An orthodontist is a person who deals with the correction and elimination of anomalies of the dental system. It is to him that people turn to with similar problems: a protruding jaw, a too narrow chin, crooked incisors, etc. Such a specialist takes on congenital, acquired in childhood and hereditary defects. Moreover, he can work with patients of any age.
Some people believe that correcting the abnormal position of teeth can only be done in childhood. This is wrong. In a child, the treatment process is simpler, but a congenital or hereditary problem can develop in adulthood or worsen over time. If this happens, do not hesitate to contact your doctor.
What diseases does an orthodontist treat?
As already mentioned, an orthodontist deals with congenital, hereditary and acquired dental defects in childhood. This doctor does not work with injuries and does not set the jaw. Most often, an orthodontist is consulted with the following problems:
- facial asymmetry;
- improper growth of teeth;
- violation of chewing functions;
- abnormal position of teeth, etc.
After the examination, the doctor assesses the patient’s condition, studies the causes of the disease and selects a treatment method. Let's take a closer look at the classification of diseases that a doctor encounters.
Anomalies of teeth
Dental anomalies are various deviations of individual elements of the dentition. The following types of abnormal dental development are distinguished:
- violation of shape (spike-shaped, Hutchinson, Fournier, Pfluger teeth);
- non-standard size (micro- and macrodentia);
- too few or too many teeth (edentia, hypodontia, hyperdontia);
- problems with tissue structure (hypoplasia, hyperplasia);
- incorrect timing of appearance (premature or late);
- incorrect position of an individual tooth in the dentition (oral, vestibular, distal, mesial, infraposition, supraposition, rotation around the longitudinal axis, transposition);
- discoloration.
The picture below shows the most common anomalies of individual teeth.
The most common dental abnormalities
Anomalies of the dentition
The dentition can also have anomalies, which sometimes greatly disturb the patient and cause problems with nutrition and speech. The following are the problems faced by orthodontists:
- violation of the row shape;
- incorrect size towards narrowing/widening or lengthening/shortening;
- violation of the sequence of teeth;
- violation of the symmetry of the position of the teeth;
- violation of contacts between teeth (twisted or sparse position).
Malocclusions
Malocclusion is the most common problem that everyone hears. Sometimes patients even get the impression that orthodontics in dentistry deals exclusively with installing braces. Of course, this is not true, but bite correction is one of the most common problems, especially in childhood.
There are five types of malocclusion:
- distal, when the upper jaw is overdeveloped and protrudes forward, significantly affecting facial features;
- mesial, in which the lower jaw is already too developed;
- cross. Its owners have free space between their teeth, and they themselves are arranged “like scissors”;
- deep, in which the lower teeth are practically hidden under the upper ones;
- open, when there is no constant contact between the lower and upper teeth, it appears only in the area of the molars.
An incorrect bite, even if it is not very pronounced, is no less dangerous a problem than a tooth out of alignment or a violation of symmetry.
Malocclusion: main types
You will find detailed information on this topic in the article: All about the bite: what it is like, why it is important to monitor it and how to treat improperly grown teeth
Jaw anomalies
The jaws may also not be positioned quite correctly, is immediately visible to the orthodontist Examples of the most common pathologies:
- altered size (macrognathia or micrognathia), when one of the jaws has reached a much larger size in development than the other. It may be different: the jaws often remain small. The problem may be with only the upper or lower jaw or both;
- incorrect location relative to the base of the skull. There are asymmetric placement, prognathia (strong protrusion forward), retrognathia (movement of the jaw backward);
- abnormal relationship of the dental arches (distal or mesial occlusion, excessive overlap, non-standard occlusions.
The types of disorders of the dental system largely overlap, because, for example, it is impossible to consider the position of the teeth without taking into account the entire dentition. Therefore, if you understand who an orthodontist is in dentistry , then we can say that he is, first of all, a practitioner. He takes into account the characteristics of a particular patient and draws up a completely individual treatment plan.
