June 3, 2021
Cancer occurs when cells begin to grow uncontrollably. Cells of almost any organ can acquire this feature. In addition, as the tumor grows, they can be transported through the blood or lymph to other areas of the body, settle there and give rise to the growth of new lesions. Such foci are called secondary cancer, or metastases, and the initial tumor, respectively, is called primary cancer.
Metastases in any organs are classified depending on which organ the tumor initially originates from. For example, a secondary focus of lung cancer in the liver will still be called lung cancer, it will just receive the prefix “secondary”. Sometimes it is not possible to determine in which organ the tumor first appeared. However, the study reveals its metastases in other parts of the body. If their primary focus cannot be determined, then doctors talk about primary cancer of unknown origin, or hidden primary cancer.
What formations on the skin should raise suspicion?
Most moles, brown spots and growths on the skin are harmless - but not always. If you have a lot of moles and freckles, you need to be very careful about any changes in pigmentation. When a mole begins to bleed or ooze fluid , you need to go to a dermatologist.
It is also necessary to monitor new formations on the skin. Many skin cancers are essentially colorless. They often appear as pink or pearly papules or scaly patches. These are signs of a primary neoplasm, and it is advisable to show them to the doctor. Bleeding and weeping skin lesions are of particular concern.
Types and forms of lip cancer
Malignant formations of soft tissues are not uncommon; they are formed literally “out of nothing.” This is what is commonly believed, but in reality not everything is so simple.
The appearance of a tumor is associated with several factors. Previously, it was believed that smoking and addiction to alcohol were to blame. Now, the risks of cancer are increasing due to frequent infection with the human papillomavirus.
There are several types of malignant process; it is worth noting that oncological formations of the lip are rarely reactive in nature (that is, they develop rapidly).
What classification does the disease have?
- Squamous cell keratinizing cancer develops slowly, the disease involves new tissues in the process, but metastases rarely appear. Due to the long course of the pathological process.
- Squamous cell non-keratinizing cancer is characterized by rapid development, the process involves nearby tissues, and metastases affect the lymph nodes of the jaw and submandibular region.
It is worth noting that in comparison with other types of malignant process, cancerous tumors of the lips rarely metastasize, but it all depends on the stage of development of the disease:
| At the first stage: | As the disease progresses, the chances of metastases increase and are: | At stage 3: | If the pathological process reaches its final stage: |
| metastases appear only in 5-8% of cases. | no more than 20%. | metastases appear in 35% of patients. | then metastasis is observed in 70% of patients. |
If we talk about the forms of the disease, there are only 3 of them:
ABCDE technique for cancer detection
The first five letters of the English alphabet are a guide to help you recognize the signs of cancer.
- A is asymmetry. Most skin cancer lesions are asymmetrical. If you draw a line through the middle of the hearth, the two halves won't line up, so it looks different from round to oval.
- B is the border. The borders of cancers tend to be jagged and may have jagged edges, while regular moles tend to have smoother, more even borders.
- C is color. Multiple colors are a warning sign. While benign moles are usually one shade of brown, cancerous moles can be various shades of tan, brown, or black. Red, white, or blue colors may also appear as they grow.
- D is the diameter. It is already worth paying attention to the spring if its size is more than 6 mm. Some experts say it's also important to look for any damage, regardless of size, that is darker than others. Sometimes, amelanotic melanomas are colorless.
- E is for evolution. Any change in the size, shape, color or height of a spot on your skin, or any new symptom in your skin, such as bleeding, itching or crusting, may be a warning sign of melanoma.
If you notice these warning signs or anything new, changing, or unusual on your skin, contact your dermatologist immediately.
Symptoms of skin metastases in cancer
Skin metastases usually occur close to the primary malignant tumor. Their appearance varies. Most often, the first sign is the appearance of a hard, round or oval, mobile, painless node. These formations have an elastic consistency, their density and size vary - from barely noticeable to large tumors. The nodules may be flesh-colored or red; in melanoma, they may be blue or black. Sometimes they are single, and sometimes multiple appear quickly. Skin metastases can disintegrate, causing ulcerations and bleeding.
