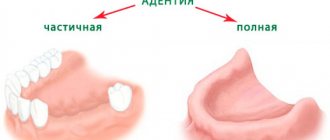
No one doubts that every tooth in the mouth is important. The only exception is the “eight”. Their absence does not cause any functional disorders, does not affect the aesthetics of a smile or the ability to chew food. All other teeth are necessary so that the dentofacial apparatus can work as a single coherent mechanism.
With the help of incisors we bite off food, canines and premolars are used to grab food, molars are used to crush and grind food. The loss of any of these teeth inevitably leads initially to discomfort, various functional inconveniences, and later to deformation of the dentition.
Increased load on other teeth
In the absence of any teeth, their function is taken over by neighboring teeth, and accordingly, the load on tooth enamel, crowns and roots increases significantly. This leads to the fact that teeth begin to deteriorate many times faster. For example, when removing molars, the incisors have to take on a task not provided for by nature - grinding food. As a result, longitudinal and transverse cracks appear on the enamel, the edges of the teeth wear off and turn yellow.
Increased load over time turns out to be fatal for the roots, as it provokes their increased mobility. If you do not reduce the constant pressure, bone tissue will also begin to suffer from overload.
Causes of tooth loss
- Periodontal diseases (may be a consequence of general disorders of the body)
- Caries and its complications (pulpitis, periodontitis)
- Injury
- Other reasons
The main motivation for dental treatment in patients with tooth loss, regardless of the cause and scale of the problem, are:
- decreased smile aesthetics
- loss of chewing efficiency
Diagnostics is the first and key step in the treatment of tooth decay and loss. Do you want to know why it’s impossible to do without diagnostics?
But, in fact, the loss of even one tooth, in addition to a banal deterioration in the quality of chewing food, can lead to a number of not obvious at first glance, but very serious and global problems. Because, one way or another, it will lead to disruption of the biomechanics of the entire human body.
Normally, if all the teeth are present in the mouth, at the moment of closure, the muscles that lift the lower jaw press it against the upper jaw. The force developed by the muscles through the upper jaw and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is further distributed throughout the entire skull.
In this case, the general vector of muscle effort is located in the middle of the upper jaw, at the level of the first upper molars. Under such conditions, the main part of the muscle effort (about 70%) will be on the chewing teeth, and a smaller part (about 30%) will be on the TMJ area.
But when the teeth are closed, it is not only the muscles that elevate the lower jaw that contract. To create a balance of forces exerted by the muscles on the skull, the muscles of the neck, the muscles of the suboccipital region and many other muscles also contract. Along the chain, from top to bottom, to the very feet. And the integrity (when all the teeth are in the mouth) and symmetry of the dentition make it possible to maximally balance the above-described muscle efforts.
During a direct examination by a specialist, you will be able to find out your exact diagnosis, as well as receive a referral for diagnosis or a treatment plan.
According to statistics, the first molars (6th teeth) are most often removed, because... They are the first of the permanent teeth to erupt. And, accordingly, they are the first to be exposed to the aggressive effects of the oral cavity and the development of the carious process. Due to their location, these teeth are the main support for the lower jaw when the teeth are closed. And in the absence of these teeth, the muscle balance when closing is disrupted. The main part of the force from the masticatory muscles begins to be distributed to the TMJ, leading to its functional overload with the subsequent development of a pathological process in it. The teeth remaining in the oral cavity also experience overload, because... anatomically not adapted to bear the excess load redistributed to them. This will be manifested by the formation of wedge-shaped defects on the remaining teeth, exposure of the necks of these teeth, atrophy of the bone tissue around them, and pathological abrasion of their enamel.
If we take a hypothetical absolutely symmetrical person with full dentition, then when his teeth are closed, the effect of the muscles that lift the lower jaw on the skull will be balanced by the muscles of the neck, suboccipital muscles, etc.
The ideal distribution of chewing load with full dentition (a complete set of teeth) stabilizes posture.
In the absence of the masticatory group of teeth on one side, the masticatory muscles of that side will contract more strongly in order to bring the lower jaw on that side into contact with the upper. To counterbalance this force, the neck muscles on that side will also contract more forcefully, causing the head to tilt and the shoulder to rise on that side. This asymmetry will spread further down the body all the way to the feet.
The consequences of this asymmetry for the body are very dire. Starting from various pain syndromes due to overload of overly tense muscles and ending with irreversible structural changes in the form of herniated intervertebral discs.
In the absence of a chewing group of teeth on one side, an imbalance in the muscle balance will lead to the development of asymmetry of the entire body - scoliosis.
