If you think that dentists never tire of repeating the importance of preventive examinations and timely treatment of caries and gum inflammation just for the sake of advertising their profession, you are mistaken. Inattention to the health of your own teeth and vain fears of dental treatment can ultimately lead to complications, the treatment of which will be both difficult and expensive. A striking example of such a complication is dental granuloma - a pathological formation that occurs in the root part of the tooth.
In the early stages of its development, granuloma does not show itself with any noticeable symptoms, but as the tumor grows and becomes inflamed, severe pain in the tooth may appear, which cannot be relieved with tablets from the pharmacy. It is possible to remove a granuloma and save a diseased tooth only in dentistry and there is no need to delay contacting a doctor, because an untreated granuloma can lead to the development of serious complications, including osteomyelitis, general infections of the body and even cancer.
In this article we will tell you:
- What causes dental granuloma?
- Symptoms of dental granuloma;
- How is dental granuloma treated?
Also in the article you will find information on the prevention of dental granuloma and prices for treatment/removal of dental granuloma in Moscow.
Granuloma and cyst: what do they have in common?
To summarize, all granulomas are divided into simple and complex. The first type is characterized by a slight compaction of granulation tissue without the release of purulent exudate. Developed forms have a pronounced focus of inflammation and large sizes (up to 10 millimeters in diameter). Some experts do not share the concepts of cyst and granuloma. This needs to be sorted out. A classic granuloma does not have clear boundaries and shape, while a cyst is a capsule with purulent fluid, much larger in size, usually with less pronounced symptoms. On the other hand, a cyst is a developed form of granuloma, i.e., in fact, its more complex type.
COMPLICATIONS
Untreated granuloma leads to:
- To complete loss of a tooth. This happens due to complete destruction of the root. As a result, soft tissues are drawn into the inflammation process, in which pus accumulates.
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw.
- Formation of a dental cyst.
- Cancerous tumors.
- Infection of other organs and the development of sinusitis, pyelonephritis and infectious myocarditis.
- If pus gets into the skull, meningitis, encephalitis and inflammation of the peripheral nerves may begin.
- The appearance of migratory granuloma. Manifests itself in the form of protrusion of the facial skin. The disease also appears in the form of abscesses and fistulas in different places.
How does the treatment of a cyst differ from the treatment of a granuloma?
Many experts distinguish three forms of the disease: granuloma, cystogranuloma and cyst. Depending on the type, a technique is selected and a detailed treatment plan is drawn up. It is believed that the initial form of granuloma can be treated conservatively, and to get rid of the cyst one cannot do without surgical intervention. This statement is partly true, but when drawing up a treatment plan, you must first of all evaluate the clinical picture. A large cyst (more than 8 millimeters in diameter), which affects the roots of healthy teeth, has penetrated the maxillary sinus, caused a serious abscess or osteomyelitis, and must definitely be removed. Granulomas and cystogranulomas of small sizes in the absence of extensive inflammatory processes with the spread of purulent exudate are today quite successfully treated with antibiotics or endodontic manipulations.
Classification of granulomas and forms
In medicine, granulomas are classified according to several criteria: etiology, pathogenesis and morphology. Specific varieties are collected in a separate group. In the group according to the criterion of etiology there are types of established and unidentified etiology: infectious and non-infectious. The latter include dust granulomas, drug-type granulomas and neoplasms around foreign bodies. Pathogenesis group: immune and non-immune. The first type includes epithelioid cell granulomas. Non-immune ones occur due to toxic factors and acute infections. The morphological group is divided into two main groups: mature and epithelioid cell. According to the morphology of granulomas, there is the formation of a diffuse-type granulomatous infiltrate and the formation of tuberculoid-type granulomas.
Main types of granulomas
In medical practice, there are many types of neoplasms of this type. They can be single or multiple. It is not always possible to see the beginning of their formation, since pathogenic cells are located deep in the layers of the dermis. Granuloma in children and adults can appear and disappear without treatment. This should justify the need for gentle therapy in the future. Granulomas of the following type are most often diagnosed in children and adults:
- ring-shaped;
- pyogenic;
- tuberculosis.
Tooth granuloma: antibiotic treatment of simple forms of the disease
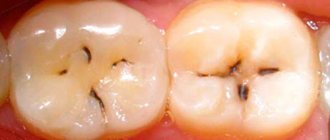
As already mentioned, granuloma at the initial stage responds well to treatment, since it is only a small nodule of connective tissue. For successful healing, as a rule, it is enough to undergo a course of treatment of dental granuloma with antibiotics. For this purpose, drugs from the group of tetracyclines (Doxycilline), lincosamides (Lincomycin) and penicillins (Amoxiclav) are usually used. The type of drug and treatment concept depend on the degree of pathology and the doctor’s recommendations. It is believed that for the simplest forms of granuloma without visible signs of inflammation, antibiotics in ampoules are prescribed, and to treat granuloma in a more advanced stage, injections are necessary. In addition, the doctor usually prescribes antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as the use of antibacterial gels and ointments.
