Hyperesthesia of hard dental tissues - their increased sensitivity to common physical and chemical irritants - has a fairly clear definition and designation in ICD-10© [1]. However, in the practice of a dentist, pain sensitivity is considered more broadly, as it is a symptom of a number of dental diseases [2]. The generalized form of hyperesthesia is usually associated with general causes (concomitant diseases), covers most teeth and can manifest itself without clinically visible pathological changes in them [4], the localized (non-systemic, limited) form of hyperesthesia is caused by local factors and defects in the hard tissues of teeth and manifests itself in areas of individual teeth [3]. Non-carious lesions of teeth that occur after eruption are almost always combined with hyperesthesia [2-4]. Thus, increased sensitivity of hard dental tissues with wedge-shaped defects occurs in 82-90% of cases and manifests itself most aggressively in young and middle-aged people [5]. Hyperesthesia with increased abrasion is detected in 80-90% of cases, with enamel erosion - in 80-85.6% of patients [4, 6].
The purpose of the study is to determine the features of the clinical course of increased sensitivity of hard dental tissues.
Dental hyperesthesia: causes, symptoms, treatment
Content:
What is dental hyperesthesia
Causes of dental hyperesthesia
How does dental hyperesthesia manifest (symptoms)
Classifications of dental hyperesthesia
Development of complications
Stages of treatment
Doctor's advice
Answers on questions
Dental hyperesthesia is a high sensitivity of enamel that occurs when exposed to various irritants.
Classification of hyperesthesia
In terms of prevalence, dental hypersensitivity can be limited or generalized. In the first case, the problem affects only one or several closely spaced teeth. In the second we are talking about a larger number or all teeth at once.
Based on severity, there are three degrees of severity of the condition:
- the first is pain in response to temperature exposure;
- the second is pain when exposed to cold, hot, sweet, sour, bitter food;
- the third is pain in response to all types of irritants, including the touch of a toothbrush.
The intensity of unpleasant sensations depends on individual susceptibility.
Causes of dental hyperesthesia
- Mechanical damage: cleaning with bleaching paste, a hard brush and/or rough cleaning.
- Exposure to acids: regular consumption of juices, sodas. Long-term exposure of these drinks to enamel leads to the destruction of hard tissue.
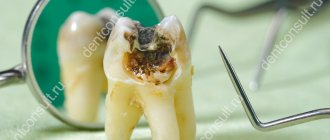
- As a symptom of caries, wedge-shaped defect.
- A decrease in the level of gums (recession), as a result of which the roots become exposed and hyperesthesia of hard tissues occurs.
- Poor-quality bleaching: the use of aggressive chemical solutions, the impact of which damages the enamel structure.
Hyperesthesia - what is it?
Name " hyperesthesia"
" comes from two Greek words meaning "increase" and "feeling". The pathology got its name from a characteristic feature - painful sensitivity of teeth to temperature, chemical, tactile (physical) influences. Hyperesthesia should not be confused with pain that occurs with carious tooth decay. Hyperesthesia often occurs with non-carious lesions of hard dental tissues and chronic periodontitis.
Manifestations of hypersensitivity in different dental pathologies are not the same. Thus, enamel erosion causes quite severe, albeit short-term pain, and with a wedge-shaped defect, the discomfort is mild, however, sometimes unpleasant sensations appear even with the slightest exposure of the neck of the tooth.
How does dental hyperesthesia manifest (symptoms)
Symptoms of hyperaesthesia:
- Pain of various types: from minor to unbearable when eating. Duration from several seconds to a minute.
- Inability to eat too cold or hot food due to pain discomfort.
- Sensitivity when breathing in cold air through the mouth.
- Pain when cleaning, when eating rough food.
It should be noted that pain can occur in one tooth or in several. In exceptional cases, the process extends to half the jaw. Cervical tooth sensitivity most often affects the upper and lower premolars.
If such symptoms occur, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor at a professional dental center.
Material and methods
The study was conducted at the Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of the Belarusian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education. Its subjects were 98 patients aged from 20 to 75 years. The assessment of the initial dental status began with a survey, clarification of complaints and collection of anamnesis. During the survey, we found out which irritants (cold, hot, acidic, mechanical, chemical) cause sensitivity of hard dental tissues, the severity of which was determined according to the following codes and criteria: no pain - 0 points, slight pain - 1 point, severe and very strong - 2 and 3 points, respectively. The index assessment involves determining the level of oral hygiene using the simplified Green-Vermillion OHI-S index (Green, Vermillion, 1964). The intensity of periodontal diseases was determined using the complex periodontal index KPI (P.A. Leus, 1988), the intensity of dental caries damage was determined using the KPI index (Klein, Palmer, 1937). The affected area was examined in detail, namely the presence of dental caries, gum recession, wedge-shaped defects, erosions, microcracks and chips of enamel, as well as abrasion of tooth crowns. We used basic and additional examination methods. Dental hyperesthesia was assessed using the dental hyperesthesia prevalence index (DHI), dental hyperesthesia intensity index (DHI); G.B. Shtorin (1986), tactile sensitivity of hard tissues of teeth - using a dental probe. The tip of the instrument was placed perpendicular to the vestibular surface of the tooth being examined and zigzag movements were made along the enamel-cement junction for several seconds. If this irritation caused a pain reaction in the patient, the presence of hyperesthesia was recorded. To assess temperature sensitivity, teeth were irrigated from a syringe with water at a temperature of 30 °C. The use of water at this temperature is explained by the fact that in case of functional enamel deficiency, tooth pain occurs under the influence of a cold stimulus whose temperature is less than 37 °C [1]. To study the reaction of the tooth to the air flow, a stream of air from a dental plaster was used for 2-3 s, directed from a distance of approximately 1 cm at an angle to the tooth surface being studied.
