Children's dental prosthetics is an opportunity to quickly restore a damaged, lost or missing primary or permanent bite unit. The dental procedure takes 20-40 minutes and is suitable for children of almost any age.
Any tooth loss before the child reaches 6 years of age is considered abnormal and requires urgent solution to the problem.
The lack of timely prosthetics leads to problems with chewing and speech, and provokes the development of bite pathologies.
What does dental prosthetics for children include?
Children's dental prosthetics with crowns is the restoration with artificial materials of one or more missing units in the dentition.
The goals of prosthetics are determined by the clinical situation. A pediatric orthopedic dentist can offer:
- aesthetic restoration of the surface - restoration of enamel or dentin;
- making crowns - for normal chewing and ensuring adequate load on the periodontium;
- protecting the tooth from further destruction - in case of severe caries, pulpitis.
By function, children's dentures are:
- preventive - stops deformation of the dentofacial rows;
- fixing – suitable for fastening orthodontic structures;
- therapeutic - restore individual units and lost functions.
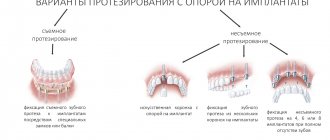
By design - removable and non-removable options.
Clinical and technical aspects of manufacturing children's removable dentures
Dr. Sandra Siepmann
Department of Prosthetic Dentistry at the University Clinic of Freiburg
Dr. Alexandra Ioana Holst
Clinic No. 3 of Orthodontics at the University of Erlangen -
Nuremberg named after Friedrich-Alexander (Erlangen)
Dr. Stefan Holst
Clinic No. 2 of Prosthetic Dentistry at the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg. Friedrich-Alexander (Erlangen)
Dr. Guido Heydecke
Professor, Clinic of Prosthetic Dentistry at the University Hospital Hamburg Eppendorf (UKE)
The manufacture of dentures in children requires special measures that take more time than when making dentures for adult patients. A condition for successful treatment in children is appropriate treatment of them, including both special and functional as well as psychological aspects. Aesthetically and functionally correctly performed dental restoration can have a positive impact on the development of a child’s self-esteem and self-confidence. This article uses a case study to demonstrate how appropriate handling of a child helps him become accustomed to the dental office environment and treatment procedures.
Introduction
Dental defects in childhood can be either congenital or acquired.
The causes of acquired dental defects can be:
- caries (Einwag, 2002a; Mandroli, 2003);
- trauma (Einwag, 2002a);
- general and local diseases.
Causes of congenital absence of teeth include oligodontia, anodontia, hypodontia, mineralization disorders (Nyguist 1968), microdontia and hypophosphatasia (van Waes & Stoeckli 2001).
Premature loss of baby teeth (less than a year before permanent teeth erupt) can cause a number of complications. These primarily include:
- loss of sagittal and vertical support (Stadelmann, 1988; Beyaert et al., 1991);
- limitation of functions (phonetics, chewing) (Margolis, 2001; Oka et al., 2003a; Oka et al., 2003b);
- development of dyskinesias;
- growth slowdown;
- influence on the process of eruption of permanent teeth (acceleration or delay);
- sometimes also difficulties in social integration (Einwag, 2002a; Lo Muzio et al., 2005).
Possible options for prosthetics in childhood include the manufacture of devices that preserve space in the dentition. Such devices can be made in the form of either a fixed or removable structure (children's removable denture). The choice of the appropriate treatment method largely depends on the cooperation of the little patient with the doctor. During the treatment process, the dentist is required to be much more sensitive than when performing dental procedures on adult patients. In order to achieve the necessary patient cooperation, it is important to take into account special psychological aspects during treatment (Siepmann et al., 2008). The tell-show-do approach produces the best results when treating children over 3 years of age (Chu, 2000; Eaton et al., 2005). Despite the fact that patients' cooperation is insufficient in many cases, they often accept prostheses well (Chu, 2000; Van den Steen & Bottenberg, 2004).
Description of a clinical case
A 5-year-old patient came to the Department of Orthopedic Dentistry at the University Clinic of Freiburg for the first time, accompanied by his mother (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Initial situation: portrait photograph of a 5-year-old patient.
Anamnesis
In the clinical case presented here, the general history is unremarkable. The patient is not taking any medications.
Special anamnesis: the patient does not have any aesthetic discomfort, as well as phonetic and functional limitations.
