norm for an adult. A cause for concern is if the white coating is dense or has a cheesy structure and is not cleaned. This may be a sign of a fungal infection. Other reasons include: monotonous diet, lack of vitamins, poor hygiene, smoking, intoxication, wearing dentures, taking medications. |
| Grey | Sometimes the tongue becomes covered with a gray coating when taking antibiotics for a long time. Also accompanies diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. |
| Yellow | Often indicates liver disease (in such cases a bitter taste is felt in the mouth). It can also occur with diseases of other organs of the digestive tract, with viral diseases, with an excess of bile in the body. |
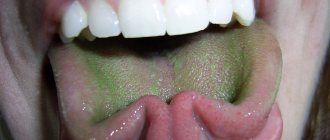
| Green | This is a rare occurrence. Most often it is an indicator of liver problems. |
| Brown | Occurs with disorders of the digestive tract, alcoholism and smoking, and abuse of brown foods (chocolate, coffee, black tea). |
| Orange | It occurs mainly with gastritis, due to the fact that gastric juice enters the oral cavity in large quantities. |
| Blue | It may appear due to problems in the cardiovascular system, kidneys, due to a lack of folic acid, iron, Vit C, Vit B12. It can also appear due to mercury and heavy metal poisoning. |
| Black | Appears in cases of liver dysfunction, lead poisoning, acute infections, Crohn's disease, acidosis. |