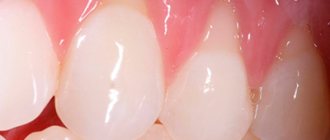
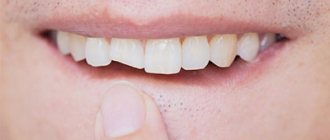
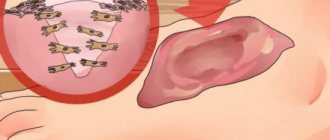
Gum inflammation is one of the most common dental problems. The cause of inflammatory processes is often poor oral care and non-compliance with rules and regulations of hygiene, as well as injuries to the mucous membranes, accompanied by a violation of their integrity. It happens that inflammation begins after treatment at the dentist. If a patient’s gums become inflamed after going to the doctor, they should visit the dental office again, since this symptom almost always indicates the need for repeated medical intervention.
Slight soreness and swelling of the gums may be normal after complex dental treatment (for example, depulpation), but these signs should not be of high intensity or last more than 24 hours. Inflammation following extraction should also resolve within 48-72 hours after surgery. In all other cases, it is necessary to find out the cause of inflammation and take timely measures to prevent complications.
The gums became inflamed after dental treatment
Causes of edema
Swelling of the gums is a consequence of penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the soft tissues, causing infection.
Provoking factors:
- tartar formed due to poor oral hygiene;
- advanced form of caries;
- untreated stomatitis;
- infectious diseases of the throat;
- mechanical damage to soft tissues;
- difficult teething;
- immunodeficiency;
- vitamin deficiency (mostly severe lack of vitamin C);
- herpes virus activity;
- allergies to dental drugs or materials;
- development of purulent processes inside the tooth;
- the presence of tumors on the tooth root;
- gum diseases.
Before making a diagnosis, the dentist will definitely prescribe diagnostics to determine the internal state of the tissues, which will more clearly define the clinical picture and identify the main cause of the pathology.
Pain at the site of a dead tooth
It happens that the nerve has been removed from the teeth, but they still hurt. If the nerve is not completely removed or the doctor put too much filling material into the canal, then the pain will not leave you for a very long time and will occur when eating hard, cold or hot foods.
Pain in a dead tooth can appear due to the fact that tissue inflammation has gone too far, and not only the nerve and pulp are affected, but also the bone tissue that surrounded the tooth, as well as due to the use of too aggressive drugs in treating the nerve.
Often, to regenerate tissue at the site of the inflamed nerve, a course of special anti-inflammatory drugs is prescribed. To avoid problems with inflammation when extracting the nerve, it is recommended to first install a temporary filling.
Associated symptoms
Often gum swelling is accompanied by other symptoms:
- swelling of the cheek;
- fistula formation;
- tooth pain;
- bleeding gums;
- sensation of a metallic bite;
- redness of the gums;
- discharge of pus from the carious cavity;
- loosening of the crown;
- the appearance of ulcers;
- increase in general body temperature;
- the appearance of white plaque on the gums.
If there are signs of a purulent process, then contacting a dentist should be done immediately. Complications can lead to serious consequences not only for the oral cavity, but also for the entire body.
Swollen gums in an adult: other clinical cases
- Injury to the gums. Thermal and chemical burns lead to tissue damage around the element of the dental system. Symptoms can be expressed in increased bleeding, redness, and plaque.
- Poor quality canal sanitation. Poor canal filling can lead to periodontal abscess and result in swelling of the gums and cheeks.
- Extraction of a dental unit. After tooth extraction, in some cases the gums become swollen. This is especially observed after extraction of the figure eight. Swelling for 2-3 days is considered normal. However, if pain persists for more than three days, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The gums may swell not only after tooth extraction, but also due to an allergic reaction to pharmaceuticals and orthopedic structures. When any pathological process is detected, an immediate search for the problem and its elimination is required. If you do not receive qualified help, this can lead to loose teeth, abscess, otitis media and even the development of a tumor.
Possible dental diseases
In 90% of cases, swelling of the soft tissues around the tooth appears with the development of periodontitis, gingivitis, periodontitis or an abscess. Other possible causes are extremely rare.
Periodontitis
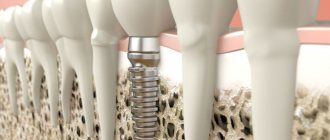
With the development of periodontitis, the inflammatory process affects the bone tissue of the jaw. The cause of the pathology is the penetration of infection of the dental root canals and its spread. Swelling of soft tissues during periodontitis is caused by the accumulation of pus. If left untreated, pus may be released through the resulting fistula. The swelling subsides during this period, but the inflammation cannot be eliminated on its own. Treatment is mandatory.
Gingivitis
A distinctive feature of gingivitis from periodontitis is the development of an infectious and inflammatory process in the soft tissues surrounding the tooth. Swelling of the gums with gingivitis mainly occurs during the period of exacerbation. The swelling of the gums can be so severe that the tissue covers the tooth.