Objective examination data
Estraoral examination
No asymmetry or sensory disturbances are detected.
Extraoral examination from an orthodontic point of view
Harmonious proportions of the face with a conditional division into three parts, straight profile. The position of the jaw in the sagittal and vertical plane is without any features.
Intraoral examination
Minor irritation of the mucous membrane in the area of the gingival margin, serous saliva, palatine tonsils without changes.
Dental condition
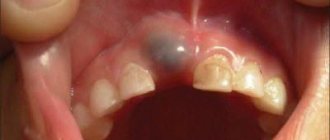
Teeth 54, 55, 64, 65, 74, 75, 84 and 85 are covered with prefabricated steel crowns for primary teeth. The 52, 51, 61, 62nd teeth are missing. The condition of the lower jaw teeth (with the exception of a small enamel defect of unknown etiology in the area of tooth 72) is unremarkable (Fig. 2)
.
Rice. 2. Initial situation in the oral cavity (without prosthesis).
To restore the dentition defect in the area of the 52–62nd teeth, a clasp prosthesis was made, fixed on the 54th, 55th, 64th and 65th teeth using Bonville clasps (Fig. 3).
Due to insufficient fixation, as well as functional problems associated with phonetics, insufficient restoration of chewing functions and aesthetics, the prosthesis did not meet the requirements. For this reason, the patient did not recognize the prosthesis and did not use it.
A functional examination also determines the visceral type of swallowing, which is the physiological norm before the eruption of the upper incisors. Despite the absence of anterior teeth, displacement or protrusion of the 73rd and 83rd teeth is not noted.
Rice. 3. Initial situation in the oral cavity. The installed clasp prosthesis does not meet the requirements.
Diagnosis
Partial absence of primary teeth in primary dentition. Condition after therapeutic and surgical sanitation of the oral cavity. The patient was given a clasp denture for the upper jaw that did not meet the requirements.
Treatment
Since the patient was only 5 years old at the start of treatment, it was difficult to predict to what extent cooperation could be achieved between patient and physician and how well the patient would accept the prosthesis. A consultation and explanatory conversation were held about possible treatment measures. After this, based on considerations of proper development of speech and aesthetics, as well as restoration of functions, a decision was made to plan the manufacture of a removable denture for the upper jaw.
When carrying out treatment, special attention should have been paid to measures aimed at overcoming the patient’s fear and achieving cooperation with the doctor.
On the second visit, the patient was introduced to the tools and materials used in a playful way. Skepticism towards a dental mirror, probe and tweezers is reduced if the patient is allowed to examine them with his own hands. In many cases, young patients will no longer be afraid of “drilling” if the rubber polishing cup or rubber polisher is touched to their finger while rotating at low speed (Chu, 2000; Eaton et al., 2005). In this case, the patient's willingness to cooperate with treatment was so high that it was finally possible to have his teeth professionally cleaned.
Taking an impression
In the case presented here, there were no indications for dental filling.
In order to prepare for taking an impression for further production of the prosthesis, the patient became familiar with the materials and instruments used for this. If the patient has an increased gag reflex, you can give the parents home selected impression trays to “practice” for subsequent impression taking. Under parental supervision, the child should try to keep the impression tray (without impression material) in the mouth for as long as possible (Köperich, 2003).
In the case described, at a subsequent visit, it was possible to immediately begin taking impressions from the upper and lower jaws. Before placing the impression tray with alginate mass in the oral cavity, a small portion of the mixed alginate mass was given to the patient. In this case, the child had to raise his hand as a signal that the alginate mass in his hands had hardened. Thus, the patient was given the impression that he could influence the course of this stage of treatment.
If necessary, an impression can be taken using a custom impression tray (Köperich, 2003).
According to the recommendations, when taking an impression from the upper jaw, the patient tilted his head in the direction of the impression tray (Köperich, 2003).
In this case, taking the impression proceeded without any particular difficulties (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4. Impression from the upper jaw.
Bite registration
To register the bite of very young patients or children with not very good cooperation, a plate of base wax should be inserted between the teeth, and then the patient should be asked to bite. An alternative is to use silicone-based bite registration materials. Such measures for registering occlusion can be limited to those cases where a sufficient number of teeth are preserved. With good patient cooperation, wax rolls can also be made to optimize the determination of the centric relation of the teeth (Einwag, 2002a; Körperich, 2003).