Own digital dental laboratory
The presence of a digital laboratory in the clinic improves the interaction between the orthopedist and the dental technician and reduces production time
- Digitalization of the production process reduces errors to a few microns
- Possibility to make a prototype and try on a crown on the day of modeling
- Accelerated production times - from 3 days
Basic methods of orthodontic treatment
Without knowing what exactly the patient came with, it is impossible to say what the orthodontist will do , because the methods of influence primarily depend on the problem and defects in the dentition. Sometimes you can get by with minimal interventions, in other cases you need to involve a dental surgeon.
The most popular methods of dental orthodontism are myotherapy or myogymnastics, hardware treatment and surgical intervention. It is rare that these methods are used in their “pure” form; usually the doctor combines them, forming the course of treatment necessary for a particular patient.
Myotherapy
Myotherapy is one of the ways to strengthen the muscles of the maxillofacial area, thanks to which the formation of anomalies in childhood can be avoided. Based on theoretical calculations about orthodontic treatment, we can conclude that this is the safest and least effective method. Therefore, myogymnastics is almost never prescribed separately.
During classes, the child needs to perform two types of exercises:
- dynamic, when the muscles of the face and jaw sometimes tense and then relax;
- static, forcing the organs to be in tension all the time.
Considering that the exercises must be systematic, classes require adult supervision. Also, it is the parent or teacher who checks that the tasks are completed correctly, because the child may forget or not understand the doctor. The specialist selects tasks, then teaches the adult the exercises, then the adult checks the child.
Myogymnastics class in a children's group: warm-up
Hardware method
The frequency of use of the method clearly shows: an orthodontist is a doctor who treats with fixed and removable hardware systems. The most famous of them are braces, mouth guards and trainers, and plates. When installed, they act on individual teeth, causing them to slowly but surely move in the desired direction. As a result, all elements of the oral cavity occupy their intended position.
Treatment with devices has certain limitations. So, corrections are possible if:
- sufficient force is applied to the tooth, i.e. the equipment is assembled correctly and installed correctly;
- the device has a reliable support and is well fixed;
- there is a place in the dentition into which a stray element can fit;
- there are no obstacles in the path of the tooth being moved.
If these rules are not followed, the dental orthodontist corrects this , and then installs braces, plates or other devices. Sometimes it takes a lot of time to prepare, because it is necessary to remove excess teeth and wait for the restoration of the oral cavity.
Surgical method
If the diagnosis shows that the deformation of the development of the dental arches, jaws or malocclusion is too pronounced, it is necessary to resort to surgical methods. The most popular types of surgical intervention:
- exposure of the crown of an impacted tooth (i.e., removal of the upper gum tissue above a tooth that has not erupted correctly);
- rotation of the tooth around its axis, as a result of which the element falls into place in the dentition correctly;
- removal of individual teeth of irregular shape, extra teeth, as well as those that cannot be “fitted” into the jaw for some reason, etc.
In some situations, surgical intervention falls under the purview of what an orthodontist does . If the specialist cannot correct the situation on his own, he gives the person a referral to a dental surgeon.
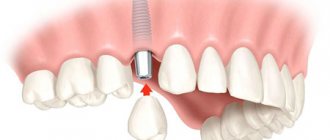
What is implantation
People who have not previously encountered implantation have somewhat generalized information about this dental procedure. The installation of implants is often mistakenly mistaken for prosthetics. However, these are mini-operations, despite the similar goals, dental restoration is a completely different procedure.
Implantation is a dental operation to insert a pin or, as they are correctly called, an implant into the jaw tissue (in place of a missing tooth). In the future, the pin will replace the root, on which a structure will be installed to replace the tooth.
The operation has many features, one of which is the absence of the need for your own bone and jaw tissue. Unlike prosthetics, this method is used even in severe cases of dental pathologies.
The success of the procedure largely depends on which doctor installs the dental implants. If a specialist makes mistakes, serious complications are possible that require immediate treatment.