Lack of proper support in the posterior region will lead to overload of both TMJs and the remaining teeth. Trying to balance the symmetrically increased forces of the masticatory muscles, the muscles of the back of the neck will contract intensely, which will lead to the formation of a forward position of the head, which is fraught with the development of headaches (due to pinching of the suboccipital nerve), impaired cerebral circulation (due to pinching of the vertebral arteries) and etc.
Bilateral symmetrical absence of the chewing group of teeth will lead to a violation of the symmetry of the body in the anteroposterior direction.
Wear of the remaining teeth and degenerative changes in the TMJ area will eventually lead to a posterior displacement of the lower jaw, which can lead to compression of the upper respiratory tract, especially at night (sleep apnea syndrome).
All these consequences do not develop instantly, but over time. And therefore they can form relatively unnoticed. However, it should be understood that the longer this situation persists, the more difficult it is to reverse it. Long-term persistence of muscle imbalance caused by missing teeth can lead, as previously mentioned, to irreversible anatomical changes in the body. Moreover, if this condition exists for a long time, its complications can acquire a character independent of the original cause. In other words, if this imbalance is eliminated in a timely manner, all changes in the body caused by it will be eliminated automatically over time. If you seek help later, eliminating these complications will require additional efforts.
Timely, rational prosthetics of missing teeth will avoid these irreversible consequences and reduce the time and money required for rehabilitation. Advanced cases (cases of long-term absence of teeth) require the mandatory participation of non-dentist specialists, who will have to eliminate the persistent consequences of the described pathological process that have arisen in the body.
Orto-Artel specialists have extensive experience in the treatment and rehabilitation of patients with partial or complete loss of teeth. Including those who have developed the complications described above. After all, it is an integrated, holistic approach and joint thoughtful efforts of dentists, general practitioners and chiropractors, based on clear diagnostics and analysis of the data obtained, that allow us to solve problems of dental prosthetics of any degree of complexity.
Bone loss
After a tooth is removed, the bone tissue begins to atrophy. Bone volume decreases by 25% per year, and the process is not as harmless as it might seem at first glance. Bone atrophy can cause adjacent teeth to become loose and even fall out.
Bone loss also creates problems with subsequent prosthetics. If a tooth is missing for too long, doctors have to perform a bone grafting procedure before installing an implant. This significantly increases the overall treatment time and cost.
Consequences of adentia or tooth loss
How are complete dentition and facial appearance related?
The loss of even one tooth already affects the patient’s appearance, let alone when teeth are completely missing. A person ages sharply, and the effect of the so-called “senile face” appears, when the distance from the tip of the nose to the top of the chin decreases greatly. This occurs due to a decrease in the height of the lower third of the face. Since there are no teeth, the support of the lower jaw by the teeth is lost, and the jaw moves backward in the joint area, and forward and upward in the chin area.
This displacement of the jaw leads to a decrease in the tone of the facial muscles, as a result of which the cheeks and chin sag, the corners of the lips go down, even the lips become smaller, as if falling inward. The face becomes more mature.
Dental restoration has a rejuvenating effect, as it allows you to return the lower jaw to its normal position, which provides the necessary support to the soft tissues and restores the smile. After treatment, patients regain confidence and quality of life improves.
How to improve your facial contour without going to a cosmetologist
The “senile face” effect can also occur with partial loss of teeth, especially the chewing group. Sometimes a woman goes to a cosmetologist to tighten her facial contour, and he refers her to a dentist to restore missing teeth. Good, responsible cosmetologists understand that any rejuvenation procedures will not give the expected effect if there are no teeth in place.
How to protect teeth from falling out?
You need to pay more attention to your lifestyle and oral hygiene. The diet must be balanced; the diet must contain fresh fruits and solid foods that contribute to the natural cleansing of tooth enamel. After each meal, it is necessary to clean the oral cavity of food residues, and in the morning and evening, be sure to brush your teeth with a brush and toothpaste.
If no alarming symptoms have preceded it, and teeth begin to fall out, it is immediately recommended to undergo a full examination of the body. Perhaps he is trying to draw your attention to health problems with the help of teeth.
Secondary consequences of edentia
Cosmetic defects and digestive disorders become noticeable almost immediately. However, there are also hidden consequences of untimely dental restoration.
In the absence of support, the tooth, which is an antagonist to the removed one, gradually moves out of the jaw. Over time, the neck of the tooth is exposed, and the tooth itself begins to sway from the slightest load. This threatens not only its loss, but also infection of the tissues surrounding it, because the space between the protruded tooth and the gum becomes an ideal object for pieces of food to get stuck and bacteria to multiply. Similar processes occur when other teeth in a row are displaced to compensate for voids.