Since the present patient had preserved teeth in the supporting areas, it was possible to register the bite using a silicone-based material (Futar-D) (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5. Bite registration.
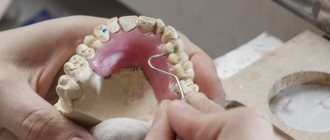
Making a prosthesis
In order for the patient to tolerate a removable denture as best as possible, the appropriate materials for its manufacture must be carefully selected. Abrasive materials (eg artificial ceramic teeth) should not be used (Nyguist, 1968). To set teeth, artificial teeth specially designed for children's dentures are used (Bambino tooth, Major Prodotti dentari, Moncalieri (TO) (Italy). The assortment includes sets of baby teeth in two colors (Köperich, 2003). The selection of color is focused on the features of the appearance of the enamel of baby teeth teeth. However, there are also large morphological differences in primary dentition teeth (including in color). Therefore, in certain cases, when setting teeth, ordinary plastic teeth used for prosthetics in adult patients should be used. In this case, they must be ground in accordance with the morphology of primary teeth (van Waes & Stoeckli, 2001).
To fix the prosthesis, it is recommended to use simple elements such as clasps used in orthodontics (Nyguist, 1968; Klähn, 1989). It is preferable to use Adams clasps (Hupfauf, 1968; Köperich, 2003), swept clasps (Bredy & Schmeil, 1990; Köperich, 2003), as well as cervical clasps (cervical, C-clasps). Due to the high risk of injury, these clasps should be made closed in very young patients (Stadelmann, 1988; Köperich, 2003). When permanent teeth begin to emerge, closed clasps should be opened to allow permanent teeth to erupt unhindered.
Clasps are made of rigid and inelastic wire with a thickness of 0.5–0.7 mm (Nyguist, 1968; Einwag, 2002a; Köperich, 2003). In some cases, it is possible to increase the retention capacity of a clasp by increasing retention with a composite filling (van Waes & Stoeckli, 2001; Siepmann et al., 2008).
For the base of the prosthesis, it is proposed to use plastics used for the manufacture of orthodontic appliances, or cold polymerized plastics with a very low content of residual monomer. Plastics can be painted in any color (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Finished prosthesis installed in the oral cavity, view of the upper jaw.
In cases where allergies are suspected, plastics of any type should be selected only after a series of allergy tests has been carried out by a dermatologist.
Experience shows that children's motivation can be increased if, before taking an impression, they are given the opportunity to choose the color they like for the base of the prosthesis. To reduce the increased likelihood of breakage of children's prostheses, the base can be reinforced using meshes made of materials based on gold-containing alloys or fiberglass (Fig. 7).
After setting the teeth, the wax structure of the prosthesis was tried on to control aesthetics, phonetics and function. At the same time, there was an additional opportunity to increase cooperation between the patient and the doctor, since during this stage of treatment the patient could also actively participate in decision making. At the same time, the child was able to mentally tune in to wearing a prosthesis (Einwag, 2002a; Köperich, 2003).
Rice. 7. Fiberglass reinforced prosthesis base.
Before installing the finished work, the child was given a prosthesis so that he could examine it carefully. During the fitting, the aesthetic, phonetic and functional features of the prosthesis were again checked. Monitoring and minor corrections of occlusion and articulation were carried out in the usual manner. After completing the correction procedure, the child could examine the installed prosthesis in the patient mirror.
If by this time there is still no tolerant attitude towards the “foreign body”, it is recommended to give the patient a denture so that he can “practice” using it in a familiar environment. Parents should first be given instructions on how to use dentures (Köperich, 2003).
Dispensary services
In any case, a follow-up examination of the patient should be carried out no later than 3 days after application of the prosthesis to again check and adjust the articulation, occlusion and correct fit of the prosthesis (Köperich, 2003).
Due to the increased risk of caries, it is recommended that dental examinations be performed every 2–3 months (Hupfauf, 1968; Nyguist, 1968; Kominek, 1985; Stadelmann, 1988; Chu, 2000). In addition, it may be necessary to activate the clasps or repair the prosthesis. The need for a new prosthesis or its addition due to the growth process arises annually, and in many cases after 6 months (Körber, 1963; Stadelmann, 1988; Schopf, 1994). According to Stadelmann, it is imperative that a new children's removable denture be made no later than after 2 years.