Urgent dental care for the development of purulent inflammation
We already wrote above that dental granuloma develops asymptomatically for a long time and this form is called chronic. But if a person experiences severe stress, catches a cold, a malfunction occurs in the immune system of his body - the granuloma will turn into an acute form, in which purulent inflammation can begin to actively develop. Its signs are excruciating pain that does not subside after taking pharmaceutical painkillers, swelling of the gums and cheeks, and increased body temperature.
Naturally, with such symptoms, you need to urgently contact the dentist to get emergency help. Treatment will depend on where the pus is located and accumulates:
- If the pus is in the granuloma itself, then assistance to the patient will consist of opening the tooth to ensure the outflow of pus through the root canals;
- If there is swelling on the gum and cheek, this indicates that the pus could go into the mucous membrane or periosteum and then the doctor will have to make an incision in the gum to drain it.
If you go to the dentist with a granuloma of a tooth that is completely destroyed, it would be advisable to remove such a tooth. But at the same time, it is important that the tooth extraction procedure is carried out efficiently and not only the tooth is extracted, but also the granuloma. If the tumor remains in the socket, alveolitis may develop - a rather serious and unpleasant complication.
If you have had a tooth with a granuloma removed, you must properly care for your teeth and oral cavity after this operation. You should:
- Temporarily stop drinking too hot food/drinks, alcohol, smoking;
- Avoid overheating and hypothermia of the body and for this purpose do not visit baths, saunas, swimming pools, be sure to dress according to the weather;
- Eliminate stress and physical activity;
- Eat soft and warm foods for a week, trying not to chew on the side of the jaw on which the extracted tooth was located.
Be sure to take all medications and carry out all procedures prescribed by your doctor! If, within 3-4 days after the removal of a tooth with a granuloma, pain and swelling do not go away, contact the clinic immediately. The persistence of pain and swelling may indicate that the inflammatory process continues for some reason.
After tooth extraction during the treatment of granulomas, prosthetics and dental implantation are carried out no earlier than six months later. Such a pause in treatment is necessary for the complete restoration of all tissues in the area of tooth extraction.
Treatment of granuloma at home
Can dental granuloma be treated with folk remedies? Yes, but only as an addition to the main therapy. Treatment with folk remedies for granulomas on the root of a tooth usually includes rinsing with various tinctures and decoctions. The most common of them are tinctures of calamus and propolis, decoctions of chamomile and calendula, as well as regular soda solution. Often, the use of folk remedies is prescribed after surgical treatment of cysts and granulomas in order to reduce the inflammatory process and pain in the postoperative period.
Symptoms of granuloma
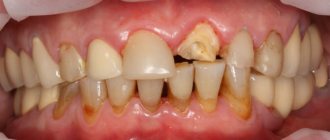
Often the chronic granulomatous form of periodontitis is asymptomatic; sometimes patients complain of minor pain when biting and discomfort in the area of the diseased tooth. When granuloma grows, the following symptoms occur:
- swelling and redness of the gums:
- darkening of the affected tooth;
- increased toothache, its bursting nature;
- sharp sharp pain in the tooth in the morning, immediately after waking up;
- discharge of pus from the subgingival space;
- development of periostitis - inflammation of the periosteum (patients call it gumboil): the gums swell greatly, the swelling spreads to the lips and cheek; toothache radiates to the ear, temporal region, eye; a fistula tract may appear through which pus is released;
- increase in body temperature to 38°C and above;
- headache;
- feeling that the tooth has grown and become taller when biting;
- general weakness.
Factors contributing to the manifestation of symptoms of the disease:
- a sharp change in climatic conditions (weather change, moving to an area with a different climate);
- stress;
- hypothermia of the body;
- previous colds;
- physical stress.
Tooth granuloma: treatment of medium forms
To treat advanced forms of granuloma, endodontic techniques are used, which involve opening the root canal cavity. Treatment of diseases at this stage takes several stages and is carried out over a number of visits to the doctor.
Main stages:
- tooth treatment, opening and antiseptic treatment of dental canals;
- antibiotic-based medications are placed into the canal cavity;
- after the required period has expired, the canal cavity is opened again and filled with calcium-containing paste;
- At the final stage, permanent canal filling and tooth restoration are performed.
Separately, it is necessary to mention two modern physiotherapeutic technologies for the treatment of granuloma, which are successfully used in endodontics.
- Depophoresis.
This is cleaning the canal cavity from pathogenic microorganisms using a copper suspension. Under the influence of electric current, the smallest particles actively move throughout the entire canal cavity and destroy the source of inflammation. - Dental microscope.
A very useful and expensive device that allows for the most precise manipulations and provides a more predictable treatment result.
Traditional methods and treatment at home
The use of traditional methods in the treatment of granuloma can lead to complications and irreparable consequences.
Under no circumstances should hot compresses be applied to the cheek on the side of the inflammation: this will accelerate the spread of pus. Even if you know the names of antibiotics used in the treatment of tooth root granuloma, you should not take them yourself. Treatment methods should only be chosen by a doctor.
The only thing that can be done while it is not possible to get an appointment with a doctor (for example, symptoms appeared late in the evening) is to take a Nurofen or Ketanov tablet to eliminate the pain.
