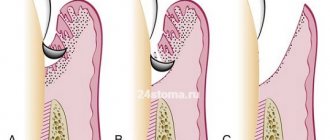
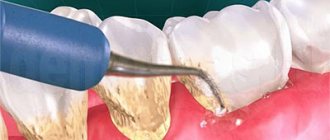
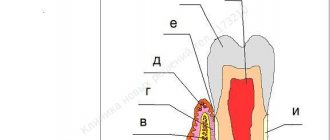
What is curettage? This is the cleaning of periodontal pockets from subgingival plaque. The structure of the gum allows plaque to accumulate between the tooth and its tissue. If oral hygiene is insufficient, plaque will accumulate there, eventually hardening and turning into tartar. And this threatens tooth loss, serious inflammation and other consequences. The need for curettage occurs when the distance between the tooth and the edge of the gum is more than 3 mm. The procedure is carried out open and closed.
How to do curettage
Curettage is a surgical operation.
Plaque, stone, and pathological tissue are removed from the periodontal pocket. If necessary, osteoplastic surgery is performed. This is necessary if bone resorption has already begun. Curettage must be carried out in the treatment of periodontitis and periodontal disease, as this is one of the most effective methods for eliminating inflammation in the gums. According to the technology of the procedure, there are two types of it:
- Open;
- Closed.
Indications and contraindications
Indications:
- Enlargement of periodontal pockets to a depth of more than 5 mm
- Destruction (resorption) of bone tissue in the area of the pathological process
Contraindications:
- Excessive tooth mobility (preliminary splinting is required)
- The presence of pus in periodontal pockets (the pathological process must first be eliminated using medication and/or surgery)
- Any disease in the acute stage
Important: sometimes the gum looks quite healthy on the outside, and only an x-ray shows the beginning of bone destruction. All branches of our clinic are equipped with modern high-precision radiographic equipment, so the identification of indications for curettage cleaning is carried out with absolute accuracy. Only after diagnosis, the periodontist chooses the curettage technology (open or closed).
Stages of performing curettage using the open method
1 Diagnostics
Identification of indications and contraindications through visual and hardware examination. Choosing a curettage technique
2 Preparation
Prof. cleaning supragingival dental plaque, if necessary, conducting a course of antibacterial therapy and splinting excessively loose teeth
3 Curettage
Local anesthesia by injection of anesthetic, detachment of the gingival mucosa. Removal of stones, deposits, granulations, antiseptic treatment. If necessary, grafting of bone material. Upon completion, suturing the surgical wound and applying a bandage
4 Rehabilitation
Antibacterial therapy, careful hygienic care
Closed curettage
Can be used if the depth of the periodontal pocket does not exceed 5 mm, and pathological changes in the bones have not yet begun. When performing closed curettage, pathological tissues are exposed to ultrasound and hand instruments in the form of hooks, with the help of which granules are removed from under the gums. There is no cutting of the gums, so the procedure can be considered more gentle.
Flaws:
- The doctor performs the operation almost blindly; he does not see the subgingival space. Therefore, it is not possible to thoroughly clean the periodontal pocket in all cases.
- There is a risk of incomplete cleaning. Success largely depends on the experience of the dentist performing the procedure.
Due to its characteristics, closed curettage is suitable for mild to moderate periodontitis and periodontal disease. Sometimes it becomes the only possible method, since others cannot be used for some reason.
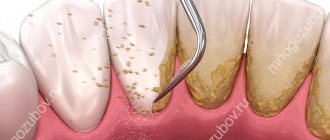
Causes of periodontitis
In most cases, the onset of the disease is preceded by mechanical damage. It can be one-time (injury) or permanent (rubbing against an incorrectly installed prosthesis). As a result, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into and under the gums.
Inflammation also provokes:
- plaque;
- tartar;
- low quality prosthetics;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- increased load on the teeth as a result of the loss of some of them;
- malocclusion;
- smoking;
- age.
First, the upper layers of tissue become inflamed, and gingivitis begins. It does not always lead to periodontitis, but it always precedes it. Bleeding gums and bad breath are reasons to consult a doctor.
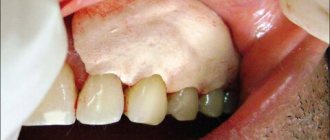
If gingivitis is not treated, it becomes chronic. The inflamed tissue becomes loose, and more and more bacteria penetrate into it. They get lodged under the gum, destroying the ligament around the tooth root. A space appears between the tooth and gum - a periodontal pocket. It accumulates minerals, waste products of bacteria, and the remains of dead tissue. Tartar forms. To get rid of it, dental curettage is performed as part of a comprehensive treatment of periodontal inflammation.
Open curettage
Used if the depth of periodontal pockets is more than 5 mm. This is a surgical intervention, but compared to a closed one, the effectiveness is much higher. Since open curettage requires cutting into the gums, the operation is performed under anesthesia.
Stages:
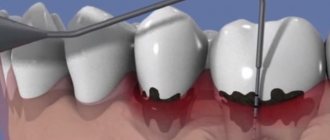
- The doctor cuts the gum and peels it away from the tooth. After exfoliation, the tooth root is completely exposed. The dentist gets full access to the bone tissue.
- Cleaning and antiseptic treatment. The roots are cleaned of accumulated plaque and stone and polished using a burr and special pastes. After this, the tissues are treated with an antiseptic.
