The formation of teeth is a complex step-by-step process that begins in the first weeks of intrauterine life. Thus, by the time of birth, the baby has the rudiments of 20 primary and 16 permanent teeth inside each jaw. But, like all stages of development, teething in children under one year and older occurs differently. Some endure this period relatively calmly, others are capricious and sleep poorly. Why this happens and how to understand that the baby is cutting teeth, we will tell you further.
Timing of teething in children
On average, the first teeth in healthy children appear at 5–6 months. But sometimes it happens that someone has a white bump visible at 4 months, and someone smiles with a toothless mouth even at 8-12 months. And this is not a deviation from the norm. According to studies by a number of authors, the timing differs depending on the region of residence, race, and gender of the child. For example, children in the southern regions develop teeth a little earlier than those in the north. The formation of temporary teeth is also influenced by the following factors:
- heredity;
- maternal toxicosis in the second and third trimester of pregnancy;
- prematurity;
- artificial feeding;
- quality of drinking water;
- hypothyroidism and other endocrine pathologies;
- infectious diseases;
- weakened immunity;
- rickets.
It is impossible to speed up the timing and influence the sequence of teething in children. The only thing parents can do at this time is to alleviate the baby’s condition if he is restless and in pain (more on this below).
Reasons for violation
The lower and upper teeth are formed in children at different times. The main factor that influences this is heredity, that is, the predisposition is laid down in genes, as is the quality of dentin, as well as the enamel layer. If mom or dad, grandfather or grandmother, or other relatives had cases of deviation from the order of appearance of chewing organs, this can be inherited by the toddler. Therefore, the child’s teeth grow out of order.
Of course, relatives are always worried when the growth process is delayed and goes astray from the generally accepted schedule. But dentists say that non-standard situations are also normal:
- When the appearance of units occurs several months earlier or later;
- If the order of appearance of the masticatory organs is disrupted;
- When the rate of growth of units does not coincide with the announced scheme;
Since the process of growth of incisors, canines, and molars begins at 12 weeks of pregnancy, it is influenced by the health of the mother. Influenza, bad habits of the mother in labor, and infectious diseases have a negative impact. Artificial feeding has a bad effect on the newborn's body. After all, sucking the mother's breast actively develops the facial muscles, and the correct development of the lower jaw occurs. Sucking from bottles occurs only with the help of the lips. As a result, the first tooth may appear in the top row. In this case, therapy is not needed. It is important that all 20 time units appear.
Remember! Medicine does not know of cases where children were left without chewing organs due to their untimely appearance. The units will appear, you just need to wait.
It wouldn't hurt to go to the dentist. If necessary, bite correction in children is carried out. In addition, a non-standard order can be observed in babies if their parents are of different nationalities, or if the climate is not suitable for the newborn. Many parents see disordered teething as a sign of rickets. Doctors explain that with rickets, babies have a large head, protruding ribs, and excessive sweating. If the pediatrician does not find these signs, then there is no reason to worry. But sometimes the absence of the first units up to a year indicates:
- Vitamin D deficiency in the body;
- Violation of metabolic processes;
- Gastrointestinal problems;
- Chronic diseases;
- Infectious diseases such as measles, scarlet fever;
- Lack of rudiments of future chewing organs;
- Horizontal position of the unit in the gum;
- Bite abnormalities;
- Dysfunction of the endocrine gland system;
- Slow development of the body;
Diagnosis and consultation with a pediatrician or pediatric dentist will clarify the situation and eliminate the problem.
Subsequence
The order in which teeth appear may vary, which is rare and is not considered pathological. For some boys and girls, the upper incisors appear first, rather than the lower incisors as usual. But basically the sequence of teething in children is as follows (teeth appear in pairs):
- lower central incisors;
- upper central incisors;
- upper lateral incisors;
- lower lateral incisors;
- first upper molars (molars);
- first lower molars;
- upper canines;
- lower canines;
- second lower molars;
- second upper molars.
By the age of 2.5–3 years, the child has a full set of baby teeth: 10 on each jaw. After about 4–6 years, the roots begin to dissolve, the teeth lose support and fall out in the same order in which they erupted.
As the jaw and facial bones grow, spaces form between the primary teeth. This provides space for permanent, larger teeth to emerge, which erupt from 5 to 15 years of age.