Also, depending on the appearance, some specific forms of skin metastases are distinguished:
- Erysipelas (erysipeloid, inflammatory) carcinomas look like red spots with sharply defined contours, hot to the touch. Cancer cells clog the lymphatic vessels, disrupting the outflow of lymph, and this can cause swelling - lymphedema. The skin thickens, resembles a “lemon peel”. Erysipelas carcinomas closely resemble an infectious process in the skin caused by certain bacteria, and when localized on the skin of the breast, they can be difficult to distinguish from mastitis. In cases of persistent skin inflammation that does not respond to conventional treatment methods, metastatic lesions should always be suspected.
- Sclerodermoid carcinomas appear as dense plaques that resemble scars. They occur when cancer cells spread into the dermis, the connective tissue layer of the skin rich in collagen.
- Telangiectatic carcinomas are red spots, plaques, or nodules that most often appear in breast cancer after surgery in the scar area. The red color is due to the fact that tumor lesions contain numerous pathologically dilated blood vessels (telangiectasia).
- Herpetiform metastases resemble herpes zoster. They look like blisters, vesicles, or nodules and are located along the nerves, similar to lesions in herpes zoster. The mechanisms of occurrence of such metastatic foci are not fully understood; it is believed that they spread through lymphatic vessels along the nerves.
- Neoplastic alopecia is a characteristic symptom of skin metastases in the scalp. A blue or purple plaque appears on the skin, resembling a scar, and hair falls out in this area. This occurs because cancer cells destroy hair follicles, causing inflammation and proliferation of connective tissue. In 84% of cases, the cause of neoplastic alopecia is malignant breast tumors.
- Paget's cancer is a lesion of the nipple and areola of the breast. According to the currently most widespread theory, a malignant tumor initially arises in the breast tissue, and only then spreads through the milk ducts into the nipple.
- Subungual metastases are usually painful and are often confused with inflammatory processes.
- Sister Mary Joseph's metastases present as dense nodules in the umbilical area. They may have a loose appearance and ulcerate. Most often, this type of metastasis occurs in cancer of the stomach, ovary, colon and rectum, and pancreas. In 29% of cases, the primary tumor cannot be detected. It is believed that Sister Mary Joseph's metastases spread to the navel directly from the affected organs, for example, through the round ligament of the liver (the so-called implantation metastasis), as well as through the blood (hematogenous), lymph (lymphogenous).
- Hidden skin metastases are not detected externally. They are detected accidentally based on the results of a histological examination performed for another reason.
Who is most at risk of skin cancer?
People with fair skin that burns easily in the sun are more likely to develop skin cancer. The skin generates its own protection against ultraviolet radiation using keratin and melanocytes , cells that produce melanin. They create a tan, protecting the skin from damage. However, when you get sunburned and your melanocytes are unable to respond quickly, you are at serious risk of developing skin cancer. Moreover, the greatest danger haunts those with blond and red hair, as they burn faster.
Precancerous diseases of the lips
Precursors of oncology are pathological processes in tissues: inflammation, infection, bacterial damage. All this can provoke the development of oncology.
What diseases can lead to the development of lip cancer:
- Leukoplakia lips.
- Precancerous cheilitis.
- Hyperkeratosis of the red border.
Recently, there has been a tendency for papillomas to degenerate into malignant formations. If a wart appears on the surface of the lips, it should be removed. This will reduce the risk of developing cancer, but will not eliminate it completely. Since HPV is in the blood, which means it can recur when the activity of the immune system decreases.
Obligate precancer
Characterizes itself by the presence in a person of an innate predisposition to the development of malignant formation.
Such diseases include xeroderma pigmentosum, which manifests itself as increased sensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet radiation.
Recommended video:
How to detect skin cancer on the body?
The best way to detect skin cancer is to examine yourself. When checking, you should look at the spots on the skin. And you should check everything from the scalp (parting the hair to check the entire scalp) to the spaces between your toes and the soles of your feet.
If possible, ask your partner to help you. He can examine hard-to-reach areas of the scalp and back.
By getting into the habit of checking your skin, you will be able to notice changes. Checking monthly can be helpful. If you have had skin cancer, your dermatologist will be able to tell you how often you should check your skin.
People of all ages get skin cancer.
