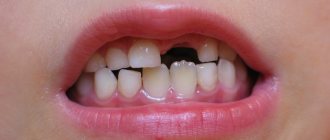
Symptoms that indicate that the process has begun:
- Some children experience an increase in temperature (up to 38). In this case, you should not hesitate; it is better to seek advice from your doctor.
- Unpleasant sensations in the gums.
- The space between the teeth increases.
- The roots begin to dissolve (The roots of baby teeth are much shorter than those of permanent teeth. When the process reaches the neck, a tooth change occurs).
- Gums are bleeding.
Forward to the future!
Of course, there is no doubt that dental bioengineering will soon become an integral part of standard protocols for the treatment of dental lesions. It is possible that regenerative dentistry techniques will allow us to create a complete dentogingival complex. It is important to remember that methods developed in accordance with the requirements and objectives of dental bioengineering will be able to spur the development of new approaches to the regeneration of other tissues and organs and thus contribute to progress not only in dentistry, but also in the field of regenerative medicine in general. Well, forward to the future!
Everything has its time
One of the most frequently asked questions to our doctors from mothers is: “In what order do teeth begin to fall out?”
It usually starts at the age of 5 years. The very first teeth that undergo this process are the incisors, then the fourth and fifth teeth of the row, then the canines. To make it more clear to you, here is a diagram of the loss and eruption of baby teeth:
Don't worry if your child is over 5 years old and his teeth aren't starting to change. Each child’s body is individual, and much depends on nutrition, dental care, daily routine, and climatic conditions. In girls, the loss of baby teeth begins a little earlier than in boys. If you are still worried, then contact your dentist and conduct an unscheduled examination.
I would also like to note the timing. Complete replacement of milk teeth with molars occurs within 6-7 years. There is no need to specifically tear them out or loosen them. Everything will happen naturally.
The doctor prescribes removal only if the baby tooth has not yet fallen out, but the root tooth is already beginning to grow.
Is it possible to speed up teething?
Medication - no. But massaging your gums won't hurt at all. Using a clean finger, gently and gently massage your baby's gums. The baby will feel better, and the tooth will cut through faster. Just do not press hard so as not to injure the gums. You can give your child a cool spoon or pacifier to hold in his mouth. Try buying special teethers with liquid. They are placed in the refrigerator for a while, and then given to the child to chew on. All these methods are good in moderation, do not overdo it.
Can bad breath occur during teething and what is the cause?
The process of teething is associated with partial decomposition (lysis) of the mucous membrane under the action of salivary enzymes. We all notice that the amount of saliva increases sharply during this period. In this case, indeed, indicators such as viscosity, color and smell of saliva may change. Another factor is the presence of weak antibacterial substances in saliva, which are designed to prevent infection of the wound when a tooth cuts through the gum. A certain amount of blood also enters the oral cavity. When it decomposes, a sour (metallic) odor may appear.
A sharp increase in temperature during teething. What to do?
Teething does not cause a temperature jump to 39-40 degrees. Only a slight increase is possible, which is normal. Be careful: teething should not cause high fever, diarrhea, vomiting, complete loss of appetite, cramps or choking. If you have such symptoms, even if you attribute it to your teeth, consult a doctor. It is also not recommended to use antipyretics and painkillers without consulting him.
What is the difference between an increase in temperature due to teething and an increase due to other reasons? How long can the elevated temperature last in the first case?
It all depends on the individual characteristics of the child. Basically, hyperthermia and diarrhea are only secondary signs of the teething process, which in itself is a serious physiological turning point for a small organism. Fever is, rather, a reaction to inflammation of the oral mucosa. After all, at the site where the tooth exits, irritation forms, often a wound that can become infected. Thus, hyperthermia is caused not by the mechanism of tooth formation itself, but by side effects. After all, the eruption of permanent teeth, despite the similarity of histological and physiological changes, causes symptoms of colds and diarrhea extremely rarely. And it is quite simple to explain their appearance in children: changes in diet and diet, constant foreign objects in the mouth, microflora disturbance, weakened immunity in the nasopharynx. So, if high fever and loose stools continue for more than 72 hours, then teething really has nothing to do with it.
Features of baby teeth
Now I will answer another very popular question: “how do baby teeth differ from molars?”
