- Acute herpetic stomatitis
- Traumatic stomatitis
- Chronic aphthous stomatitis
- Candidal stomatitis
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity. It is believed that children are most vulnerable to stomatitis. In adults, stomatitis does not occur as often. The instability of children to stomatitis is explained by the fact that they have a more delicate mucous membrane; children tend to constantly put something in their mouth and taste it, which contributes to the entry of microbes and accidental injuries. In addition, children's immunity is at the stage of formation, and therefore they are becoming acquainted with many bacteria and viruses for the first time. The first encounter with bacteria or, for example, with the herpes virus can be accompanied by a fairly violent reaction from the body.
Causes of childhood stomatitis
The immediate causes of stomatitis are bacteria, viruses and fungi. These microorganisms may be present in small quantities in a healthy child, but they begin to multiply and cause disease in the presence of certain factors.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of stomatitis
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules (the child may touch the mouth with dirty hands), hard plaque on the teeth;
- Weakened immunity;
- Long-term use of medications (especially antibiotics). Antibiotics disrupt the natural microflora, promoting the growth of fungus and the occurrence of fungal stomatitis.
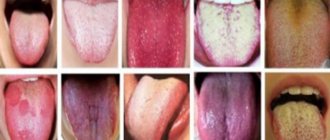
Types of stomatitis in children
Modern medicine knows a huge number of varieties of stomatitis. They can have an acute course, that is, be accompanied by pain, discomfort, and a disturbance in the general condition, or they can have a chronic course. Chronic stomatitis passes almost unnoticed for a person, pain is not expressed, general health does not suffer.
Let's look at the most common types of stomatitis in children, which dentistry in Belarus .
Acute herpetic stomatitis
Acute herpetic stomatitis is caused by the herpes virus. There are several types of herpes virus. The disease that appears on the lips and in the oral cavity is caused by the first two types of the virus. Adults remember herpes when blisters appear on the lips due to stress or hypothermia, and in children it manifests itself in the form of ulcers in the mouth and even a rise in temperature. As a rule, the disease begins with inflammation of the gums and enlarged lymph nodes. If a child looks into the mouth, you will notice several bubbles on the mucous membrane of the lip, gums, and cheeks. Over time, the membrane of the vesicles bursts and ulcers form. These ulcers are painful and the child refuses to eat. This stomatitis occurs when the baby first encounters the virus.
It is most often transmitted from parents through kissing and sharing cutlery. 98% of the world's population is infected with this virus, so it is useless to protect yourself from it. Infection with the herpes virus does not always occur with manifestations of stomatitis, and is often completely unnoticeable. But, if the latter does appear, the parents’ task is to provide proper care and alleviate the symptoms.
Traumatic stomatitis
Traumatic stomatitis is associated with mechanical damage to the mucous membrane. Children often put toys and cutlery in their mouths and can injure themselves and cause stomatitis. Stomatitis can form at the point of contact between the edges of a decayed tooth and the cheek. A bacterial infection sometimes attaches to the wound, resulting in an inflammatory process that lasts several weeks.
Chronic aphthous stomatitis
Chronic aphthous stomatitis manifests itself in the form of white spots (aphthous) on the mucous membrane of the lips, cheeks and sometimes gums. In the first days, the spot is surrounded by a red rim. Then a small ulcer forms at the site of the spot. After 7-10 days, the ulcer heals. The causes have not been fully elucidated, but it is believed that it often occurs in children with allergies, intestinal diseases and weakened immune systems.
Candidal stomatitis
Candidal stomatitis is caused by the fungus Candida Albicans. You can see red spots and ulcers in the child’s mouth. A cheesy white coating can be seen on the cheeks and tongue. Often this stomatitis appears after prolonged use of antibiotics. Children complain of pain and refuse to eat.
white spots on a child's tongue
There are times when mushrooms actually begin to grow in our mouth, as if in a forest clearing. This often happens in newborns and children under one year old, manifesting itself in the form of a persistent white coating in the baby’s mouth. Many mothers, having noticed white crumbs on the baby’s tongue and gums, believe that these are leftover food (breast milk or formula) that the baby did not swallow, or, conversely, regurgitated. Alas, most often a whitish coating signals that the newborn has developed thrush.
What kind of misfortune is thrush?
Thrush in newborns has the same nature and the same pathogen as thrush in adults - these are yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida, which “live” on the mucous membranes and skin of a person throughout life. These fungi are always present in small quantities in a woman’s vagina, as well as on the skin, mouth and rectum of any person. And only a pathological increase in the number of these same fungi leads to a disease, which in the medical community is more often called candidiasis, and among the people - thrush.