After the examination, making a preliminary diagnosis and developing a general treatment plan, information about the examination results, preliminary diagnosis and prognosis of the disease was provided in full to the patient and agreed with him. A necessary precondition for medical intervention was the voluntary informed consent of the patient.
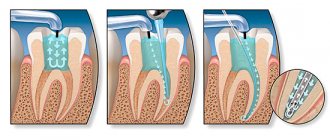
Stages of treatment
After examination and diagnosis, the dentist determines the cause of this disease. It is from this that the treatment plan for hyperesthesia of tooth enamel will be built.
- If the disease is caused by caries, then caries treatment is carried out.
- If sensitivity occurs due to incorrectly selected home hygiene products, then the doctor individually selects a brush and paste for the patient. The enamel is also treated with a special solution - remineralizing gel.
- When a patient experiences recessions, surgical operations are performed to eliminate them.
Treatment of enamel hyperesthesia is a comprehensive approach to the problem, including examination, diagnosis, elimination of the cause and symptoms.
Do not self-medicate, consult a doctor!
Don't wait for your condition to worsen!
Sign up
Diagnostics
Hyperesthesia is differentiated from other conditions that have similar symptoms:
- with inflammation of the pulp;
- with caries;
- with a cracked tooth or restoration;
- with a violation of the sealing layer.
A characteristic symptom of hypersensitivity is quickly subsiding, acute pain. To determine it, the doctor checks the condition of the nerve bundle using x-rays or electrodontometry. If the preliminary diagnosis is hypersensitivity, the dentist conducts tests to determine the degree of reaction of dental tissues to temperature, chemical, and tactile stimuli. When the degree is determined, the doctor draws up an individual treatment and prevention plan.
Doctor's advice
Prevention of hyperesthesia will include the following:
- Avoid using whitening pastes. These pastes contain high abrasive particles, which, when exposed to friction from the brush, destroy the surface layer of enamel. If the patient wants to whiten the enamel, it is better to seek professional whitening at a dental clinic.
- Reduce (or better yet eliminate) the consumption of juices/carbonated drinks. The acids contained in these drinks destroy enamel, causing not only tooth hypersensitivity, but also caries and wedge-shaped defects.
- Visiting the dentist once every six months for a preventive examination and timely treatment of caries, wedge-shaped defects, etc.
Oral care for hyperesthesia
Hygienic care in the presence of increased tooth sensitivity is especially difficult in the third stage of the disease, because in this case the patient has a reaction to tactile influence. Experts advise choosing toothbrushes with soft, rounded bristles and toothpaste labeled “for sensitive teeth.” In this case, the brush should be regularly replaced with a new one to prevent infection. Toothpaste also needs to be replaced periodically, this will increase the effect of protecting teeth. It is useful to use mouth rinses, especially after meals.
Answers on questions
When does sensitivity go away after whitening?
With proper whitening, all discomfort goes away after 3-5 days.
How to choose a toothbrush and toothpaste so as not to harm the enamel?
It is not recommended to use a hard brush or whitening paste. The selection of home hygiene products should be individual for everyone. We recommend making an appointment with a dentist.
How to get rid of sensitivity at home?
No home remedy will help eliminate this disease. Do not self-medicate: this will cause complications! It is recommended to consult a dentist so that the doctor can provide quality treatment.
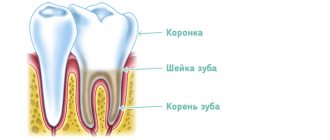
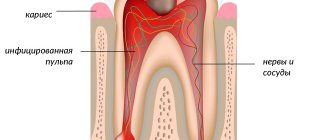
The mechanism of pain during hyperesthesia
As can be seen in this figure, enamel reliably protects the internal tissues of the tooth from any external influences. And, if for some reason a gap is formed in this protection, then external irritants affect odontoblasts (dentin cells). The dentinal tubules expand, so the speed of fluid movement in them increases. As a result, the person feels pain. It should be noted that the pain signal can be initiated both by carious destruction of enamel and dentin, and without carious pathology. Painful sensations also appear if, with the development of periodontal disease, the gums begin to recede, exposing the neck of the tooth. Dentin remains exposed, allowing access to irritants and infection.
Prevention measures
- Eliminating bad habits (biting hard objects, cracking nuts)
- Using special toothpaste and a soft brush
- Using proper brushing technique (“up and down”)
- Thorough oral hygiene at least twice a day
- Rinsing your mouth after eating
- Reducing the diet of natural juices and carbonated sweet drinks
- Regular preventive visits to the dentist
The network of dental clinics “Smile” offers services for the diagnosis and treatment of dental hyperesthesia. Contacting our specialists has a number of undeniable advantages:
- reception of highly qualified doctors;
- compliance with treatment protocols that meet international standards;
- providing family and cumulative discounts;
- transparent pricing;
- Convenient work schedule: daily until 21:00 (Sunday until 16:00).
You can make an appointment at any of the branches of our clinic in Moscow, located within walking distance from metro stations:
- Alekseevskaya (VDNKh district, etc. Mira), address: st. 3rd Mytishchiskaya house 3, building 2;
- Shelepikha, address: Shelepikhinskaya embankment, building 34, building 1.
The high qualifications of our specialists and modern equipment allow us to solve the problem of dental hyperesthesia at any stage of the disease. We guarantee the effectiveness of treatment and the safety of the methods used. Your health is in good hands!