How does a human tooth work?
The elements of a human tooth can be divided into:
The crown is located above the gum and has a special coating called enamel. Under the enamel there is a durable layer of dentin, which in its structure resembles bone tissue.
The cavity of the tooth located inside the crown is called the “pulp”. It passes into a narrow canal of the tooth root, at the base of which there is a small hole. Nerve endings and blood vessels pass through it into the tooth cavity. Inflammation of the pulp is called pulpitis. It is an indication for opening the tooth cavity and cleaning the root canals. The most difficult thing to treat is pulpitis in the cavity of three-channel units (for example, in the sixth). In advanced cases, it is necessary to remove the tooth, and if it is also on top and in the last rows (6, 7 or 8), then this is also inconvenient.
The dental neck is located inside the gum. It does not have an enamel coating, but is protected by cement. The continuation of the tooth cavity is its root. It is located in the alveolus, a small cavity in the teeth. Its structure differs from the structure of the crown and neck. The enamel layer is absent, and dentin is permeated with collagen. Nerves and blood vessels pass through the root canal into the dental cavity.
What are channels?
Each tooth has a certain number of roots located under the gum.
Read also: Dental floss
How many roots do teeth have? The answer to this question depends on several factors - the position of the unit, the person’s age, heredity, even race. It is known that Mongoloids have more roots than Caucasians.
The standard quantity is as follows:
- Incisors, canines – 1.
- Premolars – 1-3.
- Upper molars – 3-4.
- Lower molars – 2.
- Third molars – 3-5.
Inside the crown is the pulp, a tissue consisting of blood vessels and nerve endings. They pass into the pulp through the apical foramen, located at the apex of the root, and through canals, narrow cavities inside the root. Their number is not always equal to the number of roots.
The photo shows the beginning of the root canals.
Number of roots and canals in teeth
The number of channels differs from the number of root bases. The cavities of teeth such as incisors can have one, two or three canals. In order to accurately determine the number of these dental canals and their location, the doctor takes an x-ray of the patient. It helps him carry out the procedure of opening the tooth cavity more accurately.
Let's take a closer look at how many canals and roots there are in each cavity. What are the differences in their numbers on the upper and lower jaws?
On the upper jaw
According to the special dental numbering system for root teeth, their counting begins with the central incisors. The upper units, which are numbered from one to five, have one root each, 6, 7 and 8 have three roots.
In most cases, the upper incisors and canines each have one canal, the fourth unit (24th premolar) in 8% of patients has three canals, in other cases there are 2 or 1. Premolar number five (25) can have a different number of canals. In 1% of people this tooth is three-channel, in 24% it is two-channel, and in the rest it is single-channel. The sixth upper tooth (26th molar) may have three or four sockets (50:50 ratio). The seventh root in most cases (70%) has three channels, but can also have four channels (30%).
On the lower jaw
The lower units, from the first incisor to the fifth premolar, have one characteristic feature that unites them: they all have one cone-shaped root. Next come the “sixes” and “sevens” - they are two-root. The “eights” of the bottom row can have either 3 or four roots.
How many canals are there in the cavity of the lower teeth? So, in 30% of cases, the central incisors have 2 recesses, in the remaining 70% - one each. The second incisor can be either single- or double-channel (50:50), the third canine in 7% of cases is single-channel. The 4th premolar is found mainly with one root cavity, but sometimes with two. The fifth premolar is mostly single-canal. In 60% of cases, the 36th molar (6th lower tooth) has three recesses, but there may be 2 or 4. The lower “seven” in 70% of cases has 3 canals, but there are also four.
How many nerves do permanent and baby teeth have?
Each tooth has nerve endings that affect growth and development and provide sensitivity to various stimuli. The number of nerves depends on the number of roots. Thanks to them, teeth turn into independent living organisms of the oral cavity. When the pulp is removed, sensitivity at the treatment site is lost. Blood supply and mineralization stop.
The temporary dentition does not differ in the number of canals and nerves from the permanent one. There are similarities in the characteristics of the root system.
Wisdom tooth and features of its anatomical structure
The outer eighth units of the lower and upper jaw are called wisdom teeth.
The cavity of these teeth is often affected by pulpitis, since they erupt very fragile. These curved wisdom units have a unique anatomical structure of the tooth cavity. They appear later than everyone else: at 20, and at 30, and even at 40 years old. The difference in their anatomical structure lies in the number of roots, which can be from two to five. These roots are quite crooked (see photo), therefore they cause many problems during treatment procedures, and especially during determination of the working length, expansion of canals and filling. The number of channels for “eights” can reach up to five.
