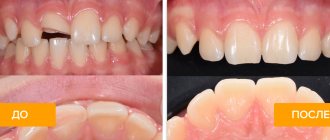
Dental injuries are a common problem in dentistry. Tooth dislocation is an injury that results in damage to the ligamentous apparatus and the tooth being displaced in its socket (photo below).
Tooth dislocation is accompanied by:
- severe pain
- bleeding
- soft tissue swelling
- appearance of tooth mobility
- change in enamel color
The causes of such injury may be:
- mechanical damage (due to impact from a fall, for example);
- biting hard food, hard objects in food;
- bad habits (crunching nuts in the shell, opening bottles with your teeth, etc.);
The diagnosis of tooth trauma (including tooth dislocation) is made based on symptoms and x-ray examination. The doctor not only determines the clinical picture, but also assesses the condition of the bone tissue at the site of dental injury. Tooth dislocation has its own types (complete, incomplete, impacted) and treatment features.
Tooth dislocation: photos and symptoms
Any injury has its own clinical picture. Tooth dislocation, photos of which can be viewed on dental websites, is also characterized by specific symptoms. During the examination, the dentist looks for signs to diagnose a luxated tooth.
The doctor also determines what type of tooth dislocation the resulting tooth is. The symptoms of each are slightly different. After analyzing the x-ray, treatment is usually prescribed.
Tooth trauma: types, methods of treatment
Tooth trauma is a violation of the natural shape of a tooth or its displacement relative to its anatomical position. Dentists divide dental trauma into two general types: chronic and acute dental trauma.
Chronic tooth injury.
Chronic tooth trauma occurs when a weak traumatic factor acts for a long time. This form of damage is associated with unsafe habits (biting hard objects, opening bottles and caps with teeth, gnawing nuts and seeds), professional actions (seamstresses cutting thread, carpenters holding nails in their teeth, etc.). Chronic tooth trauma can also occur due to malocclusion or poor-quality prosthetics.
With constant mechanical impact on the teeth, the enamel wears away, chips and microcracks appear. If you do not take action, after some time pain will arise and your teeth will become more sensitive. Treatment boils down to eliminating the traumatic factor and restoring chips.
Acute tooth trauma.
Acute tooth trauma occurs when there is a sharp, simultaneous mechanical impact, which leads to a violation of the integrity of the tooth. Traumatic factors can be very different: injury during sports, at work, falls, blows to the jaw in a fight. Very often, such tooth trauma occurs in children. This is due to their increased activity. A child can damage a tooth by falling from a bicycle or swing.
There are several types of acute dental injuries:
Bruise - characterized by the fact that the tooth remains intact externally. Symptoms: aching, persistent pain, turning into acute pain when biting and chewing. If a bruise causes a bundle of blood vessels to be damaged and blood enters the pulp, the tooth at the base will turn pink or even turn red.
Treatment of bruise. The first rule is to provide rest to the bruised area: switch to ground liquid food, do not chew on the injured side, and do not touch the tooth with your hands. Physiotherapy is often prescribed. If the pulp is damaged, in order to avoid complications, the neurovascular bundle is removed (depulped).
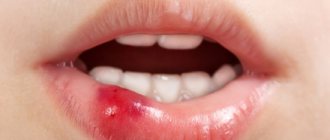
Luxation is a displacement of a tooth in its socket. It may be accompanied by damage to the soft periodontal tissues. Symptoms: painful sensations, the tooth is loose or tilted. There are complete, incomplete, and impacted dislocations.
Treatment of dislocation. The sooner the victim consults a doctor, the greater the chance of avoiding removal. A tooth placed in place in time takes root well. After the operation, the patient’s tooth is fixed using splints. When treating a dislocation, the condition and degree of damage to the neurovascular bundle and root bone tissue play a decisive role.
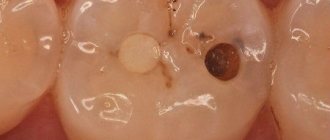
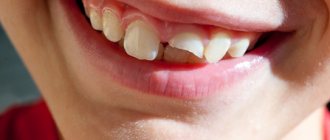
A crack can be of varying degrees of severity - from light on the tooth enamel to deep with damage to the pulp. Cracks occur in both acute and chronic tooth trauma. Symptoms: pain - from a reaction to hot and cold, to acute pain when chewing and biting.