These are the baby's very first teeth. They appear before the age of three, and begin to erupt until there are 20 teeth. See the photo above for the cutting diagram.
They do not have such deep roots as permanent teeth, have a more rounded shape and smaller size, and are white in color, while permanent teeth have a yellowish tint. By location, they are directed vertically, and the radicals are slightly outward.
Wisdom teeth cannot be milk teeth, because they grow into deep roots only by the age of 18-20, and sometimes later.
Teething in infants
Possible characteristics of teeth in children at the teething stage. Stay up to date.
The expansion of the spaces between the teeth is caused by the growth of the jaws. During the transition from baby teeth to permanent teeth, it is considered a normal condition. A wide gap between the upper anterior incisors is usually associated with a deep-lying maxillary frenulum. An orthodontist should observe and treat such a gap between the teeth;
- a blackish edging on the neck of the tooth can form when taking soluble iron supplements, as well as during a chronic inflammatory process (precipitation of bacteria from the leptotrichium group);
- yellowish-brown staining of teeth may be associated with the use of antibiotics - by the mother in the 2nd half of pregnancy or by the child himself during the formation of teeth;
- yellowish-greenish coloring is caused by severe disturbances in bilirubin metabolism, hemolytic conditions (destruction of red blood cells);
- reddish staining of tooth enamel is characteristic of a disease called porphyria - a congenital disorder of the metabolism of porphyrin pigment;
- malocclusions are formed by the uneven growth of the child’s jaws, as well as prolonged sucking of the nipples;
- Anomalies in the location of teeth occur for a number of reasons: trauma, congenital disorders of connective tissue metabolism, constitutional reasons (small jaw size), tumors of the alveolar process of the jaw.
- the absence of teeth before one year of age is extremely rarely associated with edentia (lack of tooth buds), which can be checked using radiovisiography as prescribed by a pediatric dentist.
If teeth erupt on time and in a certain order, this indicates the normal development of the child’s body. After all, this physiological process is in direct connection with the general health of the baby. Some atypical cases may indirectly indicate the presence of pathology. But only a special examination of the child can confirm or refute the assumptions made. The reasons must be identified and analyzed by a specialist.
Daily doctor's advice on caring for baby teeth:
- Start brushing your baby's teeth only after they have erupted; use a special brush for babies.
- When your child turns one year old, buy a brush with soft bristles and toothpaste without fluoride; it will not harm the child if he swallows it.
- Brush your baby's teeth 2 times a day (morning and evening)
- Don't put off going to the dentist. They should be regular, even if there are no signs of concern.
- Include more fresh greens, fruits and vegetables in your diet.
What does it cost us to build a tooth?
To use stem cells in tissue engineering, the presence of a scaffold and growth factors is required (Fig. 7). An ideal scaffold should support cell attachment, migration, proliferation, and spatial organization.
Figure 7. What does it cost us to build a tooth?
website dentistry.tamhsc.edu
Basically, a scaffold as a suitable matrix for tissue reconstruction should meet the following requirements [21]:
- Ease of use.
- The presence of pores of a certain shape and size for the diffusion of cells, growth factors, nutrients and removal of waste products.
- The ability to biodegrade, which occurs at a certain time without releasing toxins.
- Biocompatibility with body tissues.
- Low immunogenicity.
- Ability to be replaced by regenerating tissue and vascularization.
- Good physical and mechanical properties.
The materials used to form scaffolds are divided into natural and synthetic (Fig. [22]. Bioactive glass, polylactic acid, various composites (multicomponent materials based on a matrix based on metal, polymer or ceramic) - all these are synthetic materials. Despite the fact that these materials make it possible to produce scaffolds of the required shape, their use is very limited due to unsatisfactory biocompatibility and toxicity. Among the biomaterials (natural materials) used to create scaffolds, collagen, chitosan, and hyaluronic acid can be distinguished. They consist of macromolecules that They are also part of the extracellular matrix, therefore they are biocompatible and highly biodegradable, but they are less durable and can cause rejection reactions [21].
[22]. Bioactive glass, polylactic acid, various composites (multicomponent materials based on a matrix based on metal, polymer or ceramic) - all these are synthetic materials. Despite the fact that these materials make it possible to produce scaffolds of the required shape, their use is very limited due to unsatisfactory biocompatibility and toxicity. Among the biomaterials (natural materials) used to create scaffolds, collagen, chitosan, and hyaluronic acid can be distinguished. They consist of macromolecules that They are also part of the extracellular matrix, therefore they are biocompatible and highly biodegradable, but they are less durable and can cause rejection reactions [21].