The structure of teeth and their arrangement
A dental unit can be divided into 3 components:
- The crown is the visible part of the tooth that directly performs the chewing function. The top of the crown is covered with a thin protective layer of enamel, under which is the densest part – dentin. Dentin surrounds the most vulnerable and delicate part of the tooth – the pulp. It is a cavity filled with vessels and nerves.
- The cervix is a tapering part, normally hidden by the gum. Instead of enamel, it is covered with cement, and a dental canal begins inside - a narrowing of the pulp cavity.
- The root of a tooth is a part fixed in the alveolar process of the jaw. It is inside the roots that the neurovascular bundle passes, feeding all dental structures. It enters through a small hole at the top of the root. The root section is devoid of enamel coating, and the dentin in this part contains a large amount of collagen.
In dentistry, the numerical designation of dental units is accepted. All teeth are divided into 4 quadrants. The first number indicates the quadrant number (1-4 in adults and 5-8 in children), and the second number indicates the serial number of the tooth in the row (numbering is from the middle to the periphery). One quadrant includes 8 dental units: 2 anterior incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars and 3 molars.
How is root canal treatment performed?
An important step in the process of treating root cavities is determining the working length of these canals. Not everyone knows the definition of tooth root length. So, the working length of the root canal is the distance from the edge of the frontal units to the apical constriction preceding the apical foramen. There are several methods for determining the working length of the root canal. The most commonly used are the calculation method, x-ray and electrometric methods.
Read also: Is it painful to pull wisdom teeth?
Endodontics treats tooth root canals. When an endodontist treats a root canal, he performs the manipulations in the following sequence:
- diagnostics;
- X-ray;
- preparing the dental cavity for treatment;
- anesthesia;
- chemical treatment of instruments;
- opening of the tooth cavity;
- determination of the working length of root canals;
- medicinal treatment, cleaning and expansion of root canals along the entire working length;
- filling a tooth cavity.
Diagnostic methods
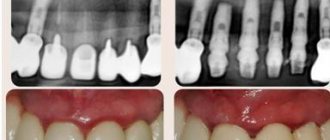
The first stage of tooth root canal treatment is diagnosis, which will help the doctor make the correct diagnosis and decide on a treatment method. To do this, the patient needs to undergo an x-ray to examine the part of the crown that the doctor cannot see. This procedure allows you to understand how many roots and canals the tooth cavity has. If the X-ray examination is ignored, then the cavity of the diseased tooth will have to be opened again.
Preparatory procedures
After the X-ray of the dental cavity has been carefully studied, the diagnosis has been made, and the stages of the upcoming therapy have been planned, it is necessary to tell the patient about everything in detail. Next, you need to obtain documented consent for the opening and further treatment of the tooth cavity.
An important point in preparing for root cavity treatment is for the doctor to obtain information about the presence of allergic reactions in the patient to anesthetics. If such information is not available, an allergy test is performed. At this stage, chemical treatment of the instruments with which the manipulations will be performed is carried out.
Administration of anesthesia and application of anesthetic
Before treatment begins, the patient is anesthetized in the area of the jaw where the intervention will be performed. Anesthesia can be superficial or in the form of an injection. The first type of anesthesia blocks sensitivity not only in the dental cavity, but also on the mucous membrane. It is usually used to numb the area where the doctor is about to inject an anesthetic.
The following drugs are used for superficial anesthesia:
- 0.5% Promecaine ointment;
- Anestezin;
- Lidocaine;
- Dicaine.
Opening a molar tooth
What is the opening of a tooth cavity? In order to remove the pulp and clean the root canals, the dentist needs to provide good access to them. Opening the tooth cavity can begin immediately after grinding the caries and removing sawdust from the dentin. The process of opening the tooth cavity begins with the smallest bur, after which a large spherical one is used.
Medicinal treatment of canals
Canal treatment is divided into mechanical (scraping out the contents using special tools) and chemical (medicinal treatment of root canals with disinfectants injected with a thin needle). Today, the following scheme for medicinal treatment of the root canal is used: sodium hypochloride is applied after using each instrument and completing mechanical cleaning, then hydrogen peroxide, and after that distilled water. Drug treatment of root canals is carried out immediately after the opening of the dental cavity is completed.