Fungi of the genus Candida live on the mucous membranes and skin of humans in the same way as marine polyps live on the bottom of pirate ships - in a strictly limited colony and throughout our entire lives. However, if on land ship polyps and mollusks quickly die, then in dry conditions Candida mushrooms, on the contrary, begin to grow pathologically to the detriment of their “host”.
But in an adult, in addition to fungi, the body also contains favorable microflora (which makes up a significant part of our immune system), which helps to inhibit the growth of pathogenic fungi. In other words, our immunity allows fungi to exist at our expense, but strictly ensures that their “village” does not turn into an “empire”.
But in the body of a newborn, such microflora is still just being formed. That is why thrush in newborns occurs much more often than in children after one year and in adults.
Signs of thrush in newborns and infants
As soon as the growth of Candida fungi on the oral mucosa increases, an inflammatory process occurs. Which every mother can visually identify by the appearance of small white spots resembling semolina crumbs on the tongue, palate and gums, as well as on the mucous membrane of the cheeks.
It is not difficult to distinguish the whitish coating caused by fungi from the plaque that may remain in a child’s mouth after spitting up milk or formula - gently rub it with a dry napkin or handkerchief. Plaque from food debris will be erased effortlessly and without a trace, but white spots from thrush will be much more difficult to erase and after their removal, red, inflamed areas will remain on the mucous membrane.
In addition, secondary signs of thrush include:
• a sharp deterioration in appetite in a newborn or infant;
• restlessness, crying, poor sleep
The main causes of thrush in newborns
Despite the fact that a newborn baby’s own immunity is still developing, he receives most of the protective functions of immune cells from his mother’s milk. And at the same time, it is from the mother that the baby most often “borrows” not only immune bodies, but also the thrush itself - either at birth or during breastfeeding. Although it is fair to say that any family member can infect a baby with candidiasis - for example, through touching while caring for a child, or through a kiss.
In most cases, thrush in newborns and infants makes itself felt in the first month of life - a persistent white coating appears in the child’s mouth, the baby loses appetite and behaves restlessly. But don’t worry - he doesn’t experience any painful sensations!
The most favorable environment for the development of thrush in newborns is the dry and hot climate in the room where the child is. The point is this: normally, in the mouth of a newborn, as in an adult, thrush fungi are constantly present in small quantities - immune bodies and special substances that make up saliva help restrain their pathogenic growth. As long as saliva is produced and moisturizes the oral mucosa, thrush does not occur. But if for any reason (dry and hot climate in the apartment, a runny nose in a child, constant crying, etc.) the oral mucosa of a newborn dries out, under these conditions the Candida fungus sharply and uncontrollably increases its population.
If the baby spends most of the time in a dry and warm room, and at the same time cries and screams a lot, expect thrush! But sometimes it is enough to humidify the room and calm the crying child for the thrush to go home with nothing.
In addition, the occurrence of thrush in a newborn can be triggered by the following circumstances:
• frequent regurgitation;
• mechanical trauma to the oral mucosa (cracks in the gums and corners of the lips);
• congenital immaturity of the oral mucosa;
• treatment with antibiotics, hormonal drugs or immunosuppressants, which greatly weaken the protective functions of the child’s body;
Professional experience allows pediatricians to claim that premature babies suffer from neonatal thrush more often and more severely than those born at term. And children who are bottle-fed suffer from candidiasis of the oral mucosa more often and more severely than those who are breastfed. In both cases, the reason is the insufficiently strong and developed immunity of premature babies and artificial babies.
Treatment of thrush in newborns: “Just add water!”
Modern pediatricians, including, for example, the well-known Dr. Komarovsky, believe that there is no need to treat thrush in newborns (especially at an early stage) with any special antifungal agents. It is enough just to normalize the humidity in the room and make sure that the baby breathes through his nose and not his mouth. In other words, as soon as the condition of the mucous membrane returns to normal (cracks heal, dry mouth disappears), the growth of fungal formations will immediately decrease and the white plaque in the child’s mouth will disappear by itself. But “self-healing” will occur only if the baby’s immunity is already sufficiently developed and strong, and if a normal, humid climate is maintained in the room where the child lives.
What does it mean: normal humid climate?
To establish and maintain favorable humidity in the home, most Russians need two things - a high-quality humidifier with climate control function and an understanding of what is normal for humidity.