Skin testing can help you detect skin cancer early, when it is highly treatable.
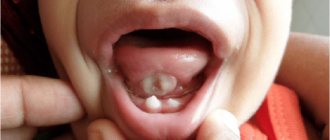
Localization
Oral cancer is usually classified by location. This is due to the fact that the area under discussion includes a large number of anatomical formations with significant diversity.
When choosing treatment tactics and the type of operation, the position of the tumor in the mouth plays a significant role. Different parts of the oral cavity are innervated differently, have different blood supply, and have different functional significance, so the prospects for treating absolutely identical tumors located in different places can differ significantly.
Based on location, oral cancer is usually divided into:
- Cheek cancer
- Floor of mouth cancer
- Tongue cancer
- Cancer in the alveolar ridge area
- Palate cancer
- Gum cancer
Cancer of the buccal mucosa
Cancer of the buccal mucosa ranks second in frequency (after cancer of the tongue) in the structure of oral cancer. Local factors, chemical and physical agents that cause chronic trauma to the mucous membrane have a significant influence on the increase in risk. To a greater extent than with cancer of other areas, such a predisposing factor as chronic traumatization by dentures and sharp edges of damaged teeth is relevant.
Floor of mouth cancer
This type of tumor accounts for 10-15% of all oral cancers. The floor of the mouth is formed by the structures between the tongue and the hyoid bone. The mucous membrane lining the bottom of the mouth has a developed submucosa, consisting of loose connective tissue and fiber. This area is richly supplied with blood. All this creates favorable conditions for tumor growth, spread and metastasis.
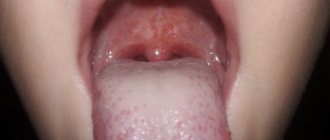
Tongue cancer
Tongue cancer is the most common type of oral cancer. The tongue is a mobile organ with a large number of nerve endings (receptors). Thanks to this, patients, as a rule, pay attention to the tumor that has arisen and have the opportunity to seek help in a timely manner. A developed network of blood and lymphatic vessels contributes to early tumor metastasis, primarily to peripheral lymph nodes.
Cancer in the alveolar ridge area
Cancer in this area develops either from mucosal cells or from the epithelial islets of Malasse. Epithelial islands of Malasse are the remains of epithelial cells in the thickness of the periodontium. Normally, these cells do not manifest themselves in any way, but under unfavorable conditions they can become a source of tumor. A distinctive feature of these tumors is the relatively early onset of symptoms, the teeth in the tumor growth area are exposed to it, and the patient begins to complain of pain.
Palate cancer
Palate cancer is rare. The hard and soft palates are separated, therefore the histological types of tumors of the soft and hard palate are different. Cylindromas and adenocarcinomas are more typical of the hard palate; the soft palate is more susceptible to squamous cell carcinoma.
What does skin cancer look like? Photos and description of signs.
Skin cancer manifests itself on the body in different ways. It might look like:
- A mole that changes or a mole that looks different from your others
- Dome-shaped growth
- scaly spot
- A wound that doesn't heal or a wound that heals and comes back
- Brown or black streak under the nail
It can also manifest itself in other ways.
To detect skin cancer on your body, you don't need to memorize a long list. Contact your dermatologist if you notice a spot on your skin that:
- Differs from others
- Changed
- Itchy
- Bleeding.
Find out if the treatment is prescribed correctly
Prognosis and survival
It is difficult to make a prognosis for oncology, but as for lip tumors, the prognosis is conditionally considered favorable.
| If the pathological process is at the initial stage of development (stage 1-2): | The survival rate for patients is good and ranges from 97-100%. |
| If cancer develops and metastases appear: | The survival rate decreases and is about 85% if the tumor can be surgically removed. |
| In severe condition, when the cancer reaches stage 4: | The survival rate of patients decreases and amounts to 55%. |
Much depends on the individual characteristics of the body. But lip tumors develop slowly, and the survival rate decreases when metastases appear. They destroy lymph nodes and jaw bones.
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, such complications can be avoided.
How do basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers manifest?