Sealing
The final stage of tooth root canal treatment is sealing the cavity. The root cavities are filled with a special filling material (usually gutta-percha). The filling helps the tooth remain strong and prevents pathogenic bacteria from entering its cavity.
Filling a tooth cavity can be:
Stages of tooth canal treatment
Endodontic treatment usually lasts several hours and includes a number of stages.
- Removal of the pulp (pulpectomy).
The inflamed soft tissue of the tooth is eliminated. - Root canal sanitation.
The procedure is a “cleaning” of bacteria and dead tissue elements. Pulpectomy and canal sanitation pursue one of the most important goals - eliminating existing inflammation. - Channel formation.
The root canal, freed from pathological contents, undergoes appropriate treatment. In addition to ensuring good passage of the canal, it is imperative to ensure that its apex reaches the apical part of the tooth. - Canal filling.
The last stage of the intervention is filling the root canal with filling material, followed by grinding.
Prevention of root canal diseases
For ideal “order” in the oral cavity you need:
- take proper care of it;
- use high-quality instruments and oral hygiene products;
- visit the dentist twice a year;
- after each meal, rinse your mouth with water;
- quit smoking and alcohol;
- reduce the amount of coffee and tea consumed;
- Healthy food.
Once I went to the dentist to have a tooth treated, in the end they pulled it out and said that the dentition was incorrect. That there should be 3 roots in a tooth, but I have 2. The doctors were mistaken, the root remained in the gum. I got it with my own strength. And they didn’t even deign to double-check everything. Just like that...
Diagnostics
Before performing dental procedures, it is extremely important to identify the features of the canal-root system in order to clean it completely. The problem is that the dentist is not always able to determine the number of strokes visually and by palpation (using a probe). They often narrow at the mouth, and the probe does not pass through the narrowing, overgrow against the background of a long-term inflammatory process, or have an atypical structure.
That is why, in most cases, the doctor sends the patient for dental x-rays before starting treatment. The photographs show the number of roots, the structure of the cavities, and indirect signs of the inflammatory process. In complex diagnostic cases, they resort to computed tomography, which helps to more clearly visualize all tooth structures.
In addition to topical diagnostics, it is also important to measure the length of the canal in order to understand at what depth the filling material should be inserted.
How many canals are there in the 5th, 6th, 7th and other teeth of the upper and lower jaw, what is the length
Teeth differ from each other in shape, structure, and number of roots. The space inside the root is called the root canal. The number of roots has a relationship with the load that falls on the tooth, but the number of canals in the tooth does not have a direct relationship with the number of roots. And even in the same tooth, the number of canals may vary among different people.
The key to high-quality endodontic treatment is the accurate determination of the tooth canals: their number, length, shape.
Typically, the deeper a tooth is in the mouth, the more canals it has. The number of canals in the teeth of the upper and lower jaws differs: the upper teeth have more of them.
A preliminary assessment of the number of canals in a tooth is carried out according to the table (the probability of a certain number of roots depending on the location of the tooth):
Thus, the canals of the 24th tooth (the left quad in the upper jaw) in 85% of cases are determined by the number 2. That is. This tooth usually has only two canals. But 9% of people can only have 1 channel, and 6% have 3 channels. On the other hand, the “seven” of the lower jaw most often (77%) has 3 canals in the teeth. We can judge with the greatest confidence how many canals there are in the front tooth on the upper jaw - only 1.
It is statistically impossible to answer the question of how many canals there are in a wisdom tooth: for the upper ones, the number varies from one to five, for the lower ones – about three.
The exact number can only be found out when opening the tooth or based on the results of radiography (targeted, for a specific tooth, or orthopantogram, to assess the condition of all teeth).
What is the cost of treatment?
How much does root canal treatment cost? The cost largely depends on the method used and the quality of the materials. When using laser and microscopic technology, nanocomposites and other advanced developments, the cost of tooth treatment with canal filling increases significantly. Approximate prices for root canal treatment in Moscow with gutta-percha filling and composite filling are presented in the table below.
| View | Price |
| Single channel tooth | 9,500 – 12,5000 rubles |
| Double channel tooth | 11,000 – 14,500 rubles |
| Three-channel tooth | 13,500 – 17,000 rubles |
The cost of root canal treatment should not be the determining factor in choosing a clinic. Contact only dentistry with a good reputation and experienced specialists who use modern equipment and the latest techniques in their work. Remember - the future fate of your teeth and the aesthetics of your smile depend on the quality of canal treatment!