- Osteoplasty. This stage is not always necessary. With advanced periodontal disease, bone resorption gradually begins around the teeth, which will lead to loosening and tooth loss. In order to restore the bone, osteoplastic material is implanted.
- Suturing. After plaque removal, the gingival flap is returned to its place and sutured. A bandage with an antiseptic solution is applied on top.
Open curettage is a more complex procedure, but more effective than closed curettage. The surgeon sees the entire subgingival space and has access to bone tissue. Therefore, the quality is very high; both plaque and granulation tissue are completely removed from under the gums.
If necessary, open curettage can be performed simultaneously with flap surgery. It is indicated if the gum tissue is loose and the gum contour is disturbed. Very often, with periodontal disease, the gums begin to overhang the teeth. This violates the aesthetics of a smile. During flap surgery, the dentist removes excess mucous membrane and then sutures the gum.
Indications for curettage:
- feeling of tension (pulsation, bloating) in the gums;
- putrid odor from the mouth that does not disappear after brushing your teeth;
- swelling, redness and soreness of the gums;
- bleeding gums under any impact, including while brushing your teeth;
- tooth mobility;
- increase in interdental spaces;
- deposition of tartar under the gum;
- destruction of periodontal tissue and jaw bone tissue (formation of replacement tissue in their place).
Curettage has contraindications. The procedure is not performed if the pocket depth is more than 6 mm, there is an abscess and pus in the periodontal pocket, as well as with thinned gums affected by fibromatosis. Obstacles to curettage include tooth mobility of degrees III–IV, infectious diseases (influenza, tonsillitis, acute respiratory infections) and any diseases in the acute stage.
Rehabilitation
Curettage of periodontal pockets is a surgical operation, after which there will be a period of rehabilitation. Following the recommendations will speed up gum healing, make it less uncomfortable, and avoid complications.
Oral care rules depend on the method:
- Closed curettage. Immediately after surgery, you should not eat for several hours. On the first day, it is better to refrain from brushing your teeth with a brush and toothpaste, replacing it with rinsing. During the entire rehabilitation period, you need to monitor your diet - exclude solid foods and foods containing dyes. After curettage, there may be increased sensitivity of the teeth and gums. A special paste that your doctor will recommend will help you remove it. It is imperative to rinse your mouth with solutions of strengthening and anti-inflammatory medications.
- Open curettage. Since this surgery requires cutting into the gum, recovery takes longer. Recommendations for the first 1-2 days after surgery are the same as for closed curettage. It is very important to minimize the possible stress on the gums and teeth. It is advisable to reduce physical activity at first. Until the stitches heal, your mouth should be rinsed with solutions of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents. This will help speed up healing and tissue regeneration.
Which treatment method is most effective?
To summarize, it must be said that each of the presented methods has both advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, at the initial stage of periodontitis, closed curettage will be the most effective treatment method. But it is worth remembering that the results of this treatment method are short-lived. Therefore, in the future it may be necessary to repeat this operation several times.
Moderate and severe forms of periodontitis require open curettage or flap surgery. These techniques can guarantee not only the elimination of the problem, but also the prevention of its progression in the future.
Regardless of the chosen treatment method, you need to remember that you should never neglect your dental health. If problems of various kinds arise, you should contact only specialized dental clinics.
Make an appointment with a therapist by phone+7(985)532-21-01
The roots of the teeth are exposed - what to do and how to treat them
Laser gingivectomy in the area of one tooth
Treatment of generalized moderate and severe periodontitis
Laser gingivotomy - surgical treatment of complex forms of periodontitis
Splinting teeth for periodontitis with fiberglass and tape
Open and closed curettage of periodontal pockets
Flaws
Gum curettage is a simple dental operation with good results. However, it is not without its drawbacks:
- Traumaticity. Like any surgical intervention, curettage injures soft tissue.
- The need for anesthesia. Normally, the operation is performed under local anesthesia. Sedation or general anesthesia is used in extreme cases or when the patient is in panic.
- Rehabilitation. The gums heal quickly, but at this time it is necessary to follow the recommendations and take care of the oral cavity. Infection of the wound can lead to complications.
Alternatives to curettage
Alternative technologies are suitable as prevention or in the early stages of pathology development. At the Zuub clinic they use:
- Comprehensive teeth cleaning. This is good prevention. It can be used as one of the stages of complex therapy, but not as an independent treatment. During cleaning, using ultrasound and a mixture of water, air and soda, tartar and plaque are removed from the surface of the teeth. You won't be able to empty your pockets this way.
- Treatment with the “Vector” device. A method for cleaning and disinfecting shallow periodontal pockets. In mild stages of periodontal disease, it can be used as an alternative to closed gum curettage, but it cannot replace open vector therapy. "Vector" is more effective than classic complex cleaning. It is based on a combination of exposure to an ultrasonic wave and a special suspension with abrasive particles. Since the ultrasonic wave is applied vertically, it penetrates deeply under the gum. In addition, ultrasound has a good disinfecting effect. Thanks to this, with a small depth of periodontal pockets and an undeveloped pathological process, it can give a good result.
The periodontist selects the gum treatment technology based on the clinical picture.
Come for a consultation with a dentist at the Zuub clinic.