When to contact an orthodontist
A child should learn who an orthodontist is before the age of 7. At this age, the permanent bite of the anterior incisors is still forming, so it is possible to stop some problems relatively painlessly. Most leaflets for parents contain the following recommendations for visiting a doctor:
- The child is one year old and parents have questions. What does an orthodontist do when the baby has no teeth yet? He examines whether the lips and those teeth that have already erupted are closing correctly;
- child is 3 years old. A visit is advisable, because at a young age, the prerequisites for incorrect development of teeth and jaws can be identified. Therefore, during such an appointment, the orthodontist always asks the parents whether the baby has bad habits, for example, sucking a pacifier, finger, tongue;
- the child has difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speech is not formed;
- you see that the child has changes in the position of the teeth or their closure.
Knowing what an orthodontist does , you can visit a specialist in advance to prevent problems in the development of the dentition and avoid their deterioration.
Possible complications
Dental implants are a foreign material for the body, so the risk of complications can never be excluded. Modern product installation methods and techniques can minimize this risk as much as possible.
Possible complications:
- seam divergence;
- severe pain for more than three days;
- formation of hematomas;
- the appearance of bleeding;
- development of soft tissue inflammation.
Such complications are rather exceptions that arise due to compliance with the doctor’s advice on care during the rehabilitation period.
Somewhat more often, implant rejection and inflammation of the bone and gum tissue near the implant occur. The cause of inflammation can be insufficient oral care or violation of doctor’s recommendations. Implant rejection is an individual reaction of the body. The result is also influenced by which doctor places the dental implants. A qualified specialist will not make mistakes during the operation, and will monitor the patient’s condition throughout the entire rehabilitation in order to take timely measures and prevent complications.
Diagnostics
On average, a diagnosis by an orthodontist takes 30 to 40 minutes, but can take several days. It all depends on the patient’s desire to take certain photographs. Standard procedures included in the diagnostic list:
- visual inspection;
- a panoramic photograph that allows you to see the full view of the jaws, including the roots of the teeth, wisdom teeth, and tooth buds;
- teleroentgenogram (TRG). It allows you to determine the cause of the anomaly, see the relationship of the jaws, and draw a conclusion about what treatment methods will be required;
- 3D scanning or taking impressions of the jaws, with the help of which the exact dimensions of the jaw are determined;
- photographing. It allows you to assess changes in the patient’s appearance and the dynamics of treatment;
- 3D analysis or computed tomography (CT). Required if the doctor suspects a non-standard tooth tilt or other complex problems;
- video recording that allows you to record functional disorders in movement.
The best dental crowns
Perhaps every patient who is thinking about prosthetics asks the question: “Which dental crowns are better?” We remind you once again that any decision, including the choice of crown material, should be made jointly by the doctor and the patient. A conscientious dentist will always tell you about the best crowns for the front teeth, all the options for prosthetics, as well as the pros and cons of one or another option specifically in your case. Thus, the best dental crowns are those that your doctor recommends. If we are talking about the advantages of materials, then the leaders here, without a doubt, are all-ceramic crowns made by pressing or by manufacturing using refractory models. They are ideal for anterior teeth from an aesthetic point of view, as they accurately reproduce the color and transparency of natural enamel, and are also strong enough to withstand the same chewing load that the patient's natural teeth can withstand.
Dental crowns on implants
When using implant prosthetics, the best option for restoring the front teeth, for which aesthetics is important, would be dental crowns made of metal-free ceramics. This is due to the fact that the metal can be seen through the ceramic, which imitates the transparency characteristic of natural dental tissue. Therefore, to achieve a high aesthetic result, the use of a zirconium abutment is recommended. When it comes to chewing teeth, aesthetics are not as important as functionality, so metal-ceramic dental crowns on implants may also be acceptable. For those patients who do not compromise between aesthetics and function, it is recommended to install zirconium dioxide crowns on the implant.
Stages of consultation and treatment
You need to understand that orthodontic treatment is a long-term process that requires several appointments, or even years of treatment. One visit won't solve anything. The doctor acts as follows:
- First comes the diagnosis, which usually includes not only a visual examination, but also a variety of research methods, for example, orthopantomogram, x-ray, teleradiography. All directions are issued at the first visit.
- Afterwards, the doctor chooses a treatment and prepares the patient for it. The specialist does a lot of work without the client’s participation, for example, everything that an orthodontist does when preparing braces, crowns, etc. The doctor works using photographs, impressions and other tools, analyzing the data obtained during diagnosis.