The length of the canals of the teeth of the upper and lower jaw
To carry out high-quality endodontic treatment, it is important to know the length of the dental canal. The length of the tooth canals (the table below) depends on the size of the tooth itself. Determining such parameters is possible in several ways.
The initial preliminary assessment is carried out in a tabular manner (average canal length and its variability in mm depending on the tooth formula):
Sometimes the length of the tooth canals can be determined from an x-ray, but the x-ray image in most cases does not reflect the true size.
Read also: Is it possible to eat ice cream after tooth extraction?
With an accuracy of 60-97%, the length is determined electrometrically (by changes in the electrical resistance of tissues) using an apex locator.
The tactile method is based on slowly immersing the probe into the canal until it jams.
According to the patient’s sensations (a slight “prick” when moving the instrument past the root apex), during treatment without anesthesia, the length of the canal is also determined approximately.
Using a combination of several approaches is effective.
If your tooth hurts after root canal treatment
If after root canal treatment your tooth hurts when you press it, this is normal. This phenomenon is associated with insufficient anesthesia in the area of endodontic intervention. Another reason why a tooth hurts after canal treatment is excessive treatment with the instrument moving beyond the apical foramen.
How long does a tooth hurt after root canal treatment? Sometimes pain persists for several days due to intensive intervention in the tissue structure in such a limited area. A similar situation occurs when an excess amount of filling material is placed into the canal, which causes discomfort when pressure is applied to the walls. As a result, the tooth “aches” after canal treatment. In any case, the presence of post-filling pain signals the need for a second visit to the dentist.
Patency of dental canals
In addition to the number and length, important information is the patency of the root canals, which depends on the degree and location of the curvature. If the curvature is less than 25 degrees, then the canal is instrumentally accessible, from 25 to 50 degrees it is difficult to access (the so-called difficult tooth canals), and over 50 degrees it is inaccessible. When the curvature is localized near the mouth of the canal, it is possible to expand the latter and improve patency.
If the examination reveals a too narrow, deep canal in the tooth, a CT scan may be required to clarify its configuration. Treatment of complex teeth requires particularly painstaking work, which can be made easier with the help of a microscope.
Sometimes the doctor cannot find the canal in the tooth. This situation is usually associated with obliteration (narrowing or overgrowing) of the canals due to an inflammatory or tumor process, incorrect treatment in the past, or age-related changes.
Remember that only a specialist can assess the condition of the root canals and, depending on their structural features, determine treatment tactics.
Channels in baby teeth
There are as many nerves in baby teeth as there are in molars—one. In addition, temporary units are similar to permanent ones in the structure of the root system. That is, a milk tooth such as the upper six or second molar has a canal system similar to its molar brother, the second premolar.
Nerve endings perform standard functions:
- signal about developing caries;
- responsible for the growth and development of teeth;
- control the flow of water and nutrients to dentin and enamel.
The root canals of baby teeth are also treated and filled, but the tactics of their treatment depend on how long ago they erupted. Under the temporary units, permanent ones are formed, so treatment should be aimed at preserving them. Milk teeth can only be removed if the permanent teeth are ready to emerge.
The roots of permanent incisors, canines and molars do not form immediately, but over the course of about 3 years. Treatment of permanent teeth with unformed roots also differs from the standard one. The canals in the teeth of patients four, five, six years old (depending on the rate of formation of the dentoalveolar apparatus) are filled with a special paste with calcium and fluoride, which helps close the roots.
How many canals are there in human teeth, features of the anatomical structure
A beautiful smile is fashionable. Therefore, great attention is paid to dental health these days. Unfortunately, not everyone can boast of their impeccable appearance, although modern dental developments can bring them as close to ideal as possible.
In our article we will not talk about this. We will discuss the anatomical structure of the human tooth, a diagram of which is given on our website.
Molars are the only human organ that does not regenerate on its own. That is why they need to be protected and regularly monitored for any changes in their condition. It is not without reason that regular examinations by a dentist every 6 months are recommended.
Molars require careful care
If we consider it enlarged, then each molar, a photo of which can be seen on our website, consists of a crown and root part. The crown part - the one that is located above the gum level, is covered on top with the strongest tissue in the human body - enamel, which protects its softer inner layer - dentin, which is the basis of the tooth.
Despite its strength and reliability, enamel is incredibly susceptible to external influences. Poor care, bad habits, and heredity can disrupt its condition. Pathogenic bacteria enter cracks in the enamel, causing intense tissue destruction. A person develops a carious process that also affects dentin.