The patient presented in this article was very cooperative with the treatment and responded positively to the maxillary partial denture (Figure 8).
He regularly comes for follow-up medical examinations every 3 months. The patient's oral hygiene is good. He shows great dexterity when using removable dentures.
Rice. 8. Final photograph of a young patient with a pediatric removable denture installed in the mouth.
Discussion
In favor of making a children's removable denture, first of all, the following arguments can be given. At the time of premature tooth loss, children are at the stage of speech development and the formation of a somatic type of swallowing. With the help of a child's removable denture, these functional developmental stages can be positively influenced.
Regardless of the existing contraindications for the manufacture of children's removable dentures, each case should be considered separately and an individual assessment of the situation should be given only after a thorough history taking and examination.
If at first there are problems with the patient's cooperation, it is possible, through targeted management and the use of special handling techniques, to significantly improve the patient's cooperation in the treatment process. Building a trusting relationship between doctor and patient is crucial for subsequent treatment planning and implementation (Künkel, 2000; Einwag, 2002b).
At the first visit, in addition to taking a medical history and performing a general dental examination, an orthodontic screening should be performed, as well as an assessment of oral hygiene. It is important to pay close attention to oral hygiene from the very beginning. This is due to the fact that as a result of improper cleaning of the denture or lack thereof, the risk of developing caries increases and the likelihood of periodontitis and gingivitis increases. If it is still not possible to achieve adequate oral hygiene, you should refrain from making a child's removable denture.
Orthodontic screening is inevitable because the upcoming orthodontic treatment may involve a fixed or removable appliance to maintain space in the dentition (Granath et al., 1994).
Summary
Siepmann S., Heydecke G., Holst S., Holst AI: Technical treatment considerations for the manufacturing of child prosthesis - Child prosthesis - Part 2 (in German). Schweiz Monatsschr Zahnmed 118: 1177–1181 (2008).The rehabilitation of a child's dentition with a removable prosthesis is more complex and time consuming, when comparing it to the one of adults. Prerequisite for a successful treatment is a careful consideration of age-related, technical, functional and psychological aspects. The aesthetic and functional replacement of the missing teeth using a removable prosthesis results in an increased self-esteem for the young patients. This case report describes the management of a young child as well as the treatment planning and the prosthetic rehabilitation process.
The list of references is in the editorial office.
Article provided by the journal of the official publication of the Swiss Dental Association (SSO) Schweizer Monatsschrift für Zahnmedizin (No. 12, 2008, pp. 1177–1181)
Translation by Inna Bichegkueva.
Captions for drawings
Rice. 1.
Initial situation: portrait photograph of a 5-year-old patient.
Rice. 2.
Initial situation in the oral cavity (without denture).
Rice. 3.
Initial situation in the oral cavity. The installed clasp prosthesis does not meet the requirements.
Rice. 4.
Impression from the upper jaw.
Rice. 5.
Bite registration.
Rice. 6.
The finished prosthesis installed in the oral cavity, view of the upper jaw.
Rice. 7.
Fiberglass reinforced prosthesis base.
Rice. 8.
Final photograph of a young patient with a
children's removable denture.
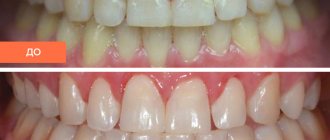
Dental prosthetics with crowns for children: indications
Children's dental prosthetics in Moscow are performed according to indications. Each situation is considered by the doctor individually, taking into account the patient’s age, health characteristics and other criteria.
Indications for prosthetics are:
- Destruction of the coronal part by half or even more - due to injuries, caries, pulpitis.
- Non-carious lesions, problems with tooth enamel in children - hypoplasia, aplasia, fluorosis.
- Removal of a baby tooth long before the start of a change in bite or permanent one.
- Gum and periodontal diseases - loosening and loss of teeth due to periodontitis, periodontitis.
- Injuries to the teeth and maxillofacial region - severe damage, chipped enamel, complete dislocation.
- Bruxism is involuntary grinding of teeth, causing deformation, destruction, and tooth loss.
- Anomalies and malformations - absence of primordia of mammary and permanent units, cleft lip and palate and other genetic abnormalities.
- Adentia - complete or partial, caused by hereditary or objective factors.
Prosthetic dental crowns for a child will help solve the problem of missing one or more units.