Most people have basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma . The most important thing to know about these types of skin cancer is that they are very superficial. They do not penetrate too deeply into the layers of the skin. Therefore, if cancer of one of these types is detected early enough, the doctor prescribes a simple resection. A dermatologist or physician may perform a biopsy to determine the nature of the growth.
Squamous cell and basal cell carcinomas are often identified by external characteristics .
It may take the form:
- clearly colored plaque;
- clusters of brown nodules;
- ulcers raised above the skin.
Such tumors are frozen, burned or excised. All of the above methods are equally effective.
It is important to start treatment as early as possible, since malignant neoplasms of these types do not grow deep into the skin . The best option is to treat cancer in Israel. In rare cases, when left untreated, basal cell and squamous cell tumors increase in size and spread into deeper layers of tissue.
Causes and risk factors
Any disease has causes; you should include a list of factors that can provoke the formation of a cancerous tumor of the lip:
- Bad habits: alcohol, nicotine.
- Infectious diseases of soft tissues.
- Metabolic disorders in the body.
- Exposure to the sun's rays.
- Mechanical injuries to the skin of the lips.
- Surgical interventions in this area.
- Poor heredity, predisposition to cancer diseases.
- Poisoning with chemical reagents, which is systematic.
- Contact with carcinogenic substances.
The risk of developing the disease increases if a person has ulcers and erosions of the skin of the lips. When damage does not heal over a long period of time, the risk of secondary infection increases. As a result, the risk of developing atypical cells in the tissues of the lips increases several times.
The seal, consisting of connective tissue, can “degenerate”. A similar thing happens with formations (papillomas, warts, creatures).
Effect of smoking
Addiction to tobacco has been linked to various forms of cancer. Including malignant formations of the lip. With systematic contact with tobacco smoke, the human body is “saturated” with carcinogens (combustion products). As a result, the risk of developing cancer diseases increases significantly.
What happens to lip tissue with systematic tobacco use:
- contact with cigarettes thins the skin;
- microcracks and erosions form on the lips, invisible to the human eye;
- tobacco smoke successfully penetrates microcracks, leading to the development of a malignant process in tissues.
If a person has a cracked lip, wound or damage to the tissue in this area, the risk of developing cancer increases.
But not only cigarettes are dangerous for humans; smoking a pipe, chewing tobacco leaves and using nasvay can also have a detrimental effect on a person’s health.
The appearance of infectious processes on the lips, cracks, the development of inflammation in the tissues - all this is regarded as a precancerous condition. Although there may not be any atypical cells in the affected area. But only diagnostic measures can refute or confirm this fact.
How does melanoma manifest?
Melanoma differs from basal cell and squamous cell skin cancer primarily in that, unlike previously described types of cancer that do not penetrate into the deeper layers of tissue, this tumor has the potential to grow and spread. The deeper it penetrates the skin, the higher the risk of its further spread throughout the body. Metastatic melanoma is an extremely dangerous disease. However, melanoma can be completely cured if it is detected at an early stage, before it has time to grow deeper into the skin and form metastases in the internal organs.
Melanoma not only penetrates deeper into the skin, but individual cells spread around the primary tumor. Therefore, when resection of melanoma, the surgeon necessarily removes a fragment of normal tissue. For example, if the tumor is comparable in size to a pencil cut, you need to additionally remove about a centimeter of healthy skin around the entire circumference of the melanoma - and possibly more if the cancer has penetrated into the deeper layers of the tissue.
When melanoma grows deep into the skin, there is a risk of it spreading to other organs. Typically, in cases of metastases, secondary lesions form in the lymphatic system, namely in the lymph nodes. Lymph nodes in the armpits, groin or neck begin to enlarge and can reach considerable sizes. From there, cancer cells can spread to internal organs. Therefore, in cases of deep germination of melanoma, the doctor not only removes the tumor itself, but also checks the lymph nodes. They should not show any signs of cancer spreading.
Check the price with a specialist
Identification example
Hidden primary cancer is uncommon. Moreover, during further examinations the primary lesion may be discovered. If this happens, the tumor is no longer considered a primary cancer of unknown origin. It is given a name in accordance with the organ of origin and, based on new data, the treatment regimen for cancer is modified.
In practice this happens as follows:
- For example, a person is found to have an enlarged lymph node in the neck.
