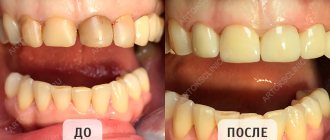
A gummy smile is a serious aesthetic defect. When a person smiles, the upper gum is visible to others - it looks ugly. Not everyone succeeds in “relearning” so that their smile becomes more closed, so many people are forced to put up with this shortcoming all their lives. Fortunately, there are modern cosmetic correction methods. Sign up for a gummy smile treatment at the BL clinic - and you will smile more often!
Causes of gummy smiles in children and adults
In adults, a gummy smile is quite rare, since this problem in most cases appears in childhood. There are several known main reasons for the appearance of this problem: improper development of the facial skeleton, a short upper lip that cannot cover the gum, or, on the contrary, an overly large gum that covers the upper row of teeth more than necessary. At the same time, a strongly pronounced gummy smile, as a rule, is a consequence of malocclusion, or anomalies in the development of the maxillofacial skeleton.
Tissue augmentation – during recession and implantation
Gum grafting with root exposure (recession)
solves not only aesthetic, but also medical issues, protecting this part of the tooth from increased sensitivity, caries formation and other problems. One of the common causes of recession is periodontitis and gingivitis. A similar disorder also occurs with periodontal disease; if the gum tissue is too thin; due to improper oral hygiene and a number of other reasons.
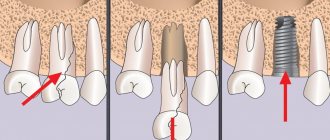
Build-up may also be required when installing an implant - when a tooth is removed, the volume of bone and gum tissue decreases over time. Accordingly, if it becomes insufficient for implantation, the tissue is built up. Sometimes it is necessary to work only on the gingival contour - so that the implant looks as aesthetically pleasing and natural as possible.
To cover exposed areas, so-called patchwork plastic surgery is often used. The doctor cuts the tissue in the treated area and replaces/extends the resulting flaps using flaps taken from the palate, cheek, and other areas of the periodontium. Then stitches are applied.
Reconstructive surgery in the treatment of gummy smiles
In situations where a gummy smile appears as a result of abnormal development of the facial skeleton, the only effective solution to the problem is surgery. For these purposes, osteotomy (correction of the upper jaw) and ostectomy (operation performed to correct the lower jaw) are used.
In the vast majority of cases, such surgical interventions are carried out in the presence of serious anomalies in the development of the bite, but can also be performed in the normal position of the jaws, for example, to correct a gummy smile.
Features of the procedure and recovery
Gingivoplasty is performed with local anesthesia
. Depending on the complexity and scope of the tasks, the procedure takes from half an hour to several hours - it includes anesthesia, disinfection, direct work on the periodontium, cleaning of dental/bacterial plaque (if necessary), suturing, etc.
Healing time
also depend on the specifics of the intervention - usually from one to several weeks. The swelling subsides within 2-7 days. While the gums are being restored, the teeth may become a little loose, and increased sensitivity may also occur, but these phenomena will pass as the tissue heals. In general, during the rehabilitation period, patients should adhere to the following recommendations:
- carefully monitor oral hygiene (rinse your mouth after eating, use special solutions), but do not brush or paste the area where the operation was performed;
- Avoid foods that may irritate tissue. Excessively hard, hot, cold, spicy, sour foods, etc. are excluded;
- avoid physical activity, excessive shaking and anything that prolongs the healing period;
- use disinfecting solutions according to the schedule prescribed by the doctor;
- wear a special mouthguard.
Your doctor will give you detailed recommendations specific to your case.
Gummy smile: gingivoplasty and botulinum toxin - the way to solve the problem
Recently, among dental patients, the demand for aesthetic rehabilitation options has increased significantly. Beyond this, the goal of dental treatment remains the same – to improve human health. The harmony of an aesthetic smile consists of three main components: teeth, gums and lips. A smile becomes attractive when these elements are correlated in a certain proportion with the level of gum exposure up to 3 mm. If the level of gum exposure exceeds 3 mm, then this provokes the development of the so-called gummy smile, which significantly affects the overall facial profile of a person.
Several treatment methods have been proposed to correct a gummy smile, including gingivoplasty, myectomy, and orthognathic surgery. The last two procedures are more invasive and provoke the development of significant postoperative discomfort and pain. A method of treating a gummy smile is also the use of botulinum toxin, injections of which allow you to achieve the desired result much faster, and most importantly, reduce the total amount of intervention to almost zero. Botulinum toxin is synthesized by the anaerobic gram-positive bacterium Clostridium botulinum and inhibits the release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction, thereby preventing muscle contraction. There are 7 different serotypes of the toxin, and type A is the most commonly used in dental practice. The effectiveness of botulinum toxin has already been proven in the treatment of not only a gummy smile, but also dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint (bruxism, clenching, hypertrophy of the masticatory muscle), sialorrhea, paralysis of the facial muscles and pain in the face and oral cavity. In this article, we will consider a clinical case of treating a patient with a pronounced gummy smile through a combination of gingivoplasty procedures and botulinum toxin injection.