Crack treatment. If the crack is superficial, grind the opposite tooth to reduce the load on the damaged one. If the crack is deep and the pulp is damaged, the tooth will most likely have to be removed.
A fracture is an acute injury when part of a damaged tooth is torn off. Symptoms: severe pain, tooth mobility, visible damage. The fracture can be displaced or non-displaced. Depending on the location of the damage, a fracture of the neck, crown or root of the tooth is distinguished.
Treatment of a fracture. The diagnosis is made only after studying a photograph of the tooth. Next, depending on the nature and direction of the damage, the doctor decides: to remove the tooth or restore it by performing pulp removal and restoration.
Types of tooth dislocations. Complete, incomplete and impacted tooth dislocation - what are the differences?
To determine what type of dislocation - complete, incomplete or impacted - the injury belongs to, you should pay attention to their differences in symptoms.
- Complete tooth luxation (photo below) is characterized by the tooth falling out of its socket. And if he is held in it, then only due to soft tissues.
- Incomplete tooth luxation is characterized by partial displacement of the root in the alveolus. Upon examination, it is noticeable that the tooth is tilted either towards the tongue, or back, or towards the cheek, or towards the lip.
- Impacted tooth dislocation is a rare type of such injury. With it, several teeth often suffer at once, which seem to go deep into the alveoli. An impacted tooth dislocation is visually recognized by a decrease in the height of its visible part (photo below). This injury leads to destruction of the jaw bone.
Complete tooth luxation, incomplete tooth luxation and impacted tooth luxation differ not only in symptoms, but also in the methods used in their treatment.
Additional treatments
Drug therapy
- When carrying out manipulations to reposition a tooth after dislocation, local anesthesia is used, for this purpose Ultracaine D-S, Ultracaine D-S Forte, Cytokartin, Septanest, Bupivacaine are used. But the effect of the anesthetic stops after some time, so painkillers from the NSAID group are prescribed: ibuprofen, nimesulide, ketorolac, dexketoprofen. Children are prescribed ibuprofen and paracetamol.
- To improve the condition of the gums after injury, use: Dentol Gel - has a local anesthetic effect.
- Gel Metrogyl Denta - contains two antibacterial components, eliminates inflammation.
- Kamistad gel is a combined drug: lidocaine has a local anesthetic effect, chamomile flower tincture produces antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects, thymol has an antiseptic effect.
- Solcoseryl dental paste - stimulates regeneration processes in tissues, thereby shortening the healing period of wounds of the mucous membrane. The composition also includes polidocanol, a local anesthetic.
Physiotherapy
After acute phenomena have subsided, the following are used to stimulate healing processes and eliminate tissue swelling:
- UHF therapy is the effect on the body of an alternating electric field with ultra-high frequency.
- Microwave therapy – uses alternating electromagnetic oscillations of ultra-high frequencies of various ranges (centimeter, decimeter and millimeter).
- Magnetotherapy is the effect of a low-frequency magnetic field on the injured area.
- Magneto-laser therapy is a complex effect of magnetic and laser radiation.
Impacted, complete and incomplete tooth dislocation What treatment is needed?
Experts note that in most cases, injured teeth can be saved. The main thing is to see a dentist in time.
If an impacted tooth luxation is diagnosed, treatment is not always required, since the tooth often returns to its previous position on its own. But sometimes the damage is so severe that this does not happen. If just such an impacted tooth dislocation occurs, treatment is prescribed as for incomplete dislocation. Tactics for impacted dislocation can be different, it all depends on the degree of damage to the bone tissue and the severity of the injury.
If a tooth is completely dislocated, treatment should begin immediately. It is advisable to insert the fallen tooth into the hole and get to the dentist as quickly as possible. The tooth must be placed in milk or held behind the cheek. If the replantation of a tooth after a complete dislocation is done within 2 hours, then the tooth will be completely engrafted without any consequences.