- A biopsy reveals that there is a malignant tumor in the lymph node.
- However, upon cytohistological examination, it turns out that the cells of this tumor are not similar to cancer cells of the lymphatic system.
- The patient is tentatively diagnosed with a primary cancer of unknown origin.
- The tumor cells found are similar to cancer cells of the oral cavity, soft tissues of the throat or larynx.
- The patient is prescribed a series of in-depth examinations.
- During these examinations, a small asymptomatic tumor lesion is found in the larynx.
- The patient's diagnosis is changed to laryngeal cancer and treatment appropriate for this type of oncopathology is prescribed.
However, in some cases, even the most thorough examination does not detect the primary focus. Moreover, it is not always possible to find it even during a pathological examination.
How the quality of medications affects the cure for skin cancer
For advanced skin cancer, especially melanoma, the main treatments are chemotherapy and immune therapy. In this case, the quality of medicines becomes of great importance. This is especially important if the patient is undergoing immune therapy, because... Such drugs are not cheap.
If you have been prescribed drug treatment for skin cancer, it is best to purchase medications in Israel.
- Counterfeiting of medicines is prohibited in Israel.
The Israeli Ministry of Health strictly controls the quality of medicines through test purchases and inspections of pharmacies. A pharmacy or pharmacist who sells a low-quality drug to a client will lose its license and face criminal charges. - In Israel, licensing of innovative drugs is carried out as quickly as possible.
This allows Israeli clinics to quickly introduce into widespread clinical practice all new effective drugs appearing in the world. - The Israeli company TEVA is a world leader in the production of medicines.
Doctors in 60 countries around the world prescribe to their patients medications developed by this company.
Stages of the disease
Stage I is characterized by the presence of a tumor up to 1-2 cm in diameter, not extending beyond the affected area (cheek, gums, palate, floor of the mouth), limited to the mucous membrane. Metastases are not detected in regional lymph nodes.
Stage II - a lesion of the same or larger diameter, which does not extend beyond any one part of the oral cavity, but extends into the submucosal layer. There are single metastases in regional lymph nodes.
Stage III - the tumor grows into the underlying tissues, but not deeper than the periosteum of the jaw, or has spread to adjacent parts of the oral cavity. In regional lymph nodes there are multiple metastases measuring up to 2 cm in diameter.
Stage IV - the lesion spreads to several parts of the oral cavity and deeply infiltrates the underlying tissues, in the regional lymph nodes there are immobile or disintegrating metastases, and the presence of distant metastases is also characteristic.
Classification by stages is periodically subject to revision; you can find a division of stages into subtypes - A and B. Currently, classification by stages is used less and less, the TNM classification is more relevant. Its principle is that this coding indicates the characteristics of the tumor itself, the condition of the closest (regional) lymph nodes, and the presence or absence of distant metastases.
In the diagnosis, the oncologist indicates the histological type of cancer, since different types of cells differ in growth rates, tendency to metastasize, and sensitivity to treatment. All types of classifications serve one purpose - to correctly assess the extent of the spread of the disease, the degree of damage and develop the right tactics of assistance.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Where can I buy Israeli medicines?
- In an Israeli pharmacy - after consulting a doctor.
If you undergo examination at the oncology center, the doctor will prescribe you the necessary medications, which can be purchased in Israel. - At your place of residence - using a telemedicine program.
As part of this program, you will also receive a consultation from an Israeli doctor - but remotely. You can order the medications prescribed by him and have them delivered to your home.
Symptoms of cancer of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses
- Long-term nasal congestion
- Pain above or below the eyes
- Unilateral obstruction of the nasal passage
- Nosebleeds
- Discharge of pus from the nasal passages
- Decreased sense of smell
- Numbness or pain in the face
- Loose teeth
- Swelling on the face, nose, or roof of the mouth
- Constant watery eyes
- Unilateral bulging eyes or blurred vision
- Pain or pressure in the ears
- Difficulty opening the mouth
- Enlarged cervical lymph nodes
Many of these symptoms can occur with other conditions, such as an infection in the nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses.
However, only a doctor can confirm or exclude the diagnosis of a tumor. In addition, you need to remember that the earlier a tumor is detected, the higher the likelihood of successful treatment.