What is milk bite? Formula
The appearance of baby teeth is a signal that the baby is growing up. From the point of view of human development, their appearance indicates the following:
- The child is ready for the transition from sucking to chewing, that is, from mother’s milk (or formula) to complementary foods and a gradual transition to normal food.
- From the intuitive production of individual sounds, the baby moves on to understanding speech addressed to him and even tries to imitate it.
The rudiments of baby teeth are formed in the womb, so the woman’s condition during the first trimester of pregnancy is responsible for the predisposition to “bad teeth”.
How many baby teeth should children have? The temporary bite has 20 teeth, of which 8 are incisors, 4 canines and 8 molars.
In dentistry, there are several ways to designate a temporary occlusion. In ordinary life, this information is unlikely to be useful to the mother, but it can help to better understand the dentist’s explanations and actions during the appointment.
- The classical Zsigmond-Palmer system, which was adopted for a long time in the USSR. In it, the milk row was designated with Roman numerals.
- A modern system accepted throughout the world, including by the International Dental Association. It involves using two numbers to designate each tooth. The first number indicates the quadrant in which the tooth is located (upper left or lower right), and the second number indicates the serial number of the tooth itself.
- An alphanumeric system in which each type of baby tooth is designated by a capital letter, and the index number is a serial number. This method is very convenient to indicate a changeable bite. To do this, you just need to replace lowercase letters with capital ones. This change is immediately noticeable.
- In America, it is customary to designate baby teeth using the letters of the English alphabet, placing them from the upper right molar to the lower right.
- You can also find the group designation of milk occlusion. In it, the number indicates the number of teeth of a certain group, and its location, in fact, the type of tooth.
- Similarly, temporary occlusion can be recorded using an alphanumeric system.
How does the jaw of baby teeth differ from permanent teeth?
There is an opinion among parents that baby teeth grow without roots. This myth appeared because during a change in bite, teeth fall out with reduced (resolved) roots. In fact, baby teeth have roots, and their number completely corresponds to that of permanent teeth. Despite the fact that the teeth of the temporary and permanent dentition are similar in appearance, there are several differences between them that help dentists accurately determine the group affiliation of the tooth.
| Milk bite | Permanent bite | |
| Number of teeth | 20 | 32 |
| Premolars | No | There is |
| Color | White-blue | Yellowish |
| Size | Small | Big |
| Crown sizes | The crown is wider than it is tall | High crown |
| Crown to root size ratio | The crown is more convex, making the roots appear smaller | Traditional ratio of crown to root sizes. |
| Presence of enamel roller | In the area of the neck of the tooth there is a thickening of the enamel, due to which the crown becomes larger. | No |
| Degree of mineralization | Low | High |
| Cavity dimensions | Extensive | Standard sizes |
| Channels | Wide canals and apical foramina | Narrow, sometimes difficult to pass with irregularly shaped branches |
| Root shape | Rounded | Long and elongated |
| Direction of root growth | Moved to the side to make room for the permanent tooth germ | Perpendicular to the jaw bone |
| Root reduction | Eat before changing bite | No |
| Tremas and diastemas (distance between teeth) | Normal physiological state as the jaw grows (from 4 to 6 years) | It shouldn't be normal. |
| Lumps and cutting edges | By the time the bite changes, they are erased (by 6 years) | Well expressed throughout life |
Symptoms
Usually, no serious problems arise during teething, but local (in rare cases systemic) disturbances are present. These include:
- swelling and soreness of the gums;
- profuse drooling;
- irritability;
- restless sleep;
- lethargy;
- the baby's need for biting and chewing;
- poor appetite.
Loose stools, low-grade fever and runny nose are less common than the above symptoms.
Important! If the body temperature rises above 38 degrees, convulsions, difficulty breathing, you need to show the baby to a doctor and call an ambulance. This may indicate a viral infectious disease and is not a sign of teething.
Some parents wonder why this process occurs differently in babies. For example, in some teething occurs with fever, in others it does not. It is noted that, among other factors, this is also influenced by the child’s constitutional type. In children of the allergic type, this period may be accompanied by increased moodiness, atopic dermatitis, and ARVI is often associated. Infants with asthenic syndrome sleep poorly, refuse to eat, and cry for a long time due to severe pain.
How to help your baby teething
To eliminate unpleasant symptoms and make the child feel better, parents are advised to:
- Buy teethers made of silicone or special soft plastic filled with water. These devices are cooled to a comfortable temperature (not frozen) and given to the baby. Cold reduces pain in the gums and relieves swelling.