Clinical case
A 36-year-old patient came to the dental clinic with complaints about her gummy smile (photo 1). Clinically, the patient showed approximately 4 mm of difference in the length of the maxillary central teeth (Figures 2-3). The length of 21 teeth was used as a reference and was 8.8 mm (photo 4). The level of the gummy smile was almost 12.7 mm in height (Figure 5).
Photo 1. Visualization of significant gum volume during a smile.
Photo 2. Differences in the length of the crowns between the teeth of the upper jaw.
Photo 3. Measuring the length of the 11th tooth using Dr. Chu's wand.
Photo 4. Measuring the length of 21 teeth using a digital pachymeter (8.8 mm).
Photo 5. Measuring the size of a gummy smile using a pachymeter (12.7 mm).
The patient's somatic history was not burdened. She was asked to undergo a gingivoplasty procedure and additionally perform a botulinum toxin injection to achieve more effective results of the intervention. The patient was informed that relapse of a gummy smile with this approach usually develops 6 months after the initial intervention. Taking into account all the above factors, the patient approved the proposed treatment plan and signed informed consent. After local anesthesia was administered, bleeding points were identified using a millimeter probe, which were subsequently combined using an electric scalpel. The length of the teeth was increased with correction of the position of the zenith of the gums. Additionally, surgical scraping of soft tissues was performed to increase the rate of mucosal repair (photo 6-7). There was no need to use any additional materials, since the intervention area healed under secondary intention. The patient was instructed about the necessary hygienic measures and the possible need for antibiotics.
Photo 6. View after performing the manipulation.
Photo 7. View after gingivoplasty.
After 30 days, successful tissue repair was noted (photo 8). Improvement in the relationship between the length and width of the teeth after the gingivoplasty procedure was diagnosed using Dr. Chu's wand (Figure 9). However, the patient's smile was still characterized by significant visualization of the gingival area (Figure 10). The length of 21 teeth was increased from 8.8 mm to 9.7 mm (photo 11). Despite the gingivoplasty, the level of gum exposure remained quite significant due to the pronounced dynamics of the upper lip (photo 12).
Photo 8. View one month after gingivoplasty.
Photo 9. Change in the ratio between the length and width of teeth after gingivoplasty.
Photo 10. Presence of a gummy smile after the gingivoplasty procedure.
Photo 11. Increasing the length of the 21st tooth.
Photo 12. Reducing the severity of a gummy smile.
During the follow-up visit, the patient received a botulinum toxin injection. Before this procedure, the skin surface was disinfected with ethanol. To increase comfort, the intervention area was additionally anesthetized (EMLA, Astra). Botulinum toxin type A (Botox 200 units, Allergan Pharmaceuticals) was diluted in 2 ml of saline according to the manufacturer's instructions, and 2 units of it were injected into the recommended area: on the side of each nostril, at the level of the ala of the nose, in the projection of the muscle that raises the superior lip. After the manipulation, the patient was advised not to tilt her head too low, and also to avoid any physical activity for the next 4 hours. After 15 days, the patient was re-examined. She had moderate, uniform drooping of the upper lip (Figure 13). No complaints or complications were registered. The clinical effect of the use of botulinum toxin lasted for 6 months.
Photo 13. View 15 days after botulinum toxin injection.
Discussion
There are several reasons for the development of a gummy smile, for example, too large a vertical dimension of the upper jaw, delayed passive teething, hyperfunction of the muscles involved in the formation of a smile, reduced length of the crowns of the front teeth. These etiological factors can be noted separately or in various combinations, and depending on this, the doctor must choose the most adequate treatment algorithm. If the cause of the development of a gummy smile is muscle hyperfunction, it is recommended to use botulinum toxin to correct it. This approach is the most conservative and safe compared to other surgical procedures (myectomy or LeFort osteotomy).
A smile is formed through the interaction of several muscles at once: the muscle that lifts the upper lip, the muscle that lifts the upper lip and ala nasi, the zygomatic major and minor muscles. The fibers of these muscles converge in one area, forming a triangle. This allows you to target all three of these muscles at once with one injection. The most recommended injection area is the area lateral to the wing of the nose. After injection, toxins spread over the adjacent 2 cm of tissue, ensuring high efficiency of manipulation. The action of the toxin is aimed at reducing the contraction of the muscles responsible for raising the upper lip, which, in turn, reduces the level of gum visualization when smiling. Botulinum toxin is a hydrophilic powder that is stored in vacuum packaging in a sterile and stable form. For injection, it is pre-diluted in saline solution (0.9% sodium chloride). It is recommended to store this drug at a temperature of 2–8 ° C. The clinical effect of the injection appears after 2–10 days, and the maximum visible effect occurs 14 days after injection. This effect lasts for approximately 3–6 months. Contraindications to the use of botulinum toxin are pregnancy and breastfeeding, the presence of neurodegenerative and autoimmune diseases, or the simultaneous use of aminoglycoside antibiotics, which enhance the effect of the toxin.