After examination by a medical specialist and preliminary examination, additional research methods may be recommended.
X-ray examination of the paranasal sinuses allows us to judge the condition of the sinuses, identify an inflammatory or tumor process in the sinuses and nearby lymph nodes, and prescribe additional examination.
Computed tomography (CT), in some cases with additional contrast, is an effective method for diagnosing tumors in these locations.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide additional information and can distinguish a malignant tumor from a benign process.
A biopsy (taking a piece of the tumor for microscopic examination) is a mandatory final examination method, which makes it possible to make a final diagnosis and justify the planned treatment tactics for the patient.
Cost of diagnosing skin cancer in Israel
In the table below, we present the cost of some procedures prescribed for the diagnosis of skin cancer at the Ikhilov Cancer Center.
| Diagnostic and treatment procedures | Price |
| PET-CT | $1491 |
| Examination and consultation with an oncologist-dermatologist | $567 |
| Biopsy revision | $511 |
| Operation Mohsa | $3318 |
| Photodynamic therapy | $361 |
| Removal of epidermal carcinoma | $511 |
| Detailed blood test | $407 |
Follow-up and control
Treatment for people diagnosed with cancer does not end when active therapy is completed. Your doctor will continue to check to see if the cancer has returned, monitor any side effects, and monitor your overall health. This is called follow-up. It consists of regular medical examinations and tests.
Relapse control
One of the goals of follow-up is to monitor relapse, that is, the reoccurrence of the disease. Cancer recurs because small clusters of malignant cells may remain in the body. Over time, these cells may increase in size until they appear on test results or cause symptoms. During follow-up, your doctor may provide you with personalized information about your risk of recurrence. Your doctor will ask specific questions about your health. You may need to have blood tests or imaging tests as part of your regular follow-up. Follow-up recommendations depend on several factors, including the type and stage of head and neck cancer initially diagnosed and the treatment received. The doctor will also tell you what signs and symptoms to monitor.
Monitoring long-term and delayed side effects
Treatment of malignant tumors is accompanied by various side effects. Long-term effects persist after a period of therapy. Delayed side effects may take months or even years to develop. Long-term and delayed effects may include physical and emotional changes.
Discuss with your doctor the risk of these side effects depending on the type of cancer, your individual treatment plan, and your overall health. If your treatment is known to have some delayed effects, you may need to undergo certain additional tests. For example, if you received radiation therapy, your doctor will recommend that you have regular blood tests to check your thyroid function. Your doctor may refer you to a specialist to treat delayed effects.
Rehabilitation is a major part of follow-up after treatment for head and neck cancer. Patients may receive physical therapy to maintain motor function and range of motion, as well as speech and swallowing therapy to regain skills such as speaking and eating. Proper assessment and treatment can often prevent long-term speech and swallowing problems. Some patients may need to learn new ways of eating or different ways of preparing food.
Patients may look different, feel tired, and be unable to speak or eat as well as before. Many people experience depression. Support groups help patients cope with changes after treatment.
Maintaining your own medical records
You and your doctor will work together to develop a personalized follow-up plan. Be sure to discuss any concerns you have about your own future physical or emotional health.
Why is it worth treating skin cancer in Israel, at the Ichilov Cancer Center?
- Accurate diagnosis.
Modern research methods and extensive experience of Israeli oncologists and pathologists, gained in leading cancer centers in the world, make it possible to accurately determine the type and stage of cancer in order to select the optimal treatment program. - World-class specialists.
The treatment of skin cancer at the oncology center is carried out by top-class professionals, such as oncologist Professor Yakov Shekhter, the author of his own method of immune therapy for metastatic melanoma. The professor selects a personalized treatment protocol for each patient, which allows him to achieve the best possible results. - Innovative treatment methods.
For skin cancer, the oncology center uses:
- Alpha-DaRT brachytherapy is a safe method for removing non-melanoma skin cancer;
- therapy of metastatic melanoma using the TIL protocol (tumor infiltration with lymphocytes).
You can take the first step towards recovery right now. To do this, fill out an application and one of our doctors will contact you within 2 hours.
