Causes of dental injuries
Damage to baby teeth can be caused by any strong force applied to the jaw. For example, if a child was running and accidentally fell with his cheek on some object (chair, curb, step), this may well lead to a bruise or fracture of a tooth. Acute injuries also occur from blows to the face when children fight or play sports like boxing and karate.
Based on the nature of the acquisition, the reasons are divided into household, sports and travel. They are sudden and very painful. There are also chronic injuries that occur due to long-term bad habits. Biting nails, felt-tip pens, ballpoint pens, threads while sewing, or cutlery thins the enamel. Thin, fragile enamel and caries of baby teeth become the main factors of toothache in a child.
Symptoms
A strong blow to a tooth is accompanied by damage to periodontal tissue, and some fibers and small blood vessels rupture. There are no visible structural damage to the tooth; upon visual inspection, it appears intact. After a bruise, the tooth remains motionless, and minor mobility is rarely observed. The gums in the area of the injured tooth swell.
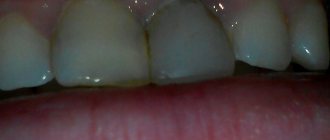
In the first hours after the impact, patients experience pain in the tooth, which intensifies when biting; the pain is aching in nature. The tooth feels high, and slight bleeding may occur from under the gum near it. When a bruise occurs, the neurovascular bundle of the tooth can be damaged, that is, the pulp is injured, and hemorrhage occurs in the pulp chamber, and the enamel becomes pink in color. A severe bruise can lead to the death of the pulp.
Often, when a bruise occurs, cracks appear on the tooth enamel, which can only be detected with a special examination.
In dentistry, the following types are distinguished:
- Bruised tooth. It can be considered the mildest type of injury, which is provoked by blows, attempts to bite through a hard object or “taste” it, which is especially typical for children 1-3 years old.
- Tooth dislocation. Such an injury means that the tooth has moved from its usual place. Typically, this type of injury requires significant force, so it does not occur as often as bruises. There are cases of complete dislocation, when the entire tooth falls out of the socket. Modern pediatric dentistry can save even a lost tooth if there are favorable conditions for this, and parents brought their child in immediately after receiving an injury.
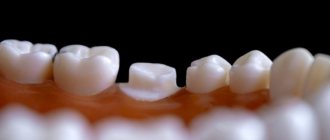
- Tooth fracture. Fractures are immediately visible - these are visible chippings of a corner, piece or most of a baby tooth. Most children break their front teeth; the most popular causes of such damage include fights.
- Fracture of the root or crown of a tooth. They are considered rarer species, because in normal everyday life and sports conditions it is extremely difficult to get such a deep fracture. Regardless of whether the child has acquired a simple tooth bruise or suffered a fracture, in any case it must be shown to a specialist so as not to endanger the health of the young body.
Diagnostics
- Patients with a tooth injury are referred for x-ray diagnostics to exclude a root fracture. To obtain information using targeted radiography, it is sometimes necessary to take several images from different angles, which is undesirable for the patient.
The most accurate information about the condition of the roots is provided by computed tomography - an x-ray examination method that allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the tooth. The examination results are displayed on the computer screen and must be transferred to a CD or USB flash drive.
An X-ray examination of a tooth bruise reveals a slight widening of the periodontal fissure.
- The condition of the pulp after injury is monitored using EDI - electroodontodiagnosis. The method consists in determining the reaction of the nerve endings of the pulp to the influence of electric current. The level of electrical excitability of the pulp depends not only on its condition, but also on the degree of formation of the tooth root.
The examination is carried out 2 or 3 days after the injury, since on the first day the pulpal response may be reduced due to traumatic neuritis. Be sure to perform an electrical test on adjacent healthy teeth to compare sensitivity levels. 3-4 weeks after the injury, EDI is repeated.
- Another method of examination for a tooth bruise is transillumination, the essence of which is to pass a beam of cold light through the tooth and evaluate shadow formation. If there are cracks in the enamel after an impact, they will be clearly visible in the stream of light; The technique also helps to detect pulpitis. In modern clinics, all dental units are equipped with light guides for transillumination examination.
Treatment
- For mild bruises, treatment consists of resting the tooth for 3-4 weeks by reducing the load during chewing: the menu includes soft and semi-liquid foods, and a blender is used to grind hard foods.