Why a child may have missing teeth at an early age
There may be several reasons why intervention by a pediatric orthopedist may be required:
- Tooth injury.
- Significant spread of caries, as a result of which the tooth simply cannot be treated.
- Edentia.
- The presence of inflammation and neoplasms in the oral cavity.
- Retention.
- Infections.
Important! Most often, children lose teeth due to caries and complications caused by this disease.
The most common occurrence is the loss of frontal teeth. It is more rare for the first molars to fall out, and even less often for the premolars.
The second leading cause of missing teeth in children is injury. Due to their high mobility and reduced caution, young children are prone to injury. And most of these injuries can adversely affect the growth and development of the jaws, as well as the eruption of teeth and the subsequent formation of the dentition.
The most common is the absence of lateral incisors in the upper row, lower and upper second premolars and third molars. Some incisors and second and first molars may be missing as a congenital defect. Absence of fangs is very rare.
Important! A child with complete edentia needs urgent prosthetics. Such children lag behind in terms of weight and height, since their body is not able to carry out the mechanical processing of food necessary for proper development.
Removable dentures in children:
Bridges
Sliding bridges for replacing several molars or incisors in a child.
Lamellar dentures
A patient-friendly option in the absence of lateral and anterior units.
Immediate dentures, “butterfly”
Nylon replacement of one or two teeth with fixation on adjacent units with clasp hooks.
Complete dentures
Necessary for toothless jaws in a child and have an elastic lining for ease of wearing and physiological comfort.
What does pediatric orthodontics do?
This section of dentistry deals with the correction of congenital and acquired malocclusion in children, and also eliminates the causes that led to its formation. Doctors working in this branch of dentistry are called orthodontists.
They do:
- preparation for orthodontic manipulations;
- prosthetics of lost primary teeth;
- correction of dental growth anomalies, defects of the facial skeleton and pathologies of jaw growth and formation.
The main task of the doctor is to correct malocclusion using all available methods. He must take all possible measures to prevent the development of these defects.
Why choose prosthetics at Aza&Buka dentistry
Dental prosthetics for children is a responsible dental procedure. The doctor must take into account many points - characteristics of the bite, growth rates, the presence or absence of certain diagnoses. The prosthetic structure should grow with the child, be comfortable to wear and not interfere with the harmonious development of the patient.
At Aza&Buka, special attention is paid to the safety and quality of dental procedures. Prosthetics in pediatric dentistry is:
- Fast and comfortable. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis immediately during the appointment and select the optimal prosthetic option.
- Complex work of specialists. If necessary, the child will be examined by an orthodontist, a dental therapist, or a dental surgeon. The best decision for the patient will be made.
- Painless at every stage. For especially young children or complex patients, prosthetics will be performed under general anesthesia or deep sedation.
- High quality result. A crown will completely replace a damaged or missing tooth - aesthetically, anatomically, functionally.
- Modern equipment, best brands. Young patients will be offered ready-made dentures or crowns made from acrylic, nylon, ceramics, metal, and zirconium dioxide.
At Aza&Buka dentistry, we provide prosthetics for permanent and baby teeth for patients of any age.
Reviews
Cvetlana R
01/07/2022 at 15:38
We have been going to this dentistry for a long time. We are seeing O.A. Hristova. Very good doctor, friendly and attentive. He quickly finds a common language with children.
Alexandra Aladina
01/06/2022 at 10:11
Doctors are experts in their field. Price-quality corresponds 100%
Danil V.
01/05/2022 at 17:49
I constantly take my son to the dental clinic, check his teeth and treat them. There is also an adult department at this address - all the staff are super!
Alexey Lyule
12/29/2021 at 10:19
Cool clinic, doctors and staff are masters of their craft. Well done to the staff, the prices are reasonable.
Alexey Lazarichev
12/26/2021 at 19:44
Excellent clinic, they put braces on my daughter, she liked everything!
Lyubov H.
12/24/2021 at 08:58
We entrusted the child with the first dental treatment and did not regret it, the doctor established contact with the child, gave anesthesia (injection), which the child did not even understand! Just a delight, thank you))
Vitaly
12/19/2021 at 22:01
Everything is fine.