If left untreated, the infection penetrates into the root part, acute pulpitis and other equally dangerous ailments develop.
As for the structure of the root part. then its main elements are arteries, veins and nerve fibers that supply the tooth. They are located in the pulp of the root canal and through the apical foramen are connected to the main neurovascular bundle.
The dentin below the gum level is covered with cement, which is attached to the periodontium with the help of collagen fibers. The roots of human teeth, as the photo illustrates them very well, are hidden in the alveoli - peculiar recesses of the jaw bone.
Any defeat requires its complete removal. A broken root cannot be restored.
The structure of the jaw and molars of an adult deserves a separate section. This will be discussed below.
When visiting a dental office, we hear different names that are unfamiliar to our ears and, sometimes, we don’t even understand what they are talking about. This section is intended to help you understand what human teeth are called so that, if necessary, you can learn to understand the extent of the dental problems you have.
So, in the mouth we have:
- Central and lateral incisors;
- Fangs;
- Premolars or small molars;
- Molars or large molars.
In order to indicate their position on the upper and lower jaws, the so-called dental formula is used in dental practice. according to which the numbers of primary teeth are written in Latin numerals, and the numbers of primary teeth are written in Arabic numerals.
With a full set of teeth in an adult, the dental formula will be as follows: 87654321 / 123465678. A total of 32 pieces.
On each side there are 2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 premolars, 3 molars. Molars also include wisdom teeth, which are the last to grow. As a rule, after 20 years. As for children.
then their dental formula will have a different appearance. After all, there are only 20 baby teeth.
But we’ll talk about this a little later, and now we’ll look at the structure of incisors, canines, premolars and molars, and also discuss their differences.
Features of the structure of the upper teeth
The smile zone includes central and lateral incisors, canines and premolars. Molars are called chewing teeth because their main purpose is to chew food. Each one looks different.
So, the ones are the central incisors. Their crown part is thickened and slightly flattened, they have one long root. The two lateral incisors also have a similar shape. They, like the central incisors, have three tubercles on the cutting edge from which three pulp spurs extend along the dental canal.
The canines are shaped like the teeth of an animal. They have a pointed edge, a convex shape and only one tubercle on their cutting part. First and second premolars. or, as dentists call them, the four and five are very similar in appearance, the difference is only in the size of their buccal surface and in the structure of the root.
Next come the molars. Six has the largest coronal part size. It looks like an impressively sized rectangle, and the chewing surface in its shape resembles another geometric figure - a rhombus. Six has 3 roots - one palatal and two buccal.
Read also: The hole hurts after tooth extraction, what to do
The seven differs from the six in slightly smaller sizes and different fissure structures. But the eight or, as popularly known, wisdom teeth do not even grow in everyone. Its classic shape should be the same as that of ordinary molars, and its root resembles a powerful trunk.
The upper wisdom teeth are considered the most capricious.
They can begin to disturb a person even at the stage of their eruption, and when removed they can create a difficult situation due to their twisted and twisted roots. Their antagonists are located on the opposite jaw. Our next section will be devoted to them.
Features of the structure of the lower teeth
The photo conveys quite accurately what human teeth and fangs are made of, as well as their appearance. From it one can judge that the structure of the teeth in the lower jaw is completely different from their structure in the upper jaw. Let's consider this point in more detail.
The teeth of the lower jaw have the same names as the upper jaw, but their structure will be slightly different.
The central incisors are the smallest in size. They have a small flat root and 3 faint tubercles. The lateral incisor is larger than the central one by only a few millimeters. It also has a very small size, a narrow crown and a small flat root.
The lower canines are similar in shape to their antagonists, but they are narrower and slightly tilted back.
The first premolar on the lower jaw has a rounded shape, a flat and flattened root, and also some bevel towards the tongue.
The second premolar is slightly larger than the first due to more developed tubercles and the presence of a horseshoe-shaped fissure between them.
The first molar, that is, the lower six, has the most cusps. Its fissure resembles the letter Z, in addition, it has as many as 2 roots. One of them has one channel, and the second has two. The second and third molars are very similar in shape to the first.
They are distinguished only by the number of tubercles and fissures located between them, which, especially on the figure eight, can have a bizarre shape.