- The third stage is the installation of hardware in the patient’s oral cavity. This usually doesn't take much time.
- Next comes monitoring how the treatment progresses. If problems are observed, the specialist will correct them in a timely manner.
- The last stage is the removal of devices to correct the dentition.
It is noteworthy that if parents know who an orthodontist is through personal experience, then the child will also most likely get to know this specialist. Many problems, unfortunately, are hereditary.
Features of the procedure
Implantation is performed in several stages, which the patient is recommended to inquire about in advance. Depending on the type of procedure and type of implants, the operation can be performed in one step, or it can stretch over several stages, which will take up to six months. If long-term treatment is expected, temporary structures and crowns are installed.
Types of implants
Dentistry offers several options for implants. However, they are all made of the same titanium. This material is considered the most reliable and safe. All products are divided into several types according to design and shape. Depending on the indications, the most suitable installation option is selected. In addition to indications, the choice of implant model is also influenced by their cost. Modern designs tend to be more expensive, but more convenient and durable.
By type of design:
- collapsible
- non-separable.
According to the shape of the products:
- lamellar - screwed into the bone tissue under the palate;
- root-shaped - installed in root canals;
- combined - placed in the root canal.
The clinic’s specialists are qualified and experienced in installing any type of implants. The dentist will recommend which type of implants is suitable, based on the patient’s indications and wishes.
Installation Methods
The A-Medic clinic is equipped with exclusively modern technology, which allows us to perform all types of dental implantation. Implantologists have sufficient experience to solve problems even with complex dental pathologies.
Surgical dentistry, depending on the characteristics of the jaw, offers three options for dental implantation:
- basal - an inexpensive and quick method that allows you to install implants, and even more than one, immediately after tooth extraction;
- intraosseous - a method recommended after bone grafting;
- laser - a low-traumatic operation, possible only if the bone is preserved with a height of at least 6 mm;
- subperiosteal - an implantation method used when the patient lacks bone tissue (does not require additional bone augmentation);
- transgingival - a minimally invasive technique is used to open the gum tissue to install one or more products;
- endodonto-endosseous - the pin is inserted into the canal (the gum is not cut), allowing the root to be preserved;
- intramucosal - used in the absence of intraosseous implantation, suitable for increasing the fixation rates of removable dentures;
- transosseous - recommended for atrophy of the soft and bone tissues of the lower jaw;
- Express - implantation - temporary introduction of an implant and a temporary crown.
The dental clinic performs operations for both partial restoration of dental organs and turnkey dental implantation. You can read reviews about the results of the specialists’ work on the company’s website and on third-party sites.
Conclusions. Expert advice
After reading the material, you understand who an orthodontist-dentist is and why you need to visit him regularly. If we summarize what has been said, we can draw the following conclusions:
- the sooner you see a doctor with a problem, the better;
- It is not necessary to prepare for the visit, but if you tell your child in advance about which specialist you are going to, this will simplify the visit to the orthodontist and make it easier for the child;
- Treatment almost always takes a lot of time, but it gives results.
In conclusion
Many people believe that installing implants is harmful to the body, since serious complications are possible. However, we should not forget that the absence of teeth also negatively affects health, since in addition to aesthetics (smile), a person’s teeth also perform a certain function (chewing food). The absence of certain teeth leads to a decrease in self-esteem, which affects a person’s psycho-emotional state, as well as problems with the gastrointestinal tract, since food is not chewed thoroughly enough.
You should not delay your visit to the doctor, assuming that implantation will cost too much or that it is not necessary. Of course, this is not a cheap service, but the result is worth the money spent.
Contraindications
Like any medical procedure, the installation of crowns has contraindications. Cases in which the procedure is not performed:
- advanced periodontitis;
- bruxism - teeth grinding;
- fragile enamel;
- teeth are small and poorly positioned;
- pathological bite, when the incisors overlap one another.
Sometimes the age of the patient may be a contraindication to installing a crown made of a certain material. Then he is offered another way to restore the integrity of the dentition.