You need to understand that the development of inflammation occurs inside the root canals and in the jaw, which cannot be reached by any folk remedies, and only the help of a specialist will help save the tooth.
Laser treatment of dental granuloma
Laser treatment is considered one of the most advanced in medicine and is also used in dentistry. It is believed that treatment of dental canal granuloma with a laser allows you to do without the use of drugs, since the beam destroys the accumulation of granulation tissue and destroys all pathogenic microorganisms. This impact has its supporters and opponents. Fans of laser treatment assure the maximum effectiveness of the technique and provide statistical data demonstrating the effectiveness of this method. On the other hand, the cost of treating dental granuloma with a laser is higher compared to classical endodontic manipulations; the use of certain medications is still required, and in case of non-standard structure of the root canals (in particular, with severe curvature), the use of a laser is less effective. It can also be used during direct surgical intervention in the process of processing and removing tissue. This reduces the invasiveness of the operation, but increases the final cost of treatment.
Why does a dental cyst appear?
What is the prerequisite for the appearance of such an unpleasant disease - dental cyst:
- physical trauma;
- periodontitis, peritonitis, pulpitis - inflammation of the soft tissues around the tooth;
- residual effects after diseases of the nasopharynx - ARVI, complications after influenza;
- decreased immunity;
- advanced caries process;
- poor oral hygiene;
- development of infection in the root canal;
- poorly placed crown, poor quality filling;
- the appearance of problems with the wisdom tooth.
Tooth granuloma: treatment of severe forms
Treatment of complex forms of granuloma, in particular large cysts, is possible only using surgical techniques. The same applies to the treatment of this disease after unsuccessful manipulations that caused numerous perforations of the tooth root. Below are the main granuloma removal techniques.
| Complex granuloma on the root of a tooth: treatment | Description of the technique |
| Cystectomy (apex resection) | The doctor removes the granuloma along with the root tip, after which the canals are filled. Before the procedure begins, it is often necessary to drain the pus, which requires an incision in the gum and a certain time for the fluid to completely drain out (on average 2-3 days). To restore bone tissue in the area of surgery, the use of osteoplastic materials is required. |
| Hemisection | The granuloma is removed along with part of the root and crown, after which the tooth is restored. This is often how granulomas are treated when a tooth canal is perforated. |
| Separation | The technique is applicable exclusively to molars. The tooth is divided into two parts, after which the doctor carries out all therapeutic and restorative manipulations through the resulting gap. |
| Removal of a tooth | An extreme measure that is resorted to when all other methods are impossible for a number of reasons. These include severe damage to the tooth, as well as numerous perforations or a vertical crack in the root. |
Important:
Treatment of tooth granuloma under the crown requires extraction and subsequent replacement of the orthopedic element. If after treatment of granuloma the tooth hurts and the severe pain does not subside after several days, you should consult a doctor.
DIAGNOSTICS
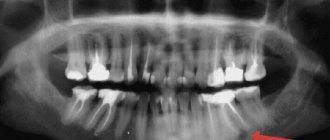
Only a dentist can make a correct diagnosis based on an x-ray. In the image you can see a small darkened area near the root of the tooth.
Radiovisiography can also be done in the hospital. This is a type of x-ray with less radiation. The results are assessed not in the picture, but on the monitor screen. For this reason, such a survey is often called digital.
Granuloma is best recognized at the first stage. It is often detected during the treatment of other dental diseases. In addition, doctors pay attention to abnormal swelling of the gums, which is very painful. Also, the protrusion of bone near the apex of the tooth comes to the attention of doctors.
A special category includes patients with installed crowns and pulpless teeth. Granuloma occurs much more often in such people. Doctors pay special attention to these people.
Causes and development factors
Granuloma annulare in children can appear for various reasons, which have not yet been fully established. The provoking factor is a focus of chronic infection in the form of rheumatism, tonsillitis. The presence of diabetes mellitus, allergic diseases, and metabolic pathologies increases the risk of development. In children, a lot depends on the immune system. If there is a failure, the development of the neoplasm will be started. Pyogenic granuloma in a child occurs due to a pyococcal infection. The reason for the development lies in skin injuries, due to which infection gets into the wounds. It is localized mainly on the face, legs, fingers and arms. Eosinophilic granuloma is rarely found in young children. The peak incidence occurs between 5 and 10 years. The causes of such granuloma in a child are ambiguous. The question still remains open. Scientists suggest that immunopathological processes are the basis.
Stages of granuloma development
From the moment of inception, the neoplasm goes through 4 stages. At the initial stage, there is an accumulation of cells with a tendency to phagocytosis. At the second stage, the process of their rapid growth begins. The third stage is characterized by the transformation of phagocytes into epithelial cells. At the last fourth stage, granuloma formation occurs directly.
Prevention in children
Any granuloma in a child is treated only after consultation with a dermatologist. There are no special methods of prevention. Granuloma annulare in children has variable causes for the development of the disease. Taking into account the influence of immunity on the occurrence of formations, it is necessary to undergo timely treatment. It is necessary to take into account the infectious nature and metabolism in the body. Any disease should receive therapy to reduce risks. This is what prevention consists of – eliminating factors that can provoke the disease.