Natalya Pogodina
11/28/2021 at 12:33 pm
Attentive doctors. Very nice staff. I only take my kids there
Svetlana Aladeva
27.11.2021 at 20:23
The best clinic with more than 20 years of experience, they work with professionals, so it can be difficult to make an appointment. Polite staff, modern equipment and sterilization of instruments.
Irina Kalashnikova
20.11.2021 at 11:07
Great center. I contacted my eldest daughter and they helped. Now we are correcting the bite of the youngest. Positive dynamics of treatment. The doctors know their stuff. Many thanks to artodontist Alexandra Mikhailovna Potryasova and Alana Borisovna.
Sergey Marchenko
08.11.2021 at 09:47
A very good clinic, competent and responsive staff, the best approach to children that I have seen.
Yulia Kuznetsova
07.11.2021 at 09:47
Many thanks to Dr. Larisa Vladimirovna and Galina Vladimirovna. You are true masters of your craft.
Sergey Shpenev
10/14/2021 at 14:02
Great.
DD
09.10.2021 at 00:16
Qualitatively and reliably, honestly and correctly. It’s good that I know that such dentistry exists! I think I'm lucky.
Kira Ivanova
06.10.2021 at 14:16
Good pediatric dentistry
Dmitry Chmarov
09.13.2021 at 11:44
The prices are not great, but at least the child is not afraid to go. They pulled out baby teeth that were deeply embedded and the child never felt pain
Anna
09/12/2021 at 00:26
Excellent children's orthodontist, prices are very reasonable, focus on treating the child, not on pumping out money like in many other places, the result is really visible, thank you, prosperity to the clinic
Dmitry Surovy
08/22/2021 at 15:38
Excellent pediatric dentistry! I really enjoyed all three visits! They came twice to remove pigmentation, once for a routine examination. The 2.5 year old child behaved calmly and fearlessly. After visiting they give you a gift))) I recommend it to everyone!
Alla I.
08/04/2021 at 14:37
We have been seeing the clinic for a long time, about 6 years, with the same dentist-therapist. I like the quality and service. Sometimes we visit a hygienist until we find a doctor who would suit us 100%. At first, the two-year-old child was very afraid to have his teeth treated, but the doctors at the clinic managed to find an approach. And they saved all our teeth.
Natalya F.
03.08.2021 at 17:01
We treat our teeth with Dr. Nenko. A very excellent doctor. My child was scared at 2 years old in a regular clinic so that he cried when he heard the word from the dentist. And he went to Alexander Vladimirovich with a smile. And now he is already 13 years old, but he only goes to him. I am very grateful to this doctor. Thank you very much !!! And regarding the prices. Damn, the prices are stinging right now. I'm not a millionaire. But wherever I was, the child was not treated better than in cramming. And really...
All reviews
What is the price of a dental plate?
A plate for straightening teeth is the most inexpensive way to correct a bite. With this method of treatment, the doctor does not have to stick a bracket on each tooth, which takes quite a lot of time and money. Adjusting the plate also takes much less time than adjusting each bracket individually.
Quite often, thanks to just one plate, the bite can be completely corrected. If the problem was too serious, there is a chance that the patient will still have to wear braces during adolescence. However, the duration of wearing them will be significantly less than if the child did without the plate in childhood - which means the cost of orthodontic services will also be lower.
ATTENTION:
After wearing fixed braces during adolescence, wearing a plate may be necessary to consolidate the effect. This will not depend on whether the child wore the record as a child.
How plates are made and put on
The treatment process begins according to the following algorithm:
- The orthodontist makes impressions of one or both jaws.
- X-ray control is carried out.
- A fitting of the preliminary plaster version is scheduled.
- A permanent plate model is made.
It is important that the plastic frame fully displays the relief pattern of the dentition. The metal parts are designed to provide the most reliable fixation.
When the plates are installed on the patient, he does not experience pain. The only difficulty at first may be related to speech, to clearly pronouncing individual sounds. Also at first there is likely to be increased salivation. However, this should pass in just a couple of days.
How to wear a dental plate?
At first, speech impairment may occur, but if you follow all the recommendations of the orthodontist, adapting to wearing the plate will be simple and quick. Caring for them is not troublesome and even a small patient can handle such a task.
The lifespan of the plate is affected by the age and complexity of the case. The period is determined by the orthodontist: from 6 months to 2 years. The plate must be replaced once a year.
The cost of a plate for a child’s teeth depends on the material, the features of the design itself and the level of complexity of the problem.