- To ensure rest for baby teeth, temporary bite separation with the help of mouth guards is used; if a permanent tooth is bruised, splinting is performed. The splint allows you to immobilize an injured tooth and redistribute the load during chewing onto healthy teeth.
- If the pulp dies due to an impact, the tooth cavity is opened and the pulp is removed, after which the root canals are filled and a permanent filling is installed. If the crown of a tooth darkens, it can be whitened.
- When a baby tooth is bruised, grinding of the cutting edge of the crown of the antagonist tooth is used to prevent tooth contact and reduce pain. This method is not used for permanent teeth.
- To relieve pain, it is recommended to take an anesthetic tablet (ibuprofen, ketorolac, nimesulide) and apply an anesthetic gel (Dentol, Kamistad) to the gums around the tooth.
- When swelling of the soft tissues of the face accompanies a bruise, cold compresses are applied: a plastic bottle with cold water (not lower than +4°C) is wrapped in a cloth and held on the area of swelling for 15-20 minutes.
- A course of magnetic laser therapy is carried out - a combined effect on injured tissue of a magnetic field and low-intensity laser radiation. The method helps improve healing processes, relieves swelling and inflammation. The course consists of 10 daily procedures lasting 5 minutes.
- UHF therapy is indicated to accelerate tissue regeneration.
Children learn about the world around them through various sensations: visual, auditory, gustatory, tactile. However, the instinct of self-preservation is not yet sufficiently developed in little fidgets, so they often commit actions, the consequence of which, for example, can be injury to baby and permanent teeth in children, i.e. deformation, violation of the anatomical integrity of the tooth and adjacent tissues.
What are the types of injuries and their characteristic symptoms?
Injury
A bruise is understood as the impact of brute force from the outside on a tooth, in which its integrity is not broken. Immediately after such damage and some time later, the baby may complain of pain when eating or during hygiene procedures. In some situations, the damaged unit may become mobile.
Dislocation
A dislocation is an injury to the ligamentous apparatus, connective (periodontal) tissue, as a result of which the coronal part or root changes its location or is displaced. There are several options for the development of events:
- when the dislocation is incomplete: the tooth is in the socket, but its crown part deviates, its position relative to other teeth changes. In this situation, the periodontal connective tissues suffer little or not at all. The baby experiences pain while eating and complains that an incorrectly positioned tooth is bothering him. Also, sometimes the lip and gums swell, and there is slight bleeding from the area of injury,
- when the dislocation is complete: the contact of the tooth with the socket is broken, i.e. connective tissue is torn. The damaged unit can either fall out completely or be held in the socket only by the gums. In the first case, a blood clot may appear in the hole; in the second, the tooth becomes extremely mobile. The damaged area hurts, sometimes it may bleed, there is swelling of the soft tissues,
- when the dislocation is impacted: this situation is considered one of the most common in primary occlusion. When damaged, the tooth is deeply immersed (hammered) into the socket (for example, due to a powerful blow) with penetration into the jaw tissue. As for the tooth itself, it is firmly held in the oral cavity, remaining immobile. However, relative to its “neighbors,” it changes its position and is positioned incorrectly (it tilts or rotates along its axis). Upon examination, it may seem that it has become shorter than other units of the dentition, and it may also completely “hide” in the gum. This option is very dangerous, because with such an injury all tissues are deeply damaged, and when the upper incisors and canines are injured, sometimes there is a risk of damaging even the nasal and maxillary sinuses. The damaged area hurts, the lip and gums in the damaged area are swollen, and the mucous membrane may bleed.
If the injury is severe, tooth dislocation may occur.
Fracture of a tooth crown or root
Dislocations occur most often in temporary and permanent dentition. Less common are root fractures. Injuries can complement each other, for example, a root fracture can be combined with a crown fracture.
Even if the damage does not seem serious, and the child does not express complaints, you need to contact the dentist as soon as possible. Only a specialist can objectively assess the overall picture and decide what to do next. Timely consultation with a doctor will help avoid unnecessary complications.
A tooth fracture implies serious injury to it due to brute force, leading to disruption of the natural structure of the crown or root. The crown can break (chip off) at the enamel level, in the dentin area, or entirely. A minor chip in the enamel does not always bother young patients and their parents, while a chip in the dentin area or a completely chipped, destroyed crown is a serious visual defect. In addition, this situation can also threaten the pulp; traumatic pulpitis often occurs against this background. Also, the sharp edges of the injured unit scratch the tongue, lip, cheek, and interfere with the complete chewing of food. Naturally, in this case, the baby may experience a painful reaction to temperature stimuli and mechanical influences.