- Massage your gums. To do this, an adult needs to wrap his finger in a clean gauze swab, moisten it in cool boiled water and lightly massage the inflamed area.
- Give ibuprofen or paracetamol if the child is very restless or has a high fever. The dosage is prescribed by the doctor.
Important! During teething, babies put everything in their mouth, which can cause a secondary infection. Therefore, parents need to carefully monitor oral hygiene, regularly wipe their face with a clean towel, and gently blot saliva.
As for special gels for gums, you need to be careful and not use them too often, as some components can cause an allergic reaction.
Caring for baby teeth
You need to take care of your teeth immediately after teething. Moms do it first. For adults, special finger brushes have been created that are convenient for cleaning teeth from plaque, but so far without toothpaste. When the baby learns to rinse his mouth and spit, they move on to brushing with children's toothpaste without fluoride (this can be done earlier if the tube indicates that the toothpaste is from 0 years). So, gradually, the child will form a useful habit of caring for the oral cavity.
Another important reason for caring for teeth from infancy is that it affects the formation of permanent teeth and bite. For example, caries of a temporary tooth can transfer to the germ of a permanent one. And early loss (before 5 years) of a baby tooth will lead to uneven dentition in the future. If the molar does not begin to grow in time, the adjacent baby teeth will move and fill the resulting space.
Symptoms and signs of a baby's first teeth
How can you tell if your child is cutting a tooth? The symptoms are extremely varied in the range of organs involved, in duration, and in intensity. Usually the baby has:
- Runny nose - clear fluid discharges from the nose, similar to that of a viral disease.
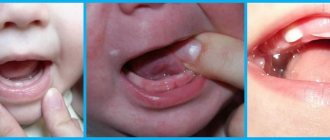
- Redness and swelling of the gums is the most striking and main symptom indicating teething.
- Temperature – may rise to individually high levels, or may be completely absent.
- Diarrhea - judging by the reviews of mothers, the eruption of baby teeth is often accompanied by severe diarrhea. The feces are quite smelly and acidic, so they quickly cause irritation on the buttocks.
- Irritability, tearfulness, refusal to eat – all these are subjective signs that may indicate a deterioration in the baby’s condition. They indicate pain, discomfort and general malaise.
How to help your child when teething?
The most important thing is to identify the problem in a timely manner. It is necessary to exclude colds, gastrointestinal diseases and other pathologies. To do this, you should see a pediatrician or pediatric dentist.
In the case where teeth are definitely involved, the following must be done:
- Provide the baby with comfort and peace. Avoid attending noisy events and receiving guests. Walk more, ventilate the room, create a favorable psychological atmosphere at home.
- Limit food. Offer breast milk or formula more often, remove complementary foods. If the child is already eating nutritious food, then do not introduce new foods.
- Provide your baby with all kinds of teethers and chewers. Carefully ensure that they are appropriate for the child’s age.
- Special anesthetic gels can be applied to the gums. All of them are divided into three types - short-acting, long-acting and without anesthetic (based on plant extracts or homeopathy). It is better to consult your doctor about which one you should buy.
- If a child develops a fever when his baby teeth are cutting in, he can be given an antipyretic and pain reliever. The dose, form and composition of which should be discussed with your doctor. It is better not to abuse this measure, since such drugs can be used for no more than 5 days in a row.
What to do when the first tooth comes out?
From the moment your baby's first tooth erupts, you need to start brushing it every day. First, mom does this by wrapping her finger in clean gauze. It gently massages the gums and cleanses the enamel of the first incisors. You can also use a finger brush for this. You don't need toothpaste at this stage yet.
As the child grows up, it is necessary to introduce him to such an important item as a toothbrush. The optimal age for this is the first birthday. If parents regularly brush their teeth in front of their baby, then the process of involving him in this fun game will be quick and painless. At this point, you can already purchase a special children's toothpaste marked from birth.
Read the age restrictions on toothpaste carefully. Typically, those suitable for children under 3 years of age do not contain aggressive substances and can be swallowed. Toothpastes intended for ages above 3 years may contain fluoride and other necessary ingredients, which, however, are not recommended to be swallowed. Manufacturers are guided by the fact that at this age the child already knows how to spit out excess toothpaste and rinse his mouth.