Or call: +972-3-376-03-58 in Israel and +7-495-777-6953 in Russia.
This consultation does not oblige you to anything and is completely free .
We guarantee you complete confidentiality and preservation of medical confidentiality. We will help you, just as we have helped other patients. [starbox]
How are cutaneous and subcutaneous metastases diagnosed?
Sometimes skin metastases can be the first manifestation of cancer, while the primary malignant tumor does not cause symptoms. In other cases, they appear after the patient is diagnosed with cancer with metastases in other organs. Also, metastatic skin lesions can be the first sign of relapse, and this often occurs a long time after surgery. The average time interval from diagnosis of the primary tumor to the appearance of skin metastases is 2–3 years, but longer intervals of up to 22 years have been described.
Skin metastases are often difficult to diagnose and can be easily confused with primary benign and malignant skin tumors, infections, eczema, and vasculitis. Dermatologists play an important role, since it is usually to them that such patients turn first.
If metastatic skin lesions are suspected, an excisional biopsy is performed. The pathological focus is completely removed and histological examination is carried out. To determine which malignant tumor the metastasis originated from, immunohistochemical analysis is performed. Certain marker proteins help identify the primary neoplasm.
Tumor atypia
Any tumor consists of stroma and parenchyma. The stroma consists of the extracellular matrix, blood vessels, and nerve endings. Parenchyma is the tumor cells themselves. Their structure, as a rule, differs from normal cells - this is atypia. The difference may lie not only in the structure of the cells themselves, but also in their functioning, metabolism, etc. Therefore, there are several types of atypia:
- Morphological atypia. Can be cellular or tissue. In the first case, tumor cells lose the ability to mature and differentiate, as a result of which they acquire a large nucleus, irregular shape, and other characteristics that distinguish them from normal cells. With tissue atypia, the ratio of various tissue elements changes, for example, the ratio of the thickness of the epidermis and dermis.
- Biochemical atypia. Characterized by changes in tumor metabolism. It is this feature that plays an important role in the uncontrolled growth of newly formed tissue. In tumor cells, almost all types of metabolism change, but the most significant is the change in carbohydrate metabolism, which increases several tens of times. Other features include the predominance of protein synthesis over its breakdown, increased absorption of amino acids and water, accumulation of potassium ions and loss of calcium ions.
- Immunological atypia. Tumors are characterized by changes in antigenic structure. For this reason, the immune system cannot effectively “attack” the changed cells, as a result of which the latter can multiply and grow uncontrollably.
- Functional atypia. This is a consequence of the changes described above. Changes in the structure and metabolism of tumor cells inevitably lead to changes in their functions. This may be increased secretion of hormones, loss of the ability to phagocytose, production of substances that are not normally formed, etc.
Some types of atypia have made it possible to develop specific antitumor drugs. In particular, some cytotoxic drugs used during chemotherapy block the uptake of glutamine and glucose. These substances are used by certain tumors in large quantities and are necessary for the growth and division of pathological cells. Immunological atypia formed the basis for cancer immunotherapy. With the help of special drugs, it is possible to eliminate the “defense mechanisms” of the tumor, which make it “invisible” to the immune system.
What happens after treatment is completed?
After cessation of special treatment, the patient should be under the supervision of doctors and periodically undergo examinations in order to identify and treat complications, as well as early diagnosis of a possible relapse (return) of the disease.
If you smoked and/or drank alcohol, you need to quit these bad habits. This will help improve your condition faster and contribute to a speedy recovery.
If necessary, a nutritionist will help you choose the right diet, taking into account the surgery, radiation and chemotherapy you have undergone, and doctors of other specialties will do everything possible to restore your lost functions of speech, swallowing, chewing, etc.
Classification
The types of lung tumors are classified according to the location of the primary focus.
Central cancer is localized in the proximal (central) parts of the bronchial tree. The first signs of lung cancer (symptoms), which should alert you, in this case are clearly expressed:
- dry, prolonged cough that cannot be treated.
- hemoptysis begins with the addition of sputum.
- blockage of the bronchial lumen by tumor masses leads to shortness of breath even at rest. In some cases, the temperature may rise.