Root fracture in childhood is not a common occurrence. The roots of the incisors in the permanent dentition are most vulnerable. A fracture of the root of a baby tooth in a child is observed in exceptional cases. This is explained by the anatomical features of the temporary units and their alveolar process. There are oblique, longitudinal, fragmentation, and combined root fractures. The child experiences pain when biting and chewing food and complains of a loose tooth.
How to solve a problem
Different types of injuries require different approaches to treatment. In all situations, the first stage remains unchanged - visiting the dentist. The doctor will ask about the cause of the injury, complaints, conduct the necessary diagnostics and, depending on the nature of the injury, prescribe treatment:
- in case of bruise: the most important thing is to provide the injured unit with rest, excluding it from the process of chewing food. The nature of the diet will need to be changed by temporarily removing solid foods rich in hard fibers from the diet. Additionally, medications with anti-inflammatory effects may be prescribed. If injury or inflammation of the pulp occurs as a result of the bruise, it will be removed and the canal will be carefully sealed,
- in case of incomplete dislocation with displacement: first of all, the tooth is returned to its correct position. Then it will be fixed with the help of special dental splints, which will not allow it to move again. During the rehabilitation period, it will also be important to follow a gentle diet,
- in case of complete dislocation: the tooth can be removed from the socket, the necessary preparatory procedures can be carried out, and then replanted again (replantation), fixed for a while with splints. In such a situation, it is important to consult a doctor as early as possible, otherwise the chance of successful replantation decreases in proportion to the increase in the time during which you ignore the problem,
- for impacted dislocation: in a child under 2 years of age, the doctor chooses a waiting tactic, because the damaged tooth can recover and continue to grow normally. If this does not happen, most often it is necessary to remove it and think about subsequent prosthetics,
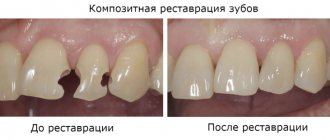
- in case of a crown fracture: if we are talking about a minor chip, then the problem can be solved with the help of restoration - applying a composite material or filling. In case of significant damage, it is more advisable to install a stump inlay or crown, build up a tooth on a pin,
- when the roots of the mammary unit are fractured: it is often simply removed. The same will be done for vertical and comminuted fractures in any bite. If the roots of permanent teeth are fractured, further treatment will depend on the condition of the pulp. Further, restoration will take place through prosthetics.
It should also be remembered that if, as a result of the removal of even the very first, baby tooth, it is very important to promptly take care of the issues of its prosthetics. There are special soft children's dentures that will allow you to preserve the aesthetics and functionality of the dentition for some time - until the primary bite is changed to a permanent one or until the jaw systems are fully formed, when it will be possible to consider the option of higher-quality prosthetics, for example, using dental implantation.
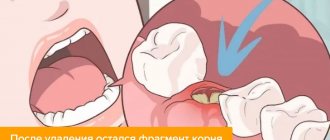
Tooth root fracture
A tooth root fracture always has more severe consequences. The child complains of pain. Bleeding is not always observed, especially if the integrity of the gums is preserved. The crown may be intact, but there is always mobility and sometimes a change in the location of the tooth.
Baby teeth with a root fracture must always be removed. Treatment of permanent teeth depends on where in the root the fracture occurred. If the root fracture occurs deeper than 4 mm under the gum, the tooth must be removed. In other cases, it is necessary to remove tooth fragments, treat root canals and plan restoration. There is no need to be afraid of having baby teeth removed. At the Family Dentistry Center, treatment and removal of teeth under anesthesia during sleep is available.
The statistics for permanent teeth are as follows:
If the tooth is returned to its place within 30 minutes, it will take root in 90 percent of cases; if replantation is delayed for up to 2 hours, it will fail in 90 percent of cases. It is clear that during the first 30 minutes, first aid to the injured child will be provided by his parents. According to Polish researchers, the percentage of medical workers willing to replant a tooth at the site of injury is only 7 percent; the rest prefer to call parents to take the child to the dentist. And this is a waste of time, reducing the chance of engraftment.
Therefore, forewarned means forearmed. Tell your friends.