The ideal level of humidity in a living space, both for adults and for a newborn baby, is from 40% to 60%. Any modern air humidifier is capable of maintaining this condition, regardless of what the weather is like outside and what kind of relationship you have with your heating company.
A reasonable question that comes to the mind of every parent: what about mold, which is also a fungus, and which develops rapidly in humid air? After all, mold spores can cause much more serious diseases than thrush.
Everything is correct! Mold is indeed a very dangerous neighbor for your baby. But you must know and remember: mold appears and lives only in places where air humidity is 75% or higher. In other words, never set your humidifier’s regulator to values higher than 70%, and no mold will settle in your nursery.
Don't create dampness! A cool, damp climate is good for a child's health, rather than a warm swamp, which is ideal for mold, frogs and mosquitoes.
Why medications are sometimes healthier than fresh air
However, when thrush in the mouth of a newborn or infant is in an advanced state, doctors resort to the use of medications. Because the rapid development of candidiasis in a child, whose immune system is still quite weak, is fraught with serious risks: the disease can affect not only the oral mucosa, but also “move” to the intestines. And this can seriously damage the formation of favorable microflora in the gastrointestinal tract and, accordingly, will seriously and permanently reduce the protective functions of the immune system.
With girls it’s even more difficult. They have thrush, even in infancy it can cause candidiasis of the vagina, vulvovaginitis. Which in some cases leads to synechiae - fusion of the delicate mucous membrane of the vagina or labia. Unfortunately, this problem can only be resolved through surgery.
Therefore, most pediatricians are inclined to believe that advanced thrush in newborns cannot be overcome with a humidifier alone, and advise using more “traditional” measures and means. For example:
Since thrush can affect not only the oral mucosa of a newborn, it is highly advisable that a specialist conduct a full examination of the child.
For initial and superficial forms of thrush, treatment consists of local external therapy - foci of inflammation in the baby’s mouth will need to be carefully cleaned and treated with special solutions or suspensions. As a rule, such medications are prescribed by a doctor.
Affected areas of the mucous membrane are usually cleaned with a sterile cotton ball moistened with a 2% solution of soda (ideal proportions: 1 tsp of baking soda diluted in a glass of water), or with a 1% solution of hydrogen peroxide.
To treat lesions, pediatricians, as a rule, prescribe an aqueous suspension of nystatin, which is easy to prepare yourself: a nystatin tablet should be crushed and diluted in water. It is necessary to treat the mucous membrane with nystatin solution every 5-6 hours
In addition, a 1% solution of clotrimazole is often prescribed for treating the oral cavity (drugs such as Candide, Canesten can be used for preparation) - this medicine is used no more than 2-3 times a day.
If the baby is breastfed, then the mother must check herself for thrush.
In severe stages of thrush development, and if external therapy is ineffective, the newborn is treated with antifungal agents (antifungal antibiotics).
In most cases, with adequate and effective treatment, the symptoms of thrush in newborns (primarily white plaque in the child’s mouth) disappear after 3-10 days. Over time, when the baby’s immunity strengthens and is fully formed, the risk of recurrent thrush will significantly decrease.
Treatment
Each type of stomatitis is treated differently depending on the cause that caused it. You should not prescribe medications yourself. Taking antibiotics for herpetic stomatitis caused by a virus will not help. But there will be wonderful prerequisites for the development of fungal stomatitis. Rinsing with antibacterial solutions for fungal stomatitis will only worsen its course. The fungus must be treated with antifungal drugs. To prescribe effective treatment, it is best to consult a specialist . Dentists in Minsk will be able to correctly diagnose and prescribe effective treatment.
At home, before going to the doctor, you can alleviate the condition by following these recommendations:
- Gently brush your teeth with a soft-bristled brush;
- exclusion from the diet of hot, sour and salty foods;
- if health worsens and the temperature rises, the child should be given plenty of water and, if necessary, given an antipyretic (in this case, a visit to the doctor should take place as soon as possible).
As a rule, doctors recommend special ointments and solutions for children, as well as medications to reduce fever or relieve pain. After each meal, be sure to rinse your mouth with water. It is important to treat children's teeth promptly.
You should not rely on folk remedies: remember, some herbal infusions and decoctions can cause a negative effect and also contribute to the development of an allergic reaction in children. Do not aggravate the situation, seek help from your dentist.