Photo 1 - Central cancer of the right lower lobe bronchus (1) with obstruction and metastases (2) to the bifurcation lymph nodes
Peripheral cancer gradually forms in the lateral parts of the lungs, slowly germinating and not detecting itself. This lung tumor may not produce symptoms for a long time; they appear with significant local spread, involvement of neighboring organs and structures, and invasion of the bronchi. Diagnosis of lung cancer of this type of localization is most often possible during a preventive examination (x-ray or computed tomography).
Photo 2 - Peripheral cancer (1) of the upper lobe of the right lung
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
A malignant neoplasm that arises in the dermis and penetrates into deeper tissues - subcutaneous fat, fascia, muscles, bones. Its origin remains unclear, since dermatofibrosarcoma can belong to all 3 types of tumors: fibroblastic, histiocytic and neuroectodermal. This cancer accounts for less than 0.1% of all malignancies and approximately 1% of soft tissue sarcomas.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans initially appears as a small, asymptomatic papule or plaque. Gradually it expands into a lumpy nodule or turns into an atrophic/sclerotic plaque ( Fig. 5 ).
The described signs are very nonspecific, so the tumor is often diagnosed at the time of its active growth. However, as it grows, it begins to aggressively penetrate the surrounding tissues, spreading tentacle-like outgrowths in front of itself - and this makes its complete removal very difficult. The presence of tumor remnants in soft tissues leads to a high rate of local relapses.
The most favorable moment for removing dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is the early stage, during which it grows very slowly. Unfortunately, it is quite difficult to suspect this type of cancer during this period. This puts regular (and better automated) skin screening at the forefront of diagnostic importance.
Rice. 5. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (Danish national service on dermato-venereology)
https://www.danderm-pdv.is.kkh.dk/atlas/7-198-1.html
Surgical method for treating lung cancer
- the main radical method for stages 1-3 of the disease. Operations performed for this disease are classified:
- by volume of resection (lobectomy (removal of a lobe of the lung), bilobectomy (removal of two lobes of the lung), pneumonectomy (removal of the entire lung)),
Photo 3 - Lobectomy
Photo 4 - Pneumonectomy
- by volume of removal of lymph nodes of the thoracic cavity (standard, expanded, super-expanded),
- by the presence of resection of adjacent organs and structures (combined operations are performed when the tumor grows into the pericardium, trachea, superior vena cava, esophagus, aorta, atrium, chest wall, spine). In addition to surgical treatment, it is possible to use an integrated approach, including radiation and chemotherapy.
When treating locally advanced malignant tumors with transition to the main bronchus and pulmonary artery, in cases where previously the only option for surgical treatment was pneumonectomy, it is now possible to perform organ-preserving operations. In this case, the affected area of the main bronchus is excised, followed by restoration of continuity (bronchoplastic and angioplastic lobectomies)
Photo 5 - Scheme of upper bronchoplastic lobectomy
Types of oncology of the anal canal
Doctors identify several types of life-threatening tumors in this area of the digestive system:
- Most cases are squamous cell carcinoma
, which begins in the squamous cells lining much of the anal canal and rim. - Much less common are adenocarcinomas
that develop in the glands or cells lining the part of the anus located near the rectum. - Basal cell carcinoma
: Forms in the perianal region - the skin located around the anus. - Melanoma
: occurs in cells that produce pigment, the substance that colors the skin brown. Such neoplasms usually appear on exposed parts of the body, and only a tiny part of them begins in the anal canal. - Gastrointestinal stromal tumors
develop in the so-called Cajal cells, which set the rhythm of intestinal contractions. They usually affect the stomach or small intestine, and very rarely the anus.
Surgery
Surgical removal of the tumor is the most affordable method of treating skin cancer. Surgery is most effective in the early stages of cancer development due to the lack of tumor growth into nearby tissues. The surgeon removes the tumor and all affected areas. In the presence of metastatic lesions of the lymph nodes, their removal is indicated. If an aggressive form of the tumor develops, surgical intervention alone is not enough to completely get rid of the pathological focus.
A modern method of surgery to remove skin cancer is micrographic surgery using the MONS method. In this case, tumor cells are removed layer by layer under microscopic control. Each removed layer is sent for histological examination.