Treatment for incomplete tooth dislocation consists of repositioning the tooth to its previous position, fixing it with a splint; if the pulp dies, the canal is treated and filled.
If you still can’t save the tooth, you can get prosthetics or implantation.
Restoration of teeth after injury by our experienced endodontists:
- extended warranty
- saving 79% of teeth with injuries of various origins
- painless restoration of tooth integrity on the day of treatment
- treatment using modern equipment under magnification and a microscope (fillings last 10-15 years or longer)
- high-quality diagnosis, not treatment by eye
- quality treatment at prices in the residential area of Yasenevo
Causes of dental damage in children
The increase in injury cases is primarily due to the growing popularity of team, contact and other sports. For example, hockey, wrestling, boxing, football and others. Also, the cause of dental damage in children of different ages can be accidental falls during active games on the street or school. No less common are injuries sustained in everyday life, fights, road accidents and other cases where there is a high probability of being hit by a hard object.
The risk of tooth damage increases if a child has orthodontic pathologies. For example, in patients with a distal bite (with protrusion of the upper jaw), injuries occur 5 times more often than in those with an orthognathic (normal) bite.
Also, dental damage often occurs in children with visual impairments, problems with the musculoskeletal system and various neuropsychiatric diseases.
What to do if a child has a dental injury
- If the injury is combined with a fall or a strong blow, you should immediately visit the emergency room and make sure that the child does not have a concussion or fractures, including facial bones - jaw, nose, etc.
- If other injuries are excluded or you are sure that it was the tooth that was damaged, you can immediately go to an urgent appointment with the dentist. If you have a tooth injury, we will see you immediately, since the speed of action often determines whether the tooth can be saved.
- The dentist numbs the area of the injury, determines the type of injury and prescribes treatment. In some cases it starts immediately, sometimes you need to wait a little. Treatment of a tooth injury can last up to a month.
It is important to correctly diagnose and treat an injured tooth to prevent complications. Meet our tooth fairies and check prices.
Types of injuries
Damage to dental tissue is acute and chronic. Acute injuries include bruise, crack, dislocation and tooth fracture.
Injury
A bruise is a closed injury and is characterized by darkening of the tooth and aching pain that intensifies when chewing. Sometimes, with bruises, damage to periodontal tissue is observed, leading to hemorrhages into the pulp chamber and death of the pulp.
Crack
It can be superficial or reach soft tissues, which determines the nature of the unpleasant sensations: from slight discomfort when chewing to severe pain when biting. The crack is invisible to the naked eye, so special fiber optic devices are used to make a diagnosis.
Prevention of dental injuries
There are typical situations in which children injure their teeth. For example, a quarter of front tooth injuries between the ages of 1 and 3 years occur in the bathtub when a child slips and hits the edge of the bathtub, so try not to leave your baby unattended in the bathtub. Pay attention to protecting your teeth with a mouthguard when your child plays sports, especially hard and contact sports (hockey, various types of wrestling, basketball), rollerblading or skateboarding. Contact your orthodontist in a timely manner, because... a large percentage of injuries to permanent teeth are associated with their incorrect position, i.e. existing bite pathology, which means an additional risk.
At the same time, you should not blame yourself for not looking after your child and causing dental injury. Children are restless, they love to explore the world and take risks, and we cannot always protect them from such accidents.
make an appointment with a pediatric dentist online or by phone: +7(812)3310000
Causes
Very often, dentists are faced with the problem of dental injuries not only in children and athletes, but also in ordinary people who are not prone to active life. After all, in order to injure a tooth, it is not necessary to practice boxing, play hockey or jump on roofs; it is enough to simply slip on level ground and fall unsuccessfully. Unfortunately, such cases are not rare.
In itself, a tooth injury is nothing more than a violation of the integrity of the natural shape and position relative to the rest of the jaw, as well as, in most cases, damage to the surrounding soft tissues. Most often, the causes of injuries are fights, industrial accidents, accidents, as a result of which the front teeth suffer for the most part, but injury to the teeth in the chewing area is not excluded.