In the clinical situation described above, we were able to achieve an effective smile correction result through a combination of gingivoplasty and botulinum toxin injection. The isolated use of these methods would not have allowed to achieve the desired outcome, but their combination contributed to this as much as possible. Gingivoplasty made it possible to form a new contour of the zeniths, thus balancing the parameters of harmony between the gums and teeth. The subsequent injection of botulinum toxin made it possible to “lower” the upper lip slightly lower, thus covering the entire profile of the exposed gums and smoothing out the lines of the nasolabial fold.
Authors: Irineu Gregnanin Pedron Marcelo do Lago Pimentel Maia Estevam Rubens Utumi João Marcelo Ferreira de Medeiros Caleb Shitsuka Leopoldo Penteado Nucci da Silva
Wrinkles in the perioral area
With age, the lips undergo a number of changes, including shortening of the lateral part, enlargement of the dermal part of the upper lip, thinning of the red border and the appearance of many vertical wrinkles around the mouth. These wrinkles, also called smoker's lines, can be the result of sun exposure, smoking, hereditary factors and overactive orbicularis oris muscle, such as in musicians. There are several ways to eliminate wrinkles on the upper lip, including filler injections and various anti-aging procedures. Botulinum therapy is used to correct age-related changes in the perioral area, especially in the presence of deep static wrinkles.
Treatment of the orbicularis oris muscle with BTA preparations is carried out with extreme caution in order to achieve the effect of reducing wrinkles and not affect the normal functioning of the oral area. In addition, it is unacceptable to administer BTA near the corners of the lips. Otherwise, relaxation of the muscles that raise the corners of the lips under the influence of the toxin will lead to ptosis of the lips and drooling. Injecting BTA above the middle of the upper lip will lead to a smoothing of the cupid's bow, which is an undesirable effect from an aesthetic point of view.
In general, 1-2 injections are made into each quarter of the perioral area. To avoid dysfunction of the oral area, it is recommended to administer BTA preparations in very small doses. When the toxin is injected 5 mm from the border of the red part of the lips, the secondary aesthetic effect of a slight eversion of the lip is achieved (Figure 13)
.
Figure 13. BTA injection points for the correction of wrinkles in the perioral region
Complications: An overdose of BTA preparations will lead to dysfunctions of the lips such as the inability to fold them into a tube, difficulty pronouncing plosive consonants, and difficulty eating and drinking. For this reason, it is recommended to start botulinum therapy in the perioral area with minimal doses and repeat them as necessary.
Comment by cosmetologist, dermatovenereologist Ya. A. Yutskovskaya:
— When performing BTA injections in the perioral area, it should be remembered that the muscles located around the lips are involved in the implementation of important physiological functions. Therefore, correction of this zone must be carried out very carefully. The orbicularis oris muscle is divided into the marginal part (pars marginalis) and the labial part (pars labialis). Injections of BTA into the labial part allow the lips to be slightly turned out, which creates the effect of increasing their area and volume. Injections into the marginal part of the orbicularis oris muscle are performed in the presence of purse-string wrinkles. Dividing the skin portion of the lip in half and retreating at least 5 mm from the columns of the philtrum and from the corners of the mouth, subcutaneous injections are usually made at 2 points on each side in a dose of 2-5 units. Dysport.
What determines the cost of the operation?
The cost of gingivoplasty depends on the chosen method and the extent of surgical intervention.
Any, even the most advanced situation on the gums can be corrected and made better and more beautiful. But in some situations, previously performed procedures complicate the process of rehabilitation with old scars.
All types of gingival margin reconstruction directly depend on the gum biotype. The thicker the gingival contour, the cheaper and simpler the treatment. If the gums are of the ultra-thin biotype, any surgical treatment will be a challenge for the patient and the doctor.
Why is it better to do gingivoplasty “in your sleep”?
If the patient is very afraid and worried about the upcoming operation, we suggest performing it under sedation. This is an immersion into a state of light sleep with the help of safe sleeping pills under the supervision of our experienced anesthesiologist.
Sleep therapy provides:
- Maximum comfort A person does not feel pain or experience emotional stress. Awakening is, as usual, quick and easy.
- High-quality treatment The doctor is 100% focused on the operation, eliminating the possibility of inaccurate actions due to random movements of the patient.
- Risk prevention The patient is not worried, the blood pressure is normal, the risk of bleeding, and therefore the formation of edema and hematomas, is lower.
- Improved healing There is no release of stress hormone, which reduces the immunological status and slows down the regeneration processes.
Preparing for gum surgery
Diagnostics
Any operation is planned based on the results of the examination. In order to choose the right method for gum correction, the periodontist conducts a visual and instrumental examination. Computed tomography allows you to obtain more detailed information about the condition of the jaw structures.
Sanitation of the oral cavity
An important point before surgery is to ensure aseptic conditions in the oral cavity to avoid infection. Therefore, before the operation, sanitation (removal of caries, removal of diseased teeth that cannot be treated) and professional hygiene are required.
Excluding the causes of the disease
If a patient is diagnosed with bite problems, consultation and treatment with an orthodontist may be required, since these pathologies are one of the main causes of gum disease.
If the gingival contour is disrupted due to a traumatic factor with crowns or dentures, it is necessary to replace the orthopedic structures.