Periodontitis
The development of periodontitis occurs against the background of advanced periodontitis. Lack of treatment provokes a purulent process with a localized abscess area. With a periodontal abscess, a cavity forms under the gum in which pus accumulates. Externally, in addition to edema, a pronounced swelling in the form of a semicircle up to 1–2 cm in size appears on the soft tissue. Treatment is carried out surgically.
How babies teeth cut: timing and development factors
The foundation of baby and permanent teeth is laid during pregnancy: their health is directly affected by the lifestyle and health of the mother.
After the birth of a child, minerals accumulate in his body, which will become building materials for teeth. The first of them appears when the baby is six months old - this happens in most situations.
But there are many cases where a child was born with a pair of ready-made teeth, or vice versa, when teeth appeared after the first year of life. This is normal: the process is influenced by many factors - from food to place of residence, when exactly teeth are cut.
In total, nature plans 20 milk teeth. They appear in pairs, so teething in infants is usually divided into 10 stages:
- First (medial) lower incisors - 6-10 months.
- First (medial) upper incisors - 8-12 months.
- Second (lateral) upper incisors - 9-13 months.
- Second (lateral) lower incisors - 10-16 months.
- First upper molars - 13-19 months.
- First lower molars - 14-18 months.
- Upper canines - 16-22 months.
- Lower canines - 17-23 months.
- Second lower molars - 23-31 months.
- Second upper molars - 23-31 months.
From 3 to 6 years old, a temporary bite forms in the child’s mouth: it changes when the baby teeth begin to fall out. A temporary bite has a huge impact on a permanent one, and a person’s smile, which will be with him all his life, depends on its correctness.
Along with 20 milk teeth, the roots of 16 permanent teeth appear. The rest grow up at a later age.
We emphasize once again that deviations from the schedule are normal, even within a few months. To be sure, consult your pediatric dentist.
Treatment methods
Depending on the cause of gum swelling and accompanying pathological processes, the doctor may prescribe conservative treatment, or resort to surgical manipulation or tooth extraction. The clinical picture is determined by the results of examination and radiography.
Conservative therapy
When visiting a dental clinic, a specialist eliminates the cause of gum swelling and then begins to eliminate inflammation, symptoms and associated pathological processes.
The patient may be prescribed drug therapy, including:
- antiviral;
- painkillers;
- antibiotics;
- antihistamines.
Local therapy that has an antiseptic effect is required. The dentist may recommend the use of special ointments or gels, rinsing the mouth with medications or herbal decoctions.
Surgery
The help of surgical dentistry is necessary for certain indications. The need for surgical intervention arises with the development of a purulent process. The specialist will need to open the gum, fistula or root canal to release the pathological fluid. Next, the affected cavity is cleaned, treated with an antiseptic, and treatment of the underlying disease begins. Swelling of the gums can be a sign of a serious pathology that requires tooth extraction. The need for extraction or the possibility of saving the tooth is assessed by the doctor.
First aid for inflammation
It is better to use any medications to combat pathological symptoms after consulting a doctor, since all medications in this group have different compositions and a list of contraindications. At home, you can use various rinses as first aid before going to the dental clinic. They are not recommended for use for more than two days, since the absence of qualified assistance for a long period of time can worsen the patient’s condition and lead to the progression of the pathology.
Calendula decoction with salt
Calendula is one of the most famous medicinal plants. Calendula flowers (marigolds) have a disinfectant, antimicrobial and healing effect, so a decoction of this plant helps to quickly cope with inflammation and speed up the healing of soft tissues. If you add salt to the decoction, you can improve the condition of the gums during purulent inflammation, since any salt perfectly draws out pus and ensures the outflow of exudate.
To prepare a medicine to treat inflammation, you must:
- Pour 100 g of calendula flowers into 700 ml of boiling water and put on low heat;
- cook for 15-20 minutes;
- add a tablespoon of salt and cook for another 5 minutes;
- leave for an hour and strain.
You should rinse your mouth with this decoction 3 to 10 times a day (depending on the degree of inflammation). Symptoms usually become less noticeable on the second day of use.
Bread crumb infusion
If you don’t have medicinal plants at hand, you can use a very simple but effective recipe and prepare an infusion from bread pulp. You can use any type of bread made from rye or peeled flour, as they contain a large amount of minerals and vitamins that have a positive effect on the condition and health of the gums.
Preparing the infusion is very simple:
- break one piece of bread (approximately 50-70 g) into small pieces and place in a shallow container;
- pour 300 ml of boiling water and add half a spoon of salt;
- leave for 5-7 minutes and cool.
You should rinse your mouth with this infusion 3-5 times a day. The product perfectly helps with any inflammatory processes, pain after treatment and tooth extraction, as well as at the initial stage of purulent-infectious processes.