Milk teeth are the predecessors of molars. They begin to appear in the first year of a baby’s life and, as a rule, the lower central incisor is the first to pierce the gums. Many parents remember the period of teething with a shudder. They cause so much suffering to the little ones. This process is not fast - it is extended over time.
From the appearance of the first tooth to the last it can take two, or even two and a half years.
The average three-year-old toddler has a full set of 20 teeth in his mouth. The child will walk with them until he is 11–12 years old. But they will begin to change to the original ones from the age of 5–7 years.
Parents keep photos of toothless school-age children in family albums. But let’s return to what it is like, the structure of baby teeth in children. Let's start with their shape.
It will be approximately the same as for permanent ones.
The only difference will be their small size and snow-white color. However, the degree of mineralization of their enamel and dentin is weak, so they are more susceptible to caries. Therefore, caring for them must be regular and thorough.
The structure of a baby tooth is also distinguished by a large volume of pulp, which is incredibly susceptible to inflammation. That is why in children, caries quickly turns into pulpitis.
Baby teeth do not have long roots. In addition, they do not sit tightly in the periodontal tissue. This greatly simplifies the process of replacing them with permanent ones. Although for children the process of removing them is always stressful.
Teeth are considered one of the most complex systems in our body. Their importance for our full life is invaluable. Therefore, you need to start taking care of their condition and health from an early age. And make it a rule to visit the dentist every six months.
Number of roots and canals in human teeth
Most of the oral cavity is occupied by organs whose main function is to chew and grind food into smaller pieces.
This promotes its complete digestion and better absorption of nutrients. A tooth is an organ that has a characteristic shape and consists of several parts.
In dentistry, the outer visible part is called the crown, and the inner part is called the root. The element connecting the crown and root is the neck.
An interesting fact is that, unlike a crown, a tooth can have more than one root. How many roots a tooth has, as a rule, depends on the location and purpose of the organ. In addition, its structure and number of roots are influenced by hereditary factors. The situation can only be definitively clarified with the help of an x-ray.
The article provides detailed information about how many roots there are in the frontal, lateral chewing teeth, as well as the number eight, or the so-called wisdom tooth. In addition, you can find out what the purpose of the tooth root is, why the chewing units need nerves. The dental advice provided in the following material will help prevent the development of dental diseases.
Accurate determination of the number of channels using an x-ray image
An x-ray allows you to determine exactly how many canals there are in a tooth. This method allows the doctor to see a complete picture of the condition of the teeth: the location of the roots, the presence of a cyst. The image helps to evaluate the quality of the filling performed, as well as to calculate how many canals there are in a particular tooth.
Some patients associate the word “X-ray” with something dangerous. However, modern devices do absolutely no harm to humans. The procedure does not require preliminary preparation; it is often carried out directly in the dentist’s office. The whole process takes no more than 5 minutes.
As a result of radiography, the doctor has a complete, and most importantly, clear picture of what is happening to the teeth. Where crowns or fillings are installed, white areas appear in the image, cavities appear black, and tissues and fluids acquire gray shades. The information obtained allows the doctor to determine the number of channels as accurately as possible and perform treatment while minimizing negative consequences.
Dental X-rays can be done even for nursing and pregnant women. Of course, there must be serious reasons for this, but in general the procedure is absolutely safe. The only unpleasant moment may be the appearance of a gag reflex. It occurs when the film is fixed to the gum. Deep breathing through the nose helps reduce the urge to vomit.
The images that can be obtained using x-rays are divided into two types:
- Orthopantogram - displays a complete picture of the condition of the teeth of the upper and lower rows. Such photographs are needed at the initial stage of treatment in order to draw up a general plan of the necessary procedures, identify pathologies, structural features, and the relative position of the teeth.
- Targeted – allow you to obtain complete information about a specific tooth. The image gives a clear idea of the internal structure, number and location of the channels, and helps make a final decision on the treatment method.
- Sight shots are sometimes called control shots. Their implementation after treatment allows us to evaluate their effectiveness and quality of implementation.
Prevention
In order not to have to endure unpleasant moments during dental treatment, it is better to promptly identify and, as far as possible, prevent caries and pulpitis. To do this, you need to follow the recommendations of dentists:
- Brush your teeth regularly.
- Use dental floss that gets into hard-to-reach places.
- Rinse your mouth after eating.
- Give up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
- Drink coffee and tea less often.
- Don't eat foods that are too cold or hot.
- Visit your dentist once every six months, even if nothing bothers you.
- Follow a diet rich in vitamins, phosphorus, fluoride, calcium.