Frequent inflammation in the oral cavity negatively affects the immune system, cardiovascular system and musculoskeletal system.
The absence of several teeth often leads to a sharp change in the bite and displacement of the lower jaw. This disrupts the functioning of the mandibular joint and provokes severe headaches and even disability.
For any degree of edentia, doctors advise planning implantation as early as possible. Missing teeth is not a cosmetic problem, but a complex problem! Call: +7 (8342) 222-888, sign up for a consultation, and our specialists will help you restore your dental health.
We live in a new way with new teeth: how life changes after implantation
Aesthetic consequences
The presence of even one gap in the dentition can change the proportions of the face over time. Age-related aging processes accelerate, become more noticeable, and intensify:
- due to alveolar bone resorption, facial height decreases;
- vertical lines become more noticeable in the area of the lips and chin, making the face look rougher;
- The bite gradually changes, which can cause the proportions of the lips to be disrupted and the chin to change;
- with edentulism in the upper jaw, the nasolabial groove deepens faster and more noticeably, which is why the face looks older;
- It is possible to form a double chin if the attachment of the muscles to the body of the lower jaw is disrupted and their tone decreases.
What complications can there be?
The complete absence of teeth inevitably causes psychological problems, functional discomfort and quite dangerous consequences for the entire body:
- problems associated with eating: the inability to bite and chew food normally leads to serious diseases of the digestive tract,
- gingival subsidence and bone tissue atrophy, which causes difficulties in prosthetics,
- deformation of the shape of the face, the appearance of wrinkles, reduction of the lower third of the face, retraction of the lips into the oral cavity. If all teeth are missing, a person looks much older than his age.
Teeth become crooked
If one, or even more so, several teeth are missing, occlusion, the correct closure of the teeth of the upper and lower jaw, is disrupted. This is inevitable even if only one tooth is lost. The opposing tooth becomes unsupported and becomes loose. Teeth adjacent to the lost one converge in an effort to fill the empty space. The entire row of teeth gradually begins to move, the bite is disturbed, after which the impact on the jaw joint appears, causing headaches and neck and back pain.
If the teeth are not replaced with dentures, the gaps between them begin to increase, food will get stuck in these crevices, causing caries and other diseases.
Changes in soft tissues
Attached soft tissues also change when bone volume changes. The gums shrink in volume and become thinner. In the lower jaw, the layer of attached soft tissue may be very thin or almost absent.
Periodontal nutrition is disrupted and blood supply deteriorates. This further accelerates destruction: surface tissues become thin, susceptible to inflammation and irritation. In advanced cases, bedsores form. Destructive processes provoke the development of chronic periodontal diseases. These, in turn, can lead to the loss of adjacent teeth.
If toothless ridges of bone tissue on the jaw have already formed, the tongue can gradually increase in size: it fills the space that was previously occupied. With the loss of one tooth, such manifestations are minimal; if there are several gaps in the dentition, the enlargement of the tongue will be clearly visible.
Methods for restoring missing teeth
The modern level of development of dentistry in almost all cases of violation of the integrity of the dentition makes it possible to solve the problem taking into account all the wishes of the patient. Types of prosthetics:
- Removable dentures. They are necessary if most of the teeth are lost or all of them are missing.
- Fixed. Their use is possible if 1-2 teeth are missing or their main part is destroyed.
- Implantation. This method of prosthetics involves implanting an implant into the bone tissue, onto which a crown is subsequently placed. Implantation is considered the best method of prosthetics, as it returns the desired functionality to the dentition.
The type of prosthetics is selected together with the doctor, taking into account all indications and contraindications.
The link between dental and heart health
Dental disease and inflammation in the mouth increase the risk of bacterial infection in the bloodstream, and this, in turn, has a negative impact on the heart valves.
Atrial fibrillation, or atrial fibrillation, is considered the most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in the world, and the condition typically involves an abnormal heart rhythm (most commonly tachycardia, a rapid heartbeat). Possible consequences of atrial fibrillation include thromboembolic disease and heart failure. Scientific research has shown that various inflammatory processes in the body, including inflammation that occurs in the oral cavity, play an important role in how atrial fibrillation begins and progresses in patients.
Missing part of teeth
If several teeth are lost, they can be replaced with dentures made of plastic or nylon, clasps and bridges. Dental prosthetics using implants installed in the jaw is considered extremely reliable. The latter method also provides the most aesthetic results. When implanting into the body of a bone, the validity period of the inserted implants is maximum; the adjacent teeth do not have to be ground down, which is necessary when using prosthetics with bridges. A dental prosthesis placed on an implant implanted into the bone is quite functional, and from an aesthetic point of view, it completely replaces the lost tooth.