Causes of plaque
Factors that provoke the appearance of light masses can also be diseases. The reasons for the appearance of a white coating on a child’s tongue often arise due to disturbances in the functioning of the body. It is very difficult, almost impossible, to remove such dense layers.
- The surface of the muscular organ suffers when hygienic manipulations of the oral cavity are violated;
- A light film covers the mucous membranes when taking certain types of medications;
- Excessive development and active reproduction of pathogenic microflora has a detrimental effect on the health of the oral cavity, so there may be a white coating on the tongue of a newborn;
And this is only a small part of those aspects that have a bad effect on the health of the mucous membranes. If symptoms of plaque appear, a small child should be shown to a local pediatrician. This is the only way to accurately determine the factors that provoked the appearance of deposits. By the way, a child may not only have a dry and burning mouth, but also a high body temperature. Often a plaque with red spots is diagnosed, which in medicine is called geographic tongue. In any case, self-medication is prohibited. Contact your pediatrician, he will competently develop a therapeutic program.
Inflammatory processes
Often a baby will develop a white coating on the tongue due to stomatitis. The symptoms of the disease are very unpleasant. The disease is characterized by deposits that have a heterogeneous structure. Whitish grains are clearly visible on the muscle organ. If you try to eliminate them, blood is released. The baby is irritable and suffers from burning and pain in the mouth, as there are ulcers on the surface of the tongue.
At 3 years of age and earlier, as a rule, stomatitis of candidal origin. Light layers are present on the cheeks, gums, and even on the lips. The pain intensifies when eating sour-tasting foods. A visit to a medical facility is mandatory. Therapy consists of anti-inflammatory and painkillers that are used to treat the affected areas.
Fungal diseases
If the treatment of baby teeth is not carried out in a timely manner, this leads to the active proliferation of pathogenic microflora, including fungi. A white film on the lips and tongue often indicates that the baby has thrush (another name for candidiasis). In babies:
- the oral mucosa turns red;
- dryness appears;
- discomfort;
The younger the children, the worse they tolerate the disease. A one-year-old child becomes very capricious, he refuses to eat. Removing the film causes bleeding. The mucous membranes become covered with plaques and papules. To alleviate the condition, remove severe burning and itching, make an appointment with a pediatrician.
Caries
With caries, a dense white mass can form on the muscular organ and in the oral cavity. It doesn’t matter whether the child is 10 years old or a baby with baby teeth. This is due to the fact that the disease in its advanced form is a source of infection. Pathogenic bacteria thrive in the whitish mass on the tongue. They actively reproduce and aggravate the situation.
At 2 years old, when the baby has unstable teeth, parents should also monitor the oral cavity and prevent carious lesions on the units. Preventing the disease is possible. It is necessary to observe the rules of oral hygiene, and regularly. This is the only way that unwanted microorganisms will not settle on the mucous tissues of the tongue and a film will not form from the products of their vital activity.
Pathologies of the respiratory systems
If the tongue is covered with a white coating, this may indicate problems in the airways. Can be diagnosed:
- Viral form of the disease;
- Diseases of a bacterial nature;
With the flu or acute respiratory infections, the temperature rises, the throat turns red, a cough appears, and the tongue becomes covered with a whitish film. A sign of pharyngitis and tonsillitis is the covering of not only the tongue, but also the tonsils with white masses. Clumps on the tip of the tongue indicate bronchitis. Deposits with a foamy consistency indicate chronic bronchitis.
Infectious diseases
When an infection enters the body, the body defends itself by raising body temperature. In this case, whitish masses of dense and thick consistency often form on the muscular organ. With scarlet fever, reddish islands are visible on the white tongue. The tonsils and the root of the tongue are covered with a particularly thick coating. Severe intoxication is detected in the child’s body.
Diphtheria affects different areas of the oral cavity. It is not uncommon for a child to develop gum inflammation. There are dots with a white tint on the tonsils, and light grayish deposits on the tongue. Remember that the formation of pus requires an immediate trip to the doctor.
Gastrointestinal diseases
When bottle-fed, formula often leaves a slight residue, which is not dangerous for the baby. But it happens that quite serious diseases develop from such food:
- The film in the central zone of the muscular organ and the formation of cracks and grooves indicate gastritis.
- A one-month-old baby is more susceptible to dysbiosis than others, since his digestive system has not yet been adjusted. In such a situation, the tongue is completely covered with whitish masses.
- At the age of 7, when hormonal changes begin and baby teeth are replaced by permanent ones, children are susceptible to enterocolitis. Inflammation in the intestines leads to deposits on the back of the tongue.