Figure 8. 3D scaffold of mouse and human teeth. a — Lower central incisor of a mouse. b — Human lower first molar. 3D reconstruction and bioprinting were used. Material: hydroxyapatite and polycaprolactone. Microchannels (d = 200 nm) into which MSCs and growth factors are introduced ( c and d ) are visualized.
[22]
The most suitable scaffold that meets most requirements is either a scaffold derived from extracellular matrix ( ECM scaffold ) or its analogue. Due to their identity with the extracellular matrix, such scaffolds are able to provide the best interaction with cells and growth factors. Dental MSCs, such as pulp and periodontal stem cells, when cultivated in ECM scaffolds, underwent differentiation in the odontogenic direction. After implantation of this scaffold, the pulp was formed [10], [23].
In addition to the scaffold and stem cells, a link is needed that connects them, which would regulate tissue growth. These can be growth factors, certain genes, and interfering RNAs [7].
Growth factors are peptide molecules that transmit signals to control cellular behavior and interact with specific receptors on the surface of cells [24]. They provide interconnection and interaction between cells and the extracellular matrix. Following cell damage, the secretion of growth factors begins, which subsequently trigger the processes of regeneration and angiogenesis. An example of the “work” of growth factors in a tooth is the formation of secondary and tertiary dentin, which occurs when the carious cavity is close to the dental pulp or when teeth are subject to increased abrasion. Key growth factors during tooth development include bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and fibroblast growth factor (FGF). They are primarily used in dental tissue engineering [25–27]. Both cells and nanoparticles, as well as the scaffold itself, can be used to deliver growth factors.
Doctor's advice when the process of changing teeth begins:
- After tooth loss, let your baby not eat for 3 hours, and you should also not drink very cold or hot drinks.
- Protect your child from sour, spicy and very sweet, astringent foods. All this has a negative impact on teeth.
- If your baby is bothered by discomfort or pain after a baby tooth falls out, then buy a special gel, but it is better to choose it on the recommendation of a dentist.
- Do not let your child touch the hole where a tooth has fallen out, as it may become infected.
- To soothe your mouth, make a decoction of chamomile.
Vitamins for teeth and gums
The baby should take vitamins to strengthen teeth and gums regularly, without missing a single day. This is the only way the child will receive a sufficient amount of nutrients. The daily complex must include:
- Retinol (vitamin A). An element necessary for bone growth. It is vitamin A that promotes protein synthesis in cartilage and bones, and also increases the cartilage layer in the growth zone. If a child's body does not have enough retinol, the process of bone tissue growth slows down, and new teeth may grow crooked. In addition, with vitamin A deficiency, the development of stomatitis and gum inflammation is often observed. In advanced cases, teeth may begin to fall out.
- Calciferol (vitamin D) is one of the key components of bone development. It is thanks to this vitamin that a child’s bones develop normally and mineral metabolism is regulated. Calciferol, as the name implies, helps absorb calcium and strengthens bone tissue. In summer and spring, a child can get vitamin D from sunlight by simply walking outside often. But in winter and autumn it is important to give children vitamin complexes with calciferol. With a deficiency of this element, mineral metabolism can be disrupted, bone tissue softens, rickets appears, and, of course, tooth enamel becomes thinner.
- Vitamin C is essential for strengthening gums. If there is a lack of ascorbic acid, the child may experience tissue bleeding, in advanced cases, ulcers appear in the mouth, an unpleasant odor disturbs, and teeth begin to loosen and fall out.
- Vitamins B6 (pyridoxine) and B12 (cyanocobalamin) are also needed to strengthen gums. It is B12 that provides tissue strength and prevents various inflammations, and the lack of cyanocobalamin makes the gums very sensitive.
- Vitamin E is involved in wound healing and helps fight pustules that so often appear on the gums of babies.
- Vitamin K (phylloquinone) strengthens connective tissue and protects gums from bleeding.
- Vitamin PP (nicotinic acid) is an important protector of gums from gingivitis